Back to Journals » Journal of Pain Research » Volume 9
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, hormones, and 11ß-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases
Authors Markey KA, Uldall M, Botfield H, Cato L, Miah M, Hassan-Smith G, Jensen R, Gonzalez AM, Sinclair AJ
Received 15 September 2015
Accepted for publication 29 December 2015
Published 19 April 2016 Volume 2016:9 Pages 223—232
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S80824
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Michael Schatman
Keira A Markey,1 Maria Uldall,2 Hannah Botfield,1 Liam D Cato,1 Mohammed A L Miah,1 Ghaniah Hassan-Smith,1 Rigmor H Jensen,2 Ana M Gonzalez,1 Alexandra J Sinclair1
1Neurometabolism, Institute of Metabolism and Systems Research, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK; 2Danish Headache Center, Clinic of Neurology, Rigshospitalet-Glostrup, University of Copenhagen, Glostrup, Denmark
Abstract: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) results in raised intracranial pressure (ICP) leading to papilledema, visual dysfunction, and headaches. Obese females of reproductive age are predominantly affected, but the underlying pathological mechanisms behind IIH remain unknown. This review provides an overview of pathogenic factors that could result in IIH with particular focus on hormones and the impact of obesity, including its role in neuroendocrine signaling and driving inflammation. Despite occurring almost exclusively in obese women, there have been a few studies evaluating the mechanisms by which hormones and adipokines exert their effects on ICP regulation in IIH. Research involving 11ß-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1, a modulator of glucocorticoids, suggests a potential role in IIH. Improved understanding of the complex interplay between adipose signaling factors such as adipokines, steroid hormones, and ICP regulation may be key to the understanding and future management of IIH.
Keywords: 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1, steroid and adipokines, obesity, leptin
Introduction
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), previously known as benign intracranial hypertension or pseudotumor cerebri, is a disabling condition of predominantly young, obese women of childbearing age. The condition results in raised ICP, of no known cause, resulting in visual loss, headaches, and papilledema. IIH without papilledema can also occur but is rare and not the focus of this review.
IIH affects 0.5–2 per 100,000 annually in the general population1,2 but increases to 12–20 per 100,000 for obese women of reproductive age.1–4 Female sex and obesity are strongly associated with the condition. In a cohort of 721 IIH patients, 91% were reported as female5 with 70%–88% being obese.6,7
A diagnosis of IIH is made using the updated modified Dandy criteria. This is based on the presence of papilledema, with an absence of secondary causes and raised cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure >25 cm CSF, measured by lumbar puncture in the lateral decubitus.8 The current management options for the condition are limited and include disease modification to promote weight loss and acetazolamide, but other diuretics may also be used. Surgical management varies although it mainly involves CSF shunting or sometimes optic nerve sheath fenestration and remains reserved for rapid or progressive loss of vision. Venous sinus stenting is used in some specialist centers although long-term efficacy data are awaited.
The etiology of this debilitating condition remains undetermined. Dysregulation of CSF dynamics is key and may involve hypersecretion of CSF at the choroid plexus, reduced drainage at the arachnoid granulations and/or lymphatics, and aberrant venous pressure gradients.9 It is unlikely that a single anatomical location for CSF dysregulation is exclusively responsible for the raised ICP in IIH, and multiple sites and mechanisms may be involved in impairing ICP homeostasis. As >70% of patients with the condition are obese, adiposity is felt to have a causative role in IIH, but the mechanisms by which obesity predisposes to the condition have not been fully elucidated.
Human fat is an active endocrine tissue, secreting a myriad of neuroendocrine molecules that could potentially play a role in IIH. Given the very strong female preponderance, steroid hormones are also likely to be involved.
This review provides an overview of the potential role of hormones, adipokines, and cytokines in IIH and describes new potential pathogenic mechanisms in this disease.
Obesity
Role of weight
Obesity is a predominant phenotype in IIH patients. A prospective study from the USA determined the occurrence of IIH among 1,084 obese women being evaluated for bariatric surgery (mean body mass index [BMI] 47.9 kg/m2). Seven patients were diagnosed with IIH suggesting an annual incidence in this population as high as 323 per 100,000.10 Similar results were reported by Daniels et al, who found that higher BMIs were associated with an increasingly greater risk of IIH.11 In the same study, weight gain within the 12 months prior to symptom onset was investigated, and this analysis showed that a recent weight gain was also strongly associated with the development of IIH. Interestingly, both previously obese and nonobese (BMI <30 kg/m2) patients who experienced a relatively moderate weight gain of 5%–15% had a similar increased risk of IIH.11 The fact that IIH can be triggered by weight gain implies a role for adiposity in disease development.
The importance of obesity in IIH etiology is further demonstrated by the role of weight loss in treating the underlying disease. Weight loss has proven to be effective for reducing ICP and improving visual outcomes for patients in several clinical studies, both employing calorie restriction12–14 and gastric surgeries.15,16 Additionally, a retrospective study found that minor weight loss of only ~6% led to a greater resolution in papilledema than those patients treated with acetazolamide alone.17 Taken together, these data imply that reduction in weight can ameliorate symptoms in the IIH patient cohort and suggest that reducing adipose tissue has a positive therapeutic effect on IIH.
