Back to Journals » Clinical Interventions in Aging » Volume 15
Health Status and Functional Abilities of Elderly Males Visiting Primary Health-care Centers in Khamis Mushait, Saudi Arabia
Authors Al-Qahtani AM
Received 2 August 2020
Accepted for publication 5 October 2020
Published 10 November 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 2129—2143
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S274318
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Walker
Awad Mohammed Al-Qahtani
Department of Family and Community Medicine, College of Medicine, Najran University, Najran, Saudi Arabia
Correspondence: Awad Mohammed Al-Qahtani
Department of Family and Community Medicine, College of Medicine, Najran University, PO Box: 1988, King Abdulaziz Road, Najran 55461, Saudi Arabia
Tel +966-17 7930 6344
Email [email protected]
Background: There is an aging population all over the world, and Saudi Arabia is no exception to it. An aging population poses several challenges to the health-care sector.
Aim: The aim of this study was to examine the health status and functional abilities of elderly people visiting primary health-care centers in Khamis Mushait, Saudi Arabia.
Methods: This cross-sectional study involved elderly male Saudi nationals aged 60 years and above. Self-rated health status and body pain, functional status, geriatric review of systems and other relevant data were collected using the Geriatric Health Questionnaire of University of Iowa Health Care. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 21.
Results: The study results showed that the overall health of the elderly was either good (32.9%) or very good (32.3%), while 14.2% rated their health as excellent. Only two participants rated their health as poor. The majority of the participants (71.9%) had no functional impairment in basic activities of daily living (BADL), while 35.7% had mild impairment in instrumental activities of daily living (IADL). Only two participants were found to have total impairment in IADL. The most common limitation among BADL was walking (21.1%) and among IADL was doing the housework. The notable factors associated with functional impairment in BADL and IADL were old age (≥ 80 years), poor eyesight, memory impairment, having trouble with control of bladder, falls twice or more, taking more than two medications, being sexually inactive, poor self-rated general health and severe self-rated body pain (all P< 0.05) among others.
Conclusion: The majority of the elderly were able to perform BADL independently and to a lesser extent IADL; the overall self-rated general health was found to be good. Further research in the field of geriatrics is warranted to plan better, and design public health policies and provide efficient care to elderly patients.
Keywords: elderly, activities of daily living, ADL, health status, Saudi Arabia
Introduction
There is a growing aging population all over the world. In 2019, there were 703 million people worldwide aged 65 or over. The number of older people is forecast to double to 1.5 billion by 2050. Globally, the proportion of the population aged 65 or over has increased from 6% in 1990 to 9% in 2019. This proportion is projected to increase by 2050 to another 16%. Globally, in 2015–2020, a person aged 65 is expected to live an additional 17 years, on average. This figure will grow to 19 years by 2045–2050.1
The demographic features of Saudi Arabia are also changing. There is an increase in proportion of elderly people. In Saudi Arabia, life expectancy has improved from 64.4 years during the 1980s to 74.3 years in the 2000s.2 In 2010 the elderly were just 3% of the Saudi population; by 2050, they would be nearly 20%.3 This increase in human longevity can be ascribed to advancing public health, medicine, and economic and social developments, as well as their contribution to the control of disease, prevention of injury, reduced fertility rates and reduced infant mortality.1,3 At the same time, an increasing aging population poses a number of challenges for the health-care sector to provide integrated health services for elderly patients.
The health and functional status of older adults is heterogeneous due to the different cumulative effects of chronic diseases and physiological decline which contribute to a vicious cycle of increased frailty.4 Psychological, social, cognitive, and functional issues affect the health of older people in addition to medical illnesses. Hearing loss, cataracts and refractive errors, back and neck pain and osteoarthritis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, depression and dementia are common conditions in older age groups. In addition, as people age, they are more likely to experience multiple conditions simultaneously.5
The World Health Organization (WHO) developed International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) that defines disability as an umbrella term including impairments, activity and participation limitations.6 The functional capacity of an individual can be measured using activities of daily living (ADL) index which can be further divided into basic activities of daily living (BADL) and instrumental activities of daily living (IADL). The BADL include skills and functions needed to perform basic physical needs such as eating, bathing, toileting, dressing among others, whereas IADL includes more complex activities necessary for independent living in the community such as using telephone, driving, managing finances, preparing meals, taking medications and doing housework.7 Self-rated health status though subjective, serves as an important indicator of health evaluation in practice. The self-rated health of the elderly is correlated with their functional abilities.8,9
A number of research studies and reviews have shown that the functional status of the elderly is influenced by a number of factors including self-rated health status,9 self-rated body pain,10 age,10–13 cognitive abilities,9,14,15 falls,14,16,17 urinary incontinence,17,18 poor vision,19–21 polypharmacy,14,22 alcohol consumption14,23–25 among others.
The Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA) is a multidimensional assessment of an older person designed to evaluate functional ability, physical health, cognition and mental health, social, economic, spiritual, and environmental circumstances. It also includes an extensive review of polypharmacy and immunization status, identification of patient’s resources, capacities and preferences.26–28 CGA proposes a methodology that centralizes around functional-related outcomes, addresses the issue of poor symptom correlation and primary causes in older people with multiple chronic diseases.29 This appraisal assists in the identification of medical conditions; implementation of treatment and follow-up plans; coordination of care management; and assessment of long-term care needs and optimal placement.27
In Saudi Arabia, there is a dearth of studies evaluating the health status and needs of elderly which has led to scarce data about the important aspects of elderly health such as physical and mental health status, cognitive capabilities and prevalence of geriatric syndromes among others. The information pertaining to these aspects of elderly health play an important role and serves as the foundation in the development of evidence based health policies and guidelines for care of elderly people. However, results of Saudi National Survey for Elderly Health (SNSEH) conducted between 2006 and 2007 and the more recently conducted Elderly Survey 2017 by General Authority for Statistics provide valuable insights into the health characteristics of the Saudi elderly population.30,31
The intent of the study was to evaluate the health status, functional status through BADL and IADL, geriatric review of the systems and other characteristics of the elderly males and relationship between these. Another intention of the study was to find the solutions based on the outcome and design better health-care interventions aimed at improving elderly care in future clinical practice. The study was conducted only in elderly males as almost all of the elderly females had not consented to participate in the study. This may be attributed to the socio-religious and cultural practices prevalent in the society. To the best of our knowledge, there is no published study wherein the health status and functional abilities of elderly males was evaluated exclusively in Khamis Mushait city. Hence with these aims, the present study was conducted.
Methodology
Study Design, Participants and Site
This was a prospective cross-sectional study designed to evaluate the health status of elderly males visiting primary health-care centers (PHCs) in Khamis Mushait, Saudi Arabia. The study was conducted between September and November 2019, and involved Saudi nationals aged 60 years or above either coming for themselves or accompanying other patients to the PHCs. The study utilized a simple random sampling technique. A total of 171 individuals took part in the study.
Exclusion Criteria
Non-Saudi nationals, people under the age of 60, people unable to complete the forms, people who were unable to follow the instructions or to give appropriate informed consent and individuals who declined to partake were excluded from the study.
Sample Size
The study conducted by Sharma et al indicated the prevalence of good health among 46.2% of the elderly people.32 This prevalence rate was used to find the optimum sample size. Using the categorical sample size formula of; N=Z2 (pq)/e2, where; N=sample size; Z=confidence level (1.96); p=estimated proportion of the event (taken from the previous study); q=1 – p; e=margin of error (0.05), the sample size required to detect a statistically significant result with 95% levels of confidence and 0.5 margin of error assuming a two-tailed statistical test was found to be 382.
Study Instrument and Data Collection
The Geriatric Health Questionnaire of University of Iowa Health Care was used to collect the data.33 Apart from this; data about age of participants was also collected. The questionnaire was translated into Arabic to be convenient for the participants. The participants completed the questionnaires in one room under the supervision of primary care physicians who were well trained prior to the commencement of the study by the investigators. The supervising physicians explained the purpose and objectives of the study to the participants and clarified and helped the participants with any doubts or difficulties that arose during completion of the questionnaire. A senior physician performed a validity check at the end of completion of questionnaires in order to ensure accuracy of data.
Translation and Validation of the Study Instrument
The Geriatric Health Questionnaire of University of Iowa Health Care was translated into Arabic. Two bilingual experts whose native language was Arabic independently translated the English version of the questionnaire into Arabic producing colloquial translations. The first translator was an associate professor of family medicine and aware of the concept being studied, while the second translator was a professor of Arabic language and was not aware of the concept being studied. The two forward translated versions were then synthesized into a single translated Arabic version. In the next step, this initially synthesized translated Arabic version was subjected to backward translation to English language by two independent bilingual experts. Both of these translators were working as professors of English language. These back-translated versions were then synthesized by another independent bilingual expert. Then the content and face validity of both the Arabic version and back-translated version was performed by a three-member expert panel. The pre-final version of the Arabic questionnaire was subjected to pilot testing in 15 elderly individuals. Based on the results of the pilot test, a final Arabic version of the questionnaire with best possible translation was prepared.
The reliability analysis was performed to ensure validity of the Geriatric Health Questionnaire of University of Iowa Health Care. As the BADL subscale comprised of five daily activities, the result of reliability analysis showed 0.857 Cronbach’s alpha value or 87.5% indicating a very good internal consistency. For the IADL subscale that consisted of seven daily activities, the reliability analysis showed a Cronbach’s alpha value of 0.914 or 91.4% indicating an excellent internal consistency. Based on the above results, the study questionnaire was deemed acceptable and valid.
Measurements
This questionnaire is a generic health status instrument that includes information on general health status of patients including bodily pain, functional status evaluated through BADL and IADL, geriatric review of systems including data on falls and alcohol consumption, social support, polypharmacy, sexual activity, immunization status, and cognition using Mini-cognitive Assessment Instrument (Mini-Cog© test).33
Self-rated health and bodily pain were measured using a Likert scale. The participant’s health was measured using a five-point Likert scale: excellent, very good, good, fair, poor, and bodily pain using a six-point Likert scale: none, very mild, mild, moderate, severe, and very severe. The functional ability was assessed by ADL including BADL, and IADL. The BADL examined included walking, dressing, bathing, eating, and toileting and the IADL included driving, using telephone, shopping, preparing meals, housework, taking medications and managing finances. These items were rated trichotomously (independent=1, require assistance=2, dependent=3) and all the responses were then summed up. The higher scores indicate greater disability. The BADL consisted of five activities and the score range possible was 5–15.34
A geriatric review of various systems was performed. The participants were screened for vision, hearing, memory, depression, unintentional weight loss, urinary and bowel incontinence. These items were scored as “yes” or “no”. An affirmative response was considered as a positive screen. Apart from these, the participants were asked about the number of falls they had in the past year and about alcohol consumption. The participants were asked to specify the number of drinks they had per week in case of drinking. The participants also reported the number of medicines being taken including prescription drugs, over the counter medicine and vitamins and also how they would manage taking their medicines. In addition, the participants were asked if they were sexually active, if anyone had intentionally tried to harm them, and if they had a shot to prevent pneumonia. Lastly, the participants were subjected to Mini-Cog© test for screening of cognitive impairment.
