Back to Journals » Psychology Research and Behavior Management » Volume 14
How to Reduce Employees’ Turnover Intention from the Psychological Perspective: A Mediated Moderation Model
Authors Yan Z , Mansor ZD, Choo WC, Abdullah AR
Received 25 November 2020
Accepted for publication 14 January 2021
Published 18 February 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 185—197
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S293839
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Igor Elman
Zhen Yan,1 Zuraina Dato Mansor,2 Wei Chong Choo,2 Abdul Rashid Abdullah2
1Faculty of Hotel Management, Qingdao Vocational and Technical College of Hotel Management, Qingdao, Shandong, People’s Republic of China; 2School of Business and Economics, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
Correspondence: Zhen Yan
Faculty of Hotel Management, Qingdao Vocational and Technical College of Hotel Management, Shandong, People’s Republic of China
Email [email protected]
Background: The hospitality industry is deemed a great generator of global GDP and employment. However, high rates of voluntary turnover have gradually undermined global service organizations and brought huge losses to them. Nowadays, the hotel sector continues to be plagued by high turnover rates.
Purpose: A research model investigating job attitudes (job satisfaction and organizational commitment) as mediators of the impact of psychological capital (PsyCap) on turnover intention and also examining position as a moderator between job attitudes and turnover intention was proposed and tested.
Methods: This study collected data from 406 employees selected from four-star and five-star hotels in the southwest region of China. Online survey questionnaires and a purposive sampling technique were employed in this study. Structural equation modeling was utilized to evaluate the direct, mediating, and moderating effects.
Results: The results showed that organizational commitment and job satisfaction fully mediated the association between PsyCap and turnover intention. Moreover, position played a moderating role on the effect of the aforementioned two job attitudes on turnover intention.
Conclusion: The findings implied that hoteliers should focus on employees’ PsyCap and job attitudes in order to mitigate serious turnover issues in the hotel sector in China. Besides, the fact that position resulted in disparity impacts in the formation of turnover intention was evidenced.
Keywords: psychological capital, organizational commitment, job satisfaction, turnover intention, position, four-star and five-star hotels in China
Introduction
The rapidly changing business world is confronting unprecedented challenges and business organizations are gradually beginning to recognize the significance of sustainability issues which will bring benefits to the global economy, the environment, and the organizations themselves.1 From a business perspective, sustainability has been regarded as an organization’s ability to achieve its business targets, which may include lowering operating costs and risks, increasing their appeal to skilled talents and competitiveness. However, it is impossible to achieve these business goals without highly qualified employees.2
The hospitality industry is deemed as a primary source of foreign currency earnings, a generator of personal and corporate income, a creator of employment, and a contributor to government revenue.3 As the World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC)4 reported, the direct contribution of the hospitality industry to Global GDP was 2,570 billion USD (accounting for 3.2% of global GDP) in 2017 and it rose by 4.0% to 2,674 billion USD in 2018. In addition, the hospitality industry’s direct contribution to global GDP is expected to grow to 3,890.0 billion USD (accounting for 3.6% of global GDP) by 2028 (see Figure 1). From the perspective of employment, WTTC4 data also showed that the hospitality industry generated 118,454,000 jobs directly (accounting for 3.8% of global employment) in 2017 and 121,356,000 jobs in 2018. By 2028, the hospitality industry will supply 150,139,000 jobs for the global labor market (see Figure 2).
 |
Figure 1 Direct contribution of hospitality to global GDP. Source: Economic Impact of Global Travel & Tourism (2018). |
 |
Figure 2 Direct contribution of hospitality to global employment. Source: Economic Impact of Global Travel & Tourism (2018). |
Despite the hospitality industry being significant in many countries, survey data has shown an endemic voluntary turnover rate in the hotel sector, which was estimated to range from 30–300%, and was far higher than other industries.5 For example, in China, data from Aon Hewitt6 indicated that between 2016 and 2017, the average turnover rate in all industries was only about 20%, yet, the voluntary turnover rate in hotels has reached approximately 40%, which was the highest in China.
All the above statistics show that the hospitality industry is indeed a great generator of global GDP and employment; on the other hand, high rates of voluntary turnover have gradually undermined global service organizations and brought huge losses to them.7 Nowadays, the hotel sector continues to be plagued by high turnover rates, that is, the causes of turnover have not been clearly and effectively explained yet in prior literature.8 Therefore, ensuring the stability of human resources in order to promote service quality and organizational performance is an important task for hotel managers. Generally, hotel management tend to focus on tangible motivation factors such as salaries, paid vacation, and working environment and neglect employees’ intangible demands. As Luthans et al9 highlighted, psychological capital (PsyCap) and attitudinal strengths have to be assessed for organizational success and sustainable development.
PsyCap, with self-efficacy, hope, optimism, and resilience as its main manifestations, is a recognized personality construct in the field of organizational behavior and management.10 According to COR theory, four components of PsyCap are individual resources that enable employees to adapt to challenging circumstances, maintain positive job attitudes in working environment, and stay with their organizations.11 This is because employees with high levels of individual resources can be thought of having “resource caravans”, which can lead to positive outcomes.12
In the current study, researchers attempted to fill in various gaps, which could contribute to extant hospitality literature. Firstly, given the fact that employees prefer to concentrate on intrinsic motivators, such as the importance to the organization, recognition of their own achievements, and responsibility rather than improved financial returns,13 it is worthwhile to make an in-depth research of hotel employees’ turnover issue from the perspectives of psychology. Secondly, PsyCap has been recognized as a significant predictive determinant of job attitudes14–16 and turnover intention.10,17 However, surprisingly, empirical studies of the impact of PsyCap on turnover intention with mediating effects of organizational commitment and job satisfaction among frontline employees in the hotel sector, especially in China, are still lacking. Thirdly, although previous studies have proved that position (line-level employee and supervisor) is correlated to organizational commitment, job satisfaction, and turnover intention,18,19 to our knowledge the moderating effects of position on the relationship between organizational commitment and turnover intention as well as between job satisfaction and turnover intention have not been examined before, especially in the hotel sector.
Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
PsyCap and Job Attitudes
The concept of PsyCap was originally put forward by Luthans and Youseff20 and was extended into the area of human resource management and organizational behavior. PsyCap is regarded as a key psychological element beyond social capital and human capital and it comprises four critical dimensions, namely hope, optimism, self-efficacy, and resilience.
Ambrose and Schminke21 suggest that organizational commitment and job satisfaction as job attitudes have been trending topics for several decades in the hotel sector. Job satisfaction (JS) is a type of positive emotional state obtained by evaluating one’s own work itself or previous working experiences.22 On the other hand, organizational commitment (OC) is a firm belief in organizational objectives and values.23
There has been adequate evidence regarding the components of PsyCap as predictors of job attitudes in existing literature on scoping the boundaries of hospitality management. To be specific, resilience is found to influence job satisfaction positively,24,25 and self-efficacy can positively influence organizational commitment.26,27 Besides, previous studies have shown that PsyCap can positively influence organizational commitment23,28 or job satisfaction.29,30 But surprisingly there are rare studies which have investigated the combined effect of four components of PsyCap on two critical job attitudes simultaneously, especially in the hotel industry. Thus, based on the content discussed above, the following hypotheses are proposed:
Hypothesis 1: PsyCap has a positive impact on job satisfaction. Hypothesis 2: PsyCap has a positive impact on organizational commitment.
Job Attitudes and Turnover Intention
Allen and Meyer31 suggest that organizational commitment is an emotional bond and it tends to prompt employees’ willingness to remain with their organizations. Commitment usually results in positive outcomes such as higher organizational performance, reduced absenteeism, and turnover.32–34 In addition, employees who possess high level of organizational commitment often express their affiliation with their organizations.35 However, some other scholars believe that only normative and affective commitments have a significant effect on turnover intention.36–38 Different findings have been obtained between the aforementioned variables in the context of hospitality.
Job satisfaction is conceptualized as a pleasant or positive emotional state derived from an assessment of one’s job or work experiences.22 When an employee fits well into the organization, job satisfaction is usually reflected.39 Many prior studies have shown a positive correlation between job satisfaction and reduced turnover.40,41
According to Joo and Park,42 job satisfaction has been proved to be a strong predictive antecedent of turnover intention in their research, which also examines organizational commitment as an antecedent. Similarly, Chan et al43 propose that organizational commitment is negatively associated with turnover intention. Accordingly, in order to clarify the correlation between job attitudes and turnover intention, we put forward the following two hypotheses:
Hypothesis 3: Job satisfaction has a negative impact on turnover intention. Hypothesis 4: Organizational commitment has a negative impact on turnover intention.
Psychological Capital and Turnover Intention
PsyCap is deemed as a personal characteristic resource which can reduce turnover intentions.44 Evidence, although limited, supports such relationships. Karatepe and Karadas10 have proved that PsyCap can negatively affect turnover intention. What’s more, Avey et al’s15 meta-analytic study also shows that PsyCap is negatively correlated with turnover intention (k=5, corrected r=−0.32 and SD=0.11). Echoing the results of the above studies, there is also sufficient evidence regarding the components of PsyCap as predictors of turnover intention in the hospitality literature.45–47 However, Abbas et al48 found that PsyCap could positively influence turnover intention. They explained that employees with high PsyCap, being more confident and skillful, may choose to seek a better working environment and begin to look for new options. So far, no consensus has been reached. Thus, hypothesis 5 is put forward:
Hypothesis 5: PsyCap has a negative impact on turnover intention.
Psychological Capital, Job Attitudes, and Turnover Intention
PsyCap is defined as an individual resource which increases employees’ awareness of their own resources and job-related outcomes.49 Prior studies have shown that PsyCap can positively affect employees’ job attitudes, including job satisfaction50–52 and organizational commitment,29,53,54 as well as job-related variables such as organizational citizenship behavior55,56 and turnover intention.17,57 Therefore, previous empirical results demonstrate that PsyCap can influence individual satisfaction with work as well as one’s commitment to it. However, the relationship between PsyCap, attitudes and turnover intention among frontline employees must be specifically studied. Accordingly, hypotheses 6 and 7 are proposed:
Hypothesis 6: Job satisfaction mediates the relationship between PsyCap and turnover intention. Hypothesis 7: Organizational commitment mediates the relationship between PsyCap and turnover intention.
Position, Organizational Commitment, Job Satisfaction, and Turnover Intention
Although hotel managerial staff such as supervisors and department managers are thought to present lower turnover rates than line-level employees, much research have shown that the differences in turnover rates between the two groups of employees were not quite as big (line-level employees: 50.74% vs managerial employees: 39.19%).58 Regarding the difference in turnover rates between supervisors and line-level employees, Carbery et al36 attribute supervisors’ lower turnover rates to their higher satisfaction with and stronger commitment to hotels (compared to line-level employees). Given that the majority of line-level employees regard their current jobs as stepping stones for a future career, they are less likely to be highly committed to and satisfied with their organizations.18 The entry-level tasks in hotels inevitably involve large amounts of repetitive work which possesses less professional skills and diversity (compared to managerial tasks) and therefore offer limited opportunities for career growth among line-level employees. In contrast, supervisors tend to engage in their work to pursue career targets, since they have more promotion opportunities than line-level employees. In addition, line-level employees receive relatively lower incomes, and less fringe benefits and paid vacation than supervisors.59 Hence, line-level employees are more likely to leave their jobs than supervisors, and the following hypotheses are proposed:
Hypothesis 8: Position moderates the relationship between job satisfaction and turnover intention. Hypothesis 9: Position moderates the relationship between organizational commitment and turnover intention.
