Back to Journals » Biologics: Targets and Therapy » Volume 8
Inactivation of chromatin remodeling factors sensitizes cells to selective cytotoxic stress
Authors Freeman M, Mazu T, Miles J, Darling-Reed S, Flores-Rozas H
Received 1 May 2014
Accepted for publication 28 June 2014
Published 14 November 2014 Volume 2014:8 Pages 269—280
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/BTT.S67046
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Miles D Freeman, Tryphon Mazu, Jana S Miles, Selina Darling-Reed, Hernan Flores-Rozas
College of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Florida A&M University, Tallahassee, FL, USA
Abstract: The SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex plays an essential role in several cellular processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, and DNA repair. Loss of normal function of the SWI/SNF complex because of mutations in its subunits correlates with tumorigenesis in humans. For many of these cancers, cytotoxic chemotherapy is the primary, and sometimes the only, therapeutic alternative. Among the antineoplastic agents, anthracyclines are a common treatment option. Although effective, resistance to these agents usually develops and serious dose-related toxicity, namely, chronic cardiotoxicity, limits its use. Previous work from our laboratory showed that a deletion of the SWI/SNF factor SNF2 resulted in hypersensitivity to doxorubicin. We further investigated the contribution of other chromatin remodeling complex components in the response to cytotoxic chemotherapy. Our results indicate that, of the eight SWI/SNF strains tested, snf2, taf14, and swi3 were the most sensitive and displayed distinct sensitivity to different cytotoxic agents, while snf5 displayed resistance. Our experimental results indicate that the SWI/SNF complex plays a critical role in protecting cells from exposure to cytotoxic chemotherapy and other cytotoxic agents. Our findings may prove useful in the development of a strategy aimed at targeting these genes to provide an alternative by hypersensitizing cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agents.
Keywords: chromatin remodeling, cancer, DNA damage/repair, heat-shock response, oxidative stress
Introduction
Chromatin remodeling plays a crucial role in gene expression. The SWI/SNF complex was identified in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by mutations, which resulted in altered regulation of the HO gene that encodes a site-specific endonuclease required for gene switching at the MAT locus through the generation of a DNA double-strand break, preventing a mating-type switch.1 Similarly, defects in the expression of the SUC2 genes encoding the invertase sucrose hydrolyzing enzyme2 were found to be the result of mutations in SNF (sucrose nonfermenting) genes,3 and were first linked with chromatin through the study of suppressors of defective subunits of the complex.4 In vitro DNase accessibility assays confirmed that the SWI/SNF complex could modify the histone-DNA structure,5 while in vivo studies proved that SWI/SNF activity allows for increased access of polymerases and transcription factors to DNA.6
Chromatin remodeling involves biochemical modifications to histones, including methylation, acetylation, and phosphorylation.7 These various modifications affect the chromatin status, affecting large regions of the genome.8,9 The SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex is essential in several cellular processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, and DNA repair.10 Loss of normal function of the SWI/SNF complex as a result of mutations in its subunits correlates with tumorigenesis in humans,11 and the status of some of the subunits, such as BRG1 and BRM, can serve as prognostic indicators in patients diagnosed with certain cancers. Individuals whose cancers were positive for both nuclear BRG1 and BRM had a 5-year survival of 72% compared with 33.6% for those with loss of these ATPases.12 The SWI/SNF complex has been implicated in the development of cancer, as its subunits have been shown either to function as tumor suppressors or to interact with known tumor suppressors and oncogenes.13 The cancers with the highest rates of mutations on SWI/SNF were ovarian clear cell (75%), clear-cell renal carcinoma (57%), hepatocellular carcinoma (40%), gastric cancer (36%), melanoma (34%), and pancreatic cancer (26%). Across all tumor types, the average frequency of SWI/SNF mutations (19%) approached that of TP53 (26%), the single most mutated tumor suppressor gene.14
Anthracycline antibiotics are commonly used as anticancer agents for a wide range of solid tumors and hematological neoplasias. Although initially an effective therapy, drug resistance can develop during the course of treatment. Anthracycline resistance cannot be overcome by increasing the dose due to the increased risk of serious side effects, such as the development of dilated cardiomyopathy.15 Cytotoxic therapy is still a relevant therapeutic approach, and efforts to make it more effective and less toxic remain an important goal.