The Mini-Cog© test consists of a three-item recall task and a clock drawing task (CDT). One point is assigned to each correctly recalled item and two points for correctly drawn clock and zero points for incorrectly drawn clock. The total achievable score was three points in the recall test and two points in CDT. The participants were given three unrelated words and were asked to repeat the same in order to confirm that the words were heard by them. Now the participants were subjected to CDT. The participants were given a blank sheet of paper and were asked to draw the face of a clock, put the numbers on it, each only once and draw the hands of a clock to read the time 11:10. The hand length was not scored. A participant could repeat the task but without any additional instructions. They were given a time of three minutes to complete the CDT, after which they were asked to repeat the three items given to them earlier. Refusal to partake in the CDT resulted in zero score. For the purpose of generating the Mini-Cog© score, the recall and CDT scores were combined. A score of 0–2 was considered positive screen for dementia and a score of 3–5, lower likelihood of dementia.35–37
Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics were presented as frequencies, proportion (%), mean and standard deviation, whenever appropriate. The association between different age bands and self-rated health status and bodily pain was evaluated. Mann–Whitney U-test or Kruskal–Wallis test were used to compare between ADL subscales among different characteristics of elderly population. A P-value of ≤0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Normality test was conducted using the Shapiro–Wilk test. All data analyses were carried out using the statistical package for social sciences, version 21 (SPSS; IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
Ethical Statement
The research was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the College of Medicine, Najran University. The objectives and procedures of the study were explained to the participants. They were informed that the participation was entirely voluntary, would be allowed to quit the study at any time and obtained information would be confidential. The investigation was carried out in conformity with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki, and an informed consent was obtained from all the participants.
Results
A total of 382 questionnaires were distributed among elderly males visiting PHCs in Khamis Mushait. A total of 171 elderly males aged between 60 and 102 years (mean age of 70.6) participated and completed the questionnaire giving an overall response rate of 44.8%. As the study was conducted only in elderly males and hence the participation of only elderly males may have led to the decreased sample size. The participants were grouped into three age groups: 60–69, 70–79 and ≥80. The self-rated health status and body pain by elderly males has been presented in Table 1. Fourteen point two percent of participants rated their health in general as excellent, 32.3% as very good, and 32.9% as good. The health status was rated as fair by 19.4% of participants and only two individuals rated their health as poor. With regard to body pain, 27.3% of participants rated body pain to be very mild, 24.7% as mild, 27.9% as moderate and 4.5% of the participants rated body pain as severe. Fifteen point six percent of participants did not report body pain. A statistically significant difference was observed in self-rated health status (χ2=18.621; P=0.017) and the self-rated body pain (χ2=28.295; P<0.001) between different age groups of the participating elderly males.
 |
Table 1 Assessment of General Health and Body Pain Among Elderly Population |
In Figure 1, assessment of ADL of participants has been presented. The most notable activities which participants could perform independently were; toileting (90.6%), eating (88.3%), dressing (86%), bathing (85.4%) and walking (78.9%). In contrast, participants were dependent in performing the following daily activities such as, housework (41.5%), followed by driving (32.7%), and preparing meals (32.2%).
 |
Figure 1 Assessment of activities of daily living of the elderly population. |
The descriptive statistics of ADL subscales has been presented in Table 2. The mean BADL score was 5.71 (SD 1.40) out of 15 points; majority of the participants (71.9%) reported no impairment while mild impairment was present in 20.5% of them. The mean IADL score was 12.3 (SD 4.28) out of 21 points; 35.7% of the participants had mild impairment; moderate impairment was reported in 23.4% of participants and severe impairment in 21.1%. No impairment was reported in 18.7% of individuals in IADL. When comparing the BADL score across the age groups, the mean BADL score was found to be significantly higher in the oldest age group (F=0.658; P=0.002). It was also observed that moderate impairment had significant relationship among the oldest age group (χ2=15.396; P=0.004). In comparison with the IADL scores, the mean IADL score was also found to be significantly higher in the oldest age group (F=39.663; P<0.001) while in comparison with the extent of IADL scores, severe impairment was found to be present significantly in the oldest age group (χ2=75.082; P<0.001).
 |
Table 2 Descriptive Statistics of Activities of Daily Living in Accordance to Age Group |
The geriatric review of systems and other related characteristics of participating elderly males are presented in Table 3. More than half of the participants reported to have difficulties in driving, watching TV or reading due to poor vision, while 18.1% were using hearing aids. It was also observed that 30.4% had problems with memory and 35.3% were often feeling sad or were depressed. Few of them (15.5%) had unintentional weight loss in the last six months, 34.1% and 15.5% had trouble with control of bladder and bowel respectively. The incidence of falls in the past one year was reported once and twice or more than twice, each in 21.3% of the participants respectively. There were 9.8% of the participants who consumed alcohol; nine individuals had alcohol less than 10 times a week, while six individuals had alcohol 10 times or more a week. When asked if the participants were living with anyone, nearly all (93.3%) had affirmative response with more than one third (35.3%) living with their relatives, followed by with their spouse (34.6%) and child (28.8%). The participants' (98.4%) spouse would help them with health-care decisions. A little less than half of the participants (45.9%) reported taking more than two medications and 45.8% used pill box to guide them for taking it. In addition, approximately 40% of the participants were still sexually active. Few of them (9.4%) reported that somebody had intentionally tried to harm them and 21.1% have had a shot to prevent pneumonia. In the Mini-Cog© test, 10.4% of the participants screened positive for dementia.
