Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 9
Therapeutic effects of C-28 methyl ester of 2-cyano-3,12-dioxoolean-1,9-dien-28-oic acid (CDDO-Me; bardoxolone methyl) on radiation-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in mice
Authors Wang Y , Zhang C, Ma Y, He Z, Zhe H, Zhou S
Received 15 January 2015
Accepted for publication 9 February 2015
Published 22 June 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 3163—3178
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S80958
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Wei Duan
Yan-Yang Wang,1,* Cui-Ying Zhang,2,* Ya-Qiong Ma,3 Zhi-Xu He,4 Hong Zhe,1 Shu-Feng Zhou5
1Department of Radiation Oncology, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, 2Graduate School, Ningxia Medical University, 3Department of Pathology, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, 4Guizhou Provincial Key Laboratory for Regenerative Medicine, Stem Cell and Tissue Engineering Research Center and Sino-US Joint Laboratory for Medical Sciences, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang, People’s Republic of China; 5Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, University of South Florida, FL, USA
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract: The C-28 methyl ester of 2-cyano-3,12-dioxoolean-1,9-dien-28-oic acid (CDDO-Me), one of the synthetic triterpenoids, has been found to have potent anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties in vitro and in vivo. However, its usefulness in mitigating radiation-induced lung injury (RILI), including radiation-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis, has not been tested. The aim of this study was to explore the therapeutic effect of CDDO-Me on RILI in mice and the underlying mechanisms. Herein, we found that administration of CDDO-Me improved the histopathological score, reduced the number of inflammatory cells and concentrations of total protein in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, suppressed secretion and expression of proinflammatory cytokines, including transforming growth factor-β and interleukin-6, elevated expression of the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10, and downregulated the mRNA level of profibrotic genes, including for fibronectin, a-smooth muscle actin, and collagen I. CDDO-Me attenuated radiation-induced lung inflammation. CDDO-Me also decreased the Masson’s trichrome stain score, hydroxyproline content, and mRNA level of profibrotic genes, and blocked radiation-induced collagen accumulation and fibrosis. Collectively, these findings suggest that CDDO-Me ameliorates radiation-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis, and this synthetic triterpenoid is a promising novel therapeutic agent for RILI. Further mechanistic, efficacy, and safety studies are warranted to elucidate the role of CDDO-Me in the management of RILI.
Keywords: CDDO-Me, radiotherapy, radiation-induced lung injury, cytokine, fibrosis, inflammation, transforming growth factor-β, mouse
Introduction
Radiotherapy is one of the essential treatment modalities for multiple locally advanced and inoperable thoracic malignancies, including lung cancer.1–3 For example, over half of patients with non-small cell lung cancer are currently treated with radiotherapy, and this may be increased to 76% in the near future when radiotherapy can be further optimized.4 However, its effectiveness is often limited by radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) and radioresistance. Clinically significant RILI occurs in up to 30% of patients irradiated for lung cancer and in about 10%–15% of other thoracic cancers, eg, mediastinal lymphoma patients, depending on the method of assessment.5–10 A far greater proportion of patients will have subclinical effects of radiation on the lung, identifiable by imaging and/or physiological testing.8,10–12 The exact mechanisms of RILI are not fully understood, but previous studies indicate that the process starts with energy deposition and generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), followed by macromolecular modification, activation of transcription factors, initiation of inflammation, angiogenesis, epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), and programmed cell death including apoptosis and autophagy, production of extracellular matrix, and cross-talk of signal transduction pathways.5,9,13 The activation of these damaging cascades and events will eventually lead to lung fibrosis. RILI is characterized by accumulation of fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, inflammatory cells including lymphocytes, monocytes and neutrophils, and extracellular matrix proteins such as collagens, with subsequent formation of a scar, which eventually result in impaired lung function.5,9 Replacement of normal lung parenchyma with fibrotic tissue is a culminating event that is refractory to treatment.
