Back to Journals » Risk Management and Healthcare Policy » Volume 14
Health-Related Quality of Life and Associated Factors Among Adult Patients with Heart Failure in Wolaita Zone Governmental Hospitals, Southern Ethiopia
Authors Molla S, Yitayal M , Amare G
Received 23 October 2020
Accepted for publication 9 January 2021
Published 22 January 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 263—271
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/RMHP.S288326
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Marco Carotenuto
Simegn Molla,1 Mezgebu Yitayal,2 Getasew Amare2
1Department of Health Systems, School of Public Health, College of Health Sciences, Mekelle University, Mekelle, Ethiopia; 2Department of Health Systems and Policy, Institute of Public Health, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Gondar, Gondar, Ethiopia
Correspondence: Getasew Amare Email [email protected]
Background: Knowing how heart failure affects patients’ quality of life and its associated factors are crucial for a better patient-centred approach and management. Therefore, this study aims to assess health-related quality of life and its associated factors among adult heart failure patients in southern Ethiopia hospitals.
Methods: The facility-based cross-sectional study design was conducted in Wolaita zone governmental hospitals from March to April 2018. The population was all adult heart failure patients in the chronic illness follow-up clinic and inpatient department. All adult heart failure patients on follow-up clinic and inpatient departments who have at least a 6-month follow-up were included in the study. In contrast, patients who had chronic comorbidities were excluded from the study. Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire (MLHFQ) tool was used to measure the outcome variable health-related quality of life (HRQoL). Interviews and client medical record reviews also collected socio-demographic, clinical and behavioural characteristics of participants. The data were analyzed using STATA version 14, and multiple linear regression analysis with P-value < 0.05 was used to measure the degree of association between HRQoL and independent variables.
Results: A total of 372 patients participated in the study. The HRQoL score for the physical, emotional, and total were 22.2, 7.7, and 46.37, respectively. HRQoL was significantly associated with gender, age, family size, occupation, residency, and recent admission within the past six months, New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class, department of treatment, salt intake, and health perception.
Conclusion: Generally, the HRQoL for patients with heart failure was found to be low. Besides the variables age and gender of participants, family size, occupation, residency, admission history, salt intake, and NYHA class were significant factors for the HRQoL of patients with heart failure.
Keywords: health-related quality of life, heart failure, Wolaita zone, Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire
Background
Heart failure (HF) is a chronic, progressive condition in which the heart muscle cannot pump enough blood to meet its blood and oxygen.1 HF is a global public health problem which affects approximately 26 million people worldwide.2 Heart failure syndrome remains a significant public health issue for many countries in Sub-Saharan Africa, including Ethiopia.3 Global Burden of Disease report showed that heart failure is the top five Couse mortality in Ethiopia.4
The impact of HF on patients can be assessed using different approaches, like morbidity and mortality, even if recently using Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) as a measurement tool also gets attention. HRQoL is an approach used to assess patients’ condition and well-being from their perspective by excluding those issues that have to directly linkage with health.5–11 Using HRQoL for HF patients helps detect the disease’s impact on their physical and emotional well-being, making it difficult to detect by using common clinical measurements. In recognition of this, HF management focuses on patient psychological support and HRQoL improvement.12–16
Heart failure affects all aspects of patients’ lives and leads to extreme physical, social, and functional debilitation and increases psychological distress17 and characterized by significantly reduced scores in all aspects of quality of life compared to a healthy reference group.18,19 Studies that used either a disease-specific instrument or a general HRQoL questionnaire have shown patients with heart failure reported lower scores in all domains of HRQoL.20–23 Different works of the literature showed that socio-demographic factors such as age, gender, educational status, and occupation significantly associate HRQoL among heart failure patients.24,25 Other studies also showed that clinical factors like NYHA functional class, left ventricular ejection fraction, and comorbidities are predictors of HRQoL.26,27
Despite different studies that have been done in Ethiopia regarding the prevalence and epidemiologic burden of heart failure, the effect of this public health problem on the quality of life parents is now well investigated. Since HF management’s primary objective is to improve the patients’ HRQoL,28 knowing the HRQoL of patients and the associated factors is very important for appropriate patient care, approach, and management. Therefore, this study was aimed to assess the HRQoL among patients with heart failure and its associated factors.