However, the relationship between obesity and IIH is complex. The degree of weight loss does not correlate directly with the reduction in ICP.12 Furthermore, it is also important to note that 29%–50% of IIH patients do not gain any weight prior to their disease onset.3,11 The weight threshold for developing IIH may be patient specific.
How obesity leads to IIH is uncertain but a number of suggestions have been made. A study by Sugerman et al suggested that central obesity raises intra-abdominal pressure, which increases cardiac filling pressure and thereby obstructs venous return from the brain, subsequently leading to increased intracranial venous pressure and the raised ICP associated with IIH.18 However, not all obese patients have intracranial hypertension. There is only a weak positive association between lumbar puncture pressure and BMI.19,20 In addition, the CSF pressure in the general population itself can range widely from 6 to 28 cmCSF.21
The distribution of adipose tissue may play a role in the development of IIH. A small cohort study reported a lower waist-to-hip ratio in IIH patients compared with non-IIH obese subjects. This suggests a relationship with lower body adiposity compared with other obesity-related conditions, for example, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, and hypertension, which are associated largely with central adiposity.22 Further evaluation of anthropological measures in IIH is needed to confirm this finding.
Obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a condition associated with both obesity and IIH. It has been implicated as a causative factor in IIH, especially in men.23 OSA could lead to raised ICP through a dual mechanism: raised venous pressure owing to higher intrathoracic pressure and cerebral vasodilation secondary to nocturnal hypoxia and hypercapnia.24 It is well recognized that in those patients with raised ICP and significant OSA, treating the nocturnal hypoxia with continuous positive airway pressure can effectively treat the intracranial hypertension in some patients. However, obesity is a risk factor for OSA, and its concurrence with IIH may be merely a coincidence. In addition, many IIH patients do not suffer from OSA, and therefore, it is unlikely to be a major causative factor.
Inflammation
Adipose tissue is a potent endocrine organ secreting a spectrum of molecules, including adipokines and cytokines. Later, we discuss which of these have been studied in IIH.
Adipokines
Adipokines are a type of cytokine that is produced predominantly by the adipose tissue and include ghrelin, resistin, adiponectin, and leptin. Of these, leptin has been the main focus of IIH research. In particular, adiponectin and resistin have not found to be significantly different in the serum and CSF of IIH when age, sex, and BMI have been taken into account.25
Clinical studies evaluating the levels of leptin in both serum and CSF in IIH have provided conflicting results. Serum leptin was measured in women with IIH (n=15) compared with obese (n=16) and lean controls (n=15). There were significantly higher levels of leptin in the IIH group (P<0.0001), and while there was a correlation with BMI in the control groups (P<0.0006), this was not observed in IIH when matched for age, sex, and weight. The differences in leptin levels between the cohorts may have been due to varying BMIs between the groups.26 A further study looked at paired serum and CSF samples in 26 IIH patients and 62 controls with other neurological diagnoses. CSF leptin was found to be significantly higher in IIH versus age, sex, and BMI-matched controls (P=0.001). Once again, leptin levels in both serum (r=0.34; P=0.007) and CSF (r=0.51; P<0.0001) correlated with BMI, apart from that in the IIH group.25 However, two more, albeit slightly smaller, studies found no difference between CSF leptin in IIH participants and controls.27,28
Leptin itself is a 16 kDa hormone that is encoded by the Ob gene and has been shown to have a wide variety of roles, including modulation of bone formation,29 initiation of puberty,30 and involvement in the immune response.31 However, its primary role is in appetite and weight regulation and as an indicator of energy stores within the body,32 as it is produced proportionally to triglyceride stores.33 Leptin signal transduction occurs via the leptin receptor (Ob-R), of which there are six known isoforms found to be distributed throughout the body. The long form of the receptor or Ob-Rb is expressed highly in the hypothalamus, particularly in the arcuate, ventromedial, dorsal medial, and paraventricular nuclei where leptin acts as an appetite signal.34 The short forms of the receptor are more involved in the transport of leptin, for example, across the blood–CSF barrier.35 In the brain, high levels of Ob-R gene expression have been shown in the choroid plexus, leptomeninges, and blood vessels, indicating that leptin binding and internalization occurs at these locations.36 The role of leptin receptors in the choroid plexus has not been fully evaluated but may be key in transporting leptin into the CSF.
Under physiological conditions, when levels of leptin are high, signaling in the hypothalamus results in decreased appetite and increased energy expenditure, leading to weight loss. The opposite is true when the levels are low, and it is for this reason that leptin is often referred to as the satiety hormone due to its role in energy homeostasis.
Leptin’s role in obesity has been highlighted in animal models. The leptin gene knockout (ob/ob) mouse model demonstrates hypoleptinemia, while the leptin Ob-Rb receptor deficient (db/db) mouse model reversely shows hyperleptinemia. However, both display an obese phenotype and hyperglycemia due to insulin resistance.37
Thus, it is possible that dysregulation of leptin signaling could lead to inappropriate weight gain, and indeed, there is a wealth of evidence linking leptin with obesity. In studies of IIH patients, preferentially high levels of leptin were noted in the CSF.25 It would be expected that high leptin levels in the CSF would reduce satiety and consequently weight in IIH; yet, these patients remain obese. Hence, the possibility of central leptin resistance in IIH has been suggested.