Two phases of RILI have been described in humans, ie, an acute phase of radiation inflammation, occurring 4-30 weeks after exposure, and a later phase of fibrosis, appearing 6-12 months after radiation and stabilizing after 2 years.7,8,14 The molecular mechanisms of these two phases of RILI are poorly understood. A complex interaction between radiation-induced damage to parenchymal cells, the supporting vasculature, and associated fibrotic reactions results in acute and late radiation-induced lung toxicities. In the lung, these changes can manifest themselves as reduced pulmonary function and a chronic inflammatory process. Inflammation is a complex biological response to harmful stimuli, and is characterized by an influx of inflammatory cells, a change in cytokine milieu, production of proinflammatory mediators, and fibroblast recruitment. There are many factors that can influence the likelihood of severe lung toxicity and fibrosis, including the volume of irradiated parenchyma, the absorbed radiation dose, radiation dose rate, pulmonary function, pre-existing lung disease, and use of radiosensitizing chemotherapy.5,15,16 Oxidative stress caused by detrimental ROS may be directly or indirectly involved in the pathogenesis of RILI.13,17,18 Ionizing radiation interacts with water molecules in biological systems and produces various ROS and reactive nitrogen species, which can directly cause cell damage and even cell death in the lung.18,19 Meanwhile, ROS is involved in the activation of multiple signaling pathways, such as hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α, which critically contribute to radiation-induced inflammation, angiogenesis, and fibrosis.9,20 Thus, antioxidant defense may have a potential role in the management of RILI. Nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) regulates the expression of a large number of important genes in response to infection, inflammation, and other endogenous and exogenous stressors.21–23 The NF-κB family of transcription factors are ubiquitously expressed, and function to regulate diverse cellular processes, including proliferation, death, survival, and immunity. Persistent activation of NF-κB is central to the pathogenesis of many inflammatory lung disorders, including cystic fibrosis, asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.24,25 NF-κB-mediated downstream effects influence the lung response to injury such as radiation. Inhibition of NF-κB activation has shown a protective effect against RILI in several studies.26–29
Cytokine release in response to ionizing radiation is considered to play a major role in the pathogenesis of RILI.9,30 A non-specific acute reaction (so-called “cytokine storming”) often occurs within 24 hours of radiotherapy. Fractionated radiation, however, creates a constant complex stress response with characteristic cytokine profiles different to those induced by a single radiation dose. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1, interferons (IFNs), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1, IL-10, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α have all been documented to play a key role in RILI.9
To date, there is no cure for RILI. There is an urgent need to develop and identify effective preventive and therapeutic methods for RILI. Triterpenoids are a large family of compounds synthesized in some plants such as the chrysanthemum flower through the cyclization of squalene, and have been used in traditional Asian medicine for disease management.31,32 C-28 methyl ester of 2-cyano-3,12-dioxoolean-1,9-dien-28-oic acid (see Figure 1; CDDO-Me is also called bardoxolone methyl), one of the synthetic triterpenoids derived from CDDO, has been found to have potent anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties in vitro and in vivo.33,34 Binding of CDDO-Me to kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) disrupts critical cysteine residues in Keap1, leading to release of nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2), which hinders its ubiquitination and finally leads to stabilization and nuclear translocation of the transcription factor. In the nucleus, Nrf2 activates the transcription of Phase II response genes, leading to a coordinated antioxidant and anti-inflammatory response.35 CDDO-Me can also bind to a cysteine residue on IκB kinase (IKKβ) and inhibit NF-κB activation. Binding of CDDO-Me to IKKβ prevents release of NF-κB from its bound complex with IκB in the cytosol, thereby inhibiting NF-κB activation and induction of downstream proinflammatory signaling.36 Because of the potential role of CDDO-Me in activation of the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway and suppression of the NF-κB proinflammatory pathway, its radioprotective effect has been tested in human colon epithelial cells in vitro.37–39 In addition, the anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic properties of CDDO-Me have been recently observed in the bleomycin-induced lung injury and fibrosis model.40 However, the therapeutic effect of CDDO-Me on RILI is still unclear. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate the therapeutic effect of CDDO-Me on radiation-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis using a C57BL/6 mouse model.
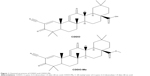  | Figure 1 Chemical structures of CDDO and CDDO-Me. |
Materials and methods
Ethics approval
Our experimental protocol was reviewed and approved by the ethics committee of the General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, Ningxia, People’s Republic of China. All animal experimental procedures were performed in accordance with the guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA.
