Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 15
Hearing Protection Outcomes of Analog Electrode Arrays Coated with Different Drug-Eluting Polymer Films Implanted into Guinea Pig Cochleae
Authors Huang Y, Yu H, Liang M, Hou S, Chen JM, Zhang F, Sun X, Jia H, Yang J
Received 29 April 2021
Accepted for publication 13 July 2021
Published 11 August 2021 Volume 2021:15 Pages 3443—3450
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S318117
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Yuyu Huang, 1, 2,* Haoran Yu, 3,* Min Liang, 1, 2 Shule Hou, 1, 2 Junmin Chen, 1, 2 Fan Zhang, 1, 2 Xiayu Sun, 1, 2 Huan Jia, 2, 4, 5 Jun Yang 1, 2, 5
1Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200092, People’s Republic of China; 2Shanghai Key Laboratory of Translational Medicine on Ear and Nose Diseases (14DZ2260300), Shanghai, 200125, People’s Republic of China; 3ENT Institute and Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Eye & ENT Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200031, People’s Republic of China; 4Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200011, People’s Republic of China; 5Ear Institute, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200031, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Correspondence: Jun Yang
ENT Ward of Xinhua Hospital, Floor 18, Building 8, 1665 Kongjiang Road, Yangpu District, Shanghai, 200092, People’s Republic of China
Tel +86 13764981808
Email [email protected]
Huan Jia
ENT Ward of Ninth People’s Hospital, Floor 2, Building 1, 639 Zhizaoju Road, Huangpu District, Shanghai, 200011, People’s Republic of China
Tel +86 13601797481
Email [email protected]
Objective: To investigate the hearing protection outcomes of different drug-eluting analog electrode arrays implanted into guinea pig cochleae.
Methods: Sixty guinea pigs were randomly divided into a negative control group and five experimental groups implanted separately with blank (drug carrier), dexamethasone (DXM), aracytine (Ara-C), Ara-C+DXM, and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) eluting analog electrode arrays. Micro CT was used to supervise the surgical procedure. Auditory brainstem response (ABR) thresholds of the guinea pigs were measured and analyzed.
Results and Conclusions: Compared with the negative control, all other groups showed a significant increase in ABR threshold (p< 0.001) after surgery. Among them, there was no obvious difference between the blank (0 vs 90 days: 59.70± 10.57 vs 64.60± 9.47 dB SPL) and the NAD+ group (0 vs 90 days: 59.90± 9.87 vs 64.70± 8.65 dB SPL). On the other hand, the ABR thresholds in the DXM (0 days: 58.10± 10.73 dB SPL; 90 days: 51.70± 9.07 dB SPL) and the Ara-C group (0 days: 59.00± 10.05 dB SPL; 90 days: 51.60± 8.48 dB SPL) decreased significantly compared with the former two groups (p< 0.001). However, the Ara-C+DXM group showed no further benefit (p> 0.05). In addition, a significantly higher survival rate of spiral ganglion neurons in cochleae was observed in the Ara-C and/or DXM groups.
Keywords: guinea pig, cochlear implant, drug-eluting electrode, hearing protection
Corrigendum for this paper has been published
Background
The cochlear implant (CI) is regarded as the most successful neural stimulation device. It is virtually the only treatment for severe and severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss. This device has been implanted in more than 600,000 people globally, but less than 50,000 in China which indicates the potential for rapid growth there.1 With the improvement in device technology, surgical practice and patient outcomes, the indications for CI candidacy have also broadened.2 Research in the area of residual hearing preservation with CI, and Electric Acoustic Stimulation (EAS) has contributed to this broadening, with patients, especially those using tonal languages such as Chinese,3 benefiting from the using of EAS if functional hearing is preserved.