Method
Participants and Procedure
A quantitative survey with research objectives to examine the postulated hypotheses was planned to be conducted after a thorough literature review. We collected data by conducting a survey of full-time frontline employees (line-level employees and supervisors) in several divisions (eg, front desk, food and beverage, and guest relations) at four four-star and four five-star hotels in China. The sampling locations were in Chengdu and Chongqing, because Chengdu is an important provincial capital city and Chongqing a municipality of China. Both of them are deemed as the most popular tourist cities in southwest China, with a booming hotel sector.
The questionnaire is originally written in English and, in order to avoid errors and ensure validity, a linguist who is good at both Chinese and English is in charge of translating and back-translating questionnaire. Prior to distribution, we carried out a pilot study with test–re-test method for the reliability of the questionnaire,60 and the content validity was examined by three professional practitioners to ensure appropriate items which were suitable to the context of the research.61 Online survey questionnaires and purposive sampling technique were employed in this study. After obtaining hotels’ approval, the hyperlink of the survey website was delivered to every potential respondent and they could complete questionnaires during their latest shifts. All of the respondents were told that participation was voluntary, but they were encouraged to complete the questionnaire with reference to their experiences. In addition, the survey included an instruction emphasizing that all responses were completely confidential and anonymous to minimize any possible bias.
With the utilization of AMOS 24.0 software, structural equation modeling (SEM) can examine the hypothesized relationships with 406 hospitality full-time line-level employees and supervisors. Three approaches were discussed in order to confirm the above sample size. Firstly, the rule of thumb for sample size, especially using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM), was considered, that is, the sample is normally larger than 200.62 Secondly, Cochran63 formula of sample size for categorical and continuous variables was considered. Thirdly, subject-to-item ratio was also taken into account. A general rule is that there should be at least five subjects for each item (5:1) and ratios higher than this are generally better.64
Measurement Tools
Four existing tools were employed in this study. Firstly, a 24-item PsyCap questionnaire (PCQ) measure proposed by Luthans et al65 was applied to evaluate PsyCap. This scale consists of four dimensions and each dimension includes six items. Before the utilization of PCQ, permission was obtained from the author. Secondly, in terms of turnover intention, a three-item scale developed by Singh et al (1996) was utilized. This scale has been used in many hotel empirical studies.10,66,67 Thirdly, the tool of organizational commitment consists of three dimensions and 18 items (three negatively worded items).31 The validity and reliability of this scale has been verified iteratively by many hospitality related studies.68,69 Lastly, the measurement of job satisfaction was derived from Weiss et al's70 Minnesota studies on Vocational Rehabilitation. This valid questionnaire has been widely used in hotel-related research.71,72
Results
Sample Characteristics
The basic demographic characteristics of the participants are as follows. Among the respondents, 187 (46.1%) were male, and 219 (53.9%) were female. Regarding marital status, 240 (59.2%) respondents reported that they were single, and 166 (40.8%) were married. In terms of age, 61.3% were 30 years old and below and 31.6% were 31–40, while the age group of 41 and above contributed 7.1% to the study. Concerning the highest level of education, 2.1% of the respondents achieved a master’s degree and above, and 29.3% attained a bachelor’s degree, while respondents with a college degree and lower accounted for 68.6%. The majority of respondents (73.2%) were line-level employees, while others were supervisors (26.8%).
Full Measurement Model Validation
In order to evaluate the fit of full measurement model, goodness-of-fit measures were adopted. Bentler and Bonett73 argue that the model will be acceptable if the chi-square is not significant. However, a number of scholars have disregarded this theory because chi-square is often reported as significant, mainly due to the sample size limitations and its sensitivity to the likelihood test ratio. In view of chi-square’s limitations, the CMIN/DF fit (X2 divided by the degrees of freedom) becomes a more appropriate fit index. If the value of CMIN/DF is less than 3, an acceptable fit will be achieved.74 The model in the current study showed an acceptable CMIN/DF of 1.172. In the light of other fit indexes, the model yielded a RMSEA of 0.021 (below the acceptable threshold of 0.070),75 a CFI score 0.979, and a TLI score 0.978, which are within the ideal ranges (>0.90) for acceptable fit.76
The full measurement model presented a satisfactory fit with the data. To be specific, all existing standardized factor loadings ranged from 0.641–0.871, meaning that all items could measure their corresponding constructs effectively. In addition, with SPSS 24.0, constructs’ Cronbach alpha coefficients range in value from 0.773–0.942. If all the Cronbach alpha coefficients are larger than 0.70, items will reflect corresponding constructs well.77 With regard to composite reliability values for all the constructs, all were larger than the minimum threshold of 0.7.78
Many measurements were performed to evaluate the construct validity of the proposed model. The construct validity comprises convergent and discriminant validity. Convergent validity refers to the proportion of shared variance by items of a specific construct and it can be satisfied based on average variance extracted (AVE) larger than 0.50.79 In this study, the latent variables’ AVE values were larger than the threshold value of 0.50, which meant convergent validity for all constructs were achieved.
Discriminant validity was assessed with the following approach. If values of AVE are larger than the corresponding squared correlation coefficients, the discriminant validity will be achieved.80 As is shown in Table 1, all constructs’ squared correlation coefficients are smaller than corresponding AVE values, which strongly proved that discriminant validity for all constructs were achieved.
 |
Table 1 The Results of Discriminant Validity Test |
Common Method Bias
In the current study, two recommended approaches have been utilized to reduce common method bias. Firstly, respondents all emphasized the survey’s confidentiality and anonymity to avoid social desirability or respondent acquiescence.81 In addition, researchers also asked respondents to answer each question as honestly as they could because there was no right or wrong answers. Secondly, we utilized Harman’s one-factor test, which consists of a factor analysis of all the items. Finally, the first factor accounted for only 21.413% of the variance in the unrotated factor analysis, which indicated common method bias was not a serious issue in the current study.82
Structural Model Estimation and Hypotheses Testing
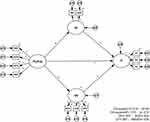
As the reliability and validity of full measurement model had been verified, the structural model was going to be evaluated and the hypotheses were going to be tested in the next step. After statistical analysis, fit indices from the following structural model (Figure 3) demonstrated that the proposed structural model was satisfactory. In addition, in order to reduce the complexity of structural model, item parceling technique was used for three second-order attitudinal constructs.