Methods
Study Design and Setting
An institution-based cross-sectional study was conducted from March to April 2018 at four governmental hospitals in Wolaita Zone, southern Ethiopia. In the Wolaita zone, there are four government hospitals to give around 1.5 million people. A total of 620 cardiac patients attended services at these hospitals as the outpatient department and inpatient department.
Study Population and Sampling Procedure
The population was all adult heart failure patients in the chronic illness follow up clinic and inpatient department. All adult heart failure patients on follow-up clinic and inpatient departments who have at least a 6-month follow-up were included in the study. In contrast, patients with chronic comorbidities (patients with diabetes mellitus and lung disease) were excluded from the study. The sample size was calculated using the mean estimation of the previous research done in Saudi Arabia29 using the mean estimation formula, and the final sample size was 388. A multistage sampling technique was used to select the study participants. A simple random sampling method was used to determine study units from the outpatient department, and consecutive sampling was used for patients from the inpatient ward.
Data Collection Tools and Procedures
The Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire (MLHFQ) is one of the most widely used health-related quality of life questionnaires for patients with heart failure (HF) and validated in many countries worldwide.14,30,31 The MLHFQ is a disease-specific HRQoL assessment tool that provides scores for two dimensions, physical and emotional, and a total score. The questionnaire was first adopted in the English language and translated to the local language, then back-translated into English to keep its consistency. The socio-demographic factors (age, sex, marital status, education level, occupation, residence, ethnicity, religion, and wealth index) and clinical factors (NYHA functional class, left ventricular ejection fraction, duration of illness, recent admission) were included in the questionnaire. Besides, lifestyle (smoking, alcohol consumption, salt intake) and general health perception were also included in the questionnaire.
Data on socio-demographics, lifestyle, and HRQoL were collected by trained interviewers, while some clinical data (comorbidities, complications, NYHA classes) were taken from patients’ medical records.
Operational Definitions
Health-Related Quality of Life
Which is the outcome variable, was measured using the MLHFQ instrument, which was developed specifically for measuring HRQoL among people with heart failure and has been validated in multi-cultural settings.32 It was a 21-items disease-specific measure of HRQoL, which has a total scale score of 105. MLHFQ reelects HF’s impact on HRQoL, from 0 (none) to 5 (very much). It provides a total score (range 0–105, from best to worst HRQoL), as well as scores for two dimensions, physical (8 items, range 0–40) and emotional (5 items, range 0–25). The other eight items (of the total of 21) are only considered to calculate the total score. Heart failure patients who score less than 24 are labelled as having (Good) HRQoL, 24–45 (Moderate), and greater than 45 as (Poor) HRQOL.33
Heart Failure
Patients are included in this study after being diagnosed and confirmed to have heart failure by physicians in the hospital.
All selected hospitals use the same criteria to diagnose heart failure patients, which is called Framingham criteria. It is the most commonly used heart failure diagnosis criterion presenting heart failure with two major or one major and two minor criteria.34
Ejection Fraction (EF)
Is a measurement determining how well the heart pumps out blood and in diagnosing and tracking heart failure. A measurement using Echocardiogram (Echo) under 40% may be evidence of heart failure.35
Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol consumption was measured using Alcohol, Smoking, and Substance Involvement Screening Test (ASSIST).36
ASSIST Total Score Risk Level
0–10 … … … … … … … … … … … Low-risk level
11–26 … … … … … … … … … …. Moderate risk level
27+ … … … … … … … … … … …. High-risk level
Smoking
It was measured using the World Health Organization Guidelines to control and monitor the tobacco epidemic.37 At the time of the survey, a smoker was smoking any tobacco product either daily or occasionally. A non-smoker was a person who, at the time of the study, was not smoking at all.
Salt Intake
A person who was using salt-containing food, even one meal, with in the last seven days, was considered as a user of salt.