Although minimally invasive cochlear implantation is widely used in CI surgery4,5 and electrode arrays are gradually becoming softer and thinner, it is still reported that more than 30% of patients will lose their residual hearing immediately or gradually after CI6 At present, there are three possible widely accepted explanations for this: intracochlear inflammatory fibrosis,7 spiral ganglion cell degeneration,8 and delayed hair cell degeneration.9 Therefore, corticosteroids such as dexamethasone (DXM) have been the subject of numerous studies in the field of residual hearing protection after CI because of their strong anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects.10,11 As for the antimitotic drug aracytine (Ara-C), it has been proved to prevent the proliferation of fibrous tissue significantly in vitro, and has little ototoxicity.12 In addition, it was not until recently that nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) was considered in this field because of its great potential in regulating oxidative stress, repairing genetic material and resisting neurodegeneration. There are also studies which have indicated that NAD+ is helpful to prevent noise deafness and spiral ganglion degeneration.13,14
In this study, the three types of drug mentioned above were used to prepare different drug-eluting regimens which were implanted into guinea pig cochleae. The auditory brainstem responses (ABR) in each group were detected so as to compare the protective effects on residual hearing after surgery.
Materials and Methods
Fabrication of Drug-Eluting Polymer Film on Analog Electrode Arrays
Carbon-fluorine fiber with 0.2 mm diameter (Shangdao, Inc, Dongyang, China) was used for the analog electrode array on which a drug-eluting polymer film was fabricated according to a published method.15 Poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA, Boli Biomaterials, Inc, Shenzhen, China) was chosen as carrier and DXM (Sigma–Aldrich, Inc, St Louis, MO, USA), Ara-C (Sigma–Aldrich), or NAD+ (Sigma–Aldrich) were impregnated in the polymer film. Finally, the drug-eluting implants were sterilized by low temperature plasma. Drug release profiles were also reported in our previous study.15
Experimental Groups
A total of 65 white female guinea pigs (weight 357 ± 44 g; Slack, Inc, Shanghai, China) were divided into six groups. The control group (n=10) received no implanted array, while the positive control group (PLGA group, n=15) was implanted with untreated PLGA-coated analog electrode arrays, and the other four experimental groups (DXM (n=10), Ara-C (n=10), NAD+ (n=10), Ara-C+DXM (n=10)) were, respectively implanted to give the corresponding drug-eluting analog electrode arrays. The drug dosage of each array was 100 μg in the DXM group, 20 μg in the Ara-C group, 200 μg in the NAD+ group, and 20 μg Ara-C + 100 μg DXM in the Ara-C+DXM group. Experimental procedures followed the guidelines approved by the Institutional Authority for Laboratory Animal Care of Xinhua Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University. All efforts were made to limit the number of animals used and their suffering.
Surgical Procedure and Drug Application
All surgical procedures were performed by the same experienced operator. Guinea pigs were intraperitoneally injected with pentobarbital sodium (2%, Longsheng Chemical, Inc, Shanghai, China) at 30 mg/kg for general anesthesia. Lidocaine (2%, Baiyunshan Mingxing, Inc, Guangzhou, China) was injected subcutaneously behind the ear for analgesia. A downward arc incision was made from the midpoint of the posterior groove of the ear. After opening the tympanic bulla of the temporal bone, the basal turn of the cochlea and the round window niche were fully exposed. A cochleostomy was performed on the basal turn and the implants were carefully inserted into the hole. After implantation, the stoma was tightly sealed with muscle tissue. The other cochlea was exposed in the same way then obliterated.
Imaging of the Guinea Pig Cochlea in vivo
Electrode arrays (Oticon, Inc, Denmark) specially designed for small animals were implanted into the guinea pig cochlea. Randomly select 5 guinea pigs in the PLGA group, the animals were sacrificed using an overdose of anesthesia and their heads were scanned by Micro CT (Skyscan 1176, Bruker, Inc, Belgium) to obtain imaging data.