Reagents and mice
CDDO-Me was obtained from Axon Medchem Inc (Reston, VA, USA) with a purity of more than 98.5%. Female C57BL/6 mice aged 6–8 weeks were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of Ningxia Medical University (Yinchuan, People’s Republic of China). The mice were housed three per cage and allowed to acclimate for 1 week prior to treatment. The cages were kept in rooms with an alternating 12-hour light/dark cycle, and standard rodent chow and water was provided ad libitum.
RILI mouse model and experiment protocol
For thoracic irradiation, the mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal administration of 5.0 mL/kg 6.5% chloral hydrate, then transferred to holders, and irradiated with a single dose of 12.5 Gy for the inflammation model and 22.5 Gy for the fibrosis model over their right hemithoraces using a linear accelerator (6 MV X-ray and 400 monitor units/minute dose rate) on day 0 as described previously.41 This dosage of irradiation did not cause significant systemic toxicities to the mice, and no deaths occurred. The non-irradiated parts of the mouse body were shielded with a multi-leaf collimator. Control mice were subjected to sham irradiation. Two sets of experiment protocols were designed. In the inflammation inhibition experiment, a total of 48 mice were randomly divided into four groups with similar age and body weight for specific experiments (n=12 in each group): a control group, an irradiated group, a group irradiated along with CDDO-Me, and a CDDO-Me only group. CDDO-Me was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide at 10 mM as a stock concentration. The CDDO-Me stock was diluted in sterile normal saline immediately prior to use (the final dimethyl sulfoxide concentration was 0.1%, v/v).
The protective effect of CDDO-Me (400 ng) had been demonstrated in bleomycin-induced lung injury in mice.40 Based on the results of that study, we selected 200, 400, 600, and 800 ng as the candidate doses of CDDO-Me, which were used every other day beginning on day −1 (days −1, 1, 3, and 5) to test the treatment efficiency of CDDO-Me in a RILI mouse model (data not shown). According to the preliminary results of the experiment, we selected 600 ng as the final dose of CDDO-Me to be used in this study. The treatment group received CDDO-Me 600 ng in 200 μL by gavage every other day beginning on day −1 (days −1, 1, 3, and 5). The control mice received 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide in saline only. The mice were humanely euthanized 3 weeks after irradiation. The right lung from six mice in each group were used for bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) analyses. The right lung from other mice in each group were processed for histopathology (upper lobe) or lung homogenates (remaining lobes) for cytokine and gene expression analysis.
For the fibrosis inhibition experiment, the mice was also divided into four groups as described above (n=10 in each group). The treatment group received 600 ng of CDDO-Me in 200 μL by gavage every other day beginning on day −1 (days −1, 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9). The mice were euthanized 12 weeks after irradiation and the lung tissues from ten mice of each group were collected for histology (upper lobe), real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR; middle lobe), and hydroxyproline (remaining lobes) analysis.
BALF analysis
The collected BALF was centrifuged at 700× g and 4°C for 10 minutes. The cell-free supernatant was subsequently stored at −20°C until ready for analyses of protein concentration using a bicinchoninic acid protein assay kit (Kaiji Bio Sci Inc, Nanjing, Jiangsu, People’s Republic of China) according to the manufacturers’ instructions. The sediment cells were stained with May-Grünwald-Giemsa (MGG) stain solution. The percentages of inflammatory cells (including neutrophils and lymphocytes) that were present were assessed by differential counts of 400 cells.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Levels of IL-6, IL-10, and TGF-β cytokines in lung tissue samples were measured with commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits (Cusabio Inc, Wuhan, Hubei, People’s Republic of China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, reactions were conducted in microtiter plate wells that had been precoated with monoclonal antibodies specific for the examined analyte as indicated. A labeled secondary polyclonal antibody was intended to bind to the primary antibody–analyte complex. Following reaction with the substrate solution, the process was terminated and absorbance at 450 nm was determined using a Synergy™ H4 Hybrid microplate reader (Bio-Tek Inc, Winooski, VT, USA). Cytokine values were normalized to total protein in the lung homogenate as determined by the bicinchoninic acid assay (Kaiji Bio Sci Inc) and expressed as ng cytokine/mg total protein.