Data Processing and Analysis
The collected data were checked for completeness. Then, codes were given to each question and entered into SPSS version 20 and exported to Stata version 14 for further analysis. A reliability test (Cronbach alpha) was performed to check the reliability of the items. The reliability (Cronbach alpha) for ASSIST was 0.89. The study also indicated that the total reliability was 0.92, for the physical dimension was 0.9, and for emotional dimension was 0.95. Summary statistics were done for the outcome and independent variables. Where an item was missing, the mean of other items in the domain was substituted. But when more than two items were missing from the domain. Model assumptions (normality, independence, equal variance, Multicollinearity, and linearity) were checked. Multiple linear regression was done, and variables with a P-value < of 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Demographic and Socioeconomic Characteristics of Study Participants
A total of 372 patients with heart failure participated in the study with a response rate of 95.9%. The mean age of study participants was 41.9 years. Among the study participants, 73%% were females, 56.7% protestant, 67.5% married, 45.2% housewives, 85% Wolaita, and 59.6% rural dwellers. The median family size was 6 (IQR=3) (Table 1).
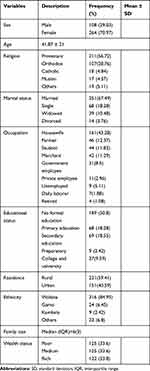 |
Table 1 Socio-Demographic and Economic Characteristics of Patients with Heart Failure in Governmental Hospitals, Southern Ethiopia, 2018 (n=372) |
Clinical/Medical Characteristics of Respondents
The majority (82.9%) of the participants were NHYA class 2 and above, and 76.34% had no history of recent admission within the past six months. The median (IQR) duration of illness month was [12 (IQR=23)], and the left ventricular ejection fraction was 55 (IQR=18). Almost 9 out of 10 (90.32%) patients were getting treatment in the outpatient department at the time of this study (Table 2).
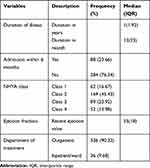 |
Table 2 Clinical/Medical Characteristics of Study Participants in Wolaita Zone Governmental Hospitals, Southern Ethiopia, 2018 (n=372) |
Lifestyle/Behavioural Characteristics and Health Perception of Respondents
In this study, 6.7% of study participants were smokers, and 76.2% reported salt intake, 16% had a history of drinking alcohol within the past three months, and 62% were at a low-risk level. The study also revealed that 68.28% of respondents perceived their health as poor (Table 3).
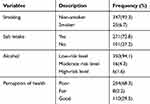 |
Table 3 Behavioral/Lifestyle/Characteristics of Study Participants at Selected Governmental Hospitals, Southern Ethiopia, 2018 (n=372) |
Health-Related Quality of Life of Patients with Heart Failure
MLHFQ assessed Health-related Quality of life showed that the mean physical, emotional, and overall HRQoL was 22.2, 7.7, and 46.37. About 50% of the participants were assessed as having a poor quality of life-related to heart failure (Table 4).
 |
Table 4 Health-Related Quality of Life of Study Participants at Selected Governmental Hospitals, Southern Ethiopia, 2018 (n=372) |
Factors Associated with Health-Related Quality of Life
The study revealed that sex, age, family size, occupation, residency, recent admission, NYHA, department of treatment, salt intake, and health perception were statistically significant variables associated with the total score of HRQoL. The final model explained 68% of the total MLHFQ scale variation.
In this study, gender and salt intake were found to be statistically associated with the emotional dimension of HRQoL. Females and respondents who reported salt intake had a higher score of emotional dimensions HRQoL.
Regarding the physical dimension, variables such as age, family size, occupation, residency, recent admission, and health perception were significantly associated with a p-value < 05. NYHA functional class and treatment department were significantly associated with physical and emotional dimensions and aggregate scores.
