Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 9
Translational challenges of animal models in Chagas disease drug development: a review
Authors Chatelain E, Konar N
Received 9 June 2015
Accepted for publication 10 July 2015
Published 19 August 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 4807—4823
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S90208
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Shu-Feng Zhou
Eric Chatelain,1 Nandini Konar2
1Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative (DNDi), Geneva, Switzerland; 2Merck & Co, Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA
Abstract: Chagas disease, or American trypanosomiasis, caused by Trypanosoma cruzi parasite infection is endemic in Latin America and presents an increasing clinical challenge due to migrating populations. Despite being first identified over a century ago, only two drugs are available for its treatment, and recent outcomes from the first clinical trials in 40 years were lackluster. There is a critical need to develop new drugs to treat Chagas disease. This requires a better understanding of the progression of parasite infection, and standardization of animal models designed for Chagas disease drug discovery. Such measures would improve comparison of generated data and the predictability of test hypotheses and models designed for translation to human disease. Existing animal models address both disease pathology and treatment efficacy. Available models have limited predictive value for the preclinical evaluation of novel therapies and need to more confidently predict the efficacy of new drug candidates in clinical trials. This review highlights the overall lack of standardized methodology and assessment tools, which has hampered the development of efficacious compounds to treat Chagas disease. We provide an overview of animal models for Chagas disease, and propose steps that could be undertaken to reduce variability and improve predictability of drug candidate efficacy. New technological developments and tools may contribute to a much needed boost in the drug discovery process.
Keywords: Trypanosoma cruzi, drug discovery, in vivo models, translation, efficacy prediction
Introduction – historical background and rationale
Chagas disease (or American trypanosomiasis) is a major public health problem that is endemic in 21 Latin American countries, with over 25 million people at risk of contracting the disease. Approximately 7 million people are infected worldwide,1 and figures from 2009 estimated 41,200 new cases per year in Latin America.2 This neglected tropical infectious disease is spreading to areas outside Latin America due to migrating human populations and is likely to present an increasing clinical challenge.1
The disease is caused by the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, transmitted by the triatomine insect vector. Humans can also be infected through ingestion of contaminated food and drink, from mother to child during pregnancy, and through contaminated blood transfusion or organ transplantation. Chagas disease is divided into two distinct clinical phases, namely the acute and chronic phases (Figure 1). Acute T. cruzi infection begins when the parasite actively proliferates in the infected individual. It is generally undiagnosed, because of the non-specific nature of symptoms and because most cases occur in regions with limited access to medical care. In the vast majority of cases, the manifestations resolve spontaneously within 2 months.3 During the acute phase, all nucleated cell types in the host are potential targets for infection. Following activation of the immune response, parasitemia reduces to subpatent levels (below the microscopic threshold), signaling the end of the acute phase. However, the parasite is not completely eliminated, and infection of specific tissues persists indefinitely.3 The acute phase is followed by a chronic disease phase, which can be indeterminate (asymptomatic) and may last decades. Approximately 30% of infected individuals eventually develop chronic symptomatic disease with clinical manifestations,3 the most common and serious being cardiomyopathy and gastrointestinal (GI) involvement. The presentation of chronic symptomatic disease varies widely according to disease duration and the extent and location of cardiac lesions. Digestive forms of the disease result from chronic inflammation and destruction of parasympathetic neurons, leading to progressive enlargement of the esophagus or colon. Chagas disease can also be reactivated if patients in the chronic phase are immunocompromised or in the case of co-infection with HIV. Progressive heart failure and sudden death are the most common causes of death in Chagas patients.3
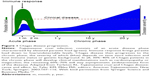  | Figure 1 Chagas disease progression. |
More than 100 years since the discovery of Chagas disease,4 and despite dramatic advances in modern drug discovery tools,5 only two drugs are available for Chagas disease treatment: benznidazole (BZN) and nifurtimox. These both require prolonged treatments, display potentially severe toxicity,6 and have controversial efficacy in T. cruzi-infected adults with chronic indeterminate status.7,8 There is therefore a critical need for new, efficacious, and safer drugs for Chagas disease treatment.
Recent outcomes from the first clinical trials in Chagas disease in 40 years evaluating novel drugs from the azole class such as posaconazole9 and the E1224 ravuconazole prodrug10 have proved disappointing. Indeed, posaconazole has for example been shown to be non-inferior to BZN when tested in murine models of choice at the time (acute model using different T. cruzi strains; Table 1 for more details). However, in clinical trials, although both compounds had anti-trypanosomal activity in chronic Chagas patients, significantly more patients had treatment failure with posaconazole (80%–90%) compared with BZN (6%) as assessed by blood polymerase chain reaction (PCR) during follow-up 12 months after end of treatment.9 These results have highlighted issues associated with Chagas disease drug discovery and the need for better tools to improve translation to humans. Specifically, animal models need to more confidently predict the efficacy of new drug candidates in clinical trials. This review highlights knowledge gaps in that area, fuels debate in the Chagas disease research community, and provides an overview of existing animal models for Chagas disease.
The Chagas disease translational challenge
Issues associated with Chagas disease drug development are manifold, from low investment to poor coordination and lack of methodological standardization between research groups. There is no consensus regarding appropriate in vitro and in vivo screening protocols, as well as a lack of biomarkers for assessing cure and treatment efficacy,11 or for predicting patients at risk of progression to chronic disease.12 In 2009, Romanha et al recommended protocols for in vitro and in vivo drug screening following an expert-led workshop, with the objective of improving harmonization in the field.13 This workshop concluded that the sequential use of murine acute models of Chagas disease was sufficient to identify trypanocidal compounds; chronic models of the disease were considered as more relevant for academic knowledge of the pathology of the disease. However, these may need adapting in light of recent clinical trial data and the US Food and Drug Administration Critical Path Initiative.9,10,14 Indeed, posaconazole has since been associated with a greater rate of treatment failure compared with BZN. This has led to a “rethink” of the screening sequence during the drug discovery process and the properties of a compound needed to move forward as well as looking at new technologies and methods for in vivo testing. For initial compound screening and prioritization, a streamlined protocol adapted from that of Romanha et al has since been proposed.5
The drug discovery process has been slowed by the complexity and heterogeneity of the T. cruzi parasite and, by extension, of the disease models used.15 Drug development in Chagas disease is hampered by a minefield of unanswered questions (Table 2). The process by which new drug candidates are selected, tested, and developed relies on the use of animal models. In the case of Chagas disease, available models have limited predictive value for the preclinical evaluation of novel therapies. There is to date no standardized Chagas disease in vivo model for drug discovery; existing models tend to be research oriented, and designed with the purpose of understanding disease pathology, rather than being validated to assess compound trypanocidal activity or treatment efficacy.
  | Table 2 Selected unanswered questions in Chagas disease |
Even in experimental conditions, Chagas disease models involve several often uncontrolled parameters, including the relationship between exposure and cure, route of administration, timing and duration of treatment, mouse lineage, host–parasite interactions, and type of immune response, in addition to other challenges such as definitions of cure criteria and disease stage (Table 3). These factors may each affect treatment outcome, and one should therefore be cautious in attributing therapeutic failure to lack of T. cruzi susceptibility to the drug tested. In vivo models described in the published literature reflect the variability in experimental conditions employed by each laboratory. For instance, assessment of posaconazole and BZN efficacy from different laboratories illustrates challenges linked to the validation/adequacy of animal models and the interpretation of data generated, since cure rates vary widely depending on the animal host and on the T. cruzi strain used (Table 1). Moreover, a lack of correlation between animal models and clinical trial data has been observed.16
  | Table 3 Some factors related to variability in experimental conditions in in vivo models |
In experimental models, the start of the chronic phase depends on the host/parasite combination. It is important to take into consideration not only the time course but also the physiological characteristics of the infection. Because the transition from acute to chronic disease can differ between species and strains, it is difficult to define a unifying standardized model. In the acute phase, the parasites are still replicating and infection is ongoing. Although replication is also ongoing in the chronic phase, some researchers believe that the parasite is in a different “stage” during chronic disease (ie, dormant amastigote), and believe that results from acute models should not be extrapolated to the chronic phase until more is known about the disease and drug mechanisms (including drug penetration into tissues).
