Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 15
Integrated System for Purification and Assembly of PCV Cap Nano Vaccine Based on Targeting Peptide Ligand
Authors Wang F, Hao J, Li N, Xing G, Hu M, Zhang G
Received 31 July 2020
Accepted for publication 16 October 2020
Published 30 October 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 8507—8517
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S274427
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
Fangyu Wang,1,* Junfang Hao,1,2,* Ning Li,3,* Guangxu Xing,1 Man Hu,1 Gaiping Zhang1,4
1Key Laboratory for Animal Immunology, Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Zhengzhou, Henan 450002, People’s Republic of China; 2College of Biology and Food, Shangqiu Normal University, Shangqiu, Henan 476000, People’s Republic of China; 3College of Food Science and Technology, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, Henan 450000, People’s Republic of China; 4College of Veterinary Medicine, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, Henan 450000, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Correspondence: Gaiping Zhang
Key Laboratory for Animal Immunology, Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 116# Huayuan Road, Zhengzhou, Henan Province 450002, People’s Republic of China
Email [email protected]
Purpose: The vaccine design has shifted from attenuated or inactivated whole pathogen vaccines to more pure and defined subunit vaccines. The purification of antigen proteins, especially the precise display of antigen regions, has become a key step affecting the effectiveness of subunit vaccines.
Materials and Methods: This work presents the application of molecular docking for a peptide ligand designed for PCV2 Cap purification and assembly in one step. Based on the PCV2 Cap protein affinity peptide (L11-DYWWQSWE), the amino terminal of PCV2 Cap was covalently coupled with the polylactic acid–glycolic acid copolymer (PLGA) carboxyl terminal through the EDC/NHS method.
Results: The PLGA had an average diameter of 106 nm. The average diameter increased to 122 nm after the PCV2 Cap protein conjugation, and the Zeta potential shifted from − 13.7 mV to − 9.6 mV, indicating that the PCV2 Cap protein stably binds to the PLGA. Compared with the free PCV2 Cap protein group, the neutralizing antibody titer was significantly increased on the 14th day after the PLGA-Cap immunization (P < 0.05). The neutralizing antibody level was extremely significant on the 28th day (P < 0.001). The CCK-8 analysis showed that PLGA-Cap had an obvious cytotoxic effect on RAW264.7 cells at the PLGA nanoparticle concentration up to 200 μg/mL but had no obvious cytotoxic effect on DC2.4 cells. Compared with the Cap protein group, the antigen-presenting cells had a stronger antigen uptake capacity and a higher fluorescence in the PLGA-Cap group. The immune effect showed that the level of the neutralizing antibody produced by this structure is much better than that of purified protein and helps improve the immune system response.
Conclusion: This technology provides a potential new perspective for the rapid enrichment of the antigen protein with the affinity peptide ligand.
Keywords: PCV2 Cap, peptide ligand, antigen display, protein assembly, nano vaccine, neutralizing antibody
Introduction
The utilized defined and purified antigens (ie, proteins, peptides, or nucleic acids) are identified as immunogenic and can be quickly manufactured in response to new outbreaks.1 Subunit antigens are much less reactive, which is an advantage in terms of local and systemic adverse reactions, but is a disadvantage in terms of strong stimulation and long-lasting immune responses. Therefore, subunit vaccines are often used with effective adjuvants to activate and regulate effective immune responses.2,3 One strategy applied to subunit vaccines is the usage of particulate carriers that are very similar to pathogens to deliver antigens, taking advantage of the immune system’s natural uptake and recognition mechanisms and ensuring that antigens and adjuvants are delivered to antigen-presenting cells (APCs).4,5
Polymers of a natural and synthetic origin have been extensively researched on for the manufacture of micro and micro-nano particle delivery systems. The particle size depends on the nature of the polymer and the model preparation. The advantages of polymer-based microparticle systems include their ability to encapsulate and protect antigens from harsh in vivo conditions6 and their ability to customize dimensions using manufacturing techniques.7 The polymer particle carrier can be widely made into polymers, such as polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer (PLGA), chitosan, silica, polylactide, polyethyleneimine, and polypropylene sulfide, and acrylic-based polymers, such as polymethyl methacrylate, poly (ethyl acrylic acid), poly (propyl acrylic acid), and poly (butyl acrylic acid). Chitosan PLGA particles are extensively studied for vaccine delivery.