It is also interesting that serum leptin exhibits sexual dimorphism, with levels higher in women than in men.38–40 The relevance to the predominantly female condition of IIH is not established.
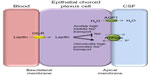
It is not clear how dysregulation of leptin in IIH influences ICP balance. Leptin does exert effects on Na+/K+ ATPase channels in the kidney, and this channel is a major driver for CSF secretion in the choroid plexus. It was shown that acute dosing of leptin in animal models led to decreased Na+/K+ ATPase activity resulting in reduced natriuresis in the kidney.41 Interestingly, long-term administration of leptin, representing a chronically elevated state led to increased Na+/K+ ATPase activity in proximal tubule cells within the renal system, probably suggesting a leptin-resistant state.41 As the choroid plexus is very similar to the renal proximal tubules in terms of function and epithelial ultrastructure,42 a chronic elevation in leptin may drive Na+/K+ ATPase activity in epithelial choroid plexus cells resulting in increased CSF secretion and hence raised ICP (Figure 1). Therefore, leptin could have a role in modulating ICP through increased CSF secretion. Further research is needed before clear conclusions can be drawn.
Cytokines and inflammation
Cytokines are small proteins involved in cell signaling that have a role in many inflammatory conditions. A number of studies have evaluated the cytokine profile in IIH (Table 1).
  | Table 1 Summary of differences in adipokines and cytokines between IIH and controls |
One study involving 26 IIH patients and 62 nonmatched controls assessed the differences in a range of cytokines in serum and CSF. These included interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6, IL-8, tumor necrosis factor-α, hepatocyte growth factor, nerve growth factor, and chemokine ligand 2, also known as monocyte chemotactic protein 1. The results from this study showed no significant differences in the cytokines tested.25
Differing results were found in a comparison of IIH (n=26) with multiple sclerosis (MS; n=13) and healthy controls (n=20). In the serum and CSF of IIH patients, there were a number of raised cytokines. Tumor necrosis factor-α was found to be elevated in the serum but not in the CSF when compared with the MS cohort.43 An alternative study demonstrated that chemokine ligand 2 was significantly raised (P<0.01) in the CSF of IIH when adjusted for BMI. However, the cohorts were small consisting of eight patients per group.27
These studies are limited by small numbers, variable sensitivities of the cytokine assays, and inconsistent control groups. However, the results could be suggestive of an inflammatory phenotype in IIH. Further studies are needed with larger IIH patient cohorts and, most importantly, healthy BMI-matched control cohorts for comparison. The mechanism by which cytokines alter ICP has not been explored to date.
Thrombotic factors
A prothrombotic state has also been noted in IIH patients, and the obesity-driven low-grade inflammation could lead to a hypercoagulable state in these patients.44 In a study of thrombotic factors in 51 IIH patients, elevated levels of factors VIII, IX, and XI, fibrinogen, and d-dimer were found. These were elevated in IIH patients who were obese compared with nonobese but only factor IX and fibrinogen positively correlated with BMI. It is possible that microthrombosis may block the arachnoid granulations or distal venous circulation impeding CSF drainage in IIH.
Steroid hormones
Sex steroids
IIH is predominantly seen in obese females of childbearing age; therefore, it is possible that female steroid hormones have a pathogenic role. However, a distinctive hormonal profile has not yet been described in IIH.
Case reports have suggested a link between the development of pseudotumor cerebri and oral contraceptives,45,46 as well as pregnancy, although the latter may also be associated with weight gain.47 These cases suggest a potential role for female sex hormones in IIH.
Increased levels of estrone have been demonstrated in the CSF of IIH patients compared with controls. However, no definitive conclusions could be made as the sample numbers in each of the studies were too low (n=548 and n=749). In one study, around half of the IIH patients were male,48 and in addition, the women’s menstrual cycle did not appear to be taken into account for either study.48,49
A larger study (n=51) that assessed the hormone profile of female IIH patients demonstrated no difference in the levels of estradiol, follicular-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, or prolactin. The study did show raised levels of androgens, including testosterone and androstenedione, in young onset (<25 years of age) female patients with IIH.50
It is not clear how sex hormones could alter ICP, but interestingly, studies in rabbits have demonstrated that estrogen and progesterone are able to reduce CSF secretion by the choroid plexus, on their own and in combination.51
Between 39% and 57% of IIH patients also suffer from polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS),52,53 which is characterized by androgen dysregulation.54 Hyperandrogenism in IIH needs to be further characterized and compared with PCOS and obese control cohorts, but it is possible that androgens could also play an important role in IIH etiology.
It is likely that a complex relationship between sex hormones and other factors such as obesity contribute to IIH. Newer hypotheses seek to connect a more multifaceted neuroendocrine mechanism with the adipose state.
