Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 15
Influence of Simvastatin-Strontium-Hydroxyapatite Coated Implant Formed by Micro-Arc Oxidation and Immersion Method on Osteointegration in Osteoporotic Rabbits
Authors Zhao B, Li X , Xu H, Jiang Y, Wang D, Liu R
Received 5 January 2020
Accepted for publication 6 March 2020
Published 16 March 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 1797—1807
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S244815
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Baodong Zhao,1,2 Xin Li,1,2 Hao Xu,1,2 Yaping Jiang,1,2 Dashan Wang,1,2 Ran Liu1,2
1Department of Oral Implantology, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, Shandong 266001, People’s Republic of China; 2School of Stomatology, Qingdao University, Qingdao, Shandong 266001, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Xin Li
The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University No. 59 Haier Road, Laoshan District, Qingdao, Shandong 266001, People’s Republic of China
Tel +86532-82913583
Email [email protected]
Purpose: Enhancing osteointegration of implants in osteoporosis patients is a necessity since implantations frequently fail in these patients. The aim of this work is to study how simvastatin-strontium-hydroxyapatite coated implants perform in rabbits with osteoporosis.
Materials and Methods: Crystalline HA and Sr-HA oxide film were prepared through micro-arc oxidation. Surface characterization including morphology, roughness, element composition, phase composition, hydrophilicity were then evaluated. Simvastatin loaded on porous films through immersion, and the effects of coatings on osteointegration in osteoporotic rabbits were investigated. All samples were obtained after 4, 8 and 12 weeks of healing. Some of them were subjected to biomechanical tests and others were subjected to histological and histomorphometric analysis.
Results: Coatings exhibited a microporous network structure with appropriate roughness and high hydrophilicity. Compared to control HA and machined surface implants, simvastatin-Sr-HA coated implants exhibited marked improvements in osteointegration, which is characterized by a quicker mineralization deposition rate, good bone formation mode (large amount of contact osteogenesis and a small amount of distance osteogenesis) and increased bone-to-implant contact and pull-out strength.
Conclusion: These biological parameters demonstrate the excellent osteoconductivity of simvastatin-Sr-HA coatings in the osteoporotic state. Overall, this suggests that simvastatin-Sr-HA coatings would be applicable in poor-quality bones of patients experiencing osteoporosis.
Keywords: osteoporosis, micro-arc oxidation, strontium, simvastatin, osteointegration, dental implants
Introduction
Dental implantation is a widely accepted treatment for patients with tooth loss or defects. However, osteoporosis, which has a high incidence rate, causes “soft bone,” leading to implant failure.1,2 Thus, enhancing the osteointegration of implants in patients with osteoporosis has become a timely topic.
Micro-arc oxidation (MAO) is a technique that directly generates ceramic oxide film on titanium (Ti), which can optimize the surface morphology of Ti as well as promoting biological activity.3–5 Many elements in electrolytes, such as Ca, P and Sr, can be added to Ti coating to increase its bioactivity.6,7 In addition, its multi-microporous structure can achieve long-term stable release of metal ions.8 Chen et al reported that crystalline hydroxyapatite (HA) can be obtained directly by MAO.9 However, high crystalline HA formed under high-temperature arc conditions is difficult to degrade and has weak biological activity and relatively single structure. Improving its crystallinity and degradability for better fusion with natural bone has become a new direction for research.
Strontium (Sr) is an essential trace element in the human body, which has dual effects of promoting bone formation10,11 and inhibiting bone resorption.12,13 Strontium ranelate has been successfully used to treat osteoporosis. What is more, it can increase the stability and bone bonding of implants by enhancing the amount and micro-framework of newly formed bone at the implant-bone interface.14,15 However, systemic application of strontium ranelate has side effects, such as drug eruption and eosinophil infiltration.16 To diminish the adverse reactions of systemic administration, Sr can be introduced into HA since it has chemical resemblance to Ca. Due to the different radii and properties of the two atoms, the lattice of Sr-doped HA can be distorted, the crystallinity and grain size of HA can decrease, and the biodegradability increases.17 Studies show that Sr-HA promotes proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts in vitro and also shows good biocompatibility and osteoconductivity in vivo.18 However, further clinical studies are needed to fully confirm these observations.
