Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 16
Interleukin-1β-Treated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit Inflammation in Hippocampal Astrocytes Through Exosome-Activated Nrf-2 Signaling
Authors Liu K, Cai GL, Zhuang Z, Pei SY, Xu SN, Wang YN, Wang H, Wang X, Cui C, Sun MC, Guo SH, Jia KP, Wang XZ, Cai GF
Received 1 November 2020
Accepted for publication 8 January 2021
Published 22 February 2021 Volume 2021:16 Pages 1423—1434
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S289914
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
Kai Liu,1,* Guo-Liang Cai,2,3 Zhe Zhuang,4,* Si-Ying Pei,1 Sheng-Nan Xu,5 Ya-Nan Wang,1 Hong Wang,1 Xin Wang,1 Cheng Cui,5 Man-Chao Sun,5 Si-Hui Guo,5 Kun-Ping Jia,1 Xiu-Zhen Wang,1 Guo-Feng Cai1
1Hanan Branch of Second Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Harbin, 150001, People’s Republic of China; 2Postdoctoral Research Workstation of Harbin Sport University, Harbin, 150001, People’s Republic of China; 3Department of Sport Science and Health, Harbin Sport University, Harbin, 150008, People’s Republic of China; 4Second Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Harbin, 150001, People’s Republic of China; 5Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Harbin, 150001, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Correspondence: Guo-Feng Cai
Hanan Branch of Second Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Harbin, 150001, People’s Republic of China
Email [email protected]
Background: Interleukin-1β (IL-1)-treated mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and IL-1-MSCs-conditioned medium (CM) exert anti-inflammatory roles. Astrocytes are essential for the modulation of synaptic activity and neuronal homeostasis in the brain. Exosomes are the critical mediators in intercellular communication. However, the mechanism underlying the anti-inflammatory effect of IL-1-treated MSCs remains unknown.
Methods: In this study, exosomes (IL-1-Exo) were isolated from IL-1-treated MSCs. In addition, lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated hippocampal astrocytes and status epilepticus (SE) mice were treated with IL-1-Exo. Inflammatory activity, astrogliosis, and cognitive performance were measured to determine the effect of IL-1-Exo on inflammation.
Results: The results revealed that IL-1-Exo significantly inhibited LPS-induced astrogliosis and inflammatory responses of astrocytes. Also, IL-1-Exo reversed the LPS-induced effect on calcium signaling. The Nrf2 signaling pathway was associated with the effect of IL-1-Exo in LPS-treated astrocytes. Furthermore, IL-1-Exo reduced the inflammatory response and improved the cognitive performance of SE mice.
Conclusion: The results suggest that IL-1-Exo inhibited LPS-induced inflammatory responses in astrocytes and SE mice and that the effect of IL-1-Exo was primarily mediated through the Nrf-2 signaling pathway. This study provides a new understanding of the molecular mechanism of inflammation-associated brain diseases and an avenue to develop nanotherapeutic agents for the treatment of inflammatory conditions in the brain.
Keywords: mesenchymal stem cells, interleukin-1β, exosome, astrocyte, inflammation, Nrf-2
Introduction
It is well studied that inflammation is a cardinal host defense mechanism in response to tissue injury, ischemia, and infectious agents.1 In general, the inflammation in the peripheral system promotes the production of cytokines, including interleukin-1β (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα), which interact with the brain to induce a series of sickness responses such as fever, increased metabolism, and reduced cognitive ability.2 To date, accumulating evidence has been demonstrated that the inflammatory response in the central nervous system (CNS) is tightly associated with neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease3 and Alzheimer’s disease. In addition, microglia participate in the innate immune system and play an essential role in immune surveillance and tissue maintenance.3 For example, TNFα synthesized in the microglia can function as a pro-inflammatory factor in the acute phase of the inflammatory response and act as an anti-inflammatory factor in the chronic phase.1 In addition, activated microglia releases IL‐1, which induces various responses, including reduced glutamate release, enhanced activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and increased growth factors.4
Human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a group of multipotent stem cells that are able to differentiate into multiple cell lineages, such as fat, bone, muscle, and marrow stroma.5 It has been reported that MSCs can migrate into the brain through crossing the blood-brain barrier (BBB) to promote the release of growth factors and cytokines, thereby promoting tissue repair.6,7 Therefore, these notable therapeutic properties allow MSCs to be promising strategies for developing the treatment of brain diseases.6 Currently, MSCs-based therapies have emerged in many CNS diseases, including Parkinson’s disease,8 ischaemic stroke,9 and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.10 However, MSCs-based therapies are still not fully applied to clinical settings, suggesting the urgent need to explore the molecular mechanisms of the therapeutic role of MSCs.