We previously reported a genome-wide genetic screening in S. cerevisiae that identified 71 deletion strains displaying varying levels of sensitivity to doxorubicin. Of these, the snf2 deletion, involving a gene that encodes components of the SWI/SNF complex, showed significant sensitivity.16 To further investigate the contribution of chromatin remodeling factors in the survival of cells exposed to cytotoxic stresses, we evaluated the survival of SWI/SNF mutant strains treated with the commonly used chemotherapeutic agents, doxorubicin and cisplatin, and other cytotoxic stresses that mediate the action of these agents, such as oxidative stress, DNA damage, and protein denaturation (heat). Our results indicate that, of the eight SWI/SNF strains tested, snf2, taf14, and swi3 were the most sensitive mutants, and suggest that the potential targeting of the human homologues may result in cancer cells’ hypersensitization to chemotherapy, while deletion of SNF5 rendered cells resistant to some cytotoxic agents.
Materials and methods
General genetic methods and strains
Yeast extract/peptone/dextrose (YPD; 1% yeast extract, 2% peptone, 2% dextrose, and 2% agar) and synthetic complete (0.67% yeast nitrogen base without amino acid, 0.087% amino acid mixture, 2% dextrose, and 2% agar) media or the corresponding drop-out media were as described.17,18 Homozygous haploid deletion strains library (parental strain BY4741: MATa his3Δ1 leu2Δ0 met15Δ0 ura3 Δ0) was obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). The gene deletions present in the strains used in this study have been validated by polymerase chain reaction (data not shown).
Chemicals
Yeast nitrogen base, yeast extract, peptone, and dextrose were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA); doxorubicin-HCl (2 mg/mL) and cisplatin (1 mg/mL) were obtained from Bedford Laboratories (Eatontown, NJ, USA); and menadione sodium bisulfite was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, MO, USA). Working solution concentrations were as follows: doxorubicin (20 μmol/L), cisplatin (80 μmol/L), menadione (6.6 mmol/L), and etoposide (1 mmol/L), prepared under sterile conditions. The concentrations of the drugs used were selected to only marginally affect the wild-type (WT) strain, but be very toxic to the control strains. Drugs were aliquoted and stored at −20°C.
Sensitivity of strains to chemotherapeutic agents and cytotoxic stressors
The concentration of the drugs used for strain exposure was determined experimentally using the WT parental strain BY4741 as previously described.16 Briefly, single colonies were grown overnight in liquid YPD media, at 30°C with shaking. Cells were then washed and resuspended in ultrapure sterile water. Strains were then separated into control and treatment groups, and exposed to drug or vehicle for 3 hours. After exposure, the cells were once again washed and suspended in sterile water. Serial dilutions were spotted onto YPD agar plates and incubated at 30°C. Heat-shock treatment was performed by plating serial dilutions of the strains and incubating at 37°C. Cell growth was monitored daily, and colonies were counted at day 3. Survival was calculated relative to the corresponding untreated control, and sensitivity was determined relative to the survival of the WT strain. Survival, as indicated in the “Results” section, is specific for that drug concentration. Each trial involved the testing of five independent colonies for each cytotoxic agent, and three trials were performed. The survival of the WT strain was defined as 100% to be able to calculate the survival between the different trials for each drug as well as to compare the sensitivity of the strains to different drugs.
Statistical analysis
Data analysis and graphing was performed using the GraphPad Prism 4 software package. Specific analysis for each experiment is indicated in Figures 1–5. The mean of at least three trials is plotted, together with the standard deviation. Differences between mean values and multiple groups were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Statistical significance was set at P<0.05.