As the delivery carrier for vaccines, the PLGA has advantages of good biocompatibility, biodegradability, and sustained and controlled release.8,9 It can also be used for the delivery of antigens, such as peptides, proteins, and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).10 The common loading methods of PLGA nanoparticles (NPs) are encapsulation and adsorption. Antigens and particles loaded by encapsulation are liable for causing antigen inactivation, which limits their immunogenicity.10,11 On the contrary, an antigen can maintain the antigen activity to a greater extent after being adsorbed and loaded, and APCs can be recruited for a short period such that the body can generate an immune response faster. At present, PLGA NPs are widely used in vaccine transport research.12 NPs can become the preferred phagocytic target of APCs after antigen adsorption or inclusion, which is an important step for the realization of an effective immune response of the body.13
Porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2), which is a pathogen porcine circovirus-associated disease, is one of the most widespread viruses that cause huge economic losses to the pig breeding industry.14–16 PCV2 belongs to the circovirus genus of the family Circoviridae and is one of the smallest DNA viruses in a single-stranded circular.17 The most effective method of controlling the PCV2 outbreak in the pig breeding industry is to develop highly effective vaccines. The unique structural protein capsid (Cap) is critical for inducing neutralizing antibodies and developing a protective immune response against PCV2 infection.18–22 Therefore, the PCV2 Cap protein is the first choice for research on PCV2 genetic engineering vaccines. PCV2 vaccines are mainly divided into two categories: PCV2 inactivated and PCV2 gene engineering vaccines. Inactivated vaccine has been reported to cause a slow and weak immune response that leads to inadequate protection.23 In contrast, genetically engineered vaccines could prevent multiple viral attacks and induce strong immune responses.24,25 Thus, the development of a novel PCV2 antigen surface display technology based on biomaterials is an important means of improving vaccine quality and preventing PCV2 infection.
As an import part of biomimetic ligands, short peptide ligands have raised increasing interest in the recent years.26 Peptide ligands have advantages of low immunogenicity, easy synthesis, easy modification, higher surface density, and more amenability for engineering at the molecular level.27 In view of a series of excellent peptide ligand properties, affinity adsorbents with peptide ligands have been developed as the main technology for target protein separation and purification.26
Based on PCV2 Cap protein affinity peptide (L11-DYWWQSWE), the amino terminal of PCV2 Cap was covalently coupled herein with the PLGA carboxyl terminal through the EDC/NHS method. Subsequently, it was incubated and centrifuged with a recombinant PCV2 Cap crude protein to obtain the PLGA nanoparticles containing the PCV2 Cap antigen (PLGA-Cap). The mechanisms of the antibody production were examined by measuring the cellular uptake efficiency of the PLGA-Cap into the APCs and subsequent cytokine secretion. The immune responses to the PLGA-Cap were evaluated in mice. This study lays a foundation for the development of the PCV2 subunit vaccine on the basis of the PLGA NPs. With the help of peptide ligands and delivery vectors, our research demonstrates an integrated purification and assembly system and realizes the construction of subunit vaccines using a simple one-step centrifugation. This technology provides new interfacial properties to NPs.