In a recent study,11 Redondo-Castro et al reported that MSCs derived from human bone innately release anti-inflammatory cytokines and trophic factors. In addition, IL-1-treatment significantly induces MSCs to produce higher levels of anti-inflammatory and pro-trophic factors, inhibiting the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory responses in BV2 microglial cells. Intriguingly, the conditioned medium (CM) of IL-1-treated MSCs can also play an anti-inflammatory role in LPS-treated BV2 cells. Due to the significant anti-inflammatory effect of MSCs, especially in MSCs-cultured CM, we were interested in elucidating the mechanism by which MSCs/MSCs-cultured CM exerts anti-inflammatory roles in astrocytes, a significant target/source of inflammatory signaling.12,13
Exosomes are nano-size membrane vesicles with 30–150 nm in diameter and can be synthesized and released from almost all types of cells.14,15 Exosomes can transport bioactive molecules, including long non-coding RNAs, mRNAs, DNAs, and enzymes, from donor cells to recipient cells, thereby regulating the cellular processes of recipient cells.16 Thus, exosomes have been considered essential information transporters in intercellular communication.16 Furthermore, growing evidence demonstrates that MSCs-derived exosomes play a critical role in neuroinflammation and neurogenesis.17,18 Given the importance of MSCs-derived exosomes in intercellular communication, we speculated that the anti-inflammatory effect of MSCs was mainly mediated by exosomes derived from IL-1-treated MSCs. Therefore, to address this hypothesis, we aimed to determine the role of exosomes derived from IL-1-treated MSCs in LPS-treated astrocytes as well as any related mechanisms.
Materials and Methods
Human MSCs
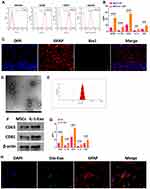
Human bone marrow-derived MSCs were purchased from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and cultured in flasks coated with 0.1% gelatin PBS solution overnight. The MSCs were then washed with PBS solution and cultured in MesenPRO RS™ Medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) supplemented with 2mM glutamine and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. When the MSCs reached about 80–90% confluency, MSCs were detached with 0.25% trypsin-EDTA solution (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) and separated into different cultured flasks. Next, MSCs were collected from passage 4–6 for subsequent experiments. In addition, the flow cytometry assay was performed to characterize MSCs through detecting MSC surface markers CD90, CD73, and CD105 (BD Biosciences, USA).
Primary Astrocytes
Primary astrocytes were isolated as previously described.19 Briefly, bilateral hippocampus tissues were collected from newborn C57BL/6 mice (SIPPR-BK Laboratory Animal Ltd., Shanghai, China). Next, hippocampus tissues were digested with 0.25% trypsin for 10 min and suspended in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) (MilliporeSigma, USA) supplemented with 2mM glutamine, 100 μg/mL penicillin and streptomycin, and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (MilliporeSigma, USA). Single-cell solution was collected through pipetting tissue fragments repeatedly and passed through cell strainers to collect astrocytes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). Fluorescence staining assay using antibodies against glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba1) (Abcam, USA) was performed to characterize isolated astrocytes. The purity of astrocytes and microglia were 95.3 ± 2.2% and 2.7 ± 0.1%, respectively.
IL-1 Treatment on MSCs and Conditioned Medium
The MSCs were treated with IL-1 (Abcam, USA) at a concentration of 10 ng/mL for 24 h. Subsequently, IL-1 receptor antagonist (Abcam, USA) was added to MSCs culture. The culture supernatants were collected for the ELISA assay. For the CM, MSCs (2x104) were cultured in 24-well plates and treated with 10 ng/mL IL-1. Next, MSCs were washed with PBS twice and cultured in fresh MesenPRO RS™ Medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) as described above. The CM (MSCs-IL-1-CM) was collected 24 h later. The CM collected from MSCs without IL-1 treatment was used as the control (MSCs-CM).