Hydroxyproline assay
Hydroxyproline (4-hydroxyproline) is a common non-proteinogenic amino acid found only in collagen and elastin in mammals. Collagen deposition was assessed by determining the total hydroxyproline content of lung tissue samples following the procedures described by Woessner.42 In brief, lung tissue was homogenized in 1.5 mL of 5% trichloroacetic acid. Pellets from the homogenates were washed with distilled water and hydrolyzed with 2 mL of 6 N HCl at 100°C overnight. After neutralizing the hydrolysates with NaOH, each sample was assayed by adding 1 mL of 0.05 M chloramine-T solution followed by color development with 1 mL of 20% p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde at 60°C for 20 minutes. Absorbance was read at 550 nm. A standard curve was prepared from purified hydroxyproline (Sigma-Aldrich). The data are expressed as μg hydroxyproline/mg wet lung.
Histopathological analysis
To assess the degree of inflammation and fibrosis in each group, sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Masson’s trichrome stain (Yili Fine Chemicals Co Ltd, Beijing, People’s Republic of China), respectively. At different time points, mice were euthanized, and the right lungs were fixed by intratracheal instillation of 4% paraformaldehyde, allowed to cure overnight, embedded in paraffin, and cut into 5 μm thick sections. Histological signs of tissue inflammation were evaluated in H&E-stained sections by a blinded pathologist. Each section was given a score from 0 to 4 for the area affected by interstitial inflammation, alveolar wall thickening, peribronchial inflammation, and interstitial edema, as previously described.43 A total lung inflammation score was calculated as the sum of these four criteria. The extent of fibrosis was evaluated by staining lung sections with Masson’s trichrome stain according to the manufacturer’s suggested protocol. A modified Ashcroft scoring system was used to evaluate the severity of lung fibrosis.40 Briefly, fibrotic changes in all tissue fields were scored, ranging from 0 to 4, and the mean score was taken as the fibrosis score of that lung section.
RNA preparation and real-time PCR assay
Total RNA was isolated from lung tissue samples with TRIzol® reagent (Invitrogen Inc, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and cDNA was synthesized using a RevertAid™ first-strand cDNA synthesis kit (Thermo Scientific Inc, Wilmington, DE, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. To evaluate the expression of each gene, cDNA was amplified by real-time PCR using Fast SYBR® Green Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc, Beijing, People’s Republic of China) and gene-specific primer mixtures in the Light Cycler® 480 real-time PCR System (Roche Diagnostics Inc, Mannheim, Germany). Primers were synthesized by Sangon Biotech Co Ltd (Shanghai, People’s Republic of China), and the sequences of each primer are described in Table 1. Expression data were normalized to 18S rRNA to control the variability in expression levels and were analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCT method.
  | Table 1 Primer sequences used for the real time-polymerase chain reaction assays |
Statistical analysis
The results are represented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. One-way analysis of variance was used to assess the difference between multiple groups, followed by Tukey’s post hoc tests for intergroup comparisons. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. Analyses were conducted using Prism 5.0 (GraphPad Software Inc, San Diego, CA, USA).
Results
CDDO-Me ameliorates radiation-induced lung inflammation and injury in mice
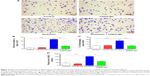
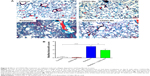
One of the characteristics of radiation-induced lung inflammation is infiltration of inflammatory cells and increased secretion of proteins in BALF.44 Therefore, we evaluated the extent of inflammatory cell infiltration in BALF using MGG staining. As shown in Figure 2A, the number of stained cells in the radiation + CDDO-Me group was lower than in the radiation group, and was comparable with the control group and the CDDO-Me only group. CDDO-Me potently and significantly reduced total radiation-induced cell infiltration in BALF by 69.7% (P<0.001; Figure 2B) and the percentage of inflammatory cells by 60.2% (P<0.01; Figure 2C). Subsequently, we assayed the concentrations of total protein in BALF, an indicator of edema and epithelial barrier breakdown.44 Compared with the radiation group, total protein was significantly suppressed after treatment with CDDO-Me (P<0.001; Figure 2D).