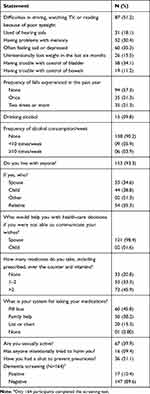 |
Table 3 Geriatric Review and Other Characteristics of Elderly Population (N=171) |
When comparing ADL subscales with the characteristics of participating elderly males, several variables such as age 80 years or over (F=6.598; P=0.001), fair self-rated general health (F=7.794; P<0.001), severe self-rated body pain (F=5.782; P<0.001), poor vision (T=3.684; P<0.001), memory problems (T=4.6767; P<0.001), unintentional weight loss in past six months (T=2.335; P=0.008), having trouble with control of bladder (T=2.986; P=0.001), two or more number of falls experienced in the past year (F=15.560; P<0.001), living with child (F=3.161; P=0.004), taking more than two medications (F=6.140; P<0.001) and being not sexually active (T=−5.239; P<0.001) were found to be significantly associated with poor BADL outcome. Likewise, various characteristics were also associated with poor IADL outcome including age 80 years or over (F=39.633; P<0.001), poor self-rated general health (F=16.273; P<0.001), severe self-rated body pain (F=20.830; P<0.001), poor vision (T=6.075; P<0.001), memory problems (T=3.682; P<0.001), having trouble with control of bladder (T=5.147; P<0.001), having experienced falls twice or more in the past year (F=24.168; P<0.001), not drinking alcohol (T=−3.912; P<0.001), living with someone (T=2.632; P=0.021), especially with children (F=5.572; P=0.002), taking more than two medicines (F=13.477; P<0.001), assistance from family in taking medications (F=48.581; P<0.001) and being not sexually active (T=−8.887; P<0.001).
Discussion
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the geriatric health of elderly which is an important investigation given that health status of elderly depends upon their functional capability, mental, physiological, and psychosocial functioning.
The mean age of the participants in our study was 70.6 years and the majority of them were in the age range of 60–69 years. The mean age of the participants in our study was comparable to that of the participants in other studies.10,38
In our study, the overall health of participating elderly males was either good (32.9%) or very good (32.3%) while only 1.3% of participants considered their health as poor. The results of a Taiwanese study yielded similar outcomes, wherein 10.8% of the participants rated their health as excellent, 31.7% as good and 4.5% as very bad.8 In a study conducted in Abha city in Saudi Arabia, 52.4% of participants rated their health status as average or poor.11 The results of our study seemed to agree with the study conducted by Sharma et al, wherein 46.2% of the participants had rated their health as good, 42.8% as average and only 11% considering their health as poor.32 In a cross-sectional survey conducted in Saudi Arabia, a sizeable majority of participants (72.2%) enjoyed good health.39
The prevalence of functional impairment was higher in IADL than in BADL. These results were similar to the findings of many other studies.8,14,32 The prevalence of functional impairment was 28.1% in BADL and 81.3% in IDAL. In a study conducted in the Abha city, Saudi Arabia, 26.6% of the participants had impaired functional capacity in BADL.11 In the cross-sectional survey conducted in Saudi Arabia, 18.8% of the participants were found to be dependent on others for BADL.39 However, functional impairment in IADL was found to be much lower at 34%, 46.3%, and 53.5% in other studies compared to the findings of our study.14,40,41 The mean BADL and IADL scores significantly differed among different age groups (P=0.002 and P<0.05). Similar findings were reported in a study performed in elderly Yi participants in China.42 In relation to BADL, the higher incidence of partial dependence was reported for walking (21.1%) followed by bathing (14.6%) and dressing (14%). However, 0.6% of the participants were totally dependent in toileting. These results are in agreement with the findings of other studies. In a study conducted in Taiwan, chair/bed transfers, bathing self and dressing were found to be the most common limitations.8 The results of the Polish study revealed bathing and dressing as the most common limitations in basic activities.10 In a study conducted in the Qassim region of Saudi Arabia, moving around indoors (13.9%), bathing (11.3%) and dressing (9.8%) were found to be the common activities with impairment.12 In an Indian study, bathing was found to be the most difficult task to perform.32 The most common activities in IADL wherein a participant was totally dependent were tidying the house (41.5%) followed by driving (32.7%) and preparing meals (32.2%). A higher proportion of the participants required assistance in IADL such as shopping (36.8%) and using the telephone (32.7%). The findings similar to our study results have been reported in other studies. In a Polish study, moving within the community was found to be the most common limitation in IADL.10 In a study conducted in the Qassim region of Saudi Arabia; the participants had functional impairment in activities of shopping (55.6%) and reaching the PHC (48.5%). In this study, 57.5% of the participants had impairment in money management, which is similar to the findings of our study, wherein, 19.3% of the participants were totally dependent in managing finances and 26.3% needed assistance.12 Transportation, shopping, housekeeping and cooking in varying proportions were found to be the most difficult tasks amongst the elderly participants in a study conducted in India.32 In a study conducted in Brazil; shopping, tidying the house, and using means of transport in varying proportions were reported to be the most common limitations.40
Moreover, when factors significantly associated with BADL and IADL were evaluated, several factors were found to contribute to decrease in functional ability both in BADL and IADL. The findings of our study showed that the functional impairment in BADL was associated with age (≥80), poor eyesight, memory impairment, and unintentional weight loss in past six months, trouble with control of bladder, falls twice or more in the past year, living with children, taking more than two medications, sexual inactivity, fair self-rated health and severe self-rated body pain. In IADL, the functional disability was associated with age (≥80), poor eyesight, and memory impairment, having trouble with control of bladder, falls twice or more in the past year, no consumption of alcohol, living with someone, especially with children, poor self-rated health and severe self-rated body pain (Table 4). Similar results have been reported in other studies.