Results
Determination of the sensitivity of SWI/SNF deletion strains to chemotherapeutic agents doxorubicin and cisplatin
To determine the contribution of the factors comprising the chromatin remodeling complex (SWI/SNF complex) to the response to chemotherapeutic agents, we determined the survival of single-gene deletion mutants after exposure to doxorubicin and cisplatin. The concentration of the drugs used in the assays was determined empirically using the WT strain (BY4741) and corresponding positive controls (sensitive strains) as indicated in the “Materials and methods” section. There are eleven genes that encode for components of the SWI/SNF complex in S. cerevisiae, as indicated in Table 1. The deletion strains used are derived from the parental strain (BY4741) and are haploids. For this reason, the role of three genes could not be tested because their deletion strains were nonviable (ARP7, ARP9, and SWI10).
  | Table 1 Yeast SWI/SNF complex subunits |
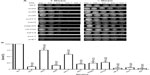
Exposure of the strains to doxorubicin clearly shows distinct levels of survival to the anthracycline. As shown in Figure 1A, no considerable growth defect is observed between the strains in the absence of the drug. The concentration of doxorubicin used only marginally affects the WT strain but, as expected, is very toxic to the control strains ssz1 (3% survival) and ydj1 (3% survival),16 which corresponds to a 14-fold and 33-fold higher sensitivity to the WT strain (P<0.05) (Figure 1A, B, and Table 2). The SWI/SNF defective strains that displayed the lowest survival were snf6 (16% survival), snf2 (10% survival), and taf14 (4% survival), which correspond to 6.3-fold, 10-fold, and 25-fold higher sensitivity compared to WT (Figure 1B and Table 2). Interestingly, the taf14 strain showed lower survival to doxorubicin than the positive control ssz1. Our data confirm that components of the SWI/SNF complex are necessary for cell viability upon exposure to doxorubicin, each providing distinct levels of protection. However, some deletion strains did not display significantly reduced survival to doxorubicin, such as snf11 (59% survival) and snf5 (76% survival, P=0.043), suggesting they may not play a major role in the response to this agent.
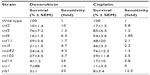  | Table 2 Sensitivity of SWI/SNF deletion strains to chemotherapeutic agents doxorubicin and cisplatin |
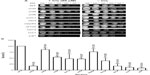
Exposure of the strains to cisplatin revealed that, as with doxorubicin, snf2 and taf14 were the most sensitive strains, with a survival of 17%, which constitutes a 5.8-fold higher sensitivity than the WT strain, for both mutants (Figure 2A, B, and Table 2). Among the least sensitive strains, snf5 displayed >80% survival. In addition, two other strains presented marginally reduced survival: snf5 (85% survival, 1.2-fold increase sensitivity relative to WT) and swp82 (76% survival, 1.3-fold higher sensitivity relative to WT) (Figure 2A, B and Table 2), a behavior that contrasts to their sensitivity to doxorubicin. The positive controls used for this assay were ssz1 and ydj1; these deletion strains behaved as expected, displaying the lowest levels of survival to cisplatin, with 11% survival for ssz1 (a 9-fold increase in sensitivity relative to WT) and 8% survival for ydj1 (a 12.5-fold increase in sensitivity relative to WT).
Determination of the sensitivity of SWI/SNF deletion strains to cytotoxic stressors
Doxorubicin and cisplatin exert their antineoplastic activity through multiple mechanisms, including DNA damage by DNA intercalation (doxorubicin) or DNA cross-linking (cisplatin); protein damage by direct binding, or through the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which also damages various cellular structures. To further elucidate the involvement of the SWI/SNF complex in the response to these types of injuries, we determined the sensitivity of the deletion strains to the oxidative stress agent menadione, the DNA-damaging chemotherapeutic agent etoposide, and the protein denaturing effect of heat shock.
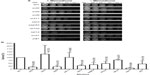
Menadione shares the same quinone ring as doxorubicin. This structure generates ROS intracellularly and mimics this property of anthracyclines. As shown in Figure 3A, the strains that displayed the lowest survival were snf2 (18% survival), snf6 (21% survival), and swi3 (30% survival) (Figure 3B), which, respectively, correspond to 5.5-fold, 4.7-fold, and 3.3-fold higher sensitivity to menadione than WT (Table 3). In contrast, the snf5 and snf11 strains exhibited no significant change in survival to menadione exposure, with a 130% and 102% survival (76-fold and 98-fold sensitivity relative to WT, respectively). The positive controls sod1 and ydj1 are highly sensitive to oxidative stress as expected, with sod1 displaying 9% survival (11-fold more sensitive than WT). Our assay indicates that some SWI/SNF components are necessary for cell viability when exposed to ROS-generating agents such as menadione.