ABR Threshold Recordings
ABR thresholds in response to pure-tone stimuli were measured (RZ6, Tucker Davis Technologies, USA) 1 hour before and after surgery and also on days 7, 14, 28 and 90 at frequencies of 4, 6, 8, 16, 24 and 32 kHz. Bioelectrical potentials were recorded using a subdermal stainless-steel needle inserted at the vertex (ground electrode), ventrolateral to the measured ear (active electrode) and contralateral to the measured ear (reference electrode). Thresholds were determined from a set of responses at varying intensities with 5-dB SPL intervals and electrical signals were averaged over 1024 repetitions. Thresholds at each frequency were verified at least twice.
Tissue Collection and Preparation
After the final ABR measurements on day 90, all guinea pigs were euthanized with carbon dioxide inhalation and were intracardially perfused with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). The electrode arrays were carefully removed to avoid damaging the cochlear structure. Then all cochleas were fixed with 4% PFA overnight, decalcified in 10% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) for 2 weeks, dehydrated in increasing concentrations of sucrose, and embedded in Tissue-Tek®O.C.T.™ compound (Sakura, Japan).
Immunohistochemistry
Frozen sections were rinsed with PBS and incubated in blocking solution (10% goat serum in PBS with 0.2% Triton X-100) for 60 minutes at room temperature. The samples were then incubated overnight at 4°C with the following primary antibodies: rabbit monoclonal anti-myosin7a (Abcam, ab155984) and rabbit monoclonal anti-neurofilament heavy polypeptide (NF200, Abcam, ab40796) and then incubated with Alexa-488-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibodies (Yeasen, 33106ES60) for 1 hour at room temperature. F-actin was stained using Alexa-568-labeled phalloidin (1:100; Invitrogen) for 1 hour at room temperature. Nuclear staining was performed with 2 mg/mL DAPI (Invitrogen). The fluorescence images were captured using a Leica TCS-SPE confocal microscope (Leica Microsystems).
Statistical Analysis
SPSS software version 18 (SPSS, Inc, Chicago, USA) was used to analyze the ABR thresholds in guinea pigs. Comparison between groups was performed using ANOVA and subsequent post-hoc Turkey test.
Results
Analog Electrode Array Implantation in Guinea Pig Cochlea
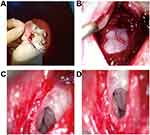
The incision behind the left ear (Figure 1A) exposed the “mastoid process” of guinea pigs (Figure 1B). Part of the bone was removed, and the cochlea was seen clearly in the auditory vesicle (Figure 1C). The length of the analog electrode array implanted in the cochlea was about 8 mm (Figure 1D). The whole operation took about 30 minutes.
Micro CT Imaging of Guinea Pigs in the PLGA Group
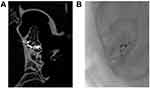
Sagittal CT images clearly demonstrated the spiral structure of the guinea pig in the PLGA group cochlea and the position of the electrode array, occupying the whole of the first turn and part of the second turn (Figure 2).
Auditory Function Evaluation
The ABR recordings showed that the average threshold of the negative control group was 27.07 ± 4.06 dB SPL (Table S1). The guinea pigs in the PLGA-positive control group and the other four experimental groups experienced full frequency hearing loss 1 hour after surgery but there was no statistically significant difference in ABR thresholds among these groups (24, 32 kHz: 65–75 dB SPL; 4, 8, 16 kHz: 45–55 dB SPL; Tables S2–S6). According to the corresponding relationship between position and frequency in the cochlea (Table S7),16,25 in these studies, the length of the analog electrode arrays inserted into the cochlea was about 8 mm which could only influence frequencies greater than 2.9 kHz, and the lower the frequency, the lower the impact.
In addition, the ABR threshold of the PLGA-positive control group (0 days: 59.70 ± 10.57 dB SPL; 90 days: 64.60 ± 9.47 dB SPL) and the NAD+ group (0 days: 59.90 ± 9.87 dB SPL; 90 days: 64.70 ± 8.65 dB SPL) showed a continuous increase (Figure 3) and there was no statistically significant difference between them either at the same time or at the same frequency (Tables S2 and S6), suggesting that NAD + had no protective effect on residual hearing after CI.