Glucocorticoids and 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
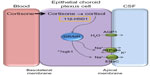
In 2012, a theory unifying various effects on the mineralocorticoid receptor was proposed by Salpietro et al to explain a possible mechanism for increased CSF production and hence ICP in secondary IIH.55 The theory describes that stimulation of the mineralocorticoid receptors in the choroid plexus epithelium increases the activity of Na+/K+ ATPase, an active transporter of sodium for potassium ions. Thus, the movement of sodium ions into the cerebral ventricles increases, creating an osmotic gradient to drive CSF secretion and increase ICP.55
Corticosteroids (mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids) have also been implicated in IIH. Addison’s disease is an endocrine disorder where the adrenal glands do not produce sufficient corticosteroids,56 and the use of exogenous glucocorticoids, particularly their withdrawal,57,58 has been found to result in secondary IIH. There have been conflicting reports that exogenous systemic corticosteroids show an acute reduction in CSF secretion at the choroid plexus in rabbits59 and dogs,60 but not rhesus monkeys.61 The lack of chronic efficacy and multiple side effects, including weight gain, means that corticosteroids are not recognized as a treatment option in IIH.
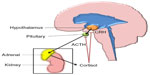
Glucocorticoids are steroid hormones with a wide range of physiological roles in the human body, including effects to the immune system, wound healing, metabolism such as gluconeogenesis and lipolysis, fetal development, and CNS maturation.62 The predominant glucocorticoid produced by the human adrenal glands is cortisol. Systemic levels of cortisol are regulated by the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) feedback system (Figure 2).
However, at a cellular specific level, the availability of active cortisol is regulated by 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (11β-HSDs). 11β-HSDs are intracellular enzymes involved in the bidirectional conversion of cellular glucocorticoids. Recently, there has been increasing interest regarding 11β-HSD type 1 (11β-HSD1) in relation to obesity, diabetes mellitus type 2, and metabolic syndrome.
11β-HSD has two isozymes (Figure 3): 11β-HSD1, which acts in a predominately oxoreductase fashion in vivo to convert inactive cortisone to active cortisol, and 11β-HSD2 that is principally a dehydrogenase, reversing the reaction in tissues such as the kidney and placenta where high glucocorticoid levels could inappropriately activate mineralocorticoid receptors. Inappropriate activation of these receptors by cortisol results in hypertension, hypokalemia, and hypernatremia.63 Hexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase colocalizes with 11β-HSD164 at the endoplasmic reticulum65 and provides energy in the form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) to the oxidized form NADP+.
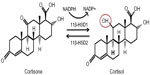  | Figure 3 11β-HSDs and GR conversion. |
11β-HSD1 activity is highest in hepatic and adipose tissue66 but has also been identified in the brain, in particular the cerebellum, neocortex, hippocampus, choroid plexus, and arachnoid granulations.67,68 Interestingly, 11β-HSD1 and key elements of the glucocorticoid signaling pathway have been found to be expressed and functional (increasing local cortisol availability) in the choroid plexus.68,69 It is possible that this local cortisol generating system could drive CSF secretion at the choroid plexus epithelium.68
Systemic administration of glucocorticoids can modify the activity of 11β-HSD1 further altering local tissue active cortisol availability. The effects of cortisol on 11β-HSD1 activity are both tissue and species specific, for example, dexamethasone can reduce 11β-HSD1 activity in rat liver and testis, thereby reducing local cortisol availability.70 In other tissues, exogenous glucocorticoids can activate 11β-HSD1. Consequently, treatment or withdrawal of systemic glucocorticoids may influence 11β-HSD1-dependent cortisol generation at the choroid plexus and in turn impact on CSF secretion.
11β-HSD1 and obesity
11β-HSD1 is dysregulated in obesity. Mice overexpressing global 11β-HSD1 demonstrate features of metabolic syndrome with visceral obesity, glucose intolerance, and dyslipidemia.71 Overexpression specifically in the liver (apoE-HSD1 transgenic model) lacks the glucose intolerance and obesity seen in the global expression model, suggesting that production of 11β-HSD1 in another tissue must be responsible for the increased weight.72 Conversely, overexpression solely in adipose tissue, known as the aP2 HSD1 transgenic model, drives a phenotype of metabolic syndrome.71 This suggests a role for adipose-derived 11β-HSD1 in the development of a metabolic syndrome. Knockout mice for 11β-HSD1 have improved glucose tolerance, hepatic sensitization to insulin, hyperglycemia resistance, and lower triglyceride levels but with associated adrenal hyperplasia.73
Obesity in human beings is associated with normal systemic cortisol levels but increased 11β-HSD1 expression and activity in subcutaneous fat.74 11β-HSD1 activity, measured by urinary cortisol metabolites, is also dysregulated in obesity.75 However, after a weight loss intervention in 12 healthy obese patients, there were no changes in global markers of 11β-HSD1 activity, which would have been expected with a reduction in adipose mass.76
11β-HSD1 and IIH
During a low calorie diet in IIH, while systemic cortisol levels remained within normal levels, urinary cortisol metabolites decreased (P=0.001) with substantial weight loss (15·7 kg [standard deviation {SD} 8.0], P<0.001) and global 11β-HSD1 activity was significantly reduced, correlating (r=0.504; P=0.028) with a fall in ICP (8 cmH2O [SD 4.2], P<0.001). In addition, after the weight loss intervention, papilledema and headaches also improved significantly. Furthermore, increases in CSF cortisone levels, suggesting decreased 11β-HSD1 activity, correlated with weight loss.69 Given the relationship between 11β-HSD1 and ICP, inhibitors of this enzyme could play a therapeutic role in IIH.