Materials and Methods
Materials
PLGA and Peptide
The PLGA nanoparticles (particle size: 106 nm, carboxyl end modification) were purchased from Sunna Biotechnology, Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The affinity peptide L1128 was synthesized by GL Biochem. (Shanghai, China). The 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) were purchased from Thermo Scientific (TMO, USA). Freund’s adjuvant was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Figure 1 presents a schematic diagram of the preparation process of the PLGA-Cap nanoparticles, where the PCV2 Cap was purified and enriched by coupling L11 to the PLGA surface. Figure 2 illustrates the PCV2 Cap structure, its epitope, and L11-binding area.
 |
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the preparation process of PLGA-Cap nanoparticles. PCV2 Cap was purified and enriched by coupling L11 to the surface of PLGA. |
Cell Lines
The APCs, including RAW264.7 macrophages and DC2.4 dendritic cells, were obtained from ATCC (Manassas, VA, USA). Fetal bovine serum was purchased from GIBCO (Carlsbad, CA, USA). Dulbecco’s modified eagle’s medium, RPMI-1640, penicillin, and streptomycin were purchased from Solarbio (Beijing, China).
Identification of L11-Binding PCV2 Cap Protein Sites
The molecular docking results showed that the key sites of the L11-binding PCV2 Cap protein were 68-His, 127-Lys, and 174-Lys. Three key sites were deleted and mutated to verify the key sites of L11 binding.
ELISA Experiment
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) plate was coated with 50 μL of a 10 μg/mL deleted and mutated six-protein solution and incubated at 4°C for 12 h. A blocking buffer containing 1% BSA was incubated at 37°C for 1 h. After washing with PBS containing 0.5% Tween-20 (PBST), L11 peptides (1 μg/mL) were added and incubated at 37°C for 30 min. The plate was washed as before. SA-HRP (1:1000) was then added and incubated at 37°C for 30 min. At the same time, PBS and purified PCV2 Cap protein were used as the negative and positive controls, respectively. The OD value of each well was measured at 450 nm using an ELISA plate reader.
LSPR Experiment
First, the Delet-1 and Delet-3 proteins were covalently immobilized on a carboxyl Au colloidal nanoparticle chip. Second, the running buffer (PBS, pH 7.4) was flowed through the chip until a smooth testing baseline was obtained. L11 was then dissolved in PBS and injected to detect the change in the resonance signal. In each cycle, 300 μL of peptide solution was injected into the flow cell of the chip for 5 min. The data were evaluated by Trace Drawer 1.7 (Nicoya, Canada) to determine the association constant (ka, 1/Ms), dissociation constant (kd, 1/s), equilibrium binding constant (KD, M), and KD = kd/ka.
Preparation and Characterization of PLGA-Cap
The PLGA-Cap Was Prepared Following the Steps Below
1) L11 was coupled with the carboxyl surface of the PLGA NPs. First, the PLGA NP solution (5 mg) was dialyzed overnight in a NaH2PO4 solution (pH 6.0). Next, 10 µL of the EDC solution (50 mg/mL) and 10 μL of the NHS solution (50 mg/mL) were added. The solution was then shaken at room temperature for 20 min and centrifuged for standby. Second, the L11 peptide (300 μg) was dissolved in a HEPES solution (pH 7.4) at 1 μg/μL concentration. Subsequently, it was fully resuspended and reacted with the PLGA NPs for 2 h. Finally, the unconjugated L11 peptide was removed by dialysis with physiological saline, and the PLGA NPs were coupled to L11 (ie, PLGA-L11).
2) The PLGA–L11 NPs were incubated with the recombinant PCV2 Cap protein for 2 h at room temperature. The PCV2 Cap PLGA NPs (PLGA–-Cap) with high purity were obtained by removing the hetero protein by vortex and repeated centrifugation (3000 rpm, 4°C, 20 min). The precipitate was resuspended in PBS for five washing cycles. The amount of Cap protein coupled with PLGA was estimated by the micro BCA protein assay.
Identification of PLGA-Cap Protein Immunoactivity
First, the PLGA-Cap protein was serially diluted to four different concentrations by a carbonate buffer (pH 9.6), coated on an ELISA plate, and incubated overnight at 4°C. After blocking with 1% BSA blocking buffer at 37°C for 1 h, a 6A5 monoclonal antibody (1:1000) was added to the ELISA plate and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. Second, an HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (1:5000) was added and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. The medium was then washed with PBST for four to five times. The OD value of each well was measured at 450 nm using an ELISA plate reader.