Females had increase total HRQoL score by 4.3 (95% CI = 0.96, 7.7) and increased emotional HRQoL score by 2.45 (95% CI=1.33, 3.57) compared to men. As age increase by one year, the total HRQoL score increased by 0.1 (95% CI = 0.01, 0.14) and increased physical dimension HRQoL by 0.04 scores (95% CI=0.01, 0.08). As family size increase by one-person total HRQoL score decreased by 0.7 (95% CI=−1.21, −0.19) and decreased physical dimension HRQoL by 0.37 score (95% CI=−0.64, −0.1).
Respondents who were recently admitted had increased total HRQoL score by 5.4 (95% CI = 2.25, 8.55) and increased physical dimensions HRQoL by 2.58 (95% CI=0.97, 4.19) compared to respondents who had no history of admission. Participants who were class-II, class-III, and class-IV (NYHA functional classification) had a higher physical domain, emotion domain, and total HRQoL score than Class-I. Respondents who were receiving treatment in the inpatient department during data collection had increased total HRQoL score by 15.9 (95% CI =10.95, 22.27) and increased score in both dimensions participants in the outpatient department.
Participants who used food containing salt had increased total HRQoL scores by 4.5 (95% CI=1.5, 7.4). Respondents who perceive their health is poor and fair had increased scores of total HRQoL by 5.2 (95% CI=1.22, 9.1) and 10.71 (95% CI=1.05, 20.38) compared to participants who perceive their health is as excellent, respectively (Table 5).
 |
Table 5 Factors Associated with Health-Related Quality of Life Among Patients with Health Failure in Governmental Hospitals, Southern Ethiopia, 2018 (n=372) |
Discussion
This study aimed to assess the HRQoL and associated factors among HF patients in the Wolaita zone, Sothern Ethiopia. The findings from this study show that HF had an impact on HRQoL patients. Socio-demographic factors such as gender, age, family size, occupation, and residency; Clinical/Medical/factors such as recent admission within the past six months, NYHA functional class, department of treatment; and Behavioral/Lifestyle/factors such as salt intake and health perception had a significant association with aggregate HRQoL. Improving the life year gain is not the only aim of HF management, but also improving the quality and minimizing patients’ disability.38,39
The mean score of the total HRQoL score was 46.37, which pointed out the disease’s influence on the HRQoL. In this study, HRQoL results are lower than studies done from Brazil with a mean HRQoL score of 34.940 and North Carolina with a mean HRQoL score of 32.341 using the same measurement tool showed better HRQoL. This could be due to a better quality of health care services in these countries.
This study showed that females were found to experience emotional symptoms and reduced total HRQoL compared to males. This is similar to a comparative study done in Spain42 and the USA43 in which females felt more socially limited and reported lower HRQoL. This could be due to females are expected to take care of their families despite their illness and are economically dependent on their spouse or family member.44
Patients from rural areas had lower overall HRQoL and physical dimension activities than urban dwellers, consistent with a study conducted in California 2014.45 Lower HRQoL in rural patients is possibly attributed to greater distance and limited access to health care services, which results in rescheduling and skipping of appointment visits, which may lead to worsening, readmission, and poor HRQoL.46
Patients in this study, who had a history of recent admission, had reduced physical HRQoL and overall HRQoL compared to patients who did not have recent admission. This is similar to the finding from Spain.42 A possible explanation might be hospitalization, and re-hospitalization reflects disease burden, disease progression, and poor HRQoL.47
This study showed a significant association between the NYHA functional class with all dimensions of HRQoL and the total HRQoL. Higher functional class indicated reduced HRQoL, which agrees with most studies.40,48–50 This is because distress and severity affect patients’ everyday lives with heart failure and lead to a diminished HRQoL.17
In this study, patients from the inpatient department had lower HRQoL in all dimensions. Compared to patients in the outpatient department, the aggregate is similar to finding a Norway study, which shows reduced HRQoL among hospitalized patients.50 This might be due to patients admitted to the inpatient department; the severity and exacerbation of their illness would be high, highly associated with HRQoL.