Causal Effects and Hypotheses Testing
As shown in Table 2, there existed a positive correlation between PsyCap and job satisfaction (β=0.561, P<0.001), which supported Hypothesis 1. Besides, there was also a positive association between PsyCap and organizational commitment (β=0.401, P<0.001), which supported Hypothesis 2. In addition, both job satisfaction (β=−0.426, P<0.001) and organizational commitment (β=−0.557, P<0.001) had a negative impact on turnover intention, which supported Hypotheses 3 and 4. However, PsyCap (β=−0.123, P=0.054) had no direct effect on turnover intention due to a P-value larger than 0.05. Hence, Hypothesis 5 was not supported. That is to say, organizational commitment and job satisfaction played a full mediating role in the relationship between PsyCap and turnover intention.
 |
Table 2 Summary of Hypotheses (Causal Effects) and Results |
Mediating Effects and Hypotheses Testing
As can be seen in Table 3, to identify the mediating role of job satisfaction and organizational commitment, bias-corrected and percentile bootstrapping methods were utilized.83 If zero is not included in bootstrapped CI, it means that the mediating effect will not equal zero. In this research, 95% bias-corrected CI and Percentile CI were estimated with 2,000 bootstrapped samples. Because the P-value of direct effect is larger than 0.05, the direct effect of PsyCap on turnover intention is not significant and accordingly a partial mediation effect is excluded. To summarize, both bootstrapping approaches showed that organizational commitment and job satisfaction could significantly and fully mediate the effect of PsyCap on turnover intention. Therefore, Hypotheses 6 and 7 were also supported.
 |
Table 3 Summary of Hypotheses (Mediating Effects) and Results |
Moderating Effects and Hypotheses Testing
The multi-group structural equation modeling within AMOS 24.0 software was utilized to investigate the differences in the strengths of the structural relationships by evaluating the moderating variable effects.84,85 The aim of multi-group analysis is to identify whether the path coefficients for the associations between job attitudes and turnover intention were equal in both line-level employee and supervisor groups. For the moderation tests, the data was divided into two subgroups based on position, respectively, 297 line-level employees and 109 supervisors. A two-step approach was used for multi-group comparison test. Firstly, the appropriate structural parameters are constrained to be equal across groups to generate an estimated covariance matrix for each group and an overall Χ2 value for the sets of sub-models as part of a single structural system. Secondly, a second Χ2 value with fewer degrees of freedom is obtained by removing the parameter equality constraints. And then, the moderating effects are examined by evaluating whether there are significant differences between the two Χ2 values. If the change in the Χ2 value is statistically significant, the null hypothesis of parameter invariance is rejected and a moderating effect is indicated.86 As is shown in Table 4, ∆Χ2/∆df=4.064 and P<0.05, which indicates that significant differences were found between employee and supervisor models. Therefore, position is a moderator for the aforementioned relationships, which supported Hypotheses 8 and 9.
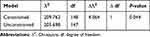 |
Table 4 Chi-Square Value and Degree of Freedom for the Constrained and Unconstrained Models |
Furthermore, Table 5 shows the results of a multi-group comparison test between line-level employees and supervisors with regard to job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention. As we can see, for line-level employees, both organizational commitment (β=−0.547, P<0.001) and job satisfaction (β=−0.426, P<0.001) have significantly negative impacts on turnover intention. On the other hand, for supervisors, organizational commitment (β=−0.669, P<0.001) and job satisfaction (β=−0.441, P<0.05) can also significantly and negatively influence turnover intention.
 |
Table 5 Results of the Multi-Group Comparison Test |
Discussions
Scholars have investigated the association of PsyCap and job satisfaction50,87 and the relationship between PsyCap and organizational commitment,54,88 however, scarce studies have examined the predictive effect of PsyCap on the aforementioned two job attitudes simultaneously.29 In accordance with the above findings, our study also revealed significant positive associations between PsyCap and job satisfaction (β=0.561, P<0.001) and organizational commitment (β=0.401, P<0.001).
In line with Siu et al,57 the results revealed that job satisfaction and organizational commitment could mediate the correlation between PsyCap and turnover intention. Furthermore, in contrast with many hotel sector studies,10,89 our findings could not support that there existed a direct negative association between PsyCap and turnover intention (β=−0.123, P=0.165). Hence, it can be seen, although PsyCap has been highlighted before as a component of reducing turnover intention,17,90 job attitudes have a more fundamental function as a cause and antecedent of turnover intention.
In addition, the results showed the indirect effect through job satisfaction (β=-0.239, P<0.001) was a little bit higher than organizational commitment (β=-0.224, P=0.001). Thus, this research offers significant and interesting findings about linking the role of job attitudes as they associate with PsyCap and turnover intention.
Another vital point produced by current research was the role of position as a moderator, and position could lead to significant difference in the association of job attitudes and turnover intention. To be specific, the negative effects of both organizational commitment and job satisfaction on turnover intention were higher for supervisors as compared to line-level employees. This finding evidenced the fact that position resulted disparity impacts in the formation of turnover intention.91 Therefore, current research breaks new ground by proposing a totally new conceptual model and conducting a rigorous empirical study which linked psychological capital, job attitudes, turnover intention, and position in the hotel sector in China.
Theoretical Implications
From a theoretical point of view, this study contributes to the theoretical field of hotel employees’ turnover intention. Scholars who aim to study hotel employees’ turnover intention can benefit from this study through a replication in different context or industry that they focus on. With theoretical directions, the results of this study will help to demonstrate how to reduce employees’ turnover intention from a psychological perspective in the hotel sector in China.