Inhibition of 11β-HSD1 has been shown to decrease intraocular pressure in ocular hypertension.77 The ocular ciliary epithelium, responsible for producing aqueous humor in the eye, has the same embryological origin as the choroid plexus and both tissues have an analogous mechanism for fluid secretion. Akin to ICP, pressure within the eye is dependent on the balance between aqueous secretion from the ciliary body and drainage through the trabecular meshwork and scleral pathways. Within the ciliary body, cortisol has been shown to activate the glucocorticoid receptors resulting in increased serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase type 1 (sgk1), subsequently driving sodium channels, such as Na+/K+ ATPase. Transport of sodium ions creates an osmotic gradient that leads to fluid transport, and thus aqueous humor production.77 Therefore, selective inhibition of 11β-HSD1 could also be effective at reducing raised ICP by reducing fluid secretion at the choroid plexus via inactivation of the glucocorticoid signaling pathway (Figure 4). In addition, it may be disease modifying by ameliorating the features of a metabolic profile such as improving glycemic control and decreasing weight.
Inhibition of 11β-HSD1
Liquorice is a naturally existing, nonselective 11β-HSD inhibitor. Excessive consumption can lead to an apparent mineralocorticoid excess presenting with hypertension, hypokalemia, and hypernatremia. However, the levels of circulating mineralocorticoids, and its upstream stimulatory hormone renin, are in fact low. This occurs as 11β-HSD2 is inhibited allowing glucocorticoids to occupy mineralocorticoid receptors resulting in activation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone pathway.
Derivatives of liquorice, including glycyrrhetinic acid and carbenoxolone, have both been used experimentally as nonselective inhibitors of 11β-HSD. Studies evaluating nonselective inhibitors in mice and nonobese diabetic human beings have demonstrated lowered plasma glucose but a concomitant increase in blood pressure and potassium.78,79 Also, carbenoxolone appeared poorer at subcutaneous fat inhibition in obese compared with lean subjects.74
There has been a focus to develop 11β-HSD1 selective inhibitors in recent years aimed at treating obesity, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes mellitus type 2.80 As the metabolic syndrome profile has a greater association with adipose 11β-HSD1 in mice, it appears that an effective 11β-HSD1 inhibitor should be both isozyme-selective and effective in the adipose tissue.
A current Medial Research Council-funded study due to finish in 2017, is assessing a selective competitive inhibitor of 11β-HSD1, AZD4017, and its effects on the ICP in IIH (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02017444). The results may offer further answers regarding the role 11β-HSD1 may play in raised ICP and IIH.
Conclusion
Obesity is strongly related to the development of IIH but it is not a lone factor; otherwise, a greater proportion of the obese population would be expected to develop this condition. The mechanism behind weight gain in IIH and its association with raised ICP remains a debated issue. Adipose tissue has been increasingly viewed as a neuroendocrine tissue releasing chemical signals, in particular adipokines such as leptin, which could act directly on the choroid plexus or arachnoid granulation tissue, or indirectly via peripheral mechanism with consequent secondary central effects that modify CSF secretion and absorption. How this tissue is distributed in IIH and the role it may have in disease development requires further investigation.
The obese state is also an inflammatory condition where chronically increased circulating or CSF cytokines may result in fibrotic changes or lead to a hypercoagulable state causing blockage of the arachnoid granulations and, therefore, reducing drainage of CSF.
The epidemiology of comorbidities such as OSA and PCOS needs to be defined regarding any involvement they may have in the IIH disease process. In particular, comparing the hyperandrogenism profile observed in IIH with a PCOS and healthy obese cohort may reveal further clues regarding the role of hormones in IIH.
The evidence supporting the role of female sex steroids is still lacking, but observationally, the clear female bias for IIH suggests they may be involved. Glucocorticoids had originally been shown to have a role anecdotally in IIH. However, as the systemic levels of cortisol and other glucocorticoids are normal in IIH, there has been a shift to look at cellular steroid regulation. Following a low-calorie dietary intervention in IIH, there was a significant weight loss and an associated reduction in ICP. In conjunction, a decrease in global 11β-HSD1 activity was observed following the intervention. 11β-HSD1 has also shown a role in ocular pressure through effects to fluid secretion into the eye. The role 11β-HSD1 may play is potentially important in the development of raised ICP in IIH and obesity. A current trial assessing the impact of an 11β-HSD1 inhibitor on ICP in IIH should clarify this role in the future.
Currently, the treatment options for IIH are limited owing to a lack of knowledge surrounding the pathogenesis of the condition. Therefore, the underlying mechanisms behind IIH remain uncertain. This review has outlined hormonal and obesity-related factors that may have a role in IIH including a potential new pathogenic mechanism involving the 11β-HSD1 enzyme and cellular glucocorticoids. Further basic and clinical research is required in these areas to confirm or refute their involvement.