Statins are widely used in the treatment of hyperlipidemia.19 Recent studies showed the beneficial effects of statins on upregulating bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) in osteoblasts to treat osteoporosis.20 However, studies on statins and the osteointegration of implants focus on systemic administration, where the average dose is not sufficient to promote osteogenesis because of the liver first pass effect.21 In contrast, high doses produce toxic side effects such as hepatotoxicity and myotoxicity. Therefore, local application of simvastatin is more effective in inducing bone formation as compared to systemic administration. The porous film formed by MAO is favorable for adsorption of simvastatin and it has an early rapid release. It was speculated that this release could affect early cell response immediately after implantation.22
In this study, crystalline HA and Sr-HA oxide film were formed by MAO and the properties of the films were evaluated. Simvastatin loaded on porous films through immersion and the effect of coating on osteointegration around implants in osteoporotic rabbits were studied dynamically.
Materials and Methods
Sample Preparation and Surface Treatment
Surface treatment of Ti samples was performed as described previously.5 Titanium plates (d=8mm) were used for characterization analysis and titanium implants (3.4*9) were used for animal experiments. All samples were divided into three groups including A: machined surface, B: micro-arc oxidation (MAO) and C: Sr-doped micro-arc oxidation (MAO-Sr). The component and concentrations of electrolytes are shown in Table 1. During the MAO process, the applied voltage, pulse frequency, duty cycle and duration time were set at 300 V, 700 Hz, 5% and 10 min, respectively, at a constant temperature of 35°C. After each treatment, samples were washed with distilled water under sonication and were then dried in air. All samples were sterilized by autoclaving prior to experimentation.
 |
Table 1 The Component and Concentrations of Electrolyte of Different Groups |
Preparation of Simvastatin Coating on Porous Surfaces
Simvastatin was dissolved in 75% alcohol and the concentration of the mixture was 10−6 mol/L. Group C implants were soaked in simvastatin solution for 48 hrs and then allowed to dry at room temperature. The other two groups were immersed in 75% alcohol only for 48 hrs. All samples were sterilized using ultraviolet light for 1 hr before implantation procedures.
Surface Characterization
Phase components of coatings were evaluated by X-ray diffraction (XRD). B and C groups were fixed on the sample table of the X-ray diffractometer with working perimeters that included a voltage of 40kV, current of 150mA, scanning mode of 2θ angle, continuous scanning and a speed of 5°/min. Data were analyzed using MDI jade 5.0 software.
Surface morphology were observed with a scanning electron microscope (SEM, ZEISS EVO®18). The elements and their distribution at three different points for every sample were analyzed using an energy dispersive spectroscope (EDS) incorporated into the SEM.
Roughness of each group at three different points was analyzed using a white light interferometer (BRUKER, Germany). The means of the three measurements were calculated. Ra is presented as the mean deviation of the profile offset by the sampling length (Profile Arithmetical Deviation)
The contact angle of deionized water on the sample surface was measured by photoelectric measuring microscope (KEYENCE, Japan). A total of 8 μL of deionized water was dropped onto the surface of each group, images were collected and the contact angles were measured.