However, in the DXM, Ara-C and Ara-C+DXM groups (Tables S3–S6), below 4 kHz, from the 14th day after surgery, and at the remaining frequencies from the 7th day after the operation, the ABR threshold decreased significantly compared with the PLGA-positive control group (P < 0.001) (Figure 3). On the 90th day after the operation, the ABR thresholds in the three groups mentioned above were lower than those on the 7th day (P < 0.05). In conclusion, either DXM or Ara-C had a significant long-term partial protective effect on residual hearing after implantation, whereas the DXM + Ara-C group did not show a better outcome than the other coatings (P > 0.05).
Histological Analysis
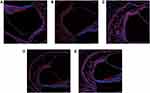
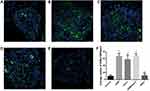
After 90 days, cochlear sections were stained with a neuronal antibody (NF200) that specifically labels spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs) and their nerve fibers. Example data from the cochleae used in this study are shown in Figure 4. Images show the SGNs within Rosenthal’s canal for different drug-treated guinea pigs. There was a clear difference in SGN survival with the cochleae that received DXM, Ara-C or DXM+Ara-C, exhibiting more SGNs compared to the positive control cochleae that received only PLGA coated-electrodes. However, there was no significant effect on the survival rate of hair cells and stria vascularis of cochlea (Figures 5 and 6).
Discussion
The drug delivery method used in this study was developed and applied for the first time by our team.15 Compared with other complex physical or chemical methods, it is simpler and more effective.17,18 In animal experiments, it should be noted that the safe dose range of pentobarbital sodium is narrow, because it is easy to cause respiratory depression due to deep anesthesia. As our experience accumulated, a dose of 30 mg/kg for one-time intraperitoneal injection was decided which could not only induce an effective sedation lasting for 60–80 minutes, but would also not affect the detection of the ABR threshold.
In addition to basic research, Lo’s team found that, although corticosteroids can inhibit tissue fibrosis around the electrode, residual hearing after cochlear implantation did not improve significantly.19 On the other hand, another study showed that whether DXM was injected through the round window membrane or intravenously, the ABR threshold could be effectively reduced 3 months after surgery.20 However, if DXM-loaded microspheres were injected through the tympanic membrane, they could only improve high frequency hearing (32 kHz),21 which may be related to the limited diffusion of the drug. In this study, in the experimental groups (DXM, Ara-C and Ara-C + DXM), the ABR thresholds of guinea pigs decreased gradually after surgery and were stable from the 28th day. On the one hand, this means that, during the designed degradation period of PLGA film (about 30 days), loaded drugs can be completely released.15 On the other hand, it also shows that DXM or Ara-C contribute to long-term hearing protection after CI. However, it is reported that intracochlear application of DXM was unable to rescue the delayed hearing loss caused by CI, which may be related to the neurotoxicity of high concentrations of DXM.12 Ara-C is much less toxic to hair cells, and therefore may replace DXM in residual hearing protection.
This study examined the feasibility and efficacy of intra-cochlear implantation of PLGA-coated analog electrodes that carried drugs to the inner ear. Following implantation of analog electrodes into the basal turn of the cochlea in guinea pigs, 90 days after surgery, we examined the histological changes of various components in the cochlea, including hair cells (HCs), stria vascularis (SV) cells, and SGNs. The results showed a significant SGN survival rate in Rosenthal’s canal treated with DXM and Ara-C compared to the cochlea treated with NAD+ or the PLGA-positive controls. The results from this study demonstrate that DXM and Ara-C could protect hearing by improving SGN survival in the cochlea. Also, the PLGA-coated analog electrode was biologically effective and could load multiple drugs that were customized to meet individualized treatment.