Exosome Isolation and Characterization
Exosomes (IL-1-Exo) were isolated from MSCs-CM or MSCs-IL-1-CM as previously described.20 Briefly, cells were removed by centrifugation at 400 g for 10 min and then the supernatants were centrifuged at 3000 g for 10 min to remove cellular debris. Apoptotic bodies were removed by centrifugation at 10,000 g for 30 min. Next, the ultracentrifugation method (100,000 g for 70 min) was used to isolate exosomes, and the isolated exosomes were suspended by PBS. Exosomal markers, CD63 and CD81 (Abcam, USA), were determined through Western blotting assays. The morphology of exosomes was determined by JEM-1230 transmission electron microscope (JEOL Ltd., Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The size distribution of exosomes was investigated by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA; Malvern Panalytical, UK) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) was used to measure exosomes’ protein content according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Fluorescence Staining
After receiving the treatments as indicated, cells, exosomes, and hippocampal tissues were collected for fluorescence staining assays as previously described.21 Briefly, the samples were first fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and incubated with the primary antibodies overnight, including antibodies against GFAP (1:1000), Iba1 (1:1000), 4ʹ, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (1:1000), C3 (1:500), CD81 (1:200), TNFα (1:200) (Abcam, USA). After incubation, samples were washed with PBS 3 times and treated with corresponding secondary antibodies for 2 h. Next, IL-1-Exo were labeled with lipophilic dye, DiO (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Finally, samples were imaged using the FluoViewFV1000 confocal microscope (Olympus, Japan).
CCK-8 Assay
Cell Counting Kit-8 kit (CCK-8; Abcam, USA) was used to determine cell viability according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Optical density (OD) was measured using a microplate reader at 450 nm (Bio-Rad, USA).
ELISA Assay
Supernatants collected from astrocyte culture and the blood sample of mice were used for ELISA analysis. The ELISA analysis kits were used to measure the levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), interleukin-10 (IL-10), and nerve growth factor (NGF) (Research And Diagnostic Systems, Inc., USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The absorbance was measured using a microplate reader at 450 nm (Bio-Rad, USA).
RNA Interference
The siRNAs against Nrf2 were purchased from the RiboBio Company (RiboBio, China). The sequence of siRNA was as follows: 5ʹ- AGAATTCCTCCCAATTCAGC-3ʹ. The siRNA sequence was transfected to astrocytes using the Lipofectamine™ 3000 Transfection Reagent according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Invitrogen, USA).
Western Blotting
Total protein was isolated using lysis buffer (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) and the protein concentration was determined using the Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes (Millipore, USA) and were incubated with primary antibodies against CD63, CD81, C3, CD81, Nrf2, p-P65, P65, Keap-1, HO-1, and β-Actin at 4°C overnight. Next, the membranes were incubated with corresponding secondary antibodies (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) for 2 h. The protein bands were imaged using the Bio-Rad imaging system (Bio-Rad, USA) and quantified using ImageJ software.
Animal Experiments
All animal experiments were carried out according to the guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health and were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Approval #: 2015483BMC-2). C57BL/6 male mice (6–8 weeks old, SIPPR-BK Laboratory Animal Ltd., Shanghai, China) were housed in a standard environment with ad libitum feeding conditions in a 12:12 h light/dark cycle. The status epilepticus (SE) mouse model was established as previously described.21 The SE mice were injected intraventricularly with 1.5 µL PBS or IL-1-Exo using a 2 μL Hamilton Syringe. The Stereotaxic coordinates were as following: Bregma: −0.6 mm, Midline: ±1.5 mm, Depth: 1.7 mm.22 Mice that received the PBS (sham procedure) were considered the control group. One-week post-SE procedure, mice were sacrificed and the hippocampus tissues and blood were collected for subsequent experiments. To assess the cognitive ability of the mice, the Morris Water Maze tracking system was performed at 8 weeks post-SE procedure as previously described.23
Statistical Analysis
Data were shown as means ± SD. The statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 8 software (Graphpad Prism, USA). The multiple comparisons were analyzed using one-way ANOVA or Student’s t-test. Each experimental group had at least three replicates. P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Results
Characterization of Exosomes Derived from IL-1-Treated MSCs
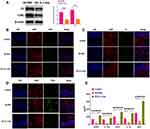
In a previous study,11 Redondo-Castro et al reported that IL-1 can increase secretions of anti-inflammatory cytokines and trophic factors in MSCs and that conditioned medium (CM) of IL-1-treated MSCs can inhibit the inflammatory response of microglial cells in response to LPS treatment. In the present study, we aimed to investigate the mechanism underlying the effect of MSCs-IL-1-CM in hippocampal astrocytes after LPS treatment. First, we identified human bone marrow-derived MSCs through flow cytometry assays, and the results showed that MSCs positively expressed MSC surface markers CD90, CD73, and CD105 (Figure 1A). Next, MSCs-IL-1-CM was collected and added to astrocytes. Compared with CM of MSCs without IL-1 treatment (MSCs-CM), MSCs-IL-1-CM notably increased secretions of anti-inflammatory cytokines and trophic factors, including BDNF, IL-1Ra, VEGF, IL-10, and NGF (Figure 1B). Additionally, the fluorescence staining assay with Iba1 (microglia marker) and GFAP (astrocyte marker) were applied to determine the identification of cultured astrocytes (Figure 1C).