Animal Model of Osteoporosis and Implantation
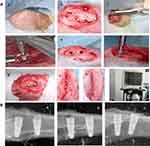
Animal experiments were approved by the Animal Research Committee of Qingdao University and conformed to ARRIVE guidelines. Sixteen female New Zealand rabbits, aged 5–6 months and weighing 3.5–4 kg, were selected for this study. Osteoporosis was induced by ovariectomy combined with injection of dexamethasone for 3 months. Successful osteoporotic models were validated by dual energy X-ray bone mineral density measurements and serum ALP detection. Osteoporotic rabbits were randomly assigned either to 4-, 8- and 12-week groups. The tibias of each rabbit had four implant sites where it randomly received different surface-treated implants. The implant installation procedure was performed under continuous irrigation with 0.9% sterile saline at 4°C, with a rotation speed of 800 r/min, depth maintained at 8 mm in contact with upper and lower cortical and implantation torque of approximately 15 N. Anesthesia and surgical procedures were similar as described in previous studies5 (Figure 1). X-rays (Kodak, America) were taken to observe the position and axis of the implants.
Fluorescence Labeling of Bone Specimens
First, rabbits were labeled with tetracycline hydrochloride (5mg/mL) 13 and 14 days before execution. Calcein (5g/l) was injected subcutaneously 3 and 4 days before execution as a second labeling method. All animals were euthanized by intravenous injection of excessive anesthetics at the auricular margin.
Implant Pull-Out Tests
Specimens were embedded in self-curing resin at a width of 9 mm and fixed on a Shimadzu universal testing machine. The implants were vertically pulled out at a crosshead speed of 1 mm/min. The force to separate the implant and bone, the maximum pull-out force, was recorded.
Histological Examination
Tibia containing implants were dissected with 2 mm of the mesial and distal bone preserved, fixed in formaldehyde solution for 7 days and then dehydrated in increasing gradients of ethanol. Then, specimens were embedded in polymethyl methacrylate resin. After hardening, blocks were ground and cut along the long axis of the implant into 200μm-thick sections using EXAKT300CP. Then, they were ground to ~40μm in final thickness using Exakt 400 CS grinding.
Slices were stained with acid fuchsin-methylene blue for static histological observation at an Olympus light microscope magnification of 100×. Fluorescence microscopy was performed for tracing tetracycline-calcein labelling. For quantitative analysis, histomorphometric parameters including bone-to-implant contact (BIC%) and mineral apposition rate (MAR) were measured on three different sections for each sample.
Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as the mean±standard deviation. Groups with the same treatment at different time nodes as well as groups with different treatments at the same time nodes were compared through single factor analysis of variance. The Student-Newman-Keuls method was used for a comparison between groups. A P <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Characterization Analysis
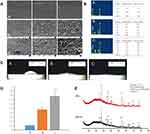
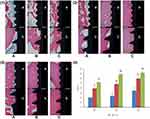
SEM images (Figure 2A). The surface of group A was relatively smooth with scratches in the same direction and the surface of group B and C exhibited “ejection holes” with sub-micron to micron diameters. Large holes embedded with small holes and connected with each other.
EDS analysis (Figure 2B). Ti was the main component of group A, and Ti, O and Ca were the main components of group B. In group C, besides Ti, O and Ca, there was a certain proportion of Sr and the atomic ratio of Sr/(Sr+ Ca) was about 12%.
Contact angle. As shown in Figure 2C and Table 2, the hydrophilicity of samples was significantly enhanced with MAO treatment, which was manifested as the smaller contact angle of groups B and C compared to group A (P < 0.01). Although the contact angle of group C was smaller than that of group B, there was no significant difference between the two (P > 0.05).
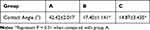 |
Table 2 Contact Angles of Each Group |
Roughness (Ra) (Figure 2D). The roughness of B and C groups was significantly higher than that of group A (P<0.05), and showed statistically significant differences between the two groups (P=0.03).
XRD spectra (Figure 2E). In group B, HA, rutile and anatase peaks were detected, while group C coatings mainly consisted of SryCa(10-y)(PO4)6(OH)2 (0 < y < 10), rutile and anatase. The characteristics of diffraction peaks of the two groups were similar since Sr and Ca are of the same family. However, in group C, the lattice constant of HA increased and the peak shifted to lower 2θ values (left).