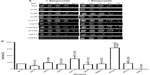
To test the effect of DNA damage, exclusively, on the SWI/SNF defective strains, we exposed the deletion mutants to the DNA-damaging agent etoposide. This agent, as with doxorubicin, inhibits DNA topoisomerase II, resulting in the accumulation of DNA double-strand breaks. When exposed to etoposide (1 mM), the majority of the SWI/SNF mutants did not display significantly reduced survival. At this drug concentration, the positive control rad52 is highly sensitive, with a survival of 0.38% (267-fold higher sensitivity than WT). However, the most doxorubicin-sensitive strains, snf2, snf6, swi3, and taf14, showed survival of 61%, 93%, 87%, and 108%, respectively, with P-values indicating that they are not significantly different from the WT strain (Figure 4A, B and Table 3). Furthermore, the rtt102 mutants (Figure 4A and B) displayed increased survival to etoposide, with a 394% survival (3.9-fold more resistant than WT; Table 3).
In thermotherapy, elevated body temperature can be an effective adjunct therapy when used with chemotherapy or radiotherapy in combating cancer.19 To investigate whether inactivation of SWI/SNF factors hypersensitizes cells to hyperthermia, we determined the viability of the deletion mutants to heat shock. The positive control ydj1 strain, which is defective in a heat-shock protein 40 (HSP40) and is essential in the heat-shock response, is highly sensitive to growth at high temperature. Among the SWI/SNF mutants, the snf6 and taf14 strains (Figure 5A) displayed the lowest survival, with 54% and 2% (which is 2-fold and 50-fold more sensitive than WT; Figure 5B and Table 3), respectively. Conversely, the swp82, swi3, and rtt102 strains (Figure 5A) exhibited the least sensitivity to heat shock, with 136%, 111%, and 133% survival, respectively (Figure 5B and Table 3).
Discussion
Cytotoxic cancer treatment is often associated with side effects and the potential development of drug resistance. However, frequently, the limited number of biological targets leaves traditional cytotoxic chemotherapy as the only therapeutic alternative. For example, patients affected by triple negative breast cancer are presently treated with single-agent or combination therapies including doxorubicin, cisplatin, epirubicin, 5-fluorouracil, paclitaxel, cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and gemcitabine.20,21 While effective, most of these chemotherapeutic agents are associated with serious side effects, such as cardiotoxicity, neutropenia, neuropathy, and persistent metastatic tumor progression.20,22 Current attempts to treat with options involving less toxicity yield a much poorer total response.23,24 Consequently, there is a need to enhance the therapeutic efficacy as well as to reduce toxic side effects.
Increasing the efficacy of chemotherapy may be achieved by hypersensitizing the cancer cells to the treatment. Sensitization may allow for the use of lower dose therapy to attain comparable response, concomitantly decreasing the risk of dose-dependent adverse effects.
Previous work from our laboratory16 identified a deletion of the SNF2 gene which hypersensitizes cells to doxorubicin, suggesting that the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex can serve as a novel target for cell sensitization to cytotoxic chemotherapy. We extended this observation by investigating the role of other SWI/SNF complex components in the response of cells to therapeutic agents, such as doxorubicin, cisplatin, and etoposide, and to defined cytotoxic stresses such as ROS and heat shock.
We tested all the nonessential mutants of the SWI/SNF complex (Table 1) to determine which deletion strains exhibited higher sensitivity in response to various forms of cytotoxic stress. Two deletion mutants, snf2 and taf14, were found to be consistently hypersensitive to all agents, except for heat shock which only significantly affected the taf14 strain.