Parasite persistence is a driving force in Chagas disease etiology.17 The presence of parasites in tissues has been demonstrated in bioluminescent mouse models,18 and this technology has illustrated the dynamic nature of infection.19,20 In the context of drug development, tissue tropism is a critical element, as it has implications on the drug metabolism and pharmacokinetic (DMPK) profile of the drugs being designed. The idea of specific tissue tropism is explained by the fact that T. cruzi enters most tissues but is cleared by the immune system (parasites are often observed in macrophages).21
Thus, a test drug would need to access all areas that the parasite can, which is a tall order in drug discovery terms. This requirement is established and is one of the properties of posaconazole, which has a very large volume of distribution.22 It will also be important to understand which tissues have detectable parasite levels in the animal model, and to ascertain whether the tested drug penetrates those same tissues. Drug disposition that does not include adequate penetration into the tissues of parasite depots could lead to a lack of efficacy. In summary, there is an urgent need to better understand the progression of parasite infection and to standardize animal models of choice in order to improve comparison of data generated and their predictability in translating to humans.
Overview of in vivo models
Available animal models used in Chagas disease research have shed light on many disease aspects, especially pathogenesis. In vivo models have also been used for drug screening,23,24 where the main objective has been to assess the trypanocidal effects of new compounds.
Considerable variability in parasite and animal strains has complicated comparisons between animal model studies (Table 3). Depending on the strains used, or on the parasite’s lifecycle stage, entirely different outcomes can be observed, in terms of drug susceptibility,25 death, parasitemia, tissue involvement, or the development of cardiomyopathy.26 Other issues affecting outcomes from animal models include the size of the inoculum, and the animal’s weight, sex, and age.27–29 It has also been demonstrated that temperature of the environment can affect disease pathology.30
Not many studies have systematically evaluated the influence of the parasite inoculation route on infection progression. This could be an important parameter, considering the outbreaks of oral infection described in the Amazon region.31 Oral inoculation has been compared with the intraperitoneal (ip) route. Mice inoculated orally with blood trypomastigotes showed lower levels of infection than via the ip route, whereas those inoculated orally with culture metacyclic trypomastigotes showed similar levels of infection to the ip route.32 In mouse models, the ip route is the most commonly used because it is easy and generally successful, although every route is capable of effectively producing severe infection.
Given the plasticity of the parasite and the different disease transmission routes in humans (blood transfusion, organ transplant, and oral ingestion), the inoculum size and parasite load might be more significant than the route of entry; even a few parasites are capable of producing an infection. Variability has been observed with the ip route, and the subcutaneous route has been shown to generate more consistent results with regard to parasitemia,23 although this is disputed. Studies using the CL Brener and bioluminescent T. cruzi strains did not show major differences between infection routes.19,20 The subcutaneous route may be considered more clinically relevant and representative of the natural infection via insect vectors. Ideally, experimental models should favor infection models that resemble human chronic infection, with appropriate tissue tropism. In the natural infection model, there is a likelihood of co-infection with multiple strains, as well as recurrent infections, which while more representative of a true infection could further complicate the results of readout methods.33 Natural infection in wild animals introduces too many additional variables that complicate result significance and interpretation. In addition, the handling of naturally infected monkeys also poses risks to animal handlers and laboratory staff via accidental exposure.34
Despite the variety of available models intended to simulate human disease, no model has so far emerged as optimally suited for predicting the outcomes of drug treatment. Although there are no systematic or standardized procedures, mice are the most commonly used animals (particularly in lead optimization), mainly for practical reasons. Compared with larger animals, mice are cheaper, can be used in greater numbers, and are easier to handle and keep. The use of larger animals is associated with ethical and cost considerations (Table 4).
  | Table 4 Some perceived advantages and disadvantages of Chagas disease in vivo models for translation |
Models mimicking the different disease stages
Acute infection models
Acute infection models allow to easily evaluate the two principal outcomes of parasitemia and mortality,35,36 and are designed so that combinations of mouse and parasite strains result in elevated parasitemia associated with death of the animals within a month of infection.13,37 Such models have been used to test drug candidates.23 However, acute T. cruzi infection is not usually fatal in humans, so these models cannot be considered faithful reproductions of the human disease course.
In order to follow the animal research guiding principle (in particular reduction of animal use) and international recommendations on animal well-being,38,39 mortality should be avoided as an endpoint, and replaced with established humanitarian endpoints such as decrease in body temperature, weight loss,40 maximum parasitemia,41 and/or non-invasive measurements of disease-influenced parameters (eg, physical characteristics or food consumption)42 to prevent unnecessary animal pain and suffering.
One perceived advantage of acute models is that they can provide results relatively quickly. Treatments are usually initiated soon after infection (Day 1 post-infection, corresponding to a more prophylactic model). The approach likely favors the efficacy of tested compounds, as parasites will not have taken hold of the host. Again, this is a poor reflection of real-life human conditions. In addition, it has been suggested that if the parasites and tested drugs are administered via the same route, the drug will affect parasites faster than in a clinical setting. In order to address these issues, alternative models of “established T. cruzi infection” are also used, in which the test compound is administered approximately 1 week after infection.23
Currently used acute models are suited to show lack of efficacy (eg, failure to control parasitemia or to eradicate parasites from tissues); most drugs, including BZN, fail to fully eliminate parasites in acute models that include immunosuppressive stages (eg, cyclophosphamide).43,44 Therefore, acute models are geared toward rapid screening of drugs to eliminate those that are not effective. Acute models are used in the majority of cases, because chronic models are thought to be inadequate in the drug discovery context of lead optimization.
Chronic infection models
Models of chronic infection are either established by infecting animals with small parasite numbers or by administering insufficient drug doses to achieve cure during the acute infection phase.45,46 These mice can survive up to 2 years with different symptoms, depending on the host and parasite strains used.45,47–49 Drug testing experiments in chronic models are time consuming and expensive: it takes several months for mice to reach a chronic infection state, and subsequent treatment courses are extended.
The choice of a chronic model depends on the study objective (eg, evaluation of myocardial fibrosis, of autoantibody generation, persistence of parasites in deep tissues, or immune response). Most studies use time post-infection to study chronic infection, considering that after a certain number of days, animals enter the chronic phase, when parasitemia is no longer detected.3 However, this definition is loose, and depends on the study group, species, and parasite strains among others, and should be tested and validated accordingly.
In chronic models, it is important to consider the role of host immunity; various knock-out mice may display different levels of drug efficacy and mortality. Genetic diversity among T. cruzi subtypes on the immunoglobulin profile during experimental infections showed a correlation of the pattern of humoral immune response with the T. cruzi genotype.50 If a drug activates macrophages, then one may expect different levels of efficacy and mortality.21
Considering that cardiac disease is the most important clinical form of chronic Chagas disease, it could be important to use animals infected with strains of the parasite that induce cardiac lesions, so that it may be possible to evaluate both the efficacy of the compound in suppressing the parasitism and/or in reducing the cardiac lesions in an animal model. Thus, it would be important to know the tissue tropism of the T. cruzi strains used in preclinical evaluations.
Animal species used
A wide variety of species and animal models have been used in Chagas disease experimental research, as described in the literature. A selection of animal models is outlined below. It is recommended that readers refer to the literature for additional reading and an exhaustive understanding of Chagas disease animal models.
Mouse models
Mouse models are the most widely used animal models in Chagas disease research. Models have been developed that give rise to organ damage approximating Chagas disease in humans. For instance, C3H/He mice infected with the Sylvio X10/4 T. cruzi strain display chronic myocarditis resembling human disease.49 One of the most widely investigated mouse models allows for evaluation of chagasic cardiomyopathy.51 Early electrocardiography (ECG) studies carried out in C3H and C57Bl/6 mice infected with various T. cruzi strains reported differences in myocardial fibrosis and in ECG parameters.52 ECG studies have also been carried out in BALB/c, SCID, C57BL/6, and CH3 mice infected with various T. cruzi strains,53 demonstrating variable outcomes depending on the mouse and parasite strains used (Table 3).