Pull-Out Tests
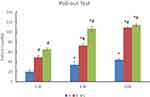
As shown in Figure 3, the maximum pull-out force in each group increased gradually with the prolongation of time. The pull-out force for group C was significantly higher than the other two groups (P < 0.01), and group B was also significantly higher than that of group A. The force of group C increased by 63% from 4 to 8 weeks, which was higher than group B (48%), while the increase declined from 8 to 12 weeks, indicating that osteointegration was almost completed by week 8. The process slowed down starting week 8.
Fluorescent Microscopy Analysis
Under the fluorescent microscope, new bone was labeled by fluorescence sequences when stimulated by green light. Old bone was characterized by dark green without a label. The tetracycline-labeled yellow fluorescence (mixed with green fluorescence, appearing as light green) represents late-stage bone remodeling and maturation. The calcein-labeled green fluorescence represents vigorous bone metabolism and growth.
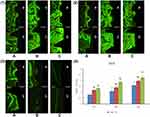
Week 4 (Figure 4(1))
In group A, little bone formation was observed at the implant-bone interface, which was manifested as fine bi-color fluorescent bands, some of which expanded outward in circular centers, resulting in multicentric osteogenesis. The yellow bands, which were present in a smaller proportion, were not in contact with implants, indicating distant osteogenesis. In group B, bi-color fluorescent bands were thicker and more numerous than that of group A, and the proportion of yellow bands coming into contact with implants were larger. Green bands were located towards both the implant and original bone, indicating that both distant and contact osteogenesis were present. In group C, bi-color fluorescent bands were obvious and thick, indicating a higher degree of bone formation and remodeling. In addition, yellow bands coming into contact with implants were the highest in group C compared to the other two groups. This demonstrated strong osteoconductivity of implants and that contact osteogenesis predominated.
Week 8 (Figure 4(2))
In group A, yellow stripes increased and two-color fluorescence gradually changed from multiple centers to a connected band. However, the fluorescent bands were narrow and the interface were mainly of green fluorescence. In group B, new bone was increasingly deposited, fluorescent bands gradually changed from sheet to strip becoming more regular and obvious and exhibited a quicker speed of osteogenesis than group A. In group C, new bone was significantly deposited, which presented characteristics of a mature trabecular. The two-color bands were much thicker and denser containing more yellow bands located around the implant and displaying superior effects of contact osteogenesis. Osteointegration was partly completed at the interface.
Week 12 (Figure 4(3))
In group A, fluorescent strips decreased and became banded. However, there were still obvious fluorescent bands at the implant-bone interface, indicating that distant osteogenesis was ongoing. In group B, the proportion of yellow bands significantly decreased. Fluorescent bands neighboring the implant reduced, which were located far from the interface, revealing that the process of osteointegration was quicker than observed in group A. In group C, the fluorescent bands almost disappeared at the interface and were further away from the implant as compared to groups A and B, suggesting that osteointegration had been completed.
Quantitative analysis of new bone formation around implants and the dynamic histomorphometric index-MAR are presented in Figure 4(4). MAR refers to the thickness of newly formed mineralized bone in unit time (ie, the average distance between the double fluorescent bands (randomly select three points to measure the distance and calculate the average value) divided by the marker interval time (10d)). The results showed that the MAR of each group increased gradually with the prolongation of time. This increase was statistically significant compared to the previous period (P < 0.01). At the same time, MAR in group C showed the greatest increase when compared with groups A and B (P < 0.01), and group B was significantly higher than group A.
Histological Examination
When analyzing with microscopy, implants appeared black, the bone marrow cavity was recorded as blue, the bone trabecula were seen as pink, the osteoblasts were dark blue, the osteocytes were black dots, the calcified bone matrix was presented as red and the fibrous tissue around the implant appeared blue.