Among the chemotherapeutic agents evaluated, doxorubicin was the most effective one, with the majority of the mutants displaying significant sensitivity relative to the WT strain. It is worth emphasizing that the concentration of the drugs used was selected to identify hypersensitive strains. Increasing the dose will eventually kill all strains, including the WT, and would not allow us to discriminate the hypersensitive strains from those unaffected. While snf2 and taf14 were hypersensitive, snf6, swi3, and swp82 displayed intermediate sensitivity and snf5, snf11, and rtt102 displayed different levels of resistance, depending on the agent. The snf5 mutant was not affected by doxorubicin, cisplatin, or etoposide, and was resistant to menadione. Similarly, the snf11 mutant was resistant to etoposide and menadione, and the rtt102 strain was highly resistant to etoposide. Proper controls were included in each experiment, with well-known hypersensitive strains, to confirm the effectiveness of the dose used.
The distinctive mechanisms of our chemotherapeutic agents may contribute to each SWI/SNF factor’s ability to protect the cell from incurring cytotoxic damage. Direct DNA damage was induced with cisplatin, which forms adducts on DNA leading to cross-linking.25 Doxorubicin has multiple cytotoxic mechanisms, including DNA damage by intercalation15 as well as the generation of free radicals15 that damage various cellular structures. To determine the mechanisms of the chemotherapeutic drugs responsible for causing the cytotoxicity in the SWI/SNF mutant strains, we selected single-action agents, such as the DNA-damaging agent etoposide, which, like doxorubicin, also inhibits DNA topoisomerase II; menadione, which generates oxidative stress; and the protein denaturing property of direct heat shock.
Interestingly, while the majority of the strains were sensitive to doxorubicin, none of them, except for snf2, was sensitive to etoposide and only partially mimicked the response when exposed to oxidative stress induced by menadione. These results suggest that anthracycline’s oxidative stress and DNA damage synergize to kill the cells.
The diverse response of the deletion strains tested may be explained by their specific interactions with distinct factors. Among the most interesting genes from our study are those that, when deleted, lead either to hypersensitivity: snf2, taf14, swp82; or to resistance: snf5, to any particular agent.
The SNF2 protein has several roles in transcriptional regulation, facilitated by its interactions with over 140 genes.26 It is required for adenosine triphosphate (ATP) hydrolysis and the conversion of the energy to power ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling, maintaining the structural integrity of the SWI/SNF complex,27 and essential for both telomere and ribosomal DNA silencing.28 The SNF2 gene has also been found to genetically interact with the DNA repair gene RAD2629 as well as the heat-shock gene HSP82. Interestingly, HSP82 interacts with SNF2, within a network of genes also interacting with SIN4, TUP1, SMT3, UBI4, SPT15, and SNF11.
TAF14 is a component of the yaf9, taf14, and sas5 YEATS domain in S. cerevisiae, which in humans includes proteins involved in acute leukemia. The YEATS domain family is essential, as a yaf9, taf14, sas5 triple mutant is nonviable.30 The YAF9 gene, which TAF14 interacts with, has been found to be required for the proper gene expression and histone acetylation near telomeres. The TAF14 gene also shows extensive genetic and physical interactions with RNA polymerase factors and TATA-binding protein-associated factors. Proper function of Taf14 is essential for RNA polymerase II transcription initiation and chromatin modification.