Toxicity, Uptake and Cytokine Production of PLGA-Cap Nanoparticles to APC Cells
The APCs were seeded at a cell density of 5×103/well (100 μL) on a 96-well cell culture plate at 37°C in 5% CO2. After the cell adherence to the wall, PLGA-Cap with different concentrations was added for incubation with the cell for 24 h. The medium was then removed and washed twice with PBS. Subsequently, 100 μL of fresh medium containing 10% cell counting kit 8 (CCK-8, Beyotime, Wuhan, China) was added and incubated for 4 h. Finally, the absorbance at 450 nm was measured using a microplate reader.
First, the APCs were seeded on a 96-well cell culture plate with a cell density of 2 ×104/well. When the cell density reached 90%, 100μL Cap protein and PLGA-Cap NPs containing the same amount of Cap protein (ie, approximately 15μg/mL) were added for the cell culture. The medium was removed after 1 h incubation. The cells were then fixed in precooled methanol for 10 min at room temperature. After blocking with 5% skim milk, the cells were incubated with an anti-PCV2 serum and with a fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled anti-mouse antibody (FITC-IgG). Finally, it was counterstained with 4ʹ,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (Beyotime, Wuhan, China). The medium obtained in each step was washed for four to five times with PBST. Subsequently, 100μL/well PBS was added, observed, and photographed under a fluorescence microscope.
First, RAW264.7 cells were sensitized with 50 ng/mL lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 4 h, which increased the IL-1β maturation. After sensitization, the cells were seeded on a 96-well cell culture plate at a density of 5×104 cells/well. After which, 100 μL of PLGA (15μg/mL), Cap (15μg/mL), or PLGA-Cap (15μg/mL) was added and incubated with the cells. The Cap and PLGA-Cap group contained the same amount of Cap protein. For the IL-12 and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) measurements, the RAW264.7 cells were not sensitized with LPS. After 24 h of incubation, the cytokine concentrations of IL-12, TNF-α, and IL-1βwere measured by ELISA according to the manufacturer’s protocol (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA)
This study was approved by the Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences Committee. All of the procedures were performed according to accepted standards of Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Age-matched female and male BALB/c mice (SYXK2019-0007) were purchased from the Henan Experimental Animal Center (Zhengzhou, Henan province, PRC). The 6 week-old female BALB/c mice were randomly divided into three groups of five mice per group. Each mouse was subcutaneously immunized with 100 μL of the indicated vaccines (ie, Cap alone and PLGA-Cap). PLGA NPs were inoculated as a negative control. Each group received the same boost for two weeks after the initial immunization. Serum was harvested at 14, 21, 28, and 35 days after immunization. The data are expressed as mean±SEM, and GraphPad Prism version 5.0 was used for statistical analysis. Statistical significance was determined by T-test.
Results
Characterization of PLGA-Cap and Identification of the Immunological Activity
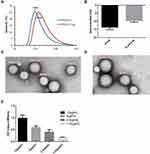
The PLGA has an average diameter of 106 nm (Figure 3A and C). The average diameter increased to 122 nm (Figure 3A and D) after the PCV2 Cap protein conjugation, and the zeta potential shifted from −13.7 mV to −9.6 mV (Figure 3B). This result illustrates that the PCV2 Cap protein stably binds to the PLGA. The 6A5 antibody is a monoclonal antibody to the PCV2 Cap that specifically recognizes the neutralizing epitopes located on the outer surface of the PCV2 Cap protein. The ELISA results in Figure 3E showed that the ratio of the diluted PLGA-Cap was well recognized by the 6A5 mAb. Furthermore, its OD value increased in a concentration-dependent manner. These results indicate that the Cap protein coupled with the PLGA has good immunogenicity and can be used in the next experiment.