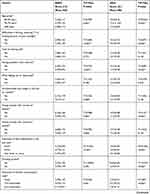 |
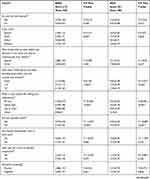 |
 |
Table 4 Characteristics of Elderly Participants and Their Functional Status Based on ADL Subscales |
In a study conducted in the Shangrao city in Jiangxi province in China, older age, poor self-rated health, cognitive impairment and visual impairment were found to be associated with poor ADL outcomes.9 In a study from Brazil, functional disability in BADL was found to be associated with age, falls, alcohol consumption, number of drugs and cognitive deficits among others while in IADL, functional disability was significantly associated with age, family arrangement, and number of drugs, alcohol consumption and cognitive deficit among others.14 In a review, unintentional weight loss was reported as a predictor of functional disability in elderly people.43
The functional impairment in BADL and IADL significantly increased with age in our study. The participants aged 80 years or more had significantly higher mean BADL and IADL scores in our study indicating higher functional impairment. Similar findings have been corroborated by many other studies. In a Polish study of participants aged 75 or above, 30.37% reported problems with ADL while 57.31% had problems with IADL.10 In a study conducted in Abha city, Saudi Arabia, participants aged 75 years and more (very old) were found to have higher impaired functional capacity compared to their younger counterparts (old).11 In the Qassim study, the advancing age was negatively associated with ability to perform BADL and IADL.12 A cross-sectional analysis by Connolly et al, revealed approximately a two-and-a-half-fold increase in the risk of functional ADL and IADL difficulties among Irish people in the 75–79 age group and a four-fold increase in risk in the 80 and older age group when compared with the people in the 65–69 group.13 Apart from age, self-rated pain was also significantly associated with functional impairment in our study. In the Polish study, the severity of pain was found to cause a significant increase in the risk of disability. A 27% increase in both ADL and IADL disability was reported with each subsequent point on the pain scale.10 Similar findings were reported by other studies as well. A two-fold increase in risk of ADL and IADL difficulty was reported in older people with pain in comparison to older people without such pain.13 A strong association between pain and disability in older people was noted by Andrews et al. They also concluded that the pain caused disability in a short time.44 Scudds et al indicated that the risk of disability in senior citizens is increased by an increase in the intensity of pain. The pain in elderly can lead to decreased ambulation, functional decline, disability and functional dependence.45
A number of studies have shown the impact of the level of cognitive functioning on ADL in elderly population. In a study conducted by Xu et al the cognitive ability was significantly associated with seniors who had poor ADL outcomes.9 The same was the case in a Brazilian study by Virtuoso Júnior, wherein, functional disability in both BADL and IADL was significantly associated with cognitive deficits.14 A recent systematic review by Lindberg et al indicated that individuals with mild cognitive impairment displayed significantly greater IADL impairment than cognitively intact controls.15 In our study, the participants who experienced falls twice or more in the past year had significantly more functional impairment in BADL and IALD compared to those who had experienced a fall once or had never experienced a fall. Many studies have highlighted the effect of falls on the ADL in the elderly. In the Brazilian study by Virtuoso Júnior, functional disability in BADL was found to be significantly associated with the falls.14 In another study carried out in functionally independent older adults aged 65 to 69 in the US, fall status in the past two years was found to be an important independent predictor of subsequent ADL difficulty.16 A similar finding was observed in a population-based cohort study carried out in the community dwelling older adults in Hong Kong, wherein, incident falls were found to have a significant negative impact on ADL functioning.17 In our study, the participants having trouble with bladder control had significantly higher functional impairment in both BADL and IADL. Similar findings have been reported in other studies. The secondary analyses of the data obtained from a cross-sectional study conducted in nursing home residents in Korea found a significantly lower performance of ADL in participants with urinary incontinence compared to those with no urinary incontinence.18 In a Brazilian study, a higher prevalence of functional disability was found in elderly individuals with urinary incontinence.46 Several studies have established the positive role of social support in performing ADL.10,47 Maintaining social relationships enhances physical and cognitive functions of the elderly via active involvement in social activities and building social networks.48 Social support makes the elderly feel adored, esteemed, keep them from feeling deserted and gives an impression that they still have someone they can count on.49 Contrary to this, in our study, participants living with someone were found to have significant functional impairment in IADL. Those living with their children had significant difficulties in BADL and IADL activities. This might be attributed to the negative effects of the help received from the social contacts or the family members when it transforms into an ongoing schedule wherein most of the day by day activities are being finished for the elderly by them.50 In our study, 98.4% of the participants received help with health-care decisions from their wives. A similar finding was reported in the study conducted in Abha city, where the wife was the main caregiver for the husband.11 The participants receiving good family support can be attributed to the cultural practices of extended family care and traditional social values underpinned by religious faith prevalent in the Saudi society.51
In our study, the participants with poor vision had significantly higher BADL and IADL scores indicating higher difficulties faced in performing these activities. These findings are similar to the results of other studies conducted elsewhere. In a study carried out in the Netherlands, the older participants with low vision reported poorer levels of performance with respect to ADLs.19 In another study, participants with low vision were reported to have poorer functional capability to carry out both BADL and IADL than their fully sighted counterparts.20 In a population-based cohort study in France, visual loss in the elderly was found to significantly increase the risk of functional decline in both BADL and IADL over time.21 In our study, functional decline was significantly associated with the number of drugs used as reported in previous studies.14,22 In our study, no consumption of alcohol was associated with higher functional decline in IADL compared to those consuming alcohol. The participants consuming alcohol compared to those not consuming it had better functional capabilities. Similar findings were obtained from other studies in Brazil, Japan and China.14,23–25 However, it should be noted that, an article by Burton and Sheron had discussed that no amount of alcohol consumption could help improve health and that the benefits associated with it are clearly outweighed by the augmented risk of health-related harms associated with it, including cancer.52 And moreover, consumption of alcohol should not be promoted in elderly considering their health conditions and physiological functioning.