Week 4 (Figure 5(1))
In group A, red-stained, newly formed bone was not abundant and came mainly from original bone without direct contact with the implant. Osteoclasts absorbed the bone matrix with many defects left and few osteoblasts attached to the surface of the implant. In group B, there were more osteoblasts seen at the implant-bone interface, pink osteoid began to appear and new bone was continuous. Some new bone made direct contact with the implant with no obvious absorption lacunae, which had been filled by osteoblasts and new bone. In group C, mature, continuous and compact new bone made contact directly with the implant, and the gaps were smaller than that of the other groups. Osteoblasts actively functioned to completely fill defects. No absorption lacunae were found, denoting that osteoclast activity had completely stopped.
Week 8 (Figure 5(2))
In group A, osteogenesis was shown to be multicentric. New bone gradually formed from original bone to the implant and the gap between them was reduced. Blue-stained osteoblasts near the concave area of the implant threads increased, indicating that bone formation gradually replaced bone resorption. However, osteoblasts were located mainly at the original bone site instead of attaching to the implant surface and the gap was still observed to be larger than the other two groups. Osteogenic efficiency of group B was higher than group A, which were manifested in calcified bone matrix filling most of the gaps between the implant and bone. However, there were still small gaps left. In group C, bone made close contact with the implant with no obvious gaps. Calcified bone matrix, osteoid, osteocytes in trabecular and bone lacunae were more numerous, and osteoblasts were more dense than observed in groups A and B.
Week 12 (Figure 5(3))
In group A, the calcified bone matrix, lacuna embedded with osteocytes and the density of osteoblasts was increased. More calcified bone matrix grew into the implant threads, and some made contact with the implant. However, observable gaps were larger than seen in groups B and C. In group B, the gap was significantly reduced and the contact area was larger than seen in group A. Calcified bone matrix and osteoid were increased, and the Haversarian system was distinct. A small number of osteoblasts were found on or near the implant surface, indicating that osteogenesis was ongoing. In group C, almost all the surface and adjacent sites of the implant were deposited with calcified bone matrix. Some osteocytes and empty lacunae were also observed; however, a large osteoblast population was not found and the Haversarian system was more obvious.
BIC refers to the bone-implant contact length/total implant length. As shown in Figure 5(4), the BIC of each group increased with the prolongation of time, to the maximum in 12 weeks. This increment compared to the previous period showed statistical significance (P < 0.01). In the same period, the BIC of group C was the highest, while that of group A was the lowest. The differences among the three groups were statistically significant (P < 0.01).
Discussion
Osteointegration of implants depends on both initial stability provided by the mechanical support of host bone and secondary stability generated by the physiological process of reconstruction and regeneration.23,24 Osteoporotic tissues could not guarantee or support initial stability of implants, often requiring longer healing time.25 The pathological process lies in the inconsistency between bone formation and resorption. In the early stages of implantation, increasing the activity of osteoblasts and inhibiting the function of osteoclasts are crucial. Current conventional surface modifications only enhance bone remodeling under physiological conditions, instead of focusing on osteoporotic pathology. Based on conventional modifications, factors or drugs for treatment of osteoporosis should be introduced into the coatings to correct this imbalance, thereby increasing success rate of implants exposed to conditions of osteoporosis.
Sr can improve the stability and bone bonding of implants. In this study, Sr was doped into HA by MAO, which not only ensured the proper concentration of Sr in the coating, but also guaranteed Sr-HA bonding strength and biodegradability. Simvastatin is liposoluble, low cost, has stable chemical properties, can enhance BMP-2 expression and improve angiogenesis.26 Utilizing BMP-2 for surface modification needs a carrier; otherwise, it will be absorbed before the osteointegration process begins. Issues with chemical instability and high cost are also problematic. The morphology of interconnected holes by MAO contributes to adsorbing simvastatin directly onto the layer. An intermediate layer of drug carrier is not needed and osteoblasts can therefore directly adhere and deposit bone matrix onto the implant surface. Local application of Sr and simvastatin could play a sustained and effective role in stimulating osteogenesis in osteoporosis.