Identification of L11-Binding PCV2 Cap Protein Sites
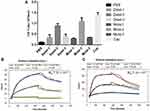
The ELISA results in Figure 4 depicted that compared with the positive control Cap, the deletion and the mutation of 68-His and 174-Lys (Delet-1, Muta-1; Delet-3, Muta-3) significantly reduced the binding activity to L11, whereas 127-Lys (Delet-2, Muta-2) was not affected. In other words, the key binding sites of L11 and PCV2 Cap protein may be 68-His and 174-Lys, respectively. The characterization of PLGA-Cap and the identification of the immunological activity are presented herein. Two proteins (ie, Delet-1 and Delet-3) were coupled to the LSPR chip to determine their affinity with L11. Figure 4B and C show that the L11 peptide exhibited a different binding strength for Delet-1 and Delet-3 with various KD values. The L11 peptide had a lower binding affinity to Delet-1 and Delet-3, with a KD of 103 nM. These results demonstrate that the L11 peptide affinity is in a good agreement with the ELISA results. In conclusion, the key binding sites of L11 and PCV2 Cap protein are 68-His and 174-Lys, respectively.
Detection of Antibodies Levels
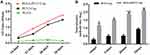
The immunization results showed that both PLGA-Cap and free PCV2 Cap protein can significantly increase the antibody level against Cap in mice. The antibody level significantly increased with the extended immunization time (Figure 5A). Figure 5B depicts that compared with the free PCV2 Cap protein group; the neutralizing antibody titer was significantly increased on the 14th day after the PLGA-Cap immunization (P < 0.05). The neutralizing antibody level was extremely significant on the 28th day (P < 0.001).
Toxicity, Uptake and Cytokine Production of PLGA-Cap Nanoparticles to APC Cells
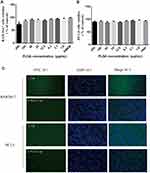
The CCK-8 analysis showed that the PLGA-Cap had an obvious cytotoxic effect on the RAW264.7 cells at the PLGA NPs concentration up to 200 μg/mL (Figure 6A), but had no obvious cytotoxic effect on the DC2.4 cells (Figure 6B). The in vitro data indicated that the PLGA with a 106 nm diameter was a safe carrier.
The Cap protein uptake by the APCs was detected by an indirect immunofluorescence assay. Its fluorescence intensity corresponded to the number of Cap protein within the APCs. Figure 6C exhibits that compared with the Cap protein group, APCs had a stronger antigen uptake capacity and a higher fluorescence in the PLGA-Cap group. These data indicated that the PLGA with 106 nm diameter improved the amount of Cap protein in the intrinsic APCs. Moreover, the Cap protein was distributed in the cytoplasm, not in the nucleus.
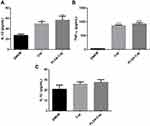
We next investigated the immunostimulatory effect of the PLGA-Cap conjugates and detected three types of cytokines, namely IL-12 (Figure 7A), TNF-α (Figure 7B), and IL-1β (Figure 7C). IL-12 and TNF-α play pivotal roles in eliciting the innate immune responses and regulating the adaptive immune responses mainly produced by T cells and APCs.29,30 It is known that inflammatory bodies are activated when exposed to nanoparticles due to lysosome damage. Our research focused on IL-1β, which can promote the inflammatory response and are strictly regulated by inflammatory bodies. The concentration of IL-1β was very low, which indicated that RAW264.7 cells did not produce inflammatory bodies after PLGA-Cap uptake.
Discussion
The ORF2 of the PCV2 virus encodes the Cap protein with 234 amino acids and a molecular weight of approximately 27.8 kDa. It is the only structural protein of the virus and constitutes the viral capsid. The protein structure has been clearly resolved and can induce the body to generate an immune response and produce antibodies against Cap. It is also an ideal target for antibody detection and vaccine design. The recombinantly expressed Cap protein can self-assemble into virus-like particles (VLPs) in vitro. Several expression systems, including bacteria, yeast, and insect cells, have been utilized to produce PCV2 VLPs. However, in some cases, the recombinant Cap proteins produced in bacteria and yeast do not spontaneously assemble.