The Snf5 protein, which is encoded for by the SNF5 gene, is involved in the downregulation of transcriptional gene silencing (prevention of gene expression) through interactions with histone H2A and H2B31 proteins that are needed for the assembly of chromatin and the proper function of chromosomes. The SNF5 gene interacts with every factor of the SWI/SNF complex.26
The biological process of Swp82, as well as its molecular function, remains unknown. SWP82 interacts with 34 genes, including histones, ubiquitin protease, transcription factors, and the other subunits of the SWI/SNF complex.26
Several of the SWI/SNF genes that display sensitivity to our induced cytotoxic stress, such as SNF2, SWI3, and SNF5, have human homologues BRG1 or hBRM, BAF155, BAF170, and SNF5/INI1 or BAF47, respectively. The potential targeting of these factors to hypersensitize cancer cells to chemotherapy is an attractive possibility and has support from a recent study which showed that BRCA1 CpG island promoter hyper-methylation-associated silencing predicts enhanced sensitivity to platinum-derived drugs such as cisplatin.32
While subunits of the SWI/SNF complex may be mutated in human cancers, only the SNF5/INI1 (BAF47) subunit of the mammalian SWI/SNF complex, a homologue of S. cerevisiae SNF5,33 has been shown to function as a tumor suppressor.34 A recent report correlating the expression levels of the SWI/SNF factor with cancer prognosis suggests that other components of the complex may, as well, act as tumor suppressors.35
Considering the direct role of the SWI/SNF complex in the assembly of nucleosomes, alterations in the composition of the complex may play a significant role in the expression of genes directly involved in the sensitivity to drugs. Reorganization of nucleosomes may occur in the mutant strains, which alters expression of genes, concomitantly affecting drug resistance. In fact, a recent report describes the reactivation of drug resistance by reassembly of nucleosomes at sites that block expression of MLH1.36 It would be interesting to determine the expression differences between the SWI/SNF mutant strains to determine the genes involved in the cellular response to cytotoxic drugs, and correlate these expression changes with nucleosome repositioning in the genome in these strains.
Additional research will elucidate the role of these genes in mammalian cells as a required step to consider these genes and/or the pathways they participate in as potential druggable targets that can be used to enhance chemotherapeutic treatment.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the support provided by the Gene and Cell Manipulation Facility, Florida A&M University. This project was supported by the National Center for Research Resources and the National Institute of Minority Health and Health Disparities of the National Institutes of Health through grant numbers 2 G12 RR003020 and 8 G12 MD007582-28.
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Kostriken R, Strathern JN, Klar AJ, Hicks JB, Heffron F. A site-specific endonuclease essential for mating-type switching in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1983;35:167–174. | |
Lutfiyya LL, Johnston M. Two zinc-finger-containing repressors are responsible for glucose repression of SUC2 expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:4790–4797. | |
Sudarsanam P, Winston F. The Swi/Snf family nucleosome-remodeling complexes and transcriptional control. Trends Genet. 2000;16:345–351. | |
Perez-Martin J, Johnson AD. The C-terminal domain of Sin1 interacts with the SWI-SNF complex in yeast. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18:4157–4164. | |
Kingston RE, Narlikar GJ. ATP-dependent remodeling and acetylation as regulators of chromatin fluidity. Genes Dev. 1999;13:2339–2352. | |
Kingston RE, Bunker CA, Imbalzano AN. Repression and activation by multiprotein complexes that alter chromatin structure. Genes Dev. 1996;10:905–920. | |
Turner BM. Reading signals on the nucleosome with a new nomenclature for modified histones. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005;12:110–112. | |
Kornberg RD, Lorch Y. Chromatin-modifying and -remodeling complexes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999;9:148–151. | |
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th ed. New York City: Garland Science; 2002. | |
Kothandapani A, Gopalakrishnan K, Kahali B, Reisman D, Patrick SM. Downregulation of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling factor subunits modulates cisplatin cytotoxicity. Exp Cell Res. 2012;318:1973–1986. | |
Reisman DN, Sciarrotta J, Wang W, Funkhouser WK, Weissman BE. Loss of BRG1/BRM in human lung cancer cell lines and primary lung cancers: correlation with poor prognosis. Cancer Res. 2003;63:560–566. | |