Disclosure
Alexandra J Sinclair is funded by an NIHR Clinician Scientist Fellowship (NIHR-CS-011-028), and Keira A Markey is funded by the Medical Research Council, UK (MR/K015184/1). The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Radhakrishnan K, Ahlskog JE, Cross SA, Kurland LT, O’Fallon WM. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Descriptive epidemiology in Rochester, Minn, 1976 to 1990. Arch Neurol. 1993;50(1):78–80. | |
Raoof N, Sharrack B, Pepper IM, Hickman SJ. The incidence and prevalence of idiopathic intracranial hypertension in Sheffield, UK. Eur J Neurol. 2011;18(10):1266–1268. | |
Craig JJ, Mulholland DA, Gibson JM. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension; incidence, presenting features and outcome in Northern Ireland (1991–1995). Ulster Med J. 2001;70(1):31–35. | |
Kesler A, Stolovic N, Bluednikov Y, Shohat T. The incidence of idiopathic intracranial hypertension in Israel from 2005 to 2007: results of a nationwide survey. Eur J Neurol. 2014;21(8):1055–1059. | |
Bruce BB, Kedar S, Van Stavern GP, et al. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension in men. Neurology. 2009;72(4):304–309. | |
Durcan FJ, Corbett JJ, Wall M. The incidence of pseudotumor cerebri. Population studies in Iowa and Louisiana. Arch Neurol. 1988;45(8):875–877. | |
Galvin JA, Van Stavern GP. Clinical characterization of idiopathic intracranial hypertension at the Detroit Medical Center. J Neurol Sci. 2004;223(2):157–160. | |
Friedman DI, Liu GT, Digre KB. Revised diagnostic criteria for the pseudotumor cerebri syndrome in adults and children. Neurology. 2013;81(13):1159–1165. | |
Markey KA, Mollan SP, Jensen RH, Sinclair AJ. Understanding idiopathic intracranial hypertension: mechanisms, management, and future directions. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(1):78–91. | |
Hamdallah IN, Shamseddeen HN, Getty JLZ, Smith W, Ali MR. Greater than expected prevalence of pseudotumor cerebri: a prospective study. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2013;9(1):77–82. | |
Daniels AB, Liu GT, Volpe NJ, et al. Profiles of obesity, weight gain, and quality of life in idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Am J Ophthalmol. 2007;143(4):635–641. | |
Sinclair AJ, Burdon MA, Nightingale PG, et al. Low energy diet and intracranial pressure in women with idiopathic intracranial hypertension: prospective cohort study. Br Med J. 2010;341:c2701. | |
Newborg B. Pseudotumor cerebri treated by rice reduction diet. Arch Intern Med. 1974;133(5):802–807. | |
Skau M, Sander B, Milea D, Jensen R. Disease activity in idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a 3-month follow-up study. J Neurol. 2011;258(2):277–283. | |
Fridley J, Foroozan R, Sherman V, Brandt ML, Yoshor D. Bariatric surgery for the treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neurosurg. 2011;114(1):34–39. | |
Sugerman HJ, Felton WL 3rd, Sismanis A, Kellum JM, DeMaria EJ, Sugerman EL. Gastric surgery for pseudotumor cerebri associated with severe obesity. Ann Surg. 1999;229(5):634–640. discussion 40–42. | |
Johnson LN, Krohel GB, Madsen RW, March GA Jr. The role of weight loss and acetazolamide in the treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Ophthalmology. 1998;105(12):2313–2317. | |
Sugerman HJ, DeMaria EJ, Felton WL 3rd, Nakatsuka M, Sismanis A. Increased intra-abdominal pressure and cardiac filling pressures in obesity-associated pseudotumor cerebri. Neurology. 1997;49(2):507–511. | |
Berdahl JP, Fleischman D, Zaydlarova J, Stinnett S, Allingham RR, Fautsch MP. Body mass index has a linear relationship with cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(3):1422–1427. | |
Whiteley W, Al-Shahi R, Warlow CP, Zeidler M, Lueck CJ. CSF opening pressure: reference interval and the effect of body mass index. Neurology. 2006;67(9):1690–1691. | |
Lee SC, Lueck CJ. Cerebrospinal fluid pressure in adults. J Neuroophthalmol. 2014;34(3):278–283. | |
Kesler A, Kliper E, Shenkerman G, Stern N. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension is associated with lower body adiposity. Ophthalmology. 2010;117(1):169–174. | |
Fraser JA, Bruce BB, Rucker J, et al. Risk factors for idiopathic intracranial hypertension in men: a case-control study. J Neurol Sci. 2010;290(1–2):86–89. | |
Jennum P, Borgesen SE. Intracranial pressure and obstructive sleep apnea. Chest. 1989;95(2):279–283. | |
Ball AK, Sinclair AJ, Curnow SJ, et al. Elevated cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leptin in idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH): evidence for hypothalamic leptin resistance? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2009;70(6):863–869. | |
Lampl Y, Eshel Y, Kessler A, et al. Serum leptin level in women with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002;72(5):642–643. | |
Dhungana S, Sharrack B, Woodroofe N. Cytokines and chemokines in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Headache. 2009;49(2):282–285. | |
Behbehani R, Mabrook A, Abbas JM, Al-Rammah T, Mojiminiyi O, Doi SA. Is cerebrospinal fluid leptin altered in idiopathic intracranial hypertension? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2010;72(6):851–852. | |
Ducy P, Amling M, Takeda S, et al. Leptin inhibits bone formation through a hypothalamic relay: a central control of bone mass. Cell. 2000;100(2):197–207. | |