It has been well studied that exosomes derived from MSCs function primarily as information transporters in intercellular communication and thereby regulate biological processes in recipient cells.24,25 Thus, we speculated that exosomes derived from IL-1-treated MSCs are essential for the effect of MSCs-IL-1-CM on the inflammatory response of astrocytes. Through ultracentrifugation, exosomes derived from MSCs-IL-1-CM (IL-1-Exo) were isolated and the morphology of IL-1-Exo was determined by transmission electron microscope (Figure 1D). The size distribution of IL-1-Exo ranged from 50–150 nm (Figure 1E). Western blotting assay revealed that IL-1-Exo positively expressed exosomal markers, CD63 and CD81 (Figure 1F). In addition, the levels of BDNF, IL-1Ra, VEGF, IL-10, and NGF were higher in IL-1-Exo than exosomes derived from MSCs (Exo) (Figure 1G). Furthermore, by using lipophilic dye, Dio, to label IL-1-Exo, we observed that IL-1-Exo was taken up by astrocytes and was enriched in the cytoplasm (Figure 1H). Collectively, we successfully isolated IL-1-Exo from MSCs-IL-1-CM, and IL-1-Exo could be internalized by astrocytes.
IL-1-Exo Attenuates LPS-Associated Effect on Astrocytes
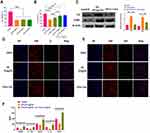
During in vitro studies, LPS has been widely used to induce neuroinflammation.26 In the present study, astrocytes were subjected to different concentrations of LPS, ranging from 0.5 to 2.0 μg/mL. The cell viability was evaluated through CCK8 assays which showed that the LPS treatment significantly decreased cell viability with all concentrations (Figure 2A). Notably, IL-1-Exo attenuated the effect of LPS (0.5 μg/mL) on the cell viability of astrocytes, and the role of IL-1-Exo displayed a dose-dependent pattern (Figure 2B). In addition, we determined the protein expressions of C3, an A1 astrocyte marker,27 and CD81, an indicator of astrocytic activation,28 by Western blotting (Figure 2C). The results suggest that IL-1-Exo could inhibit the protein levels of C3 and CD81 after treating with LPS (0.5 μg/mL). These results were also confirmed by the fluorescence staining assay (Figure 2D and E). Meanwhile, the levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines and trophic factors, such as BDNF, IL-1Ra, VEGF, IL-10, and NGF were increased by IL-1-Exo in the presence of LPS treatments (Figure 2F). Furthermore, the expression of Ki67, a marker of cell proliferation,29 was also inhibited by IL-1-Exo in LPS-treated astrocytes (Figure 3A). Taken together, these results demonstrate that IL-1-Exo may suppress the LPS-induced activities in astrocytes.
IL-1-Exo Reverses LPS-Associated Effect on Calcium Signaling of Astrocytes
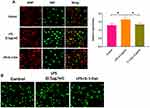
Next, we continued exploring the effect of IL-1-Exo on calcium signaling of LPS-treated astrocytes. As shown in Figure 3B, we used a calcium indicator to determine the intracellular level of Ca2+, and the results showed that astrocytes displayed distinct Ca2+ dynamic after being treated with LPS or LPS plus IL-1-Exo. Collectively, IL-1-Exo reverses the LPS-induced effect on calcium signaling of astrocytes.