Various imaging techniques have been used in T. cruzi-infected mice to investigate the presence of megasyndromes. X-ray studies have shown delayed intestinal transit time during the chronic phase of infection, and digestive tract dilation.54,55 Charcoal was used for the evaluation of intestinal motility in a murine model (Swiss Webster) of T. cruzi infection (Y strain), demonstrating that infected mice presented a significant increase in charcoal defecation time.56 Intestinal dilation was reported 30 days post-infection in C57BL/6 mice infected with T. cruzi (Brazil strain), suggesting that GI alterations may begin during the acute infection stage,57 raising questions about the validity of these models in human disease. Furthermore, CD1 mice infected with the T. cruzi Brazil strain display hepatosplenomegaly, which has been reported in some Chagas disease patients.58
Trypanosoma cruzi has been shown to persist in tissues of infected experimental animals and humans. Experiments in infected mouse adipocytes demonstrated that adipocytes are readily invaded by trypomastigotes (T. cruzi Brazil strain) and may serve as a reservoir from which the infection can be reactivated. Surprisingly, infected mice gained more weight than controls, and those with dilated cardiomyopathy had reduced fat stores,59 as a result of decreased food intake and infection-associated lipolysis.60 In analogy, T. cruzi parasite was detected in adipose tissue of 3/10 elderly patients with chronic Chagas disease.61
Other rodent models
Potential therapeutic strategies with a tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonist, investigation of pro-inflammatory cytokine responses, cardiac autonomic dysfunction, and mechanisms that lead to chronic chagasic cardiomyopathy have been investigated in rat models.62–65 Together, these studies cemented the role of pro-inflammatory cytokine production and the parasympathetic nervous system in the pathophysiology of chagasic cardiomyopathy.
The role of beta-blockers in cardiac remodeling and mortality was evaluated in hamster models. Treatment improved survival in the acute phase, but did not attenuate cardiac remodeling or mortality.66 A similar study investigated aldosterone antagonism and also reported evidence of myocardial protection.67 An acute cardiomyopathy model explained cardiac parasitism, cytokine expression, and molecular and cellular changes associated with alterations in the cardiomyocyte cytoskeleton.68 Other models studied ultrastructural, morphologic, morphometric, echocardiographical, and histopathological changes from chronic chagasic hamsters, similar to human Chagas disease cardiomyopathy.69–71
Guinea pigs have also been used as a model for experimental T. cruzi infection for acute and chronic Chagas disease.72 The model was investigated to develop detection of T. cruzi (Y strain) antigens in urine, to be used as a diagnostic tool. T. cruzi antigens and DNA were detected in urine samples, and were associated with kidney injury and systemic parasite detection.73
Rabbit models
Similar to mouse models, variability in parasite strains and resulting parasitemia have been reported in rabbit models for Chagas disease.74 There were no detectable ECG alterations in infected rabbits during the acute phase, whereas symptoms of cardiac involvement were frequently recorded in the chronic infection phase. In this respect, rabbits exhibit lesions and characteristic chronic pathology similar to human disease, such as diffuse myocarditis and signs of heart failure. Megacolon was seen in 2/34 rabbits.75 Other studies in rabbits also reported parasitological and immunological alterations similar to those observed in humans, although not systematically.76,77
Chicken models
Teixeira et al have investigated the chicken as an animal model to explain the pathogenesis of Chagas disease. Rather than parasite persistence, this model postulates that autoimmunity explains the pathogenesis of Chagas disease. Specifically, transfer of parasite mitochondrial kinetoplast DNA (kDNA) to the host genome may be the underlying factor. Chagas disease has been proposed to be a genetically-driven autoimmune disease related to T. cruzi kDNA integration into the host genome.78,79 A chicken model evaluating the effect of genotype alterations on autoimmune processes found that kDNA-mutated chickens developed severe cardiomyopathy, suggesting that inflammatory cardiomyopathy in Chagas disease could be a genetically-driven autoimmune disease that occurs in the absence of T. cruzi parasites.79–81 This may explain why T. cruzi acute infections seem asymptomatic, but progress to chronic infection in approximately a third of cases after several decades (Figure 1).
Dog models
Dogs are an important reservoir of the parasite and are considered as a good model to study the pathogenesis of T. cruzi infection, in particular the immunopathogenic mechanisms involved in chronic chagasic infection.82 The use of larger animal models is, however, associated with prohibitive costs. In naturally infected stray dogs, 3/9 seropositive dogs presented ECG alterations.83 A series of other small studies in dogs infected with T. cruzi strains reported ECG alterations.84 Dogs have also been investigated as experimental models for acute and chronic phases of Chagas disease, before and after BZN treatment (using the same regimen as in humans). Outcomes reflected those reported in human clinical trials in both disease phases. The study also reported that tests for monitoring cure were similar to those obtained in human trials.36
Non-human primate models
Non-human primates (NHPs, eg, baboons, macaques, and capuchin monkeys) have been explored as models for Chagas disease.85–93 Early studies in capuchin monkeys revealed that ECG changes in infected monkeys correlated with specific anatomic lesions, but a later study reported that capuchin monkeys infected with different T. cruzi strains showed no ECG abnormalities, and only 3/12 monkeys exhibited chronic myocarditis at autopsy.90,92 Another study in seropositive baboons used myocardial contrast ECG to investigate the pathogenesis of chagasic cardiomyopathy. Chagasic heart disease was present in 4/17 seropositive baboons, but there was no significant difference in the coronary microcirculation pattern, suggesting preservation of microvascular integrity.94 GI alterations were observed in capuchin monkeys infected with three T. cruzi strains (CA1, Colombian, or Tulahuen). Analyses showed enlargement and dilation of the colon in 3/18 infected animals.95
Outcome measures and test of cure: readouts
Methods for measuring treatment outcomes in animal models are a potential source of variability (Table 3). Problems related to Chagas disease treatment are the unsatisfactory evaluation of therapy efficacy and diagnosis of cure. Outcome measures must convincingly demonstrate parasitological cure. In that respect, animal models have the advantage of allowing parasite assessment in both blood and organs.
Parasitemia and parasite suppression can be quantified under a microscope with a hemocytometer. Microscopy as a test for parasitemia is not only limited in sensitivity, but also in the time frame during which it is useful. Because parasites may circulate at low levels in the blood or may integrate tissues, this technique is only useful during the acute infection phase, and is not suitable for demonstrating cure.96
More sensitive methods include xenodiagnosis, hemoculture, or PCR on blood or tissues such as cardiac and skeletal muscle, but negative readings do not consistently correspond with parasitological cure.96,97 Nucleic acid-based assays such as quantitative PCR offer the highest sensitivity and lowest detection limit, with the caveat that blood is not an indicative tissue for chronic infection.
Treatment success can be assessed by the disappearance of specific anti-T. cruzi IgG antibodies (seroconversion), while therapeutic failure is gauged by parasite persistence. Unfortunately, due to the nature of the disease in humans, serological markers may take up to 10 years to disappear.98 Variable seroconversion rates were reported for patients in Guatemala vs Bolivia treated with BZN, further highlighting the complexity and heterogeneity of the disease: the variability in apparent treatment effectiveness may reflect differences in patient and parasite populations, and illustrates the limitations of current treatments and measures of efficacy.99
In animal models, one of the most sensitive methods to evaluate cure is achieved following immunosuppressive therapy (eg, cyclophosphamide) after completion of drug treatment.23 Immunosuppressive therapy rekindles blood parasitemia, and allows for the detection of residual infection.46,100,101 This approach is not representative of the natural course of infection (except in immunosuppressed hosts), and it may be preferable to keep the immune system intact when developing drugs for Chagas disease. There is also no guarantee that immunosuppressive treatment would remove all parasites from tissues, and this has to be assessed using different techniques. This knowledge gap remains to be tested.
A more representative mouse model of Chagas disease might require following the infection for 6 months to a year post-therapy without immunosuppression. Given the average lifespan of a mouse (~2–3 years), this would be akin to following the clinical course in human infection for 10–20 years with the goal of preventing progression to severe and life-threatening cardiac or GI manifestations. In other words, if the disease-free interval could be extended from 10 years to 30 years, then this would certainly be a valid therapeutic outcome, even if some parasites remained in circulation. The disadvantages of this model would be the delay in obtaining results, and experiments would be much more labor-intensive and expensive.
Animal models do not reflect human immunity, which is an issue from a drug development standpoint. There is evidence that some patients may spontaneously cure infection through a directed immune response.102 This is another reason why immunosuppression is not considered a valid test of a drug lead. If T. cruzi-infected mice were given a compound that significantly reduces parasite load to undetectable levels by hemoculture 30 days after infection, then the human host might eliminate the remaining cryptic parasites via an immune response. Courses of immunosuppression would not provide infected hosts a chance for the immune response to operate and add to the effect of the drug.