The findings from our study indicate that more attention should be given to the needs of the elderly and more specialized clinics and community health-care centres should be established for elderly population. The specific counselling services should be provided for the caregivers of the elderly. The factors affecting functional impairment in ADL and other geriatric health issues should be identified for better planning and designing the public health policies aimed at improving geriatric care. Comprehensive health care should be provided to the elderly in an efficient and timely manner. We further suggest that the instruments used to collect the data should take socio-religious and cultural aspects of society into considerations. The use of geriatric assessment tools should be incorporated in regular clinical practice. The findings from our study and other such studies should be taken into consideration to promote active and healthy ageing, delay onset of dependence in the elderly and reduce disability, and plan future clinical interventions for the aging population. The health-care professionals including primary care physicians and nurses should be provided with regular training and education in the area of geriatrics to support the ever growing needs of the elderly. Sufficient geriatric content should be included in the curricula of health science disciplines and students should be encouraged to take up specialization in gerontology. The professionals with geriatric expertise should be recruited and retained by offering several types of incentives.
Limitations
The present study has certain limitations and these must be mentioned. The first limitation is that the study was carried out only in male participants and hence gender-specific differences could not be studied and established. The information regarding other important sociodemographic characteristics such as marital status, employment status and monthly income, level of education were not collected and hence not studied in relationship with ADL. The study was a cross-sectional study and hence temporal relationship between study variables and the functional status is difficult to establish due to the possibility of reverse causality bias. Cohort studies should be conducted to establish the causal-relationship between the ADL and associated factors. The study sample size was not provincially or nationally representative and hence results cannot be extrapolated to the entire province or country. And moreover, the elderly who could attend the PHCs were included in the study and elderly with severe functional disability who could not attend or those under institutional care were not part of the study. Lastly, comparison of our results with the findings of other studies was difficult and limited, because of multiple instruments and parameters utilized for classifying and assessing functional status in elderly and in some cases because of different cutoff points even if the instruments used were same.
Conclusion
The majority of the elderly were able to perform BADL independently and to a lesser extent IADL; the overall self-rated general health was reported to be good. Increasing age, weak vision, impaired memory, having trouble with control of bladder, incidence of falls more than once, living with children, taking more than two medications, assistance of family members on taking medications and being sexually inactive, significantly affected functional capabilities. Existing national surveys should be continued and further research should be carried out in the future to fill the gap in scientific literature by conducting studies evaluating health and functional status, needs of elderly and various other areas of geriatric health in different parts of Saudi Arabia. The national policies and clinical practice guidelines addressing the health of the elderly should be updated regularly in light of the recent advancements and data.
Disclosure
The author reports no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. United Nations. World population ageing 2019: highlights. Available from: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/publications/pdf/ageing/WorldPopulationAgeing2019-Highlights.pdf.
2. World Bank. World databank: world development indicators (1960–2014). 2014. Available from: http://databank.worldbank.org/data.
3. Abusaaq H. Population aging in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency; 2015. Available from: http://www.sama.gov.sa/en-US/EconomicResearch/WorkingPapers/population%20aging%20in%20saudi%20arabia.pdf.
4. Sternberg SA, Wershof Schwartz A, Karunananthan S, Bergman H, Mark Clarfield A. The identification of frailty: a systematic literature review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(11):2129–2138. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03597.x.
5. World Health Organization. Ageing and health. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health#:~:text=Older%20age%20is%20also%20characterized,are%20commonly%20called%20geriatric%20syndromes.
6. Kostanjsek N. Use of the international classification of functioning, disability and health (ICF) as a conceptual framework and common language for disability statistics and health information systems. BMC Public Health. 2011;11:S3. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-11-S4-S3.
7. Storeng SH, Sund ER, Krokstad S. Factors associated with basic and instrumental activities of daily living in elderly participants of a population-based survey: the Nord-Trøndelag Health Study, Norway. BMJ Open. 2018;8(3):e018942. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018942.