Patients who used to eat salt-containing food had reduced HRQoL compared to those who did not. The possible explanation may be salt/sodium results in fluid retention, which will lead to shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling, and acute exacerbation of heart failure.51
Limitation of the Study
Minnesota Living with Heart Failure is HF-specific instruments that measure the specific problems of disease and sensitive enough to detect small but essential changes in the effect of illness on QoL. However, this instrument is not generic and does not allow for comparisons across diverse conditions or diseases and interventions. This study was not supported by laboratory diagnostic tests like Red blood cell count or Hematocrit to indicate the association between anaemia and HRQoL.
Conclusion
Heart Failure has an impact on the patients’ HRQoL. Around half of the heart failure patients in this study assessed as having poor HRQoL. Being female, living in rural, higher in age and lower family size, history and current admission, salt intake, and higher NYHA classes were associated with worsen HRQoL. Giving psychological support for females besides the medical intervention and more individualized education and treatment adjustments helps them manage their daily lives for patients with severe functional class and elders.
Abbreviations
HRQoL, health-related quality of life; HF, heart failure; MLHFQ, Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire; NYHA, New York Heart Association; WHO, World Health Organization.
Data Sharing Statement
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are available upon request to the corresponding author. Due to data protection restrictions and participant confidentiality, we do not make participants’ data publicly available.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical clearance was obtained from the Ethical Review Committee of Institute of Public Health, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Gondar (Ref.no/IPH/266/2017). Written informed consent was taken from each participant. Moreover, verbal informed consent was obtained from those participants who could not read and write, approved by the ethical committee. Each eligible participant was informed about the purpose of the study. Participants were also assured that their name was not written on the data’s questionnaire and confidentiality kept at all levels.
Acknowledgments
We are very thankful to the University of Gondar to approve the ethical issue and its technical and financial support. We forward our appreciation to the hospital managers for allowing us to conduct this research and their cooperation. Finally, we would like to thank study participants for their volunteer participation and also data collectors and supervisors for their genuineness and quality of work during data collection.
Author Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current Journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Funding
There is no funding to report.
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest for this work.
References
1. McMurray JJV, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, et al. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012;14(8):803–869. doi:10.1093/eurjhf/hfs105
2. Ambrosy AP, Fonarow GC, Butler J, et al. The Global Health and Economic Burden of Hospitalizations for Heart Failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(12):1123–1133. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.053
3. Bloomfield GS, Barasa FA, Doll JA, Velazquez EJ. Heart failure in sub-Saharan Africa. Curr Cardiology Rev. 2013;9(2):157–173. doi:10.2174/1573403X11309020008
4. IHME. GBD Compare Ethiopia; 2018.
5. Farquhar M. Definitions of quality of life: a taxonomy. J Adv Nurs. 1995;22(3):502–508. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2648.1995.22030502.x
6. Karimi M, Brazier J. Health, health-related quality of life, and quality of life: what is the difference? Pharmacoeconomics. 2016;34(7):645–649. doi:10.1007/s40273-016-0389-9
7. McDowell I, Newell C. Measuring health: A guide to rating scales and questionnaires. Psyccritiques. 1997;42:11.
8. Wilson IB. Linking clinical variables with health-related quality of life: a conceptual model of patient outcomes. JAMA. 1995;273(1):59–65. doi:10.1001/jama.1995.03520250075037
9. Verster JC, Pandi-Perumal SR, Streiner DL. Sleep Quality Life Clin Med. Springer; 2008.
10. Spertus J. Barriers to the use of patient-reported outcomes in clinical care. Circulation. 2014;7(1):2–4. doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.113.000829
11. Hamming J, De Vries J. Measuring quality of life. Br J Surg. 2007;94(8):923–924. doi:10.1002/bjs.5948
12. Anker SD, Agewall S, Borggrefe M, et al. The importance of patient-reported outcomes: a call for their comprehensive integration in cardiovascular clinical trials. Eur Heart J. 2014;35(30):2001–2009. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehu205
13. Moon JR, Jung YY, Jeon E-S, Choi J-O, Hwang JM, Lee S-C. Reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire. Heart Lung. 2012;41(1):57–66. doi:10.1016/j.hrtlng.2011.09.011
14. Rector TS, Cohn JN. Assessment of patient outcome with the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure questionnaire: reliability and validity during a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of pimobendan. Am Heart J. 1992;124(4):1017–1025. doi:10.1016/0002-8703(92)90986-6
15. Alla F, Briançon S, Guillemin F, et al. Self-rating of quality of life provides additional prognostic information in heart failure. Insights into the EPICAL study. Eur J Heart Failure. 2002;4(3):337–343. doi:10.1016/S1388-9842(02)00006-5