Since the role of immunosuppression remains unclear, some researchers compromise by defining parasitological cure as: no blood parasites by direct diagnostic methods such as microhematocrit concentration method or PCR in blood and/or target tissues (mainly skeletal muscle, heart, and brain), no parasitemia reactivation after drug discontinuation, and no reactivation of parasitemia after four weekly cycles of cyclophosphamide at 200 mg/kg. This immunosuppression schedule leads to reactivation for most drugs, including BZN, even in models with “BZN susceptible” T. cruzi strains.43 However, it is not established which tissues should be sampled, thus limiting PCR as a readout tool, as false negatives could be observed if the wrong tissue was sampled. PCR is technically demanding, requires the right primers, and is associated with a high contamination risk with foreign or T. cruzi DNA. Moreover, parasite persistence in humans may differ from that of animals.
Reservoirs of parasites in heart muscle tissue, skeletal muscle, and the GI tract have been described in addition to those in adipose tissue. As discussed, candidate drugs would therefore need to have the appropriate DMPK properties and mechanism of action (MoA) in order to reach these tissues (ie, good volume of distribution).22 In addition to reducing the number of animals used, non-invasive bioluminescent models may be very useful tools to assess parasite integration into tissues and drug penetration. Real-time monitoring of mice infected with transgenic parasites containing the luciferase gene, supplemented with quantitative tissue PCR to confirm the tissue parasite persistence, allows for in vivo imaging and semi-quantitative evaluation of efficacy through time.19,20,103 Combined with existing techniques, this highly sensitive in vivo imaging system based on bioluminescent T. cruzi might prove a useful tool in drug development programs, in successfully defining efficacy outcomes and setting a cure criterion.
The lack of a standardized optimal marker for indicating parasitological cure and limitations of systems for assessing drug efficacy both in vitro and in vivo are important obstructions in the development of more effective drugs for Chagas disease (Table 3).104 It is not clear whether results obtained in an acute model can be applied to a chronic model of disease. In general, the efficacy of a drug could be demonstrated by improvement of prognosis and the absence of chronic Chagas disease manifestations.
What is the most appropriate animal model for translation into humans?
Because of the variety and lack of standardization in available animal models, and the resulting difficulties in comparing experimental outcomes, it is unclear which animal model is the most appropriate for translation into humans. Differences between the pathological processes in mice and humans have led some researchers to question the validity of extrapolating findings from mouse models when informing therapeutic interventions, similar to concerns that have been raised in the field of malaria.105 However, despite variability and pitfalls (Tables 1, 3, and 4), most researchers feel that the mouse model is the most appropriate and well-understood for the drug screening process.
The target product profile (TPP) stipulates that the population for which treatment is intended should ideally include patients in both the acute and the chronic indeterminate phases of the disease, although a treatment for patients in the chronic indeterminate phase only is acceptable (Table 5). Given that the dog, rabbit, and NHP animal models show progression to a chronic phase that more closely reflects human disease (Table 4), it may be concluded that these are the best available in vivo models. Indeed, other models that do not progress beyond the acute or indeterminate phases may either identify inefficient chronic phase compounds or miss them altogether. Importantly, a suitable animal model does not necessarily need to closely reproduce human disease, only to find an acceptable balance between relevance to human disease and capacity to answer a specific hypothesis. Once a drug with appropriate DMPK properties is identified, the ideal animal model should be able to demonstrate: 1) non-inferiority or superiority to BZN; 2) parasitemia suppression (with the goal of parasite elimination or sterile cure) and/or improvement of symptoms associated with chronic disease; 3) which tissues the drug penetrates; 4) whether drug pharmacokinetic (PK) correlate with pharmacodynamic (PD) properties or efficacy (PK/PD relationships). From the testable hypothesis viewpoint, if a compound has adequate DMPK properties, it may be efficient in both acute and chronic stages. It is essential that drug discovery and product development are committed to clinical research, as stipulated in the US FDA Critical Path Initiative, which aims to improve the drug development process, the quality of evidence generated, and the clinical outcomes of drugs by incorporating recent scientific advances.14
  | Table 5 Target product profile (2010) |
In drug screening, a standardized mouse–parasite combination with a non-lethal strain and dose (eg, CD1 male mice with Brazil strain or Swiss mice with Y strain) with defined age and weight is considered as a good starting point. Testing a drug candidate against the BZN standard of care in an acute model, followed by a chronic model and by further testing in a higher order mammal would inform decision making before proceeding to a clinical trial in humans. Some believe that screening in an NHP might be more representative of prognosis in humans: posaconazole was effective in murine models but not in baboons and humans, highlighting the need for standardization and optimization of the drug screening process. There is no evidence supporting an NHP model as being more predictive of clinical outcome.
It has been suggested that using so-called BZN-resistant T. cruzi strains may be better for chronic disease models. This is debatable, as resistant strains might not be appropriate to compare efficacy of a new compound against BZN, at least during the first steps of drug screening.13 Most patients in clinical practice do not present BZN-resistant strains and there is no clinical evidence of resistance to BZN. The choice of comparator drugs as controls is also the subject of discussion. In addition to testing new compounds against the positive control of BZN, an infected untreated placebo group can be used as a negative control.
An ideal chronic model should reproduce several aspects of Chagas disease: symptoms and lesions, immune response, and human PK/PD. The best chronic model would offer tests for IgG negativity, negative parasitemia, positive serology, high survival rates, and measures of alterations and inflammation markers in heart and other organs. A consensus on preclinical studies validation needs to be agreed on, conducted with common criteria and repeatable results that could be compared between research groups. If the candidate compound showed good parasite response without toxicity in animal studies, then it would then be appropriate to initiate a human Phase I clinical study.
Which steps could be undertaken to reduce variability and improve predictability?
It is established that animal studies are not without flaws and might not provide adequate answers to allow translation into humans, due to discordance between animal models and clinical disease or publication bias.106 The main reasons are assigned either to inadequate animal data, poor methodologies, overoptimistic conclusions and misinterpretations derived from studies, or simply to biological differences between animals and humans that complicate data interpretation.107 In light of the frequent failure of investigational drugs during clinical translation, a systematic review of preclinical research guidelines intended to improve the design and execution of in vivo animal studies identified the most recurrent recommendations in experimental practice, providing a basis for developing, standardizing, and improving preclinical research guidelines for specific diseases.108 In vitro compound efficacy should be determined in drug assays under controlled conditions and from normalized data, and this parameter should be considered a key in determining T. cruzi susceptibility to a compound, before proceeding to in vivo efficacy evaluations. Data generated in a suitable and validated animal model should serve to build confidence and move a compound forward together with other data.
Standardization of animal and parasite strains
For the purposes of experimental evaluation of compound efficacy, controlling for certain factors (such as mouse lineage, age, sex, or parasite strain) might limit variability and enable better reproducibility of results. Standardization of the “primary” parasite strain used would also help reduce variability in experimental outcomes. The use of a parasite strain that induces cardiac lesions in a chronic disease experimental model is advisable. Owing to newly developed bioluminescence techniques,19,20,103 ease of infection and parasite distribution could be measured and used to make an informed choice. Any “hit” compound worth pursuing would be expected to work against all parasite strains.
The breeding methodology of the animal host is another factor affecting variability. The use of inbred mice strains is said to minimize biological diversity and allows experiment-to-experiment comparison. For the purposes of toxicology and drug development, inbred strains are recommended, to control for individual differences and obtain valid and repeatable results.109 Commonly used BALB/c mice are an example of inbred strain susceptible to T. cruzi infection that yield uniform and repeatable treatment responses.42,110
Standardization of analytical tools
Over the last few years, new technologies and development of in vitro tools such as high throughput screening and dose–response curves, parasite stage-specific assays, and time-kill and washout/reversibility assays have proved useful in drug discovery and development.5 Questions addressed by animal models should be clearly defined, eg, parasite eradication or parasite load reduction. In the example of parasite eradication, relevant readout methods that allow the measurement of this objective are required, possibly using BZN as a benchmark. An enzyme-linked aptamer (ELA) assay detected residual parasitemia in treated mice, suggesting that the ELA assay can be used in drug discovery to assess treatment efficacy in vivo.111 Analytical tools used to assess cure (eg, bioluminescent mouse models, PCR, and ELA) need to be standardized to allow for better reproducibility of results. For instance, in the acute model, mortality has been used as an endpoint to test compound efficacy. Other endpoints include measuring parasitemia rather than survival. This endpoint is considered more valuable in animal models, and allows for a more quantitative assessment of exposure response. In other words, it may be preferable to infect with a sublethal amount of parasite and then measure parasitemia (the “tissue burden” model).