8. Hu YN, Hu GC, Hsu CY, Hsieh SF, Li CC. Assessment of individual activities of daily living and its association with self-rated health in elderly people of Taiwan. Int J Gerontol. 2012;6:117–121. doi:doi:10.1016/j.ijge.2012.01.024.
9. Xu R, Zhou X, Cao S, et al. Health status of the elderly and its influence on their activities of daily living in Shangrao, Jiangxi Province. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(10):1771. doi:10.3390/ijerph16101771.
10. Ćwirlej-Sozańska A, Wiśniowska-Szurlej A, Wilmowska-Pietruszyńska A, Sozański B. Determinants of ADL and IADL disability in older adults in southeastern Poland. BMC Geriatr. 2019;19(297). doi:10.1186/s12877-019-1319-4.
11. Abolfotouh MA, Dafallah AA, Khan MY, Khattab MS, Abdulmoneim I. Psychosocial assessment of geriatric subjects in Abha City, Saudi Arabia. East Mediterr Health J. 2001;7(3):481–491.
12. Al-Mahadi MA, Elzubier AG. Assessment of the functional status of elderly subjects in Qassim Region, Saudi Arabia. J Roy Soc Health. 1997;117(5):313–318. doi:10.1177/146642409711700509.
13. Connolly D, Garvey J, McKee G. Factors associated with ADL/IADL disability in community dwelling older adults in the Irish longitudinal study on ageing (TILDA). Disabil Rehabil. 2017;39(8):809–816. doi:10.3109/09638288.2016.1161848.
14. Virtuoso Júnior JS, Martins CA, Roza LB, de Paulo TRS, Ribeiro MCL, Tribess S. Prevalence of disability and associated factors in the elderly. Text Context Nurs. 2015;24(2):521–529. doi:10.1590/0104-07072015001652014.
15. Lindbergh CA, Dishman RK, Miller LS. Functional disability in mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychol Rev. 2016;26(2):129–159. doi:10.1007/s11065-016-9321-5.
16. Choi H, Hayward RA, Langa KM. Fall associated difficulty with activities of daily living (ADL) in functionally independent older adults aged 65 to 69 in the United States: a cohort study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013;61(1). doi:doi:10.1111/jgs.12071.
17. Chu LW, Chiu AYY, Chi I. Impact of falls on the balance, gait, and activities of daily living functioning in community-dwelling Chinese older adults. J Gerontol a Biol Sci Med Sci. 2006;61(4):399–404. doi:10.1093/gerona/61.4.399.
18. Hong GRS, Park J, Kang HK, Palmer MH. Activities of daily living and cognitive status: associations with urinary incontinence in Korea. Int J Urol Nurs. 2014;8(3):130–136. doi:10.1111/ijun.12050.
19. Kempen GIJM, Ballemans J, Ranchor AV, van Rens GHMB, Zijlstra GA. The impact of low vision on activities of daily living, symptoms of depression, feelings of anxiety and social support in community-living older adults seeking vision rehabilitation services. Qual Life Res. 2012;21(8):1405–1411. doi:10.1007/s11136-011-0061-y.
20. Flores V, Coco R, Alamo T, Ortiz E, Coco B. The Impact of low vision in the activities of daily living and emotional state of elderly people. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(14):4413.
21. Pérès K, Matharan F, Daien V, et al. Visual loss and subsequent activity limitations in the elderly: the French three-city cohort. Am J Public Health. 2017;107(4):564–569. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2016.303631.
22. Wang R, Chen L, Fan L, et al. Incidence and effects of polypharmacy on clinical outcome among patients aged 80+: a five-year follow-up study. PLoS One. 2015;10(11):e0142123. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0142123.
23. Santos JLF, Lebrão ML, Duarte YAO, Lima FD. Functional performance of the elderly in instrumental activities of daily living: an analysis in the municipality of São Paulo, Brazil. Cad Saude Publica. 2008;24(4):879–886. doi:doi:10.1590/S0102-311X2008000400019.
24. Suzuki T, Yukawa H, Yoshida H, et al. Alcohol consumption and change of activity of daily living among the elderly living in an urban community. Jpn J Geriatr. 2000;37(1):41–48. doi:10.3143/geriatrics.37.41.
25. Lee YH, Lu P, Chang YC, Shelley M, Lee YT, Liu CT. Associations of alcohol consumption status with activities of daily living among older adults in China. J Ethn Subst Abuse. 2019;1–16. doi:10.1080/15332640.2019.1664961.
26. World Health Organization. WHO guidelines on integrated care for older people (ICOPE). Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/258981/9789241550109-eng.pdf;jsessionid=EBBC3F7CD4A7E7781C72823BA8F1CC8D?sequence=1.
27. Elsawy B, Higgins KE. The geriatric assessment. Am Fam Physician. 2011;83(1):48–56.
28. Rosen SL, Reuben DB. Geriatric assessment tools. Mt Sinai J Med. 2011;78(4):489–497. doi:10.1002/msj.20277.
29. Seematter-Bagnoud L, Büla C. Brief assessments and screening for geriatric conditions in older primary care patients: a pragmatic approach. Public Health Rev. 2018;39:8. doi:10.1186/s40985-018-0086-7.
30. Khoja AT, Aljawadi AH, Al-Shammari SA, et al. The health of Saudi older adults; results from the Saudi national survey for elderly health (SNSEH) 2006–2015. Saudi Pharm J. 2018;26(2):292–300. doi:10.1016/j.jsps.2017.11.008.