Sanchez-Garrido MA, Tena-Sempere M. Metabolic control of puberty: roles of leptin and kisspeptins. Horm Behav. 2013;64(2):187–194. | |
Lord GM, Matarese G, Howard JK, Baker RJ, Bloom SR, Lechler RI. Leptin modulates the T-cell immune response and reverses starvation-induced immunosuppression. Nature. 1998;394(6696):897–901. | |
Klok MD, Jakobsdottir S, Drent ML. The role of leptin and ghrelin in the regulation of food intake and body weight in humans: a review. Obes Rev. 2007;8(1):21–34. | |
Jequier E. Leptin signaling, adiposity, and energy balance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;967:379–388. | |
Elias CF, Kelly JF, Lee CE, et al. Chemical characterization of leptin- activated neurons in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 2000;423(2):261–281. | |
Hileman SM, Pierroz DD, Masuzaki H, et al. Characterization of short isoforms of the leptin receptor in rat cerebral microvessels and of brain uptake of leptin in mouse models of obesity. Endocrinology. 2002;143(3):775–783. | |
Bjorbaek C, Elmquist JK, Michl P, et al. Expression of leptin receptor isoforms in rat brain microvessels. Endocrinology. 1998;139(8):3485–3491. | |
Harris RB. Parabiosis between db/db and ob/ob or db/+ mice. Endocrinology. 1999;140(1):138–145. | |
Nam SY, Kratzsch J, Kim KW, Kim KR, Lim SK, Marcus C. Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma concentrations of leptin, NPY, and alpha-MSH in obese women and their relationship to negative energy balance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86(10):4849–4853. | |
Schwartz MW, Peskind E, Raskind M, Boyko EJ, Porte D, Jr. Cerebrospinal fluid leptin levels: relationship to plasma levels and to adiposity in humans. Nat Med. 1996;2(5):589–593. | |
Ostlund RE Jr, Yang JW, Klein S, Gingerich R. Relation between plasma leptin concentration and body fat, gender, diet, age, and metabolic covariates. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81(11):3909–3913. | |
Beltowski J. Leptin and the regulation of renal sodium handling and renal na-transporting ATPases: role in the pathogenesis of arterial hypertension. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2010;6(1):31–40. | |
Damkier HH, Brown PD, Praetorius J. Cerebrospinal fluid secretion by the choroid plexus. Physiol Rev. 2013;93(4):1847–1892. | |
Altiokka-Uzun G, Tuzun E, Ekizoglu E, et al. Oligoclonal bands and increased cytokine levels in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Cephalalgia. 2015;35(13):1153–1161. | |
Kesler A, Kliper E, Assayag EB, et al. Thrombophilic factors in idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a report of 51 patients and a meta-analysis. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2010;21(4):328–333. | |
Finsterer J, Kues EW, Brunner S. Pseudotumour cerebri in a young obese woman on oral contraceptives. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2006;11(3):237–240. | |
Chan JW. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension associated with depot medroxyprogesterone. Eye (Lond). 2006;20(12):1396–1397. | |
Kesler A, Kupferminc M. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension and pregnancy. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2013;56(2):389–396. | |
Toscano V, Sancesario G, Bianchi P, Cicardi C, Casilli D, Giacomini P. Cerebrospinal fluid estrone in pseudotumor cerebri: a change in cerebral steroid hormone metabolism? J Endocrinol Invest. 1991;14(2):81–86. | |
Donaldson JO, Horak E. Cerebrospinal fluid oestrone in pseudotumour cerebri. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982;45(8):734–736. | |
Klein A, Stern N, Osher E, Kliper E, Kesler A. Hyperandrogenism is associated with earlier age of onset of idiopathic intracranial hypertension in women. Curr Eye Res. 2013;38(9):972–976. | |
Lindvall-Axelsson M, Owman C. Changes in transport functions of isolated rabbit choroid plexus under the influence of oestrogen and progesterone. Acta Physiol Scand. 1989;136(1):107–111. | |
Glueck CJ, Aregawi D, Goldenberg N, Golnik KC, Sieve L, Wang P. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, polycystic-ovary syndrome, and thrombophilia. J Lab Clin Med. 2005;145(2):72–82. | |
Glueck CJ, Golnik KC, Aregawi D, Goldenberg N, Sieve L, Wang P. Changes in weight, papilledema, headache, visual field, and life status in response to diet and metformin in women with idiopathic intracranial hypertension with and without concurrent polycystic ovary syndrome or hyperinsulinemia. Transl Res. 2006;148(5):215–222. | |
O’Reilly MW, Taylor AE, Crabtree NJ, et al. Hyperandrogenemia predicts metabolic phenotype in polycystic ovary syndrome: the utility of serum androstenedione. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(3):1027–1036. | |
Salpietro V, Polizzi A, Berte LF, et al. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a unifying neuroendocrine hypothesis through the adrenal-brain axis. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2012;33(6):569–573. | |
Sharma D, Mukherjee R, Moore P, Cuthbertson DJ. Addison’s disease presenting with idiopathic intracranial hypertension in 24-year-old woman: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2010;4:60. | |
Zada G, Tirosh A, Kaiser UB, Laws ER, Woodmansee WW. Cushing’s disease and idiopathic intracranial hypertension: case report and review of underlying pathophysiological mechanisms. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(11):4850–4854. | |