Pooled parasitemia and PK data could be used to develop mathematical semi-mechanistic models not only to describe the exposure-response, but also to aid in the translation from in vitro to in vivo, and from animal models to human projections. The use of such tools could add a level of objectivity to the analysis and allow for a fuller understanding of the parasite’s growth cycle and of drug regimens and efficacy. Failure to properly predict a drug’s PK profile at the preclinical stage can be the reason for failing to demonstrate favorable clinical response.
Standardization of treatment protocols
The timing of treatment initiation, dosing regimen, and treatment duration may all affect outcomes (Tables 1 and 3). These parameters have not been systematically compared or established. A drug should ideally rapidly kill parasites within 1 week of infection, in order to avoid development of drug resistance.112 It is generally agreed that treatment should be initiated after parasite detection in peripheral blood. In an experimental setting, time to parasite detection varies depending on the T. cruzi strain and the host (usually 4–10 days). In practice, however, and according to the TPP (Table 5), the objective is to treat after the acute phase peak during the chronic phase (Figure 1), which may prove difficult to adapt to a lead optimization program, as short assay durations are preferred. However, a way to overcome this issue is to infect different cohorts at regular intervals, so that there are mice available for testing compounds in the chronic stage of infection.
In acute phase models, treatment is initiated soon after infection, which does not reflect clinical conditions, since the parasite does not go through its complete life cycle. Other infection models postulate treatment initiation 4–7 days after infection when all infected animals present patent parasitemia (at least 10–12 K bloodstream trypomastigotes/mL), allowing the parasite to go through at least one life cycle. In such a model, it may take approximately 20 days of BZN treatment to see a cure in mice. For the purposes of the TPP, one should aim to keep this duration under 20 days.
In chronic phase models, treatments can be initiated after the acute phase parasitemia peak. There appears to be a correlation between activity against T. cruzi strains and the time required to exert trypanocidal effects. Establishing the appropriate dosing regimen that provides adequate drug levels and does not lead to low levels that would introduce selective pressure is important. From a patient perspective, a treatment duration of ≤60 days of the BZN standard of care is necessary, because an antichagasic agent that requires a longer time to achieve efficacy compared with BZN may lead to drug resistance.
Dosing regimens depend on the PK properties and MoA of the candidate drug. Compound efficacy may vary depending on the class of compound or the regimen used (eg, frequency and duration of treatment, prolonged low dose, or short high dose). For example, BZN is effective in curing dogs infected with the T. cruzi Y strain when administered for 60 days, whereas 90 days of treatment were required with albaconazole.113 Commonly used dosing regimens in mice range from 20 to 28 days, once or twice a day (depending on drug properties) on consecutive days, by the oral route. However, this dosing regimen was established without any clear rationale (other than mimicking human treatment to some extent). Alternative schedules should be investigated, including combined treatment protocols.103 In light of data suggesting that BZN serum concentration is suboptimal in chronic disease patients with the standard treatment regimen,114 there is an urgent need to understand how and when BZN and other compounds are curative. This knowledge could then be applied to the development of in vivo assays that can correlate and possibly predict clinical performance of new drug candidates.
Conclusion
Before testing compounds in Proof of Concept (Phase II PoC) clinical studies, a consensus on preclinical studies validation is required. A main common goal in Chagas disease drug discovery and development should be to improve the predictability of test hypotheses and models designed for translation to human disease. A standardized predictive Chagas disease in vivo model for drug discovery and for the study of treatment efficacy needs developing and validating. A better understanding of animal models and of Chagas disease treatment will be achieved through the generation of systematic data obtained via the drug discovery process. Ultimately, validation of the findings will only occur in clinical trials.
Innovation on processes and assays for successful drug discovery and development for Chagas disease is crucial. Chagas disease drug discovery programs would benefit from the establishment of a translational platform composed of in vitro and in vivo preclinical assays that could confidently predict the efficacy of drug candidates in clinical trials, allowing for early termination of compounds that do not meet required criteria.
Pathological differences between mice and humans have raised concerns regarding extrapolation of findings from mouse models. These are nevertheless considered the most appropriate and well-understood models for initial drug screening processes. Experimental infection models should not necessarily accurately reflect human disease, but must retain the potential to address clinically relevant issues, including tissue tropism, symptoms, immune response, and human PK/PD. No model has so far combined these aspects. The chronic Chagas disease model would ideally offer tests for IgG negativity, negative parasitemia, positive serology, survival, and measures of inflammation markers in the heart and other organs. Ideally, test drugs need to access all areas that the parasite accesses, highlighting the importance of detecting parasite levels in host tissue. Failure to include adequate penetration into the tissues could lead to a lack of efficacy and generate parasite resistance.
From a predictable animal model standpoint, considering the unknowns regarding disease progression and the paucity of available compounds, it would be ideal if all models (both in vitro and in vivo) collected data on parasitemia, drug PK, and MoA in every experiment. These would be helpful in predicting potential safety issues and monitoring specific parameters during drug development.
Drug discovery in chronic Chagas disease is associated with translational challenges, in that research data need to translate to assays compatible with drug discovery and development processes. Translation of data from in vitro to in vivo models and from animals to humans needs improving. Researchers in the field of chronic Chagas disease drug development need to ensure that the models used address the right questions. Available preclinical assays should be further expanded, for instance by evaluating PK/PD relationships and developing biomarkers to test for treatment efficacy. Data from in vitro assays, animal models, and from the clinic must be compared and standardized, to improve therapy for Chagas disease patients. Current developments in the field are moving in the right direction, with new technologies and models being assessed and the generation of systematic data with the objective of standardizing Chagas disease animal models. As the statistician George Box stated: “Essentially, all models are wrong, but some are useful”.115 Indeed, as for other diseases, animal models are a simplification of reality but can help explain and interpret data and possibly predict efficacy of compounds in humans or build drug developers’ confidence in moving compounds forward into clinical trials. In the long run, only human clinical trial data will validate a standardized animal model.