Principally, this study seeks to make an original contribution to the body of knowledge by investigating psychological determinants in affecting hotel employees’ turnover intention. In addition, the present study also extends COR theory by integrating job satisfaction and organizational commitment as mediating variables to provide better clarity on the interactions between all related variables and to explain the phenomenon of turnover intention.
Practical Implications
The results of the current research have implied that hotel management should adopt relevant strategies to develop employees’ psychological resources in order to advance their positive organizational attitudes and behaviors. In the first place, hotel management is supposed to realize the significance of PsyCap and proactively develop relating training programs to maintain their staff’s PsyCap at a high level.92 Through training, hotel staff can learn how to protect, maintain, and accumulate their PsyCap more effectively. Besides, more comprehensive training programs which cover PsyCap and positive job attitudes will be more effective. Therefore, line-level employees and supervisors in hotels who have received such trainings can master how to avoid the loss of resources. If they are able to maintain a high level of psychological resources, they will be highly satisfied with and more committed to their jobs. Simultaneously, they also feel a strong sense of belonging with their current jobs and have less intention to withdraw from their organizations.93
Furthermore, we have chosen employees who work in four-star and five-star hotels as respondents because such hotels are the pioneers in human resource management and often make their efforts visible compared to other hotels with lower star ratings.94 More importantly, four-star and five-star hotels of the same brand have a relatively uniform management system and standards. That is to say, the management problems existing in China (such as high turnover rate) may also exist in other regions or countries. Therefore, the conclusions of this research have great reference value for hotels of the same brand in other regions or countries.
Despite this research making some significant contributions to existing knowledge in human resource management in the hotel industry, we must acknowledge that there are still some specific limitations which can put forward feasible prospects for future studies.
Limitation and Direction for Future Studies
Firstly, since the process of data collection is cross-sectional, two recommended approaches have been carefully implemented to control potential common method bias (a) the design of the study’s procedures, and (b) statistical checks. Nevertheless, the data may still be at risk of common method bias. Hence, in subsequent research, the measurement of predictor and criterion variables should be separated by time to make a firm relationship of employee attitudes and behaviors.81
Secondly, only two cities were selected, which may limit the generalizability and representativeness. Future research can remove this limitation by sampling employees in various hotel settings in other regions or countries, and also a larger sample size is recommended.
Thirdly, this research has used an important individual psychological determinant called psychological capital. Future empirical studies should try to investigate more employees’ individual psychological determinants that can affect job attitudes, job performance, and even withdrawal behaviors in the hotel sector.
Finally, this study also reveals how the relationships between work-related variables vary across employees’ positions. In later research, more demographic factors such as gender, age, and tenure can be taken into account, so that hotel managers are able to derive a more in-depth understanding of employee’ turnover issues through the combinative role of individual differences.
Conclusions
This research has investigated organizational commitment and job satisfaction as mediators of the relationship between PsyCap and turnover intention in the hotel sector in China. As hypothesized, job attitudes were verified as significant and positive outcomes of PsyCap and also significant and negative antecedents of turnover intention. The role of job attitudes in this model could be explained via Conversation of Resource Theory.95 Furthermore, this study has also examined the moderating effect of position on the association between job attitudes and turnover intention. The results imply that hotel line-level employees and supervisors who possess a high level of PsyCap and positive job attitudes have a tendency to stay in their organizations15 and position can generate a significant difference in the relationship between job attitudes and turnover.91 The findings demonstrate that training programs which include PsyCap and positive job attitudes should be widely promoted. As a result, line-level employees and supervisors in hotels who have received such trainings are able to avoid the loss of resources as much as possible. If hotel employees can maintain a high level of psychological resources, they will be highly satisfied with and more committed to their organizations. Besides, they also feel a strong sense of belonging and identity and have less intention to quit.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Jones P, Hillier D, Comfort D. Sustainability in the hospitality industry: some personal reflections on corporate challenges and research agendas. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag. 2016;28(1):36–67. doi:10.1108/IJCHM-11-2014-0572
2. Lopez-Cabrales A, Valle-Cabrera R. Sustainable HRM strategies and employment relationships as drivers of the triple bottom line. Hum Resour Manag Rev. 2020;30(3):100689. doi:10.1016/j.hrmr.2019.100689
3. Dei Mensah R, Mensah I. Management of Tourism and Hospitality Services. Xlibris Corporation; 2013.
4. World Travel&Tourism Council. Economic impact of global travel& Tourism. Published 2018. Available from: https://wttc.org/research/economic-impact.
5. Baum T, Cheung C, Kong H, et al. Sustainability and the tourism and hospitality workforce: a thematic analysis. Sustain. 2016;8:8. doi:10.3390/su8080809
6. Hewitt A. China posts an average salary increase rate of 6.7% and turnover rate of 20.8% in 2016. Published 2017. Available from: https://www.aonhewitt.com.cn.