Additionally, we explored the therapeutic effect of CDDO-Me on RILI by scoring the histopathologic abnormalities of H&E-stained lung sections. Lung specimens from the radiation only mice displayed evident histopathologic abnormalities, including alveolar wall thickness, interstitial edema, interstitial inflammation, and peribronchial inflammation (Figure 3A). However, lung specimens from the radiation + CDDO-Me group showed mostly normal bronchioles, alveoli, and blood vessels, with minimal inflammatory infiltrate and hemorrhage, indicating milder lung inflammation when compared with the radiation group (Figure 3A). The score for the H&E-stained lung sections in the radiation + CDDO-Me group was lower than in the radiation group (P<0.001; Figure 3B).
CDDO-Me modulates inflammatory cytokine expression in mice exposed to radiation
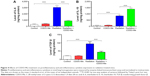
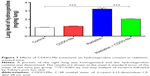
A variety of proinflammatory and profibrotic cytokines and chemokines, including TGF-α, TGF-β, and ILs, have been implicated in the development and persistence of RILI.45,46 To further investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of CDDO-Me on radiation-induced lung inflammation in C57BL/6 mice, we measured levels of inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, IL-10, and TGF-β, by ELISA in lung homogenates from mice 3 weeks after radiation. Basal levels of IL-6 and IL-10 in lung homogenates were 299.84±69.13 ng/mg and 67.89±10.12 ng/mg, respectively. The levels of these two cytokines were elevated in the radiation group. Three weeks after radiation, IL-6 and IL-10 levels in the lung homogenates were increased to 3,021.81±294.26 ng/mg (P<0.001 versus control group) and 834.05±73.65 ng/mg (P<0.001 versus the control group), respectively (Figure 4A and B). For TGF-β, the basal level concentration in lung homogenates was 21.83±1.31 ng/mg (P<0.001 versus the control group; Figure 4C). At 3 weeks post-radiation, the TGF-β concentration increased significantly to 94.06±12.53 ng/mg.
Treatment of CDDO-Me for radiation-challenged mice efficiently suppressed the expression level of IL-6 and elevated the expression level of IL-10. IL-6 and IL-10 levels in lung homogenates from the CDDO-Me + radiation group were 869.49±95.79 ng/mg (P<0.001 versus radiation group) and 1,379.43±88.48 ng/mg (P<0.001 versus radiation group), respectively (Figure 4A and B). In the CDDO-Me +radiation group, the concentration of TGF-β declined significantly to 44.11±5.84 ng/mg (P<0.001 versus radiation group; Figure 4C).
CDDO-Me suppresses upregulated profibrotic genes in mice exposed to radiation
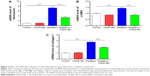
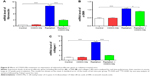
To determine the early antifibrotic effect of CDDO-Me on RILI, we quantified expression levels of three profibrotic genes, including for fibronectin, α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), and collagen I, in mouse lungs using real-time PCR. mRNA levels of fibronectin, α-SMA, and collagen I were all significantly increased at 3 weeks post-radiation. After treatment with CDDO-Me, mRNA levels for fibronectin, α-SMA, and collagen I were reduced by 53.9% (P<0.001 versus radiation group; Figure 5A), 38.7% (P<0.001 versus radiation group; Figure 5B), and 31.4% (P<0.001 versus radiation group; Figure 5C), respectively. These data show that CDDO-Me exerted an early antifibrotic effect via suppression of expression of profibrotic genes in the lung.
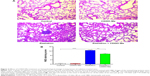
CDDO-Me attenuates radiation-induced lung fibrosis in mice
Because radiation-induced lung inflammation is associated with development of fibrosis,14 the effect of CDDO-Me on this late event was also examined in this study. Mice were euthanized after 12 weeks of radiation, and fibrosis was evaluated by staining collagen fibers with Masson’s trichrome stain. Irradiation caused an increase in collagen fibers supporting the vessel walls and bronchioles, a key outcome measure of fibrosis9 (Figure 6A). Interestingly, the deposition and overall distribution of collagen was restricted in mice receiving CDDO-Me + radiation (Figure 6A). The final semiquantitative Ashcroft scores47 in the radiation group and the CDDO-Me + radiation group were 2.80±0.29 and 1.90±0.31, respectively (P<0.05; Figure 6B).