Newton M, Cooper BT. Benign intracranial hypertension during prednisolone treatment for inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1994;35(3):423–425. | |
Lindvall-Axelsson M, Hedner P, Owman C. Corticosteroid action on choroid plexus: reduction in Na+-K+-ATPase activity, choline transport capacity, and rate of CSF formation. Exp Brain Res. 1989;77(3):605–610. | |
Sato O, Hara M, Asai T, Tsugane R, Kageyama N. The effect of dexamethasone phosphate on the production rate of cerebrospinal fluid in the spinal subarachnoid space of dogs. J Neurosurg. 1973;39(4):480–484. | |
Martins AN, Ramirez A, Solomon LS, Wiese GM. The effect of dexamethasone on the rate of formation of cerebrospinal fluid in the monkey. J Neurosurg. 1974;41(5):550–554. | |
Sapolsky RM, Romero LM, Munck AU. How do glucocorticoids influence stress responses? Integrating permissive, suppressive, stimulatory, and preparative actions. Endocr Rev. 2000;21(1):55–89. | |
Ferrari P, Lovati E, Frey FJ. The role of the 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 in human hypertension. J Hypertens. 2000; 18(3):241–248. | |
Wyrwoll CS, Holmes MC, Seckl JR. 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases and the brain: from zero to hero, a decade of progress. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2011;32(3):265–286. | |
Banhegyi G, Benedetti A, Fulceri R, Senesi S. Cooperativity between 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 and hexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(26):27017–27021. | |
Chapman K, Holmes M, Seckl J. 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases: intracellular gate-keepers of tissue glucocorticoid action. Physiol Rev. 2013;93(3):1139–1206. | |
Lakshmi V, Sakai RR, McEwen BS, Monder C. Regional distribution of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in rat brain. Endocrinology. 1991;128(4):1741–1748. | |
Sinclair AJ, Onyimba CU, Khosla P, et al. Corticosteroids, 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase isozymes and the rabbit choroid plexus. J Neuroendocrinol. 2007;19(8):614–620. | |
Sinclair AJ, Walker EA, Burdon MA, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid corticosteroid levels and cortisol metabolism in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a link between 11beta-HSD1 and intracranial pressure regulation? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(12):5348–5356. | |
Tomlinson JW, Walker EA, Bujalska IJ, et al. 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1: a tissue-specific regulator of glucocorticoid response. Endocr Rev. 2004;25(5):831–866. | |
Masuzaki H, Paterson J, Shinyama H, et al. A transgenic model of visceral obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Science. 2001;294(5549):2166–2170. | |
Paterson JM, Morton NM, Fievet C, et al. Metabolic syndrome without obesity: hepatic overexpression of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(18):7088–7093. | |
Morton NM, Holmes MC, Fievet C, et al. Improved lipid and lipoprotein profile, hepatic insulin sensitivity, and glucose tolerance in 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 null mice. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(44):41293–41300. | |
Sandeep TC, Andrew R, Homer NZ, Andrews RC, Smith K, Walker BR. Increased in vivo regeneration of cortisol in adipose tissue in human obesity and effects of the 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor carbenoxolone. Diabetes. 2005;54(3):872–879. | |
Wake DJ, Walker BR. 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2004;215(1–2):45–54. | |
Tomlinson JW, Moore JS, Clark PM, Holder G, Shakespeare L, Stewart PM. Weight loss increases 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 expression in human adipose tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89(6):2711–2716. | |
Rauz S, Cheung CM, Wood PJ, et al. Inhibition of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 lowers intraocular pressure in patients with ocular hypertension. QJM. 2003;96(7):481–490. | |
Nuotio-Antar AM, Hachey DL, Hasty AH. Carbenoxolone treatment attenuates symptoms of metabolic syndrome and atherogenesis in obese, hyperlipidemic mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007;293(6):E1517–E1528. | |
Andrews RC, Rooyackers O, Walker BR. Effects of the 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitor carbenoxolone on insulin sensitivity in men with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88(1):285–291. | |
Boyle CD. Recent advances in the discovery of 11beta-HSD1 inhibitors. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2008;11(4):495–511. | |
Subramanian PS, Goldenberg-Cohen N, Shukla S, Cheskin LJ, Miller NR. Plasma ghrelin levels are normal in obese patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Am J Ophthalmol. 2004;138(1):109–113. | |
Edwards LJ, Sharrack B, Ismail A, et al. Increased levels of interleukins 2 and 17 in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2013;2(3):234–244. | |
Kermani HR, Faramarzi MSG, Ansari M, Gharfarinejad, A. Cerebrospinal fluid concentration of interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Med Sci. 2008;8(2):205–208. |
 © 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.