To explain the mechanism of the protective effect of Ara-C at the molecular level, researchers have found that electrode implantation can stimulate the release of inflammatory factors and growth factors from fibroblasts and macrophages.12 The former can further activate MAPK/JNK-mediated apoptosis promoting a cascade reaction, leading to apoptosis of the outer hair cells.22 The latter promotes the proliferation of fibrous tissue, resulting in scar formation around the electrode. The antimitotic drug Ara-C can inhibit the secretion of TGF-β1 by immune cells and the proliferation of fibroblasts, and further the formation of fibrous tissue.12 However, it should be noted that, in the Ara-C+DXM group, the combination of the two drugs had no cumulative benefit. This may be because, although their pharmacological actions and signaling pathways are different, they may ultimately regulate the same target.
In recent years, NAD+ has been shown to be an excellent molecule for decreasing oxidative stress and inhibiting neuronal apoptosis. It has been reported that NAD+ can not only regulate the JNK pathway through PARP-1, but also inhibit chronic cell damage and reduce the degeneration of cochlear axons and hair cells.14 However, in this study, the NAD+ group did not show the expected effects. Perhaps because of its high molecular weight, it is difficult to enter the cells without a continuous highly concentrated exposure.23 In addition, NAD+ is also unstable and may be inactivated during the preparation of drug-loaded electrode arrays.
Conclusions
Micro CT can show the fine structure in the temporal bone which makes guinea pigs an ideal animal model for the study of cochlear implants. DXM or Ara-C loaded in biodegradable polymer film coatings on electrode arrays provide a significant contribution to postoperative hearing protection but there is no benefit to be gained from simultaneous use. Compared with DXM, Ara-C has more potential theoretical advantages;24 however, further investigation is required to discover new biomaterials and further elucidate the cellular and molecular mechanisms of proliferation of cochlear fibrosis in response to foreign body implantation, so that more specific targets and drugs can be identified, improve the treatment effect of EAS, and allow more patients to benefit.
Data Sharing Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The animal experiments followed the guidelines approved by the Institutional Authority for Laboratory Animal Care of Xinhua Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University. Follow the Code of Ethics of the International Council for Laboratory Animal Science (ICLAS). All efforts were made to limit the number of animals used and their suffering.
Funding
This work was supported by the Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (17ZR1416100), Shanghai Academic Leadership Program (16XD1402200), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (81200742, 81800903).
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
1. Li JN, Chen S, Zhai L, et al. The advances in hearing rehabilitation and cochlear implants in China. Ear Heart. 2017;38(6):647–652. doi:10.1097/AUD.0000000000000441
2. Heman-Ackah SE, Roland JJ, Haynes DS, Waltzman SB. Pediatric cochlear implantation: candidacy evaluation, medical and surgical considerations, and expanding criteria. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2012;45(1):41–67. doi:10.1016/j.otc.2011.08.016
3. Deroche M, Lu HP, Kulkarni AM, et al. A tonal-language benefit for pitch in normally-hearing and cochlear-implanted children. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):109. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-36393-1
4. Miranda PC, Sampaio AL, Lopes RA, Ramos VA, de Oliveira CA. Hearing preservation in cochlear implant surgery. Int J Otolaryngol. 2014;2014:468515. doi:10.1155/2014/468515
5. Cui D, Shi Y, Su Q, Liu T, Han D, Li Y. Minimal incision access for pediatric and adult cochlear implantation. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(13):2434–2437.
6. Adunka OF, Dillon MT, Adunka MC, King ER, Pillsbury HC, Buchman CA. Hearing preservation and speech perception outcomes with electric-acoustic stimulation after 12 months of listening experience. Laryngoscope. 2013;123(10):2509–2515.