Traditional purification techniques mostly use microfiltration, ultrafiltration, precipitation (PEG precipitation, ammonium sulfate precipitation, etc.), ultracentrifugation, and other primary purification methods. However, these purification methods have a limited effectiveness in removing impurities, which leads to low vaccine purity and poor safety. Some new purification systems have been applied to the PCV2 Cap protein purification to obtain higher-purity proteins. Wu31 et al, established a single-column, high-throughput fractionation procedure based on the size exclusion chromatograph for the PCV2 Cap purification. Q Sepharose XL was used for the initial separation of the VLPs from the residual host nucleic acids and some host cell proteins.32 Recyclable ATPS was prepared using two pH-responsive copolymers (ie, PADB4.99 and PMDM7.08) and applied for the purification of the PCV2 Cap protein fermentation broth.33 Compared with other purification methods, the centrifugation method herein has great advantages in terms of ease of operation.
The VLP formation is the most common method for displaying the epitopes of subunit vaccine antigens. The recombinant Cap protein can self-assemble into VLPs in vitro, which is particularly an opportunity to develop the PCV2 VLPs vaccine in Escherichia coli because the cost of the vaccine must be weighed against the value of the vaccinated pig when it is used to extend the usage of the VLP vaccine of PCV2.31–34 Overall, the efficiency of forming a VLP by self-assembly alone is not high. Through the protein structure analysis, the establishment of a highly efficient epitope display system will become the key research field of subunit vaccines. The results of this study showed that the level of neutralizing antibodies produced by nanoparticles is much higher than that of specific antibodies. In other words, the vaccine assembly system based on targeting high-affinity peptides has a much better display effect on antigen epitopes than single protein immunization.
In the biomedicine field, the PLGA polymer approved by the FDA has excellent biodegradability and biocompatibility. PLGA NPs have been the focus of current research on delivery vehicles for drugs and vaccines.35 We prepared PLGA–L11 nanoparticles by covalently coupling COOH–PLGA with the amino acid of the L11 peptide through EDC/NHS and obtained PLGA-Cap by repeated centrifugation. The obtained results indicate that the PLGA-Cap can enhance the phagocytosis and presentation of exogenous antigens by APCs and stimulate the cytokine secretion. In short, PLGA-Cap can be used as a new vaccine for inducing cellular immunity.
PLGA NPs can become the preferred phagocytic target of APCs after antigen adsorption or inclusion, which is an important step in realizing an effective immune response of the body. The ability of APCs to phagocytoze nanoparticles is affected by the particle size in vivo. The particle size of PLGA nanoparticles has the greatest effect on the cell uptake, while the Zeta potential mainly affects the intracellular transport of the nanoparticles.36 The process of phagocytozing nanoparticles by APCs mainly includes two steps: adsorption and internalization. The most important nanoparticle mechanism for improving the subunit vaccine effectiveness is increasing the amount of the antigen taken by the APCs.37,38 The phagocytosis and uptake of APCs are the first steps in developing an antigen-induced immune response.39 Because PLGA-Cap nanoparticles can be better recognized by APC cells for ingestion and phagocytosis, the immune response effect caused by them is strong, so the secretion level of IL-1β, IL-12 and TNF-α in RAW264.7 cells is required slightly higher than the Cap group. The PLGA NPs modified with the L11 affinity peptide can specifically enrich the PCV2 Cap, enhance the targeting of APCs to antigens, and promote the uptake of APCs.
Data Sharing Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Ethics Approval
This study was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences. (Ethic number: SYXK2019-0007). All of the procedures were performed according to accepted standards of Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFC1602902 & 2016YFD0500701).
Author Contributions
All authors made a significant contribution to the work reported, whether that is in the conception, study design, execution, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation, or in all these areas; took part in drafting, revising or critically reviewing the article; gave final approval of the version to be published; have agreed on the journal to which the article has been submitted; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interests in this work.
References
1. Nabel GJ. Designing tomorrow’s vaccines. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(6):551–560. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1204186
2. Tandrup SS, Foged C, Korsholm KS, Rades T, Christensen D. Liposome-Based Adjuvants for Subunit Vaccines: formulation Strategies for Subunit Antigens and Immunostimulators. Pharmaceutics. 2016;8.