CDDO-Me reduces lung hydroxyproline content in mice exposed to radiation
The hydroxyproline content in lung tissues reflects the proportion of tissue with collagen fibers, and was measured in this study.42 The lung tissues in the control group contained hydroxyproline at 1.04±0.03 μg/mg lung. The hydroxyproline content increased significantly at 12 weeks post-irradiation (P<0.001; Figure 7). CDDO-Me administration significantly reduced the hydroxyproline content of the lung tissue in radiation-challenged mice (2.05±0.05 μg/mg lung in CDDO-Me + radiation group versus 3.22±0.13 μg/mg lung in radiation only group, P<0.001; Figure 7).
CDDO-Me downregulates biomarkers for lung fibrosis
As in the inflammatory model of this study, three lung fibrosis biomarkers, including fibronectin, α-SMA, and collagen I, were also examined in the fibrosis model using real time-PCR. Consistent with the results in the inflammatory model, mRNA expression levels of fibronectin, α-SMA, and collagen I increased to a greater extent in the radiation group than in the control group. However, administration of CDDO-Me significantly downregulated the mRNA expression levels of these three markers (P<0.001 for fibronectin and collagen I; P<0.05 for α-SMA; Figure 8A–C).
Discussion
Radiation-induced acute inflammatory pneumonitis and late pulmonary fibrosis lead to compromised lung function, affecting the breathing capacity of patients and their quality of life.8,9,14 However, effective therapeutic strategies for these patients are lacking. Therefore, development of novel agents to prevent and treat the two phases of RILI can be of great benefit for this patient population. As a multifunctional agent, the radioprotective potential of CDDO-Me has been tested in previous studies.37–39 The efficiency of CDDO-Me against a heavy ion-induced increase in proliferation rate and anchorage-dependent and anchorage-independent colony formation was demonstrated recently in human corneal epithelial cells.37,38 This effect was likely achieved by induction of Nrf2 by CDDO-Me. Upregulation of Phase II enzymes by Nrf2 reduced oxidative stress, which led to decreases in ROS and DNA double-strand breaks after irradiation. Subsequently, the same group investigated whether CDDO-Me mitigated ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage in immortalized normal corneal and bronchial epithelial cells.39 They showed that CDDO-Me accelerated defense mechanisms involving the epidermal growth factor receptor and DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit pathway in noncancerous human cells, leading to increased repair of DNA damage and cell survival in mice with radiation-induced injury. However, the radioprotective or mitigating effect of CDDO-Me has not been examined in vivo, especially for RILI.
In this study, we explored the therapeutic effect of CDDO-Me on RILI, including radiation-induced inflammation and fibrosis, using a C57BL/6 mouse model. Changes in cell populations in BALF and in permeability have often been considered to reflect inflammatory changes in the lung.44 Hence, the proportions of inflammatory cells and protein concentrations in BALF were measured to estimate the extent of the inflammatory response. It was observed that CDDO-Me significantly decreased the total cell counts and the proportion of inflammatory cells in BALF, and also reduced BALF protein concentrations. Thorax irradiation causes delayed damage to resident lung cells and often results in apoptosis of primarily bronchiolar epithelial cells and loss of barrier function.
Myofibroblasts, which produce collagens I and III, fibronectins, and other matrix molecules, may play a key role in the pathogenesis of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis.48 In addition to resident fibroblasts and circulating fibroblast-like cells, injured lung epithelial cells may be a source of myofibroblasts via EMT, a process by which fully differentiated epithelial cells undergo a phenotypic transition into migratory mesenchymal cells, often fibroblasts and myofibroblasts.49,50 Overall, lung fibroblasts may originate from various sources, such as bone marrow stem cells, resident mesenchymal cells, and epithelial cells.