31. Elderly Survey. General authority for statistics. Available from: https://www.stats.gov.sa/sites/default/files/elderly_survey_2017en.pdf.
32. Sharma D, Parashar A, Mazta SR. Functional status and its predictor among elderly population in a hilly state of North India. Int J Health Allied Sci. 2014;3:159–163. doi:DOI:10.4103/2278-344X.138593.
33. Geriatric health questionnaire. University of Iowa Health Care. Available from: http://www.med.illinois.edu/depts_programs/clinicalaffairs/Document/health%20questionairre.pdf.
34. Vittengl JR, White CN, McGovern RJ, et al. Comparative validity of seven scoring systems for the instrumental activities of daily living scale in rural elders. Aging Ment Health. 2006;10(1):40–47. doi:10.1080/13607860500307944.
35. Borson S, Scanlan J, Brush M, Vitaliano P, Dokmak A. The mini-cog: a cognitive ‘vital signs’ measure for dementia screening in multi-lingual elderly. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2000;15(11):1021–1027. doi:10.1002/1099-1166(200011)15:11<021::aid-gps234>3.0.co;2-6.
36. Borson S, Scanlan JM, Watanabe J, Tu SP, Lessig M. Improving identification of cognitive impairment in primary care. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2006;21(4):349–355. doi:10.1002/gps.1470.
37. Scanlan J, Borson S. The mini-cog: receiver operating characteristics with expert and naïve raters. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2001;16(2):216–222. doi:10.1002/1099-1166(200102)16:2<216::aid-gps316>3.0.co;2-b.
38. Bang KS, Tak SH, Oh J, Yi J, Yu SY, Trung TQ. Health status and the demand for healthcare among the elderly in the rural Quoc-Oai District of Hanoi in Vietnam. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:4830968. doi:10.1155/2017/4830968.
39. Al-Shammari SA, Al Mazrou Y, Jarallah JS, Al Ansary L, El Shabrawy AM, Bamgboye EA. Appraisal of clinical, psychosocial, and environmental health of elderly in Saudi Arabia: a household survey. Int J Aging Hum Dev. 2000;50(1):43–60. doi:10.2190/17YQ-9R9E-YG86-HYN1.
40. Farías-Antúnez S, Lima NP, Bierhals IO, Gomes AP, Vieira LS, Tomasi E. Disability related to basic and instrumental activities of daily living: a population-based study with elderly in Pelotas, Rio Grande do Sul, 2014. Epidemiol Serv Saude. 2018;27(2):e2017290. doi:10.5123/S1679-49742018000200005.
41. Millán-Calenti JC, Tubío J, Pita-Fernández S, et al. Prevalence of functional disability in activities of daily living (ADL), instrumental activities of daily living (IADL) and associated factors, as predictors of morbidity and mortality. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2010;50(3):306–310. doi:10.1016/j.archger.2009.04.017.
42. Ran L, Jiang X, Li B, et al. Association among activities of daily living, instrumental activities of daily living and health-related quality of life in elderly Yi ethnic minority. BMC Geriatr. 2017;17(1):74. doi:10.1186/s12877-017-0455-y.
43. Vermeulen J, Neyens JCL, van Rossum E, Spreeuwenberg MD, de Witte LP. Predicting ADL disability in community-dwelling elderly people using physical frailty indicators: a systematic review. BMC Geriatr. 2011;11:33. doi:10.1186/1471-2318-11-33.
44. Andrews JS, Cenzer IS, Yelin E, Covinsky KE. Pain as a risk factor for disability or death. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013;61:583–589. doi:10.1111/jgs.12172.
45. Scudds RJ, Robertson JM. Pain factors associated with physical disability in a sample of community-dwelling senior citizens. J Gerontol a Biol Sci Med Sci. 2000;55:M393–9. doi:10.1093/gerona/55.7.m393.
46. Kessler M, Facchini LA, Soares MU, Nunes BP, Franca SM, Thume E. Prevalence of urinary incontinence among the elderly and relationship with physical and mental health indicators. Rev Bras Geriatr Gerontol. 2018;21(4):397–407. doi:10.1590/1981-22562018021.180015.
47. Pachana NA, McLaughlin D, Leung J, McKenzie SJ, Dobson A. The effect of having a partner on activities of daily living in men and women aged 82–87 years. Maturitas. 2011;68(3):286–290. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2010.11.009.
48. Ali T, Nilsson CJ, Weuve J, Rajan KB, de Leon CF. Effects of social network diversity on mortality, cognition and physical function in the elderly: a longitudinal analysis of the Chicago health and aging project (CHAP). J Epidemiol Community Health. 2018;72(11):990–996. doi:10.1136/jech-2017-210236.
49. Reblin M, Uchino BN. Social and emotional support and its implication for health. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2008;21(2):201–205. doi:10.1097/YCO.0b013e3282f3ad89.
50. Candela F, Zucchetti G, Ortega E, Rabaglietti E, Magistro D. Preventing loss of basic activities of daily living and instrumental activities of daily living in elderly: identification of individual risk factors in a holistic perspective. Holist Nurs Pract. 2015;29(5):313–322. doi:10.1097/HNP.0000000000000106.
51. Al Senany S, Al Saif A. Assessment of physical health status and quality of life among Saudi older adults. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015;27(6):1691–1695. doi:10.1589/jpts.27.1691.
52. Burton R, Sheron N. No level of alcohol consumption improves health. Lancet. 2018;392(10152):987–988. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31571-X
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