16. McMurray JJV, Adamopoulos S, Anker S, et al. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012;14(8):803–869.
17. Blinderman CD, Homel P, Billings JA, Portenoy RK, Tennstedt SL. Symptom distress and quality of life in patients with advanced congestive heart failure. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2008;35(6):594–603. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2007.06.007
18. Wu J-R, Lennie TA, Frazier SK, Moser DK. Health-Related Quality of Life, Functional Status, and Cardiac Event-Free Survival in Patients With Heart Failure. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2016;31(3):236. doi:10.1097/JCN.0000000000000248
19. Brostrom A, Stromberg A, Dahlstrom U, Fridlund B. Sleep difficulties, daytime sleepiness, and health-related quality of life in patients with chronic heart failure. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2004;19(4):234–242. doi:10.1097/00005082-200407000-00003
20. Calvert MJ, Freemantle N, Cleland JGF. The impact of chronic heart failure on health-related quality of life data acquired in the baseline phase of the CARE-HF study. Eur J Heart Fail. 2005;7(2):243–251. doi:10.1016/j.ejheart.2005.01.012
21. Heo S, Doering LV, Widener J, Moser DK. Predictors and effect of physical symptom status on health-related quality of life in patients with heart failure. Am J Critical Care. 2008;17(2):124–132. doi:10.4037/ajcc2008.17.2.124
22. Pressler SJ, Subramanian U, Kareken D, et al. Cognitive deficits and health-related quality of life in chronic heart failure. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2010;25(3):189–198. doi:10.1097/JCN.0b013e3181ca36fe
23. McCarthy M, Katz SD, Schipper J, Dickson VV. “I just can’t do it anymore” patterns of physical activity and cardiac rehabilitation in african americans with heart failure: a mixed method study. Healthcare. 2015;3(4):973–986. doi:10.3390/healthcare3040973
24. Hou N, Chui MA, Eckert GJ, Oldridge NB, Murray MD, Bennett SJ. Relationship of age and sex to health-related quality of life in patients with heart failure. Am J Critical Care. 2004;13(2):153–161. doi:10.4037/ajcc2004.13.2.153
25. Sawafta F, Chen X. Quality of life of Chinese heart failure patients and their family caregivers. Int J Appl Sci Tech. 2013;3:2.
26. De Leon CFM, Grady KL, Eaton C, et al. Quality of Life in a Diverse Population of Patients With Heart Failure. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2009;29(3):171. doi:10.1097/HCR.0b013e31819a0266
27. Mbakwem A, Aina F, Amadi C, Akinbode A, Mokwunyei J. Comparative analysis of the quality of life of heart failure patients in South Western Nigeria. World J Cardiovas Dis. 2013;03(01):146–153. doi:10.4236/wjcd.2013.31A021
28. Yancy C, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128(16):e240.
29. AbuRuz ME, Alaloul F, Saifan A, Masa’Deh R, Abusalem S. Quality of life for Saudi patients with heart failure: a cross-sectional correlational study. Glob J Health Sci. 2016;8(3):49.
30. ABd L, Leite ALC, Salerno GRF, Fernandes M, Blascovi-Assis S. Instruments to assess quality of life in patients with heart failure. Fisioterapia Em Movimento. 2015;28(4):851–858.
31. Garin O, Herdman M, Vilagut G, et al. Assessing health-related quality of life in patients with heart failure: a systematic, standardized comparison of available measures. Heart Fail Rev. 2014;19(3):359–367. doi:10.1007/s10741-013-9394-7
32. Marques de Sousa M. Quality of life of patients with heart failure: integrative review. J Nurs UFPE. 2017;11:3.
33. Behlouli H, Feldman DE, Ducharme A, et al. Identifying relative cut-off scores with neural networks for interpretation of the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure questionnaire.