Acknowledgments
Nandini Konar was a Richard T Clark Fellow under the MSD Fellowship for Global Health. We wish to thank all those who provided insight into the topics discussed in the review. We thank Dr Vanessa Gray-Schopfer, OmniScience SA, who provided medical writing services on behalf of Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative (DNDi). The authors were fully responsible for contents and editorial decisions for this manuscript. For Chagas disease drug discovery, DNDi received financial support from the following donors: Department for International Development (DFID), UK; Reconstruction Credit Institution-Federal Ministry of Education and Research (KfW-BMBF), Germany; GiZ on behalf of the Government of the Federal Republic of Germany, Germany; Ministry of Foreign and European Affairs (MAEE), France; Spanish Agency for International Development Cooperation (AECID), Spain; Directorate-General for International Cooperation (DGIS), the Netherlands; Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC), Switzerland; Médecins Sans Frontières (Doctors without Borders); and a Swiss foundation. The donors had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
WHO. World Health Organisation. Third WHO report on neglected tropical diseases 2015: investing to overcome the global impact of neglected tropical diseases. WHO/HTM/NTD/2015.1; 2015. | ||
Moncayo A, Silveira AC. Current epidemiological trends for Chagas disease in Latin America and future challenges in epidemiology, surveillance and health policy. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2009;104(Suppl 1):17–30. | ||
Rassi A Jr, Rassi A, Marin-Neto JA. Chagas disease. Lancet. 2010;375(9723):1388–1402. | ||
Chagas C. Nova tripanozomiase humana: Estudos sobre a morfolojia e o ciclo evolutivo do Schizotrypanum cruzi n. gen., n. sp., ajente etiolojico de nova entidade morbida do homem. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1909;1:159–218. | ||
Chatelain E. Chagas disease drug discovery: toward a new era. J Biomol Screen. 2015;20(1):22–35. | ||
Apt W. Current and developing therapeutic agents in the treatment of Chagas disease. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2010;4:243–253. | ||
Rodriques Coura J, de Castro SL. A critical review on Chagas disease chemotherapy. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2002;97(1):3–24. | ||
Bern C, Montgomery SP, Herwaldt BL, et al. Evaluation and treatment of chagas disease in the United States: a systematic review. JAMA. 2007;298(18):2171–2181. | ||
Molina I, Gomez i Prat J, Salvador F, et al. Randomized trial of posaconazole and benznidazole for chronic Chagas’ disease. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(20):1899–1908. | ||
Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative. Drug trial for leading parasitic killer of the americas shows mixed results but provides new evidence for improved therapy [press release]; 2013 [November 14]. Avaiable from: http://www.dndi.org/media-centre/press-releases/1700-e1224.html. Accessed July 3, 2015. | ||
Pinazo MJ, Thomas MC, Bua J, et al. Biological markers for evaluating therapeutic efficacy in Chagas disease, a systematic review. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2014;12(4):479–496. | ||
Requena-Mendez A, Lopez MC, Angheben A, et al. Evaluating Chagas disease progression and cure through blood-derived biomarkers: a systematic review. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2013;11(9):957–976. | ||
Romanha AJ, Castro SL, Soeiro Mde N, et al. In vitro and in vivo experimental models for drug screening and development for Chagas disease. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2010;105(2):233–238. | ||
Woodcock J, Woosley R. The FDA critical path initiative and its influence on new drug development. Annu Rev Med. 2008;59:1–12. | ||
Manoel-Caetano Fda S, Silva AE. Implications of genetic variability of Trypanosoma cruzi for the pathogenesis of Chagas disease. Cad Saude Publica. 2007;23(10):2263–2274. | ||
Moreno M, D’Avila DA, Silva MN, et al. Trypanosoma cruzi benznidazole susceptibility in vitro does not predict the therapeutic outcome of human Chagas disease. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2010;105(7):918–924. | ||
Nagajyothi F, Machado FS, Burleigh BA, et al. Mechanisms of Trypanosoma cruzi persistence in Chagas disease. Cell Microbiol. 2012;14(5):634–643. | ||
Hyland KV, Asfaw SH, Olson CL, Daniels MD, Engman DM. Bioluminescent imaging of Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Int J Parasitol. 2008;38(12):1391–1400. | ||
Lewis MD, Fortes Francisco A, Taylor MC, et al. Bioluminescence imaging of chronic Trypanosoma cruzi infections reveals tissue-specific parasite dynamics and heart disease in the absence of locally persistent infection. Cell Microbiol. 2014;16(9):1285–1300. | ||
Lewis MD, Francisco AF, Taylor MC, Kelly JM. A new experimental model for assessing drug efficacy against Trypanosoma cruzi infection based on highly sensitive in vivo imaging. J Biomol Screen. 2015;20(1):36–43. | ||
Zhang S, Kim CC, Batra S, McKerrow JH, Loke P. Delineation of diverse macrophage activation programs in response to intracellular parasites and cytokines. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010;4(3):e648. | ||
Buckner FS, Urbina JA. Recent developments in sterol 14-demethylase inhibitors for Chagas disease. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2012;2:236–242. | ||
Buckner FS. Experimental chemotherapy and approaches to drug discovery for Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Adv Parasitol. 2011;75:89–119. | ||
Buckner FS, Navabi N. Advances in Chagas disease drug development: 2009–2010. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2010;23(6):609–616. | ||
Neal RA, van Bueren J. Comparative studies of drug susceptibility of five strains of Trypanosoma cruzi in vivo and in vitro. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1988;82(5):709–714. | ||
Trischmann T, Tanowitz H, Wittner M, Bloom B. Trypanosoma cruzi: role of the immune response in the natural resistance of inbred strains of mice. Exp Parasitol. 1978;45(2):160–168. | ||
de Souza EM, Rivera MT, Araujo-Jorge TC, de Castro SL. Modulation induced by estradiol in the acute phase of Trypanosoma cruzi infection in mice. Parasitol Res. 2001;87(7):513–520. | ||
McHardy N. Effect of sex of mice in relation to their response to immunization with vaccines prepared from Trypanosoma cruzi. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(2):201–202. | ||
Maletto BA, Gruppi A, Moron G, Pistoresi-Palencia MC. Age-associated changes in lymphoid and antigen-presenting cell functions in mice immunized with Trypanosoma cruzi antigens. Mech Ageing Dev. 1996;88(1–2):39–47. | ||
Ming Z, Davis CD. CD8+ T lymphocytes required for enhanced survival of Trypanosoma cruzi-infected mice at elevated environmental temperature. J Parasitol. 2003;89(3):630–632. | ||
Toso MA, Vial UF, Galanti N. [Oral transmission of Chagas’ disease]. Rev Med Chil. 2011;139(2):258–266. | ||
Dias GB, Gruendling AP, Araujo SM, Gomes ML, Toledo MJ. Evolution of infection in mice inoculated by the oral route with different developmental forms of Trypanosoma cruzi I and II. Exp Parasitol. 2013;135(3):511–517. | ||
Ndao M, Kelly N, Normandin D, et al. Trypanosoma cruzi infection of squirrel monkeys: comparison of blood smear examination, commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and polymerase chain reaction analysis as screening tests for evaluation of monkey-related injuries. Comp Med. 2000;50(6):658–665. | ||
Sullivan JJ, Steurer F, Benavides G, Tarleton RL, Eberhard ML, Landry S. Trypanosomes and microfilariae in feral owl and squirrel monkeys maintained in research colonies. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1993;49(2):254–259. | ||
Brener Z. Therapeutic activity and criterion of cure on mice experimentally infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1962;4:389–396. | ||
Guedes PM, Veloso VM, Tafuri WL, et al. The dog as model for chemotherapy of the Chagas’ disease. Acta Trop. 2002;84(1):9–17. | ||
Zingales B, Pereira ME, Almeida KA, et al. Biological parameters and molecular markers of clone CL Brener – the reference organism of the Trypanosoma cruzi genome project. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1997;92(6):811–814. | ||
National Research Council. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th ed. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2011. | ||
Festing MF. Reduction of animal use: experimental design and quality of experiments. Lab Anim. 1994;28(3):212–221. | ||
Olfert ED, Godson DL. Humane endpoints for infectious disease animal models. ILAR J. 2000;41(2):99–104. | ||
Villalta F, Dobish MC, Nde PN, et al. VNI cures acute and chronic experimental Chagas disease. J Infect Dis. 2013;208(3):504–511. | ||