7. Chen HT, Wang CH. Incivility, satisfaction and turnover intention of tourist hotel chefs: moderating effects of emotional intelligence. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag. 2019;31(5):2034–2053. doi:10.1108/IJCHM-02-2018-0164
8. Wen B, Zhou X, Hu Y, Zhang X. Role stress and turnover intention of front-line hotel employees: the roles of burnout and service climate. Front Psychol. 2020;11:1–13. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00036
9. Luthans F, Norman SM, Avolio BJ, Avey JB. The mediating role of psychological capital in the supportive organizational climate — employee performance relationship. J Organ Behav. 2008;29:219–238. doi:10.1002/job
10. Karatepe OM, Karadas G. The effect of psychological capital on conflicts in the work–family interface, turnover and absence intentions. Int J Hosp Manag. 2014;43:132–143. doi:10.1016/j.ijhm.2014.09.005
11. Kim T, Karatepe OM, Lee G, Lee S, Hur K, Xijing C. Does hotel employees’ quality of work life mediate the effect of psychological capital on job outcomes? Int J Contemp Hosp Manag. 2017;29(6):1638–1657. doi:10.1108/IJCHM-04-2016-0224
12. Paek S, Schuckert M, Kim TT, Lee G. Why is hospitality employees’ psychological capital important? The effects of psychological capital on work engagement and employee morale. Int J Hosp Manag. 2015;50:9–26. doi:10.1016/j.ijhm.2015.07.001
13. Delaney ML, Royal MA. Breaking engagement apart: the role of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation in engagement strategies. Ind Organ Psychol. 2017;10(1):127–140. doi:10.1017/iop.2017.2
14. Avey JB. The left side of psychological capital: new evidence on the antecedents of PsyCap. J Leadersh Organ Stud. 2014;21(2):141–149. doi:10.1177/1548051813515516
15. Avey JB, Reichard RJ, Luthans F, Mhatre KH. Meta-analysis of the impact of positive psychological capital on employee attitudes, behaviors, and performance. Hum Resour Dev Q. 2011;22(2):127–152. doi:10.1002/hrdq.20070
16. Luthans F. Potential added value of psychological capital in predicting work attitudes. J Leadersh Organ Stud. 2006;13(2):75–92. doi:10.1177/10717919070130020601
17. Karatepe OM, Avci T. The effects of psychological capital and work engagement on nurses’ lateness attitude and turnover intentions. J Manag Dev. 2017;36(8):1029–1039. doi:10.1108/JMD-07-2016-0141
18. Lu L, Chieh LAC, Dogan G, Robert NN. Work engagement, job satisfaction, and turnover intentions: a comparison between supervisors and line-level employees. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag. 2016;28(4):737–761. doi:10.1108/IJCHM-07-2014-0360
19. Yao-Fen W. Constructing career competency model of hospitality industry employees for career success. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag. 2013;25(7):994–1016. doi:10.1108/IJCHM-07-2012-0106
20. Luthans F, Youssef CM. Human, social, and now positive psychological capital management: investing in people for competitive advantage. Organ Dyn. 2004;33(2):143–160. doi:10.1016/j.orgdyn.2004.01.003
21. Ambrose ML, Arnaud A, Schminke M. Individual moral development and ethical climate: the influence of person–organization fit on job attitudes. J Bus Ethics. 2008;77(3):323–333. doi:10.1007/s10551-007-9352-1
22. Locke EA. What is job satisfaction? Organ Behav Hum Perform. 1969;4(4):309–336. doi:10.1016/0030-5073(69)90013-0
23. Allen NJ, Meyer JP. Organizational socialization tactics: a longitudinal analysis of links to newcomers’ commitment and role orientation. Acad Manag J. 1990;33(4):847–858. doi:10.5465/256294
24. Meneghel I, Borgogni L, Miraglia M, Salanova M, Martínez IM. From social context and resilience to performance through job satisfaction: a multilevel study over time. Hum Relations. 2016;69(11):2047–2067. doi:10.1177/0018726716631808
25. Karatepe OM, Karadas G. Do psychological capital and work engagement foster frontline employees’ satisfaction? A study in the hotel industry. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag. 2015;27(6):1254–1278. doi:10.1108/IJCHM-01-2014-0028
26. Law FM, Guo GJ. Correlation of hope and self-efficacy with job satisfaction, job stress, and organizational commitment for correctional officers in the Taiwan prison system. Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2016;60(11):1257–1277. doi:10.1177/0306624X15574997
27. Niu H-J. Investigating the effects of self-efficacy on foodservice industry employees’ career commitment. Int J Hosp Manag. 2010;29(4):743–750. doi:10.1016/j.ijhm.2010.03.006
28. Kwon SM, Kwon M-S. Effect of nurse’s self-leadership, and self-efficacy on job involvement. J Korea Acad Coop Soc. 2019;20(4):284–292. doi:10.5762/KAIS.2019.20.4.284
29. Idris AM, Manganaro M. Relationships between psychological capital, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment in the Saudi oil and petrochemical industries. J Hum Behav Soc Environ. 2017;00(00):1–19. doi:10.1080/10911359.2017.1279098
30. Yildiz E. The effect of the psychological capital and personality characteristics of employees on their organizational commitment and contribution to the work: a qualitative research on managers. J Manag Strategy. 2017;8(4):34–46. doi:10.5430/jms.v8n4p34
31. Allen NJ, Meyer JP. The measurement and antecedents of affective, continuance and normative commitment to the organization. J Occup Psychol. 1990;63:1–18.