34. King M, Kingery JE, Casey B. Diagnosis and evaluation of heart failure. Am Fam Physician. 2012;85(12):1161–1168.
35. Paulus WJ, Tschöpe C, Sanderson JE, et al. How to diagnose diastolic heart failure: a consensus statement on the diagnosis of heart failure with normal left ventricular ejection fraction by the Heart Failure and Echocardiography Associations of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2007;28(20):2539–2550. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehm037
36. Group WHOASSISTW. The alcohol, smoking and substance involvement screening test (ASSIST): development, reliability and feasibility. Addiction. 2002;97(9):1183–1194. doi:10.1046/j.1360-0443.2002.00185.x
37. Organization WH. Guidelines for Controlling and Monitoring the Tobacco Epidemic. World Health Organization; 1998.
38. Audi G, Korologou A, Koutelekos I, et al. Factors affecting health related quality of life in hospitalized patients with heart failure. Cardiol Res Pract. 2017;2017:2017. doi:10.1155/2017/4690458
39. Polikandrioti M, Ntokou M. Needs of hospitalized patients. Health Sci j. 2011;5(1):15.
40. Pelegrino VM, Dantas RAS, Clark AM. Health-related quality of life determinants in outpatients with heart failure. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2011;19(3):451–457. doi:10.1590/S0104-11692011000300002
41. Wu J-R, Lennie TA, Frazier SK, Moser DK. Health-Related Quality of Life, Functional Status, and Cardiac Event-Free Survival in Patients With Heart Failure. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2016;31(3):236–244.
42. Comin-Colet J, Anguita M, Formiga F, et al. Health-related Quality of Life of Patients With Chronic Systolic Heart Failure in Spain: results of the VIDA-IC Study. Rev Española De Cardiología. 2016;69(3):256–271. doi:10.1016/j.rec.2015.07.030
43. Hou N, Chui MA, Eckert GJ, Oldridge NB, Murray MD, Bennett SJ. Relationship of age and sex to health-related quality of life in patients with heart failure. Am J Critical Care. 2004;13(2):153–161.
44. Lailulo YA, Susuman AS, Blignaut R. Correlates of gender characteristics, health and empowerment of women in Ethiopia. BMC Women Health. 2015;15(1):116. doi:10.1186/s12905-015-0273-3
45. Nesbitt T, Doctorvaladan S, Southard JA, et al. Correlates of quality of life in rural patients with heart failure.. Circulation. 2014;7(6):882–887. doi:10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.113.000577
46. Kurpas D, Mroczek B, Bielska D. Rural and urban disparities in quality of life and health-related behaviors among chronically ill patients.. Rural Remote Health. 2014;14(2):2485.
47. Nieminen MS, Dickstein K, Fonseca C, et al. The patient perspective: quality of life in advanced heart failure with frequent hospitalisations. Int J Cardiol. 2015;191:256–264. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.04.235
48. Azevedo A, Bettencourt P, Alvelos M, et al. Health-related quality of life and stages of heart failure. Int J Cardiol. 2008;129(2):238–244. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2007.07.091
49. Huang T-Y, Moser DK, Hwang S-L, Lennie TA, Chung M, Heo S. Comparison of health-related quality of life between American and Taiwanese heart failure patients. J Trans Nurs. 2010;21(3):212–219. doi:10.1177/1043659609358779
50. Rustoen T, Stubhaug A, Eidsmo I, Westheim A, Paul SM, Miaskowski C. Pain and quality of life in hospitalized patients with heart failure. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2008;36(5):497–504. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2007.11.014
51. Alejandro D, Cleto C, Mariano E, Alberto B, Sabrina M, Alejandro F. Precipitating factors leading to decompensation of chronic heart failure in the elderly patient in South-American community hospital. J Geriatric Cardiol. 2011;8(1):12–14. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1263.2011.00012
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