3. Reed SG, Bertholet S, Coler RN, Friede M. New horizons in adjuvants for vaccine development. Trends Immunol. 2009;30(1):23–32. doi:10.1016/j.it.2008.09.006
4. Bobbala S, Hook S. Is There an Optimal Formulation and Delivery Strategy for Subunit Vaccines? Pharm Res -Dordr. 2016;33:2078–2097.
5. Neumann S, et al. Synthetic TRP2 long-peptide and alpha-galactosylceramide formulated into cationic liposomes elicit CD8+ T-cell responses and prevent tumour progression. Vaccine. 2015;33:5838–5844.
6. Gordon S, et al. Chitosan hydrogels containing liposomes and cubosomes as particulate sustained release vaccine delivery systems. J Liposome Res. 2012;22:193–204.
7. Danhier F. PLGA-based nanoparticles: an overview of biomedical applications. J Control Release. 2012;161:505–522.
8. Vasir JK, Labhasetwar V. Biodegradable nanoparticles for cytosolic delivery of therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2007;59:718–728.
9. Wendorf J, et al. A Practical Approach to the use of Nanoparticles for Vaccine Delivery. J Pharm Sci -US. 2006;95:2738–2750.
10. Varshochian R, Jeddi-Tehrani M, Mahmoudi AR, et al. The protective effect of albumin on bevacizumab activity and stability in PLGA nanoparticles intended for retinal and choroidal neovascularization treatments. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2013;50(3–4):341–352. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2013.07.014
11. Yadav SC, Kumari A, Yadav R. Development of peptide and protein nanotherapeutics by nanoencapsulation and nanobioconjugation. Peptides. 2011;32(1):173–187. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2010.10.003
12. Wendorf J, Singh M, Chesko J, et al. A Practical Approach to the use of Nanoparticles for Vaccine Delivery. J Pharm Sci -US. 2006;95(12):2738–2750. doi:10.1002/jps.20728
13. Kwon YJ, Standley SM, Goh SL, Fréchet JMJ. Enhanced antigen presentation and immunostimulation of dendritic cells using acid-degradable cationic nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2005;105(3):199–212. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2005.02.027
14. Afghah Z, Webb B, Meng X, Ramamoorthy S. Ten years of PCV2 vaccines and vaccination: is eradication a possibility? Vet Microbiol. 2017;206:21–28. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.10.002
15. Seo HW, Han K, Park C, Chae C. Clinical, virological, immunological and pathological evaluation of four porcine circovirus type 2 vaccines. Veterinary J. 2014;200(1):65–70. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2014.02.002
16. Palinski R, et al. A Novel Porcine Circovirus Distantly Related to Known Circoviruses Is Associated with Porcine Dermatitis and Nephropathy Syndrome and Reproductive Failure. J Virol. 2017;91.