Nrf2 is Associated with the Effect of IL-1-Exo in Astrocytes
It has been well documented that Nrf2-associated pathways are involved in the inflammatory response of astrocytes.30–32 Thus, we measured the protein expressions of inflammatory factors, including p-P65 and P-65, and antioxidant factors, including Nrf2, Keap1, and HO-1. We found that LPS treatment significantly increased the levels of these inflammatory and antioxidant factors, and IL-1-Exo reversed this effect of LPS on astrocytes (Figure 4A). Furthermore, we used siRNA against Nrf2 to treat astrocytes and the results revealed that Nrf2 knockdown inhibited the expressions of P-65, Keap1, and HO-1. Meanwhile, LPS treatment and LPS plus IL-1-Exo reversed the effect of Nrf2 knockdown by increasing the levels of these inflammatory and antioxidant factors, of which the combinational treatment of LPS plus IL-1-Exo played a more potent role than LPS treatment only (Figure 4B). These results together suggest that the Nrf2 signaling pathway is associated with the effect of IL-1-Exo in LPS-treated astrocytes.
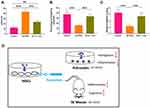
IL-1-Exo Attenuates Inflammatory Response and Behavioral Impairment in SE Mice
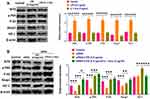
Pilocarpine-induced SE mice were used to further investigate the effect of IL-1-Exo on astrocytes in vivo. Compared with control mice treated with PBS, SE mice treated with IL-1-Exo had lower expressions of C3 and CD81 in the hippocampal tissues (Figure 5A), which was confirmed by fluorescence staining assays (Figure 5B and C). The inflammatory factor, TNFα, was increased in the hippocampus of SE mice and was reduced by the IL-1-Exo treatment (Figure 5D). Similar to the observation of the in vitro experiments, the levels of BDNF, IL-1Ra, VEGF, IL-10, and NGF were inhibited by LPS treatment in SE mice, but were increased by IL-1-Exo treatment (Figure 5E). Regarding the behavioral impact of IL-1-Exo, we performed the Morris Water Maze learning and memory behavioral assay. The results demonstrated that IL-1-Exo could notably improve the learning and memory performance of SE mice through decreasing escape latency time (Figure 6A), increasing time spent in the target quadrant (Figure 6B), and the number of platform crossings (Figure 6C). Together, these results indicate that IL-1-Exo attenuates the inflammatory response and cognitive impairment of SE mice.
Discussion
As demonstrated by Redondo-Castro et al,11 IL-1-treated MSCs exert anti-inflammatory responses in LPS-activated microglial cells, providing a promising therapeutic approach for neuroinflammation-associated CNS diseases. To address the molecular mechanism underlying the anti-inflammatory effect of IL-1-treated MSCs, we hypothesized that IL-1-Exo was a significant mediator for the role of IL-1-treated MSCs in the regulation of the inflammatory response. In the present study, we reported that IL-1-Exo could attenuate LPS-induced inflammation in astrocytes through inhibiting astrogliosis and generating inflammatory cytokines and trophic factors. We also observed that IL-1-Exo ameliorated inflammation-associated responses in SE mice and impaired cognition. Moreover, the effect of IL-1-Exo was mediated by the Nrf2 signaling pathway (Figure 6D).
Inflammation in the brain has been gradually recognized as a crucial pathological manifestation in neuronal disorders, such as traumatic brain injury,13 stroke,33 Alzheimer’s disease,34 and epilepsy.35 Astrocytes are the most abundant cell type in the brain36 and play a critical role in the modulation of synaptic activity and providing support for neuronal homeostasis under normal physiological conditions.37 In pathological processes, astrocytes are activated, namely astrogliosis, in response to pathological alterations, including trauma, tumorigenesis, and neurodegeneration.38 Regarding neuroinflammation, astrocytes are responsible for regulating the entrance of peripheral proinflammatory leukocytes to the brain.39,40 Essentially, astrocytes have been demonstrated to modulate the activity of oligodendrocytes and microglia and participate in the regulation of adaptive immune responses.41 Moreover, astrogliosis is more potent and persistent in proinflammatory processes, relative to microgliosis, leading to severe impairment of the brain.42 Thus, it is essential to investigate the molecular mechanism involved in the role of astrocyte activation in the neuroinflammatory processes. In the present study, we reported that LPS-induced inflammatory responses of astrocytes could be attenuated by MSCs-IL-1-CM, in which the astrogliosis was inhibited, as well as the levels of proinflammatory cytokines and trophic factors were increased. These observations collectively demonstrated that the MSCs-IL-1-CM-induced anti-inflammatory effect may be a potential avenue to effectively regulate the neuroinflammation of astrocytes.