Fukuoka J, Fujii T, Shih JH, et al. Chromatin remodeling factors and BRM/BRG1 expression as prognostic indicators in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:4314–4324. | |
Inoue H, Giannakopoulos S, Parkhurst CN, et al. Target genes of the largest human SWI/SNF complex subunit control cell growth. Biochem J. 2011;434:83–92. | |
Shain AH, Salari K, Giacomini CP, Pollack JR. Integrative genomic and functional profiling of the pancreatic cancer genome. BMC Genomics. 2013;14:624. | |
Minotti G, Menna P, Salvatorelli E, Cairo G, Gianni L. Anthracyclines: molecular advances and pharmacologic developments in antitumor activity and cardiotoxicity. Pharmacol Rev. 2004;56:185–229. | |
Xia L, Jaafar L, Cashikar A, Flores-Rozas H. Identification of genes required for protection from doxorubicin by a genome-wide screen in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cancer Res. 2007;67:11411–11418. | |
Kolodner RD, Alani E. Mismatch repair and cancer susceptibility. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1994;5:585–594. | |
Tishkoff DX, Boerger AL, Bertrand P, et al. Identification and characterization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae EXO1, a gene encoding an exonuclease that interacts with MSH2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:7487–7492. | |
Lee Titsworth W, Murad GJ, Hoh BL, Rahman M. Fighting fire with fire: the revival of thermotherapy for gliomas. Anticancer Res. 2014;34:565–574. | |
Gehl J, Boesgaard M, Paaske T, Vittrup Jensen B, Dombernowsky P. Combined doxorubicin and paclitaxel in advanced breast cancer: effective and cardiotoxic. Ann Oncol. 1996;7:687–693. | |
van Kuilenburg AB, Maring JG. Evaluation of 5-fluorouracil pharmacokinetic models and therapeutic drug monitoring in cancer patients. Pharmacogenomics. 2013;14:799–811. | |
O’Shaughnessy JA, Fisherman JS, Cowan KH. Combination paclitaxel (Taxol) and doxorubicin therapy for metastatic breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 1994;21:19–23. | |
Ozkan M, Berk V, Kaplan MA, et al. Gemcitabine and cisplatin combination chemotherapy in triple negative metastatic breast cancer previously treated with a taxane/anthracycline chemotherapy; multicenter experience. Neoplasma. 2012;59:38–42. | |
Kohail H, Shehata S, Mansour O, et al. A phase 2 study of the combination of gemcitabine and cisplatin in patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer previously treated with anthracyclines with/without taxanes. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2012;5:42–48. | |
Siddik ZH. Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene. 2003;22:7265–7279. | |
Saccharomyces Genome Database [database on the Internet]. Stanford, CA: Stanford University. Available from: http://www.yeastgenome.org. Accessed 28 October, 2014. | |
Richmond E, Peterson CL. Functional analysis of the DNA-stimulated ATPase domain of yeast SWI2/SNF2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996;24:3685–3692. | |
Dror V, Winston F. The Swi/Snf chromatin remodeling complex is required for ribosomal DNA and telomeric silencing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:8227–8235. | |
Malik S, Chaurasia P, Lahudkar S, Uprety B, Bhaumik SR. Rad26p regulates the occupancy of histone H2A-H2B dimer at the active genes in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:3348–3363. | |
Zhang H, Richardson DO, Roberts DN, et al. The Yaf9 component of the SWR1 and NuA4 complexes is required for proper gene expression, histone H4 acetylation, and Htz1 replacement near telomeres. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:9424–9436. | |
Geng F, Cao Y, Laurent BC. Essential roles of Snf5p in Snf-Swi chromatin remodeling in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:4311–4320. | |
Stefansson OA, Villanueva A, Vidal A, Marti L, Esteller M. BRCA1 epigenetic inactivation predicts sensitivity to platinum-based chemotherapy in breast and ovarian cancer. Epigenetics. 2012;7:1225–1229. | |
Muchardt C, Sardet C, Bourachot B, Onufryk C, Yaniv M. A human protein with homology to Saccharomyces cerevisiae SNF5 interacts with the potential helicase hbrm. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995;23:1127–1132. | |
Muchardt C, Yaniv M. When the SWI/SNF complex remodels 1/4 the cell cycle. Oncogene. 2001;20:3067–3075. | |
Numata M, Morinaga S, Watanabe T, et al. The clinical significance of SWI/SNF complex in pancreatic cancer. Int J Oncol. 2012;42:403–410. | |
Hesson LB, Patil V, Sloane MA, et al. Reassembly of nucleosomes at the MLH1 promoter initiates resilencing following decitabine exposure. PLoS Genet. 2013;9:e1003636. |
 © 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.