Based on characterization analysis, Ti samples exhibited optimum roughness and surface appearance after MAO treatment. Surface roughness is conducive to the formation and growth of new bone around implants and is necessary for long-term stability.27 A 10nm-10μm roughness is generally believed to be more favorable for biocompatibility. The nano-to micron-scale holes contribute to the attachment of osteoblasts HA deposition, improves mechanical chimerism and enhances biological activity.28 In addition, the porous morphology promotes the fluid flow in the structure, increasing hydrophilicity, which can accelerate bone bonding, shortening healing time and improving the success rate of implants.
Except for favorable changes in topology, Ca and Sr, which availed chemical bonding between implant and bone, were introduced into the oxide layer. Rutile, anatase and crystalline HA were also confirmed in the coatings. Rutile and anatase demonstrated that the oxide film is a dense ceramic layer, its biocompatibility prevails over pure titanium and has the ability to induce bone-like apatite formation.29 HA with high crystallinity has been proven both in vivo and in vitro to accelerate cell proliferation.30,31 Group C coatings have higher biological activity due to the incorporation of Sr, which decreases lattice energy, reduces crystallinity and increases the biodegradability of HA.32
Tetracycline-calcein fluorescence labeling is a common method to dynamically analyze new bone formation around an implant. New bone forms in two ways including contact osteogenesis and distant osteogenesis.33 Contact osteogenesis refers to the orientation of bone growth from implant to bone, which occurs on bioactive surfaces with osteoconductive properties. Osteoblasts can directly anchor, grow and divide on the surface to form new bone and achieve osteointegration.34 In contrast, distant osteogenesis progresses from the original bone to implant. Contact osteogenesis was 30% faster than distant osteogenesis in studies via fluorescence labeling.35 By comparing the fluorescent images horizontally and vertically, group C exhibited excellent and active contact osteogenesis. As another dynamic indicator of fluorescence labeling, MAR of group C exhibited the greatest and showed statistical significance compared to the other two groups. It is speculated that Sr and simvastatin in group C enhanced the activity of osteoblasts under osteoporosis, which adheres to the implant surface at early stage to form new bone and effectively deposit minerals.
Methylene blue-acid fuchsin staining is a suitable method to study the cytology of interface and distinguish the implant from new bone. Results showed that implants in group C made closer contact with bone, had abundant bone matrix, exhibited numerous osteoblasts and osteocytes and showed an outstanding Haversarian system close to implant as compared with group A and B. Even in osteoporotic states, many osteoblasts on the implant and red-stained bone matrix could be observed at week 4, indicating that Sr and simvastatin enhanced the activity of osteoblasts, promoting their proliferation and differentiation to secrete matrix and mineralization.
Bonding strengths of the implant-bone is an important factor to determine the success and service life of an implant. BIC and pull-out tests are common indicators to evaluate the degree of bonding. In this study, BIC% and maximum pull-out force of implants in group C were significantly higher than those of groups A and B, demonstrating the greatest bonding strength. The bonding strength is not only related to the surface morphology, but also to osteotropic factors in the coating. Even without significant differences in morphology and hydrophilicity between groups B and C, bonding strength of group C still exceeded that of group B significantly, which indicated that Sr and simvastatin played an important role in enhancing the bone bonding of implants.
From these analyses, we can conclude that the appropriate roughness and the topology of micro-nano holes, high hydrophilicity, excellent osteoconductivity of HA, increased degradation of Sr-HA, physiological effects of Sr and simvastatin equip implants with sufficient properties to prompt osteointegration under osteoporotic states.