In the study reported by Redondo-Castro et al,11 one of the intriguing findings is that CM of IL-1-treated MSCs has a similar anti-inflammatory role in LPS-treated microglia, suggesting that the functional anti-inflammatory components exist in CM. Accumulating evidence demonstrated that MSCs-CM plays biological roles in recipient cells through exosomes derived from donor MSCs.43–45 Exosomes have emerged as an essential mediator in the intercellular communication through transporting bioactive molecules, including nucleic acids, proteins, and enzymes.46 Also, exosomes derived from MSCs have been reported to alleviate inflammatory responses in the brain. For example, exosomes derived from bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) play a neuroprotective role in mice with traumatic brain injury through attenuating neuroinflammatory activation of microglia.47 In perinatal brain injury, exosomes derived from umbilical cord MSCs dampen microglia-associated with inflammation through the TLR4/CD14 signaling pathway.48 Consistent with these previous studies, we found that exosomes derived from IL-1-treated MSCs reduced LPS-induced inflammation in hippocampal astrocytes, in which the astrogliosis was inhibited, and the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and trophic factors were elevated. Moreover, we found that IL-1-Exo exerted neuroprotective roles in SE mice through attenuating the inflammatory response, as well as improving SE-associated cognition and memory performance. Thus, our findings suggest that IL-1-Exo may be a promising therapy for treating astrocytes with inflammation.
Next, we attempted to further investigate the molecular mechanism by which IL-1-Exo inhibited LPS-induced inflammation in astrocytes. Innamorato et al reported that Nrf2, a regulator of redox homeostasis, is a target in LPS-induced inflammatory responses in the hippocampus.49 Meanwhile, the upregulation of Nrf2 promotes heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) activation, which is thought to regulate the acute inflammatory response in the CNS.49 In general, inflammation and oxidative stress takes place simultaneously in brain diseases,50 in which the interaction between Nrf2 and NF-κB signaling pathways is an essential regulatory mechanism.51 In the present study, LPS treatment promoted the levels of inflammatory factors, including p-P65 and P-65, and antioxidant factors, including Nrf2, Keap1, and HO-1, which were significantly reversed by IL-1-Exo treatment. In addition, Nrf2 knockdown inhibited the inflammatory and antioxidant factors, which was reversed by IL-1-Exo treatment. These results suggest that Nrf2-related signaling pathways were activated in the presence of neuroinflammation in astrocytes and that Nrf2 could be used as a target for IL-1-Exo to synergistically modulate hippocampal inflammation.
Conclusion
The results indicate that IL-1-Exo inhibited the inflammatory responses in hippocampal astrocytes and SE mice and that the effect of IL-1-Exo was mainly mediated through the Nrf-2 signaling pathway. This study provides a new avenue to develop nanotherapeutic agents for the treatment of inflammatory conditions in the brain.
Funding
The study was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (H2018066); Scientific Research Fund of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2019MS19); State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Heilongjiang Province, No. ZHY16-027.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Lucas SM, Rothwell NJ, Gibson RM. The role of inflammation in CNS injury and disease. Br J Pharmacol. 2006;147(S1):S232–S240. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706400
2. Konsman JP, Parnet P, Dantzer R. Cytokine-induced sickness behaviour: mechanisms and implications. Trends Neurosci. 2002;25(3):154–159. doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(00)02088-9
3. Cameron B, Landreth GE. Inflammation, microglia, and alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2010;37(3):503–509. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2009.10.006
4. Rothwell NJ, Luheshi GN. Interleukin 1 in the brain: biology, pathology and therapeutic target. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23(12):618–625. doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(00)01661-1
5. Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. science. 1999;284(5411):143–147. doi:10.1126/science.284.5411.143
6. Kalladka D, Muir KW. Brain repair: cell therapy in stroke. Stem Cells Cloning. 2014;7:31. doi:10.2147/SCCAA.S38003
7. Torres-Espín A, Hernández J, Navarro X. Gene expression changes in the injured spinal cord following transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells or olfactory ensheathing cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e76141. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076141
8. Joyce N, Annett G, Wirthlin L, Olson S, Bauer G, Nolta JA. Mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of neurodegenerative disease. Regen Med. 2010;5(6):933–946. doi:10.2217/rme.10.72
9. Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, et al. Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke. 2001;32(4):1005–1011. doi:10.1161/01.STR.32.4.1005
10. Boido M, Piras A, Valsecchi V, et al. Human mesenchymal stromal cell transplantation modulates neuroinflammatory milieu in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cytotherapy. 2014;16(8):1059–1072. doi:10.1016/j.jcyt.2014.02.003
11. Redondo-Castro E, Cunningham C, Miller J, et al. Interleukin-1 primes human mesenchymal stem cells towards an anti-inflammatory and pro-trophic phenotype in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):79. doi:10.1186/s13287-017-0531-4
12. Iyer A, Zurolo E, Prabowo A, et al. MicroRNA-146a: a key regulator of astrocyte-mediated inflammatory response. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44789. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044789
13. Aschner M. Astrocytes as mediators of immune and inflammatory responses in the CNS. Neurotoxicology. 1998;19(2):269–282.