17. Guo LJ, Lu YH, Wei YW, Huang LP, Liu CM. Porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2): genetic variation and newly emerging genotypes in China. Virol J. 2010;7(1):273. doi:10.1186/1743-422X-7-273
18. Saha D, Huang L, Bussalleu E, et al. Antigenic subtyping and epitopes’ competition analysis of porcine circovirus type 2 using monoclonal antibodies. Vet Microbiol. 2012;157(1–2):13–22. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.11.030
19. Hamel AL, Lin LL, Nayar GP. Nucleotide sequence of porcine circovirus associated with postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome in pigs. J Virol. 1998;72(6):5262–5267. doi:10.1128/JVI.72.6.5262-5267.1998
20. Lefebvre DJ, Van Doorsselaere J, Delputte PL, Nauwynck HJ. Recombination of two porcine circovirus type 2 strains. Arch Virol. 2009;154(5):875–879. doi:10.1007/s00705-009-0379-8
21. Nawagitgul P, et al. Open reading frame 2 of porcine circovirus type 2 encodes a major capsid protein. J Gen Virol. 2000;81(9):2281–2287. doi:10.1099/0022-1317-81-9-2281
22. Ding P, Zhang T, Li Y, et al. Nanoparticle orientationally displayed antigen epitopes <br>improve neutralizing antibody level in a model of porcine circovirus type 2. Int J Nanomed. 2017;12:5239–5254. doi:10.2147/IJN.S140789
23. Fan Y, Guo L, Hou W, et al. The Adjuvant Activity of Epimedium Polysaccharide-Propolis Flavone Liposome on Enhancing Immune Responses to Inactivated Porcine Circovirus Vaccine in Mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:972083. doi:10.1155/2015/972083
24. Hu G, Wang N, Yu W, et al. Generation and immunogenicity of porcine circovirus type 2 chimeric virus-like particles displaying porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus GP5 epitope B. Vaccine. 2016;34(16):1896–1903. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.02.047
25. Piñeyro PE, et al. Expression of antigenic epitopes of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) in a modified live-attenuated porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) vaccine virus (PCV1-2a) as a potential bivalent vaccine against both PCV2 and PRRSV. Virus Res. 2015;210:154–164.
26. Fang Y, Lin D, Yao S. Review on biomimetic affinity chromatography with short peptide ligands and its application to protein purification. J Chromatogr A. 2018;1571:1–15. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2018.07.082
27. Lowe DG, Fendly BM. Human natriuretic peptide receptor-A guanylyl cyclase. Hormone cross-linking and antibody reactivity distinguish receptor glycoforms. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:21691–21697.
28. Hao J, Wang F, Xing G, et al. Design and preliminary application of affinity peptide based on the structure of the porcine circovirus type II Capsid (PCV2 Cap). PeerJ. 2019;7:e8132. doi:10.7717/peerj.8132
29. Novelli F, Casanova J. The role of IL-12, IL-23 and IFN-γ in immunity to viruses. Cytokine Growth F R. 2004;15:367–377. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2004.03.009
30. Wajant H, Scheurich P. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 2 and its role in TNF signaling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2001;33(1):19–32. doi:10.1016/S1357-2725(00)00064-9
31. Wu P, Chen T, Chi J, Chien M, Huang C. Efficient expression and purification of porcine circovirus type 2 virus-like particles in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol. 2016;220:78–85. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.01.017
32. Zaveckas M, Snipaitis S, Pesliakas H, Nainys J, Gedvilaite A. Purification of recombinant virus-like particles of porcine circovirus type 2 capsid protein using ion-exchange monolith chromatography. J Chromatography B. 2015;991:21–28.
33. He J, Wan J, Yang T, Cao X, Yang L. Recyclable aqueous two-phase system based on two pH-responsive copolymers and its application to porcine circovirus type 2 Cap protein purification. J Chromatogr A. 2018;1555:113–123. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2018.04.032
34. Yin S, et al. Self-assembly of virus-like particles of porcine circovirus type 2 capsid protein expressed from Escherichia coli. Virology Journal. 2001;33(1):166. doi:10.1186/1743-422X-7-166
35. Gupta AK, Curtis ASG. Lactoferrin and ceruloplasmin derivatized superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for targeting cell surface receptors. Biomaterials. 2004;25(15):3029–3040. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.09.095
36. Panyam J, Sahoo SK, Prabha S, Bargar T, Labhasetwar V. Fluorescence and electron microscopy probes for cellular and tissue uptake of poly(d, l-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2003;262(1–2):1–11. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(03)00295-3
37. Lopez-Sagaseta J, Malito E, Rappuoli R, Bottomley MJ. Self-assembling protein nanoparticles in the design of vaccines. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2016;14:58–68.
38. Smith DM, Simon JK, Baker JJ. Applications of nanotechnology for immunology. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13:592–605.
39. Kumar S, Anselmo AC, Banerjee A, Zakrewsky M, Mitragotri S. Shape and size-dependent immune response to antigen-carrying nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2015;220:141–148.
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.