Conclusions
Sr-HA-simvastatin coating prepared by MAO significantly improves the osteointegration of implants in osteoporotic states, which is characterized by quicker mineralization deposition rates (MAR), good bone formation modes (large amount of contact osteogenesis and a small amount of distance osteogenesis) and increased bone bonding strength.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the expert technical assistance of WeiGao Biomaterials Co., Ltd. and Professor Fengying Yan in Qingdao University of Science and Technology for her support and guidance.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Hui C, Nizhou L, Xinchen X, et al. Smoking, radiotherapy, diabetes and osteoporosis as risk factors for dental implant failure: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e71955. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0071955
2. Chrcanovic BR, Kisch J, Albrektsson T, et al. Factors influencing early dental implant failures. J Dent Res. 2016;95:995–1002. doi:10.1177/0022034516646098
3. Durdu S, Korkmaz K, Aktuğ SL, et al. Characterization and bioactivity of hydroxyapatite-based coatings formed on steel by electro-spark deposition and micro-arc oxidation. Surf Coat Technol. 2017;326(Part A):111–120. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.07.039
4. Jing W, Zhang M, Jin L, et al. Assessment of osteoinduction using a porous hydroxyapatite coating prepared by micro-arc oxidation on a new titanium alloy. Int J Surg. 2015;24(Pt A):51–56. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2015.08.030
5. Li X, Xu H, Zhao B, et al. Accelerated and enhanced osteointegration of MAO-treated implants: histological and histomorphometric evaluation in a rabbit model. Int J Oral Sci. 2018;10:11. doi:10.1038/s41368-018-0008-z
6. Hu CJ, Hsieh MH. Preparation of ceramic coatings on an Al–Si alloy by the incorporation of ZrO2 particles in microarc oxidation. Surf Coat Technol. 2014;258:275–283. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.09.012
7. Yang SP, Lee TM, Lui TS. Biological response of Sr-containing coating with various surface treatments on titanium substrate for medical applications. Appl Surf Sci. 2015;346:554–561. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.03.190
8. Huang Q, Liu X, Elkhooly TA, et al. Preparation and characterization of TiO2/silicate hierarchical coating on titanium surface for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng. 2016;60:308–316. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2015.11.056
9. Chen JZ, Shi YL, Wang L, et al. Preparation and properties of hydroxyapatite-containing titania coating by micro-arc oxidation. Mater Lett. 2006;60:2538–2543. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2006.01.035
10. Diepenhorst NA, Leach K, Keller AN, et al. Divergent effects of strontium and calcium-sensing receptor positive allosteric modulators (calcimimetics) on human osteoclast activity. Br J Pharmacol. 2018;175:4095–4108. doi:10.1111/bph.14344
11. Lavet C, Mabilleau G, Chappard D, et al. Strontium ranelate stimulates trabecular bone formation in a rat tibial bone defect healing process. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28:3475–3487. doi:10.1007/s00198-017-4156-3
12. Steffi C, Shi Z, Kong CH, et al. Use of polyphenol tannic acid to functionalize titanium with strontium for enhancement of osteoblast differentiation and reduction of osteoclast activity. Polymers. 2019;11:1256. doi:10.3390/polym11081256
13. Pilmane M, Salma-ancane K, Loca D, et al. Strontium and strontium ranelate: historical review of some of their functions. Mater Sci Eng. 2017;78:1222–1230. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2017.05.042
14. Scardueli CR, Bizelli-silveira C, Marcantonio RAC, et al. Systemic administration of strontium ranelate to enhance the osseointegration of implants: systematic review of animal studies. Int J Implant Dent. 2018;4:21. doi:10.1186/s40729-018-0132-8
15. Apostu D, Lucaciu O, Lucaciu GD, et al. Systemic drugs that influence titanium implant osseointegration. Drug Metab Rev. 2017;49:92–104. doi:10.1080/03602532.2016.1277737