14. Ela S, Mäger I, Breakefield XO, Wood MJ. Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12(5):347–357. doi:10.1038/nrd3978
15. Kahlert C, Kalluri R. Exosomes in tumor microenvironment influence cancer progression and metastasis. J Mol Med. 2013;91(4):431–437. doi:10.1007/s00109-013-1020-6
16. Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;110(1):13–21. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.04.033
17. Yang Y, Ye Y, Su X, He J, Bai W, He X. MSCs-derived exosomes and neuroinflammation, neurogenesis and therapy of traumatic brain injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017;11:55. doi:10.3389/fncel.2017.00055
18. Reza-Zaldivar EE, Hernández-Sapiéns MA, Minjarez B, Gutiérrez-Mercado YK, Márquez-Aguirre AL, Canales-Aguirre AA. Potential effects of MSC-derived exosomes in neuroplasticity in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:317. doi:10.3389/fncel.2018.00317
19. Rocchio F, Tapella L, Manfredi M, et al. Gene expression, proteome and calcium signaling alterations in immortalized hippocampal astrocytes from an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(1):1–18. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-1264-8
20. Sun Z, Shi K, Yang S, et al. Effect of exosomal miRNA on cancer biology and clinical applications. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):147. doi:10.1186/s12943-018-0897-7
21. Long Q, Upadhya D, Hattiangady B, et al. Intranasal MSC-derived A1-exosomes ease inflammation, and prevent abnormal neurogenesis and memory dysfunction after status epilepticus. Proc Nat Acad Sci. 2017;114(17):E3536–E3545. doi:10.1073/pnas.1703920114
22. Dong HW. The Allen Reference Atlas: A Digital Color Brain Atlas of the C57bl/6J Male Mouse. John Wiley & Sons Inc; 2008.
23. Long Q, Hei Y, Luo Q, et al. BMSCs transplantation improves cognitive impairment via up-regulation of hippocampal GABAergic system in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Neuroscience. 2015;311:464–473. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.10.055
24. Toh WS, Lai RC, Hui JHP, Lim SK MSC exosome as a cell-free MSC therapy for cartilage regeneration: implications for osteoarthritis treatment. Paper presented at: Seminars in cell & developmental biology 2017.
25. Lai RC, Arslan F, Lee MM, et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2010;4(3):214–222. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2009.12.003
26. Liu B, Jiang J-W, Wilson BC, et al. Systemic infusion of naloxone reduces degeneration of rat substantia nigral dopaminergic neurons induced by intranigral injection of lipopolysaccharide. J Pharmacol Experimental Therapeutics. 2000;295(1):125–132.