7. O’Leary SJ, Monksfield P, Kel G, et al. Relations between cochlear histopathology and hearing loss in experimental cochlear implantation. Heart Res. 2013;298:27–35. doi:10.1016/j.heares.2013.01.012
8. Kopelovich JC, Reiss LA, Etler CP, et al. Hearing loss after activation of hearing preservation cochlear implants might be related to afferent cochlear innervation injury. Otol Neurotol. 2015;36(6):1035–1044. doi:10.1097/MAO.0000000000000754
9. Eshraghi AA, Gupta C, Van De Water TR, et al. Molecular mechanisms involved in cochlear implantation trauma and the protection of hearing and auditory sensory cells by inhibition of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase signaling. Laryngoscope. 2013;123(Suppl 1):S1–S14. doi:10.1002/lary.23902
10. Shaul C, Venkatagiri PK, Lo J, et al. Glucocorticoid for hearing preservation after cochlear implantation: a systemic review and meta-analysis of animal studies. Otol Neurotol. 2019;40(9):1178–1185. doi:10.1097/MAO.0000000000002383
11. Wrzeszcz A, Steffens M, Balster S, et al. Hydrogel coated and dexamethasone releasing cochlear implants: quantification of fibrosis in guinea pigs and evaluation of insertion forces in a human cochlea model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(1):169–178. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.33187
12. Jia H, Francois F, Bourien J, et al. Prevention of trauma-induced cochlear fibrosis using intracochlear application of anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative drugs. Neuroscience. 2016;316:261–278. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.12.031
13. Okur MN, Mao B, Kimura R, et al. Short-term NAD(+) supplementation prevents hearing loss in mouse models of Cockayne syndrome. NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2020;6:1. doi:10.1038/s41514-019-0040-z
14. Ying W. NAD+/NADH and NADP+/NADPH in cellular functions and cell death: regulation and biological consequences. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2008;10(2):179–206. doi:10.1089/ars.2007.1672
15. Yu H, Tan H, Huang Y, et al. Development of a rapidly made, easily personalized drug-eluting polymer film on the electrode array of a cochlear implant during surgery. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;526(2):328–333. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.171
16. Young YH. Inner ear test battery in guinea pig models - a review. Acta Otolaryngol. 2018;138(6):519–529. doi:10.1080/00016489.2017.1419576
17. Yu HR, Jia H, Yang J. [The progress of topical drug delivery to the inner ear for the inhibition of inflammation and fibrosis following cochlear implantation]. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019;54(1):69–72. (Chinese).
18. Kikkawa YS, Nakagawa T, Ying L, et al. Growth factor-eluting cochlear implant electrode: impact on residual auditory function, insertional trauma, and fibrosis. J Transl Med. 2014;12:280. doi:10.1186/s12967-014-0280-4
19. Lo J, Campbell L, Sale P, et al. The role of preoperative steroids in atraumatic cochlear implantation surgery. Otol Neurotol. 2017;38(8):1118–1124. doi:10.1097/MAO.0000000000001505
20. Lee J, Ismail H, Lee JH, et al. Effect of both local and systemically administered dexamethasone on long-term hearing and tissue response in a Guinea pig model of cochlear implantation. Audiol Neurootol. 2013;18(6):392–405. doi:10.1159/000353582
21. James DP, Eastwood H, Richardson RT, O’Leary SJ. Effects of round window dexamethasone on residual hearing in a Guinea pig model of cochlear implantation. Audiol Neurootol. 2008;13(2):86–96. doi:10.1159/000111780
22. Eshraghi AA, Lang DM, Roell J, et al. Mechanisms of programmed cell death signaling in hair cells and support cells post-electrode insertion trauma. Acta Otolaryngol. 2015;135(4):328–334. doi:10.3109/00016489.2015.1012276
23. Sultani G, Samsudeen AF, Osborne B, Turner N. NAD(+): a key metabolic regulator with great therapeutic potential. J Neuroendocrinol. 2017;29(10). doi:10.1111/jne.12508
24. Grant S. Ara-C: cellular and molecular pharmacology. Adv Cancer Res. 1998;72:197–233.
25. Hochmair I, Hochmair E, Nopp P, Waller M, Jolly C. Deep electrodeinsertion and sound coding in cochlear implants. Heart Res. 2015;322:14–23. doi:10.1016/j.heares.2014.10.006
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.