32. Jacobsen DI, Fjeldbraaten EM. Exploring the links between part-time employment and absenteeism: the mediating roles of organizational commitment and work-family conflict. Public Organ Rev. 2020;20(1):129–143. doi:10.1007/s11115-018-00437-x
33. Labrague LJ, McEnroe–Petitte DM, Tsaras K, Cruz JP, Colet PC, Gloe DS. Organizational commitment and turnover intention among rural nurses in the Philippines: implications for nursing management. Int J Nurs Sci. 2018;5(4):403–408. doi:10.1016/j.ijnss.2018.09.001
34. Qureshi MA, Qureshi JA, Thebo JA, Shaikh GM, Brohi NA, Qaiser S. The nexus of employee’s commitment, job satisfaction, and job performance: an analysis of FMCG industries of Pakistan. Cogent Bus Manag. 2019;6(1):22–39. doi:10.1080/23311975.2019.1654189
35. Meyer JP, Allen NJ. A three-component conceptualization of organizational commitment. Hum Resour Manag Rev. 1991;1(1):61–89. doi:10.1016/1053-4822(91)90011-Z
36. Carbery R, Garavan TN, O’Brien F, McDonnell J. Predicting hotel managers’ turnover cognitions. J Manag Psychol. 2003;18(7–8):649–679. doi:10.1108/02683940310502377
37. Nadiri H, Tanova C. An investigation of the role of justice in turnover intentions, job satisfaction, and organizational citizenship behavior in hospitality industry. Int J Hosp Manag. 2010;29(1):33–41. doi:10.1016/j.ijhm.2009.05.001
38. Yang J-T. Antecedents and consequences of job satisfaction in the hotel industry. Int J Hosp Manag. 2010;29(4):609–619. doi:10.1016/j.ijhm.2009.11.002
39. Chen P, Sparrow P, Cooper C. The relationship between person-organization fit and job satisfaction. J Manag Psychol. 2016;31(5):946–959. doi:10.1108/JMP-08-2014-0236
40. Roy A, van der Weijden T, de Vries N. Relationships of work characteristics to job satisfaction, turnover intention, and burnout among doctors in the district public-private mixed health system of Bangladesh. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):421. doi:10.1186/s12913-017-2369-y
41. Scanlan JN, Still M. Relationships between burnout, turnover intention, job satisfaction, job demands and job resources for mental health personnel in an Australian mental health service. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):62. doi:10.1186/s12913-018-3841-z
42. Joo B, Park S. Career satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention: the effects of goal orientation, organizational learning culture and developmental feedback. Leadersh Organ Dev J. 2010;31(6):482–500. doi:10.1108/01437731011069999
43. Chan SH, Ao CT. The mediating effects of job satisfaction and organizational commitment on turnover intention, in the relationships between pay satisfaction and work – family conflict of casino employees. J Qual Assur Hosp Tour. 2019;20(2):206–229. doi:10.1080/1528008X.2018.1512937
44. Hobfoll SE. Social and psychological resources and adaptation. Rev Gen Psychol. 2002;6(4):307–324. doi:10.1037/1089-2680.6.4.307
45. Albrecht SL, Marty A. Personality, self-efficacy and job resources and their associations with employee engagement, affective commitment and turnover intentions. Int J Hum Resour Manag. 2020;31(5):657–681. doi:10.1080/09585192.2017.1362660
46. Guo Y, Plummer V, Lam L, Wang Y, Cross W, Zhang J. The effects of resilience and turnover intention on nurses’ burnout: findings from a comparative cross‐sectional study. J Clin Nurs. 2019;28(3–4):499–508. doi:10.1111/jocn.14637
47. Khan NA, Khan AN, Moin MF, Pitafi AH. A trail of chaos: how psychopathic leadership influence employee satisfaction and turnover intention via self-efficacy in tourism enterprises. J Leis Res. 2020;1–23. doi:10.1080/00222216.2020.1785359
48. Abbas M, Raja U, Darr W, Bouckenooghe D. Combined effects of perceived politics and psychological capital on job satisfaction, turnover intentions, and performance. J Manage. 2014;40(7):1813–1830. doi:10.1177/0149206312455243
49. Sweetman D, Luthans F. The power of positive psychology: psychological capital and work engagement. In: Work Engagement: A Handbook of Essential Theory and Research. 2010:54–68.
50. Badran A, Youssef-Morgan M. Psychological capital and job satisfaction in Egypt. J Manag Psychol. 2015;30(3):354–370. doi:10.1108/JMP-06-2013-0176
51. Cheung FYL, Wu AM, Ching Chi L. Effect of job insecurity, anxiety and personal resources on job satisfaction among casino employees in macau: a moderated mediation analysis. J Hosp Mark Manag. 2019;28(3):379–396. doi:10.1080/19368623.2019.1525332
52. Kwok SYCL, Cheng L, Wong DFK. Family emotional support, positive psychological capital and job satisfaction among Chinese white-collar workers. J Happiness Stud. 2015;16(3):561–582. doi:10.1007/s10902-014-9522-7
53. Tang Y, Shao Y-F, Chen Y-J. Assessing the mediation mechanism of job satisfaction and organizational commitment on innovative behavior: the perspective of psychological capital. Front Psychol. 2019;10:2699. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02699
54. Wu C, Chen T. Collective psychological capital: linking shared leadership, organizational commitment, and creativity. Int J Hosp Manag. 2018;74:75–84. doi:10.1016/j.ijhm.2018.02.003
55. Bogler R, Somech A. Psychological capital, team resources and organizational citizenship behavior. J Psychol. 2019;153(8):784–802. doi:10.1080/00223980.2019.1614515
56. Yildiz H. The interactive effect of positive psychological capital and organizational trust on organizational citizenship behavior. SAGE Open. 2019;9(3):1–15. doi:10.1177/2158244019862661
57. Siu OL, Cheung F, Lui S. Linking positive emotions to work well-being and turnover intention among hong kong police officers: the role of psychological capital. J Happiness Stud. 2015;16(2):367–380. doi:10.1007/s10902-014-9513-8
58. Davidson MCG, Timo N, Wang Y. How much does labour turnover cost? A case study of Australian four- and five-star hotels. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag. 2010;22(4):451–466. doi:10.1108/09596111011042686
59. Janta H, Ladkin A, Brown L, Lugosi P. Employment experiences of Polish migrant workers in the UK hospitality sector. Tour Manag. 2011;32(5):1006–1019.
60. Nunnally JC. Psychometric Theory 3E. Tata McGraw-hill education; 1994.
61. Aiken LR. Content validity and reliability of single items or questionnaires. Educ Psychol Meas. 1980;40(4):955–959. doi:10.1177/001316448004000419
62. Kline RB. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling. Guilford publications; 2015.
63. Cochran WG. Sampling Techniques.
64. Hatcher L, Stepanski EJ. A Step-By-Step Approach to Using the SAS System for Univariate and Multivariate Statistics. SAS Institute; 1994.