Thorax irradiation can also trigger recruitment of various immune effector cells into the lung, such as monocytic cells, neutrophils, basophils, and lymphocytes, which are associated with characteristic changes in local and systemic expression of cytokines and chemokines.9,46,51,52 Classical and alternative mechanisms of activating macrophages have been proposed to play a role in RILI and fibrosis. M2 macrophages produce growth factors, including TGF-β1, TNF-α, and other cytokines that stimulate epithelial cells and fibroblasts.9,53,54 Up until now, elevated plasma levels of TGF-β and IL-6, as well as decreased levels of IL-10, have been proposed as biomarkers for radiation-induced lung inflammation.55,56 Thus, these three markers were tested in the current study using ELISA. The results showed that expression levels of the proinflammatory cytokines TGF-β and IL-6 in the lung were strongly suppressed; however, the lung expression level of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was elevated by administration of CDDO-Me.
TGF-β, which is activated at sites of injury after radiation, plays a critical role in the pathological processes of RILI.9,14,46,57 TGF-β is produced by numerous inflammatory, mesenchymal, and epithelial cells, and converts fibroblasts and other cell types into functional myofibroblasts that generate matrix molecules, cytokines, and chemokines.58 Once released, TGF-β mediates signals through pairs of type I and type II receptors. The result of ligand binding is activation of the type II receptor, which then phosphorylates the type I receptor. The active receptor complex then phosphorylates the so-called R (receptor)-Smad2 or Smad3 that propagates the signal.58 TGF-β has a multitude of functions, such as controlling the breakdown of connective tissue, inhibiting epithelial cell proliferation, and contributing to the structural changes that occur during airway remodeling in response to asthmatic inflammation by inducing the synthesis of extracellular matrix proteins, such as collagens and matrix-modifying enzymes, such as matrix metalloproteinases.59,60 TGF-β is important for induction of the fibrosis often associated with the chronic phase of inflammatory disease. The principal function of TGF-β in the immune system is to inhibit proliferation and activation of lymphocytes and other leukocytes.61 Irradiation of the bronchi and alveoli only slightly activated TGF-β1 on day 1 and strongly activated it on day 14 post-irradiation. The first expression peak on day 1 is due to enhanced activation of latent TGF-β1 by extracellular enzymes, while the second peak on day 14 after irradiation is a result of de novo synthesis. This indicates that particular bronchial and alveolar cells may participate in the complex process of radiation-induced lung fibrosis by acting as cellular sources of active TGF-β.62 Irradiation-induced activation of TGF-β1 is rapid, and prolonged exposure to TGF-β1 is a strong stimulus that initiates and maintains EMT in various biological systems and pathophysiological contexts by activating major signaling pathways and transcriptional regulators that are integrated into extensive signaling networks.9,58,61 As a consequence, the extracellular matrix is qualitatively and quantitatively altered. Overexpression of prolyl-hydroxyprolinase-β promotes synthesis of collagen I, III, and IV, while repression of degrading enzymes, such as matrix metalloproteinase-1, and induction of tissue inhibitors suppress the degrading pathways.58
During an immune response, naive CD4+ T helper (Th) cells can differentiate into at least two functional subsets: Th1 cells, which secrete Th1 cytokines, such as IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-2, and IL-12; and Th2 cells, which secrete Th2 cytokines, such as IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-13. Th1 and Th2 cytokines are crucial to Th1 and Th2 immune reactions, both of which promote the proliferation and differentiation of their respective T-cell subsets and inhibit proliferation and differentiation of the opposing subsets of T-cells.63,64 TNF-α is a key mediator in the pathogenesis of RILI and causes cachexia, tissue damage, and irreversible shock effects. IL-2 is important for the growth and activation of T-cells and IFN-γ is an important activator of macrophages and inducer of class II major histocompatibility complex molecule expression. IL-2 is mainly produced by T-cells65 and IFN-γ is produced predominantly by natural killer and natural killer T-cells as part of the innate immune response, and by CD4+ Th1 and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes once antigen-specific immune response is triggered.66 IL-6 is secreted by T-cells and macrophages to stimulate the immune response during infection and after trauma (especially burns, irradiation, and other tissue damage), leading to initiation of the inflammatory process. IL-8 (also called CXCL8 and neutrophil chemotactic factor) is a chemokine produced by macrophages and other cell types, such as epithelial cells, airway smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells. IL-8 induces chemotaxis in target cells (primarily neutrophils but also other granulocytes) toward the site of infection and induces phagocytosis. IL-10 inhibits the secretion of IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-3, TNF-α, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor by activated macrophages and by helper T-cells.63 TNF-α is mainly produced by activated macrophages (M1), although it can be produced by many other cell types such as CD4+ T lymphocytes, monocytes, natural killer cells, neutrophils, mast cells, eosinophils, and neurons.67 The primary role of TNF-α is in regulation of immune cells. TNF-α induces fever, apoptosis, and inflammation, inhibits tumorigenesis and viral replication, and respond to sepsis via IL-1 and IL-6 producing cells.67
The histological changes after administration of CDDO-Me were also evaluated in this study. Irradiated lung tissue showed thickening of the alveolar septa, which is indicative of pneumonitis,57 as well as damage to alveolar structures, bronchioles, and vessel integrity. In radiation-induced lung fibrosis, thickening of the airway wall is characterized by increased fibrotic deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, vascularization, and thickening of the epithelial layer. In contrast, lungs treated with radiation combined with CDDO-Me showed milder pneumonitis.