Silva DR, Castro SL, Alves MC, Batista Wda S, Oliveira GM. Acute experimental Trypanosoma cruzi infection: establishing a murine model that utilises non-invasive measurements of disease parameters. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2012;107(2):211–216. | ||
Bahia MT, de Andrade IM, Martins TA, et al. Fexinidazole: a potential new drug candidate for Chagas disease. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6(11):e1870. | ||
Cencig S, Coltel N, Truyens C, Carlier Y. Evaluation of benznidazole treatment combined with nifurtimox, posaconazole or AmBisome(R) in mice infected with Trypanosoma cruzi strains. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012;40(6):527–532. | ||
Molina J, Martins-Filho O, Brener Z, Romanha AJ, Loebenberg D, Urbina JA. Activities of the triazole derivative SCH 56592 (posaconazole) against drug-resistant strains of the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma (Schizotrypanum) cruzi in immunocompetent and immunosuppressed murine hosts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000;44(1):150–155. | ||
Bustamante JM, Bixby LM, Tarleton RL. Drug-induced cure drives conversion to a stable and protective CD8+ T central memory response in chronic Chagas disease. Nat Med. 2008;14(5):542–550. | ||
Araujo MS, Martins-Filho OA, Pereira ME, Brener Z. A combination of benznidazole and ketoconazole enhances efficacy of chemotherapy of experimental Chagas’ disease. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2000;45(6):819–824. | ||
Buckner FS, Wilson AJ, Van Voorhis WC. Detection of live Trypanosoma cruzi in tissues of infected mice by using histochemical stain for beta-galactosidase. Infect Immun. 1999;67(1):403–409. | ||
Marinho CR, Nunez-Apaza LN, Bortoluci KR, et al. Infection by the Sylvio X10/4 clone of Trypanosoma cruzi: relevance of a low-virulence model of Chagas’ disease. Microbes Infect. 2009;11(13):1037–1045. | ||
dos Santos DM, Talvani A, Guedes PM, Machado-Coelho GL, de Lana M, Bahia MT. Trypanosoma cruzi: genetic diversity influences the profile of immunoglobulins during experimental infection. Exp Parasitol. 2009;121(1):8–14. | ||
Garcia S, Ramos CO, Senra JF, et al. Treatment with benznidazole during the chronic phase of experimental Chagas’ disease decreases cardiac alterations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49(4):1521–1528. | ||
Postan M, Bailey JJ, Dvorak JA, McDaniel JP, Pottala EW. Studies of Trypanosoma cruzi clones in inbred mice. III. Histopathological and electrocardiographical responses to chronic infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987;37(3):541–549. | ||
Eickhoff CS, Lawrence CT, Sagartz JE, et al. ECG detection of murine chagasic cardiomyopathy. J Parasitol. 2010;96(4):758–764. | ||
Mori T, Yoon HS, Iizuka FH, et al. Intestinal transit and opaque enema study in chagasic mice. Rev Hosp Clin Fac Med Sao Paulo. 1995;50(1):63–66. | ||
Guillen-Pernia B, Lugo-Yarbuh A, Moreno E. [Digestive tract dilation in mice infected with Trypanosoma cruzi]. Invest Clin. 2001;42(3):195–209. | ||
de Oliveira GM, de Melo Medeiros M, da Silva Batista W, Santana R, Araujo-Jorge TC, de Souza AP. Applicability of the use of charcoal for the evaluation of intestinal motility in a murine model of Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Parasitol Res. 2008;102(4):747–750. | ||
Ny L, Li H, Mukherjee S, et al. A magnetic resonance imaging study of intestinal dilation in Trypanosoma cruzi-infected mice deficient in nitric oxide synthase. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008;79(5):760–767. | ||
Jelicks LA, Tanowitz HB. Advances in imaging of animal models of Chagas disease. Adv Parasitol. 2011;75:193–208. | ||
Combs TP, Nagajyothi, Mukherjee S, et al. The adipocyte as an important target cell for Trypanosoma cruzi infection. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(25):24085–24094. | ||
Nagajyothi F, Zhao D, Machado FS, et al. Crucial role of the central leptin receptor in murine Trypanosoma cruzi (Brazil strain) infection. J Infect Dis. 2010;202(7):1104–1113. | ||
Ferreira AV, Segatto M, Menezes Z, et al. Evidence for Trypanosoma cruzi in adipose tissue in human chronic Chagas disease. Microbes Infect. 2011;13(12–13):1002–1005. | ||
Perez AR, Fontanella GH, Nocito AL, Revelli S, Bottasso OA. Short treatment with the tumour necrosis factor-alpha blocker infliximab diminishes chronic chagasic myocarditis in rats without evidence of Trypanosoma cruzi reactivation. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009;157(2):291–299. | ||
Chandrasekar B, Melby PC, Troyer DA, Colston JT, Freeman GL. Temporal expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inducible nitric oxide synthase in experimental acute Chagasic cardiomyopathy. Am J Pathol. 1998;152(4):925–934. | ||
Junqueira Junior LF, Beraldo PS, Chapadeiro E, Jesus PC. Cardiac autonomic dysfunction and neuroganglionitis in a rat model of chronic Chagas’ disease. Cardiovasc Res. 1992;26(4):324–329. | ||
Labrador-Hernandez M, Suarez-Graterol O, Romero-Contreras U, Rumenoff L, Rodriguez-Bonfante C, Bonfante-Cabarcas R. The cholinergic system in cyclophosphamide-induced Chagas dilated myocardiopathy in Trypanosoma-cruzi-infected rats: an electrocardiographic study. Invest Clin. 2008;49(2):207–224. | ||
Pimentel Wde S, Ramires FJ, Lanni BM, et al. The effect of beta-blockade on myocardial remodelling in Chagas’ cardiomyopathy. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2012;67(9):1063–1069. | ||
Ramires FJ, Salemi VM, Ianni BM, et al. Aldosterone antagonism in an inflammatory state: evidence for myocardial protection. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2006;7(3):162–167. | ||
Bilate AM, Teixeira PC, Ribeiro SP, et al. Distinct outcomes of Trypanosoma cruzi infection in hamsters are related to myocardial parasitism, cytokine/chemokine gene expression, and protein expression profile. J Infect Dis. 2008;198(4):614–623. | ||
Colmanetti FH, Teixeira Vde P, Rodrigues ML, Chica JE, Reis M, dos Santos VM. Myocardiocyte ultrastructure and morphometrical analysis in hamsters experimentally infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2005;29(2):139–147. | ||
Bilate AM, Salemi VM, Ramires FJ, et al. The Syrian hamster as a model for the dilated cardiomyopathy of Chagas’ disease: a quantitative echocardiographical and histopathological analysis. Microbes Infect. 2003;5(12):1116–1124. | ||
Chapadeiro E, Silva EL, Silva AC, Fernandes P, Ramirez LE. [Cardiac neuronal depopulation in hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus) chronically infected with Trypanosoma cruzi]. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 1999;32(1):35–39. | ||
Castro-Sesquen YE, Gilman RH, Yauri V, et al. Cavia porcellus as a model for experimental infection by Trypanosoma cruzi. Am J Pathol. 2011;179(1):281–288. | ||
Castro-Sesquen YE, Gilman RH, Yauri V, et al. Detection of soluble antigen and DNA of Trypanosoma cruzi in urine is independent of renal injury in the guinea pig model. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58480. | ||
Ramirez LE, Brener Z. Evaluation of the rabbit as a model for Chagas’ disease. I. Parasitological studies. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1987;82(4):531–536. | ||
Teixeira AR, Figueiredo F, Rezende Filho J, Macedo V. Chagas’ disease: a clinical, parasitological, immunological, and pathological study in rabbits. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983;32(2):258–272. | ||
Figueiredo F, Marin-Neto JA, Rossi MA. The evolution of experimental Trypanosoma cruzi cardiomyopathy in rabbits: further parasitological, morphological and functional studies. Int J Cardiol. 1986;10(3):277–290. | ||
da Silva AM, Eduardo Ramirez L, Vargas M, Chapadeiro E, Brener Z. Evaluation of the rabbit as a model for Chagas disease-II. Histopathologic studies of the heart, digestive tract and skeletal muscle. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1996;91(2):199–206. | ||
Hecht MM, Nitz N, Araujo PF, et al. Inheritance of DNA transferred from American trypanosomes to human hosts. PLoS One. 2010;5(2):e9181. | ||
Teixeira AR, Hecht MM, Guimaro MC, Sousa AO, Nitz N. Pathogenesis of chagas’ disease: parasite persistence and autoimmunity. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011;24(3):592–630. | ||
Teixeira AR, Gomes C, Nitz N, et al. Trypanosoma cruzi in the chicken model: Chagas-like heart disease in the absence of parasitism. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011;5(3):e1000. | ||
Teixeira AR, Nitz N, Bernal FM, Hecht MM. Parasite induced genetically driven autoimmune Chagas heart disease in the chicken model. J Vis Exp. 2012(65):3716. | ||
Guedes PM, Veloso VM, Afonso LC, et al. Development of chronic cardiomyopathy in canine Chagas disease correlates with high IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, and low IL-10 production during the acute infection phase. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2009;130(1–2):43–52. | ||
Cruz-Chan JV, Bolio-Gonzalez M, Colin-Flores R, Ramirez-Sierra MJ, Quijano-Hernandez I, Dumonteil E. Immunopathology of natural infection with Trypanosoma cruzi in dogs. Vet Parasitol. 2009;162(1–2):151–155. | ||