16. Moreno-higueras M, Callejas-rubio JL, Gallo-padilla L, et al. Dress syndrome and bilateral panuveitis caused by strontium ranelate. Med Clín. 2017;149:317–318. doi:10.1016/j.medcli.2017.05.031
17. Li ZY, Lam WM, Yang C, et al. Chemical composition, crystal size and lattice structural changes after incorporation of strontium into biomimetic apatite. Biomaterials. 2007;28:1452–1460. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.11.001
18. Panzavolta S, Torricelli P, Casolari S, et al. Strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite-gelatin biomimetic scaffolds modulate bone cell response. Macromol Biosci. 2018;18:e1800096. doi:10.1002/mabi.201800096
19. Hamelin BA, Turgeon J. Hydrophilicity/lipophilicity: relevance for the pharmacology and clinical effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1998;19:26–37. doi:10.1016/S0165-6147(97)01147-4
20. Shahrezaee M, Oryan A, Bastami F, et al. Comparative impact of systemic delivery of atorvastatin, simvastatin, and lovastatin on bone mineral density of the ovariectomized rats. Endocrine. 2018;60:138–150. doi:10.1007/s12020-018-1531-6
21. Bellosta S, Fed N, Bernini F, et al. Non-lipid-related effects of statins. Ann Med. 2000;32:164–176. doi:10.3109/07853890008998823
22. Nyan M, Hao J, Miyahara T, et al. Accelerated and enhanced bone formation on novel simvastatin‐loaded porous titanium oxide surfaces. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015;16:675–683. doi:10.1111/cid.12045
23. Shibata Y, Tanimoto Y, Maruyama N, et al. A review of improved fixation methods for dental implants. Part II: biomechanical integrity at bone–implant interface. J Prosthodont Res. 2015;59:84–95. doi:10.1016/j.jpor.2015.01.003
24. Li X, Zhang J, Wang X. Bone minimodeling, a special modeling pattern and potential as therapeutic target for osteoporosis. Curr Mol Med. 2018;18:233–240. doi:10.2174/1566524018666181004113128
25. Liu Y, Rath B, Tingart M, et al. Role of implants surface modification in osseointegration: a systematic review. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2020;108:470–484. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.36829
26. Liu X, Tu Y, Zhang L, et al. Prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors protect from the bone loss in ovariectomy rats by increasing bone vascularity. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;69:141–149. doi:10.1007/s12013-013-9780-8
27. Wei N, Bin S, Jing Z, et al. Influence of implant surface topography on bone-regenerative potential and mechanical retention in the human maxilla and mandible. Am J Dent. 2014;27:171–176.
28. Lin DJ, Fuh LJ, Chen WC. Nano-morphology, crystallinity and surface potential of anatase on micro-arc oxidized titanium affect its protein adsorption, cell proliferation and cell differentiation. Mater Sci Eng. 2020;107:110204. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2019.110204
29. Pan X, Li Y, Abdullah AO, et al. Micro/nano-hierarchical structured TiO2 coating on titanium by micro-arc oxidation enhances osteoblast adhesion and differentiation. R Soc Pen Sci. 2019;6:182031. doi:10.1098/rsos.182031
30. Su Y, Cockerill I, Zheng Y, et al. Biofunctionalization of metallic implants by calcium phosphate coatings. Bioact Mater. 2019;4:196–206. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2019.05.001
31. Jeong J, Kim JH, Shim JH, et al. Bioactive calcium phosphate materials and applications in bone regeneration. Biomater Res. 2019;23:4. doi:10.1186/s40824-018-0149-3
32. O’donnell MD, Fredholm Y, De RA, et al. Structural analysis of a series of strontium-substituted apatites. Acta Biomater. 2008;4:1455–1464. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2008.04.018
33. Orsini E, Salgarello S, Martini D, et al. Early healing events around titanium implant devices with different surface microtopography: a pilot study in an in vivo rabbit model. Sci World J. 2012;2012:349842. doi:10.1100/2012/349842
34. Kuzyk PR, Schemitsch EH. The basic science of peri-implant bone healing. Indian J Orthop. 2011;45:108–115. doi:10.4103/0019-5413.77129
35. Raghavendra S, Wood MC, Taylor TD, et al. Early wound healing around endosseous implants: a review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2005;20:425–431.
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.