27. Clarke LE, Liddelow SA, Chakraborty C, Münch AE, Heiman M, Barres BA. Normal aging induces A1-like astrocyte reactivity. Proc Nat Acad Sci. 2018;115(8):E1896–E1905. doi:10.1073/pnas.1800165115
28. Peduzzi J, Grayson T, Fischer F, Geisert JE. The expression of TAPA (CD81) correlates with the reactive response of astrocytes in the developing rat CNS. Exp Neurol. 1999;160(2):460–468. doi:10.1006/exnr.1999.7234
29. Montine TJ, Vandersteenhoven JJ, Aguzzi A, et al. Prognostic significance of Ki-67 proliferation index in supratentorial fibrillary astrocytic neoplasms. Neurosurgery. 1994;34(4):674–679. doi:10.1227/00006123-199404000-00016
30. Zhao B, Ren B, Guo R, et al. Supplementation of lycopene attenuates oxidative stress induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment via Nrf2/NF-κB transcriptional pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017;109:505–516. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2017.09.050
31. Lee E, Yin Z, Sidoryk-Węgrzynowicz M, Jiang H, Aschner M. 15-Deoxy-Δ12, 14-prostaglandin J2 modulates manganese-induced activation of the NF-κB, Nrf2, and PI3K pathways in astrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012;52(6):1067–1074. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.12.016
32. Zhao M, Wang FSL, Hu X, Chen F, Chan HM. Acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in primary astrocytes and microglia: roles of the Nrf2-ARE and NF-κB pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017;106:25–35. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2017.05.007
33. Shi K, Tian D-C, Li Z-G, Ducruet AF, Lawton MT, Shi F-D. Global brain inflammation in stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(11):1058–1066. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30078-X
34. Yin F, Sancheti H, Patil I, Cadenas E. Energy metabolism and inflammation in brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;100:108–122.
35. Vezzani A, Aronica E, Mazarati A, Pittman QJ. Epilepsy and brain inflammation. Exp Neurol. 2013;244:11–21. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.09.033
36. Haydon PG, Carmignoto G. Astrocyte control of synaptic transmission and neurovascular coupling. Physiol Rev. 2006;86(3):1009–1031. doi:10.1152/physrev.00049.2005
37. Seifert G, Schilling K, Steinhäuser C. Astrocyte dysfunction in neurological disorders: a molecular perspective. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7(3):194–206. doi:10.1038/nrn1870
38. Pekny M, Nilsson M. Astrocyte activation and reactive gliosis. Glia. 2005;50(4):427–434. doi:10.1002/glia.20207
39. Myer D, Gurkoff GG, Lee S, Hovda D, Sofroniew MV. Essential protective roles of reactive astrocytes in traumatic brain injury. Brain. 2006;129(10):2761–2772. doi:10.1093/brain/awl165
40. Voskuhl RR, Peterson RS, Song B, et al. Reactive astrocytes form scar-like perivascular barriers to leukocytes during adaptive immune inflammation of the CNS. J Neurosci. 2009;29(37):11511–11522. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1514-09.2009
41. Mayo L, Quintana FJ, Weiner HL. The innate immune system in demyelinating disease. Immunol Rev. 2012;248(1):170–187.
42. Hirsch EC, Hunot S. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: a target for neuroprotection? Lancet Neurol. 2009;8(4):382–397. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70062-6
43. Qamar AY, Fang X, Kim MJ, Cho J. Improved post-thaw quality of canine semen after treatment with exosomes from conditioned medium of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Animals. 2019;9(11):865. doi:10.3390/ani9110865
44. Gong M, Yu B, Wang J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells release exosomes that transfer miRNAs to endothelial cells and promote angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(28):45200. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.16778
45. Lin R, Wang S, Zhao RC. Exosomes from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote migration through Wnt signaling pathway in a breast cancer cell model. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;383(1–2):13–20. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1746-z
46. Simons M, Raposo G. Exosomes–vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21(4):575–581. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.03.007
47. Ni H, Yang S, Siaw-Debrah F, et al. Exosomes derived from bone mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate early inflammatory responses following traumatic brain injury. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:14. doi:10.3389/fnins.2019.00014
48. Thomi G, Surbek D, Haesler V, Joerger-Messerli M, Schoeberlein A. Exosomes derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in perinatal brain injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):105. doi:10.1186/s13287-019-1207-z
49. Innamorato NG, Rojo AI, García-Yagüe ÁJ, Yamamoto M, De Ceballos ML, Cuadrado A. The transcription factor Nrf2 is a therapeutic target against brain inflammation. J Immunol. 2008;181(1):680–689. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.181.1.680
50. Abdul-Muneer P, Chandra N, Haorah J. Interactions of oxidative stress and neurovascular inflammation in the pathogenesis of traumatic brain injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;51(3):966–979.
51. Sivandzade F, Prasad S, Bhalerao A, Cucullo L. NRF2 and NF-қB interplay in cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative disorders: molecular mechanisms and possible therapeutic approaches. Redox Biol. 2019;21:101059.
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.