Barbabosa-Pliego A, Diaz-Albiter HM, Ochoa-Garcia L, et al. Trypanosoma cruzi circulating in the southern region of the State of Mexico (Zumpahuacan) are pathogenic: a dog model. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009;81(3):390–395. | ||
Bonecini-Almeida Mda G, Galvao-Castro B, Pessoa MH, Pirmez C, Laranja F. Experimental Chagas’ disease in rhesus monkeys. I. Clinical, parasitological, hematological and anatomo-pathological studies in the acute and indeterminate phase of the disease. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1990;85(2):163–171. | ||
Falasca CA, Grana DR, Mareso EA, Gomez E, Gili MM. Electrocardiographic changes in chronic Trypanosoma cruzi infected Cebus apella monkeys. Arq Bras Cardiol. 1991;56(4):287–293. | ||
Samudio M, Montenegro-James S, Kasamatsu E, et al. Local and systemic cytokine expression during experimental chronic Trypanosoma cruzi infection in a Cebus monkey model. Parasite Immunol. 1999;21(9):451–460. | ||
Rosner IM, Bellasai J, Schinini A, et al. Cardiomyopathy in Cebus apella monkeys experimentally infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Trop Med Parasitol. 1989;40(1):24–31. | ||
Malchiodi EL, Carbonetto CH, Grana D, et al. Immune response against Trypanosoma cruzi antigens in Cebus apella monkeys. Trop Med Parasitol. 1993;44(2):86–90. | ||
de Almeida EA, Navarro MR, Guariento ME, Carvalhal Sdos S. [The experimental infection of Cebus apella sp. monkeys with Trypanosoma cruzi. Its clinical, electrocardiographic and anatomicopathological assessment]. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 1992;25(1):7–12. | ||
de Meirelles Mde N, Bonecini-Almeida Mda G, Pessoa MH, Galvao-Castro B. Trypanosoma cruzi: experimental Chagas’ disease in rhesus monkeys. II. Ultrastructural and cytochemical studies of peroxidase and acid phosphatase activities. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1990;85(2):173–181. | ||
Milei J, Bolomo NJ, Vazquez A, Nagle CA. Normal and pathological electrocardiographic patterns in the Cebus monkey. J Med Primatol. 1982;11(1):10–19. | ||
Bolomo N, Milei J, Cossio PM, et al. Experimental Chagas disease in a South American primate (Cebus sp). Medicina (B Aires). 1980;40(6/1):667–672. | ||
Zabalgoitia M, Ventura J, Lozano JL, et al. Myocardial contrast echocardiography in assessing microcirculation in baboons with chagas disease. Microcirculation. 2004;11(3):271–278. | ||
Falasca CA, Merlo AB, Gomez E, Grana D, Malateste C, Mareso E. Gastric acid secretion response in the Cebus apella. A monkey model of chronic Chagas’ disease. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1992;34(6):489–498. | ||
Canavaci AM, Bustamante JM, Padilla AM, et al. In vitro and in vivo high-throughput assays for the testing of anti-Trypanosoma cruzi compounds. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010;4(7):e740. | ||
Britto CC. Usefulness of PCR-based assays to assess drug efficacy in Chagas disease chemotherapy: value and limitations. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2009;104(Suppl 1):122–135. | ||
Andrade SG, Magalhaes JB, Pontes AL. Evaluation of chemotherapy with benznidazole and nifurtimox in mice infected with Trypanosoma cruzi strains of different types. Bull World Health Organ. 1985;63(4):721–726. | ||
Yun O, Lima MA, Ellman T, et al. Feasibility, drug safety, and effectiveness of etiological treatment programs for Chagas disease in Honduras, Guatemala, and Bolivia: 10-year experience of Medecins Sans Frontieres. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009;3(7):e488. | ||
Pereira ME, Santos LM, Araujo MS, Brener Z. Recrudescence induced by cyclophosphamide of chronic Trypanosoma cruzi infection in mice is influenced by the parasite strain. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1996;91(1):71–74. | ||
Dos Santos FM, Caldas S, de Assis Cau SB, et al. Trypanosoma cruzi: induction of benznidazole resistance in vivo and its modulation by in vitro culturing and mice infection. Exp Parasitol. 2008;120(4):385–390. | ||
Sabino EC, Lee TH, Montalvo L, et al. Antibody levels correlate with detection of Trypanosoma cruzi DNA by sensitive polymerase chain reaction assays in seropositive blood donors and possible resolution of infection over time. Transfusion. 2013;53(6):1257–1265. | ||
Bustamante JM, Craft JM, Crowe BD, Ketchie SA, Tarleton RL. New, combined, and reduced dosing treatment protocols cure Trypanosoma cruzi infection in mice. J Infect Dis. 2014;209(1):150–162. | ||
Bustamante JM, Tarleton RL. Methodological advances in drug discovery for Chagas disease. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2011;6(6):653–661. | ||
Taylor-Robinson A. Validity of modelling cerebral malaria in mice: argument and counter argument. J Neuroparasitol. 2010;1. Article ID N100601. | ||
Perel P, Roberts I, Sena E, et al. Comparison of treatment effects between animal experiments and clinical trials: systematic review. BMJ. 2007;334(7586):197. | ||
van der Worp HB, Howells DW, Sena ES, et al. Can animal models of disease reliably inform human studies? PLoS Med. 2010;7(3):e1000245. | ||
Henderson VC, Kimmelman J, Fergusson D, Grimshaw JM, Hackam DG. Threats to validity in the design and conduct of preclinical efficacy studies: a systematic review of guidelines for in vivo animal experiments. PLoS Med. 2013;10(7):e1001489. | ||
Festing MF. Inbred strains should replace outbred stocks in toxicology, safety testing, and drug development. Toxicol Pathol. 2010;38(5):681–690. | ||
Gulin JE, Eagleson MA, Postan M, et al. Efficacy of voriconazole in a murine model of acute Trypanosoma cruzi infection. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013;68(4):888–894. | ||
de Araujo FF, Nagarkatti R, Gupta C, Marino AP, Debrabant A. Aptamer-based detection of disease biomarkers in mouse models for chagas drug discovery. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015;9(1):e3451. | ||
Mejia AM, Hall BS, Taylor MC, et al. Benznidazole-resistance in Trypanosoma cruzi is a readily acquired trait that can arise independently in a single population. J Infect Dis. 2012;206(2):220–228. | ||
Guedes PM, Urbina JA, de Lana M, et al. Activity of the new triazole derivative albaconazole against Trypanosoma (Schizotrypanum) cruzi in dog hosts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48(11):4286–4292. | ||
Pinazo MJ, Guerrero L, Posada E, Rodriguez E, Soy D, Gascon J. Benznidazole-related adverse drug reactions and their relationship to serum drug concentrations in patients with chronic chagas disease. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(1):390–395. | ||
Box GEP, Draper NR (1987). Empirical Model-Building and Response Surfaces. John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY; 1987:424. | ||
Ferraz ML, Gazzinelli RT, Alves RO, Urbina JA, Romanha AJ. The anti-Trypanosoma cruzi activity of posaconazole in a murine model of acute Chagas’ disease is less dependent on gamma interferon than that of benznidazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51(4):1359–1364. | ||
Keenan M, Chaplin JH, Alexander PW, et al. Two analogues of fenarimol show curative activity in an experimental model of Chagas disease. J Med Chem. 2013;56(24):10158–10170. | ||
Diniz PP, Morton BA, Tngrian M, et al. Infection of domestic dogs in peru by zoonotic bartonella species: a cross-sectional prevalence study of 219 asymptomatic dogs. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7(9):e2393. | ||
Olivieri BP, Molina JT, de Castro SL, et al. A comparative study of posaconazole and benznidazole in the prevention of heart damage and promotion of trypanocidal immune response in a murine model of Chagas disease. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2010;36(1):79–83. | ||
Urbina JA, Payares G, Contreras LM, et al. Antiproliferative effects and mechanism of action of SCH 56592 against Trypanosoma (Schizotrypanum) cruzi: in vitro and in vivo studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42(7):1771–1777. | ||
Teston AP, Monteiro WM, Reis D, et al. In vivo susceptibility to benznidazole of Trypanosoma cruzi strains from the western Brazilian Amazon. Trop Med Int Health. 2013;18(1):85–95. | ||
Fortes Francisco A, Lewis MD, Jayawardhana S, Taylor MC, Chatelain E, Kelly JM. The limited ability of posaconazole to cure both acute and chronic Trypanosoma cruzi infections revealed by highly sensitive in vivo imaging. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(8):4653–4661. | ||
Molina J, Brener Z, Romanha AJ, Urbina JA. In vivo activity of the bis-triazole D0870 against drug-susceptible and drug-resistant strains of the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2000;46(1):137–140. | ||
Tarleton RL. Trypanosoma cruzi and Chagas disease: cause and effect. In: Tyler KM, Miles MA, editors. American Trypanosomiasis. New York; Springer; 2003:107–116. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.