65. Luthans F, Avolio BJ, Avey JB, Norman SM. Positive psychological capital: measurement and relationship with performance and satisfaction. Pers Psychol. 2007;60(3):541–572. doi:10.1111/j.1744-6570.2007.00083.x
66. Karatepe OM, Azar AK. The effects of work–family conflict and facilitation on turnover intentions: the moderating role of core self-evaluations. Int J Hosp Tour Adm. 2013;14(3):255–281. doi:10.1080/15256480.2013.809987
67. Karatepe OM, Magaji AB. Work-family conflict and facilitation in the hotel industry: a study in Nigeria. Cornell Hosp Q. 2008;49(4):395–412. doi:10.1177/1938965508326282
68. Kalidass A, Bahron A. The relationship between perceived supervisor support, perceived organizational support, organizational commitment and employee turnover intention. Int J Bus Adm. 2015;6(5):82–89. doi:10.5430/ijba.v6n5p82
69. Yao T, Qiu Q, Wei Y. Retaining hotel employees as internal customers: effect of organizational commitment on attitudinal and behavioral loyalty of employees. Int J Hosp Manag. 2019;76(September2017):1–8. doi:10.1016/j.ijhm.2018.03.018
70. Weiss DJ, Dawis RV, England GW. Manual for the Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire. Minnesota Stud Vocat Rehabil. 1967;22:120.
71. Yurcu G, Akinci Z. Influence of organizational citizenship behavior on hotel employees’ job satisfaction and subjective well-being. Adv Hosp Tour Res. 2017;5(1):57–83. doi:10.1007/s10902-014-9513-8
72. Escortell R, Baquero A, Delgado B. The impact of transformational leadership on the job satisfaction of internal employees and outsourced workers. Cogent Bus Manag. 2020;7(1):1837460. doi:10.1080/23311975.2020.1837460
73. Bentler PM, Bonett DG. Significance tests and goodness of fit in the analysis of covariance structures. Psychol Bull. 1980;88(3):588–606. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.88.3.588
74. Tabachnick BG, Fidell LS, Ullman JB. Using multivariate statistics.
75. Steiger JH. Understanding the limitations of global fit assessment in structural equation modeling. Pers Individ Dif. 2007;42(5):893–898. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2006.09.017
76. Hair JF, Black WC, Babin BJ, Anderson RE. Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global Perspective. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice hall; 1998.
77. Hair JF, Tatham RL, Anderson RE, Black W. Multivariate data analysis, 5/E. Technometrics. 1998;30(1):130–131.
78. Hulland J. Use of partial least squares (PLS) in strategic management research: a review of four recent studies. Strateg Manag J. 1999;20(2):195–204. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0266(199902)20:2<195::AID-SMJ13>3.0.CO;2-7
79. Bagozzi RP, Yi Y. On the evaluation of structural equation models. J Acad Mark Ence. 1988;16(1):74–94. doi:10.1007/BF02723327
80. Henseler J, Ringle CM, Sarstedt M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J Acad Mark Sci. 2015;43(1):115–135. doi:10.1007/s11747-014-0403-8
81. Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie SB, Lee JY, Podsakoff NP. Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J Appl Psychol. 2003;88(5):879–903. doi:10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879
82. Podsakoff PM, Organ DW. Self-reports in organizational research: problems and prospects. J Manage. 1986;12(4):531–544. doi:10.1177/014920638601200408
83. Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1986;51(6):1173–1182. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.51.6.1173
84. Arbuckle JL, Wothke W. Amos 4.0 User’s Guide. Chicago, IL: SmallWaters Corporation; 1999.
85. Byrne BM. Structural equation modeling with AMOS, EQS, and LISREL: comparative approaches to testing for the factorial validity of a measuring instrument. Int J Test. 2001;1(1):55–86. doi:10.1207/S15327574IJT0101_4
86. Brockman BK, Morgan RM. The role of existing knowledge in new product innovativeness and performance. Decis Sci. 2003;34(2):385–419. doi:10.1111/1540-5915.02326
87. Bergheim K, Nielsen MB, Mearns K, Eid J. The relationship between psychological capital, job satisfaction, and safety perceptions in the maritime industry. Saf Sci. 2015;74:27–36. doi:10.1016/j.ssci.2014.11.024
88. Paek S, Schuckert M, Terry T, Lee G. Why is hospitality employees ’ psychological capital important? The effects of psychological capital on work engagement and employee morale. Int J Hosp Manag. 2015;50:9–26. doi:10.1016/j.ijhm.2015.07.001
89. Ozturk A, Karatepe OM. Frontline hotel employees ’ psychological capital, trust in organization, and their effects on nonattendance intentions, absenteeism, and creative performance. J Hosp Mark Manag. 2018;00(00):1–23. doi:10.1080/19368623.2018.1509250
90. Agarwal UA. Examining links between abusive supervision, PsyCap, LMX and outcomes. Manag Decis. 2019;57(5):1304–1334. doi:10.1108/MD-02-2017-0103
91. Lu L, Lu AC, Gursoy D, et al. Work engagement, job satisfaction, and turnover intentions. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag. 2016;28(4):737–761. doi:10.1108/IJCHM-07-2014-0360
92. Luthans BC, Luthans KW, Jensen SM. The impact of business school students’ psychological capital on academic performance. J Educ Bus. 2012;87(5):253–259. doi:10.1080/08832323.2011.609844
93. Meyer JP, Tett RP. Job satisfaction, organizational commitment, turnover intention, and turnover: path analyses based on meta-analytical findings. Pers Psychol. 1993;46:259–293. doi:10.1111/j.1744-6570.1993.tb00874.x
94. Stylos N, Vassiliadis C. Differences in sustainable management between four-and five-star hotels regarding the perceptions of three-pillar sustainability. J Hosp Mark Manag. 2015;24(8):791–825. doi:10.1080/19368623.2015.955622
95. Hobfoll SE. Conservation of resource caravans and engaged settings. J Occup Organ Psychol. 2011;84:116–122. doi:10.1111/j.2044-8325.2010.02016.x
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.