After irradiation, macrophage infiltration in the lung was observed in our study. Activation of macrophages in the lung is considered to play an important role in the occurrence of RILI.9 IL-1β is produced by activated macrophages as a proprotein, which is proteolytically processed to its active form by caspase 1. This cytokine is an important mediator of the inflammatory response, and is involved in a variety of cellular activities, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Macrophages predominantly expressing the killer phenotype are called M1 macrophages, whereas those involved in tissue repair are called M2 macrophages.68 The primary role of macrophages is to phagocytose or engulf and then digest cellular debris and pathogens; they also stimulate lymphocytes and other immune cells to respond to pathogens. M1 macrophages are activated by IFN-γ and secrete high levels of IL-12 and low levels of IL-10, whereas M2 macrophages secrete high levels of IL-10 and TGF-β and low levels of IL-12.68 IL-12 is involved in stimulation and maintenance of Th1 cellular immune responses and also has an important role in enhancing the cytotoxic function of natural killer cells. Macrophages can be identified by specific expression of a number of proteins including CD14, CD40, CD11b, CD64, F4/80 (mice)/EMR1 (human), lysozyme M, MAC-1/MAC-3, and CD68.
Neutrophilic inflammation is a hallmark characteristic of RILI and fibrosis, and was observed in this study. IL-8 is the main chemotactic mediator for neutrophils, having been established as the key mediator driving neutrophilic inflammation in vitro and in vivo.69 The neutrophil elastase inhibitor sivelestat significantly decreased collagen deposition and neutrophil accumulation in the lung parenchyma and improved the static lung compliance of injured lungs in murine models.70–72 In the case of RILI, the immediate release of proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6, after lung irradiation is closely related to lung toxicity. The increase in these cytokines activates neutrophils, resulting in accumulation of activated neutrophils in the lung and release of elastase. Neutrophil elastase is present in the azurophil granules of neutrophils, which are involved in the non-specific phylaxis of neutrophils. When neutrophils are activated by stimulation, neutrophil elastase is released from the granules extracellularly, thereby accelerating the permeability of the vascular endothelial and alveolar cells of the lung. Due to its low substrate specificity, neutrophil elastase disintegrates the extracellular matrices, including collagen, proteoglycan, and fibronectin, and impairs tissue, thereby causing lung injury.70,72 Neutrophil elastase plays an important role in the development of RILI. Sivelestat sodium hydrate is thus expected to suppress radiation-induced lung toxicity by suppressing release of neutrophil elastase from neutrophils. Therefore, sivelestat is more effective when administered during the early stages of lung injury. Further studies are ongoing to establish the role of sivelestat in the treatment of RILI.
Recent progress in molecular pathology and radiobiology has revealed that duration and severity of acute lung inflammation could increase the risk of late lung fibrosis.14 Therefore, early modulation of profibrotic genes by CDDO-Me was also evaluated in our inflammation model. The results demonstrated that CDDO-Me could downregulate these profibrotic genes, including fibronectin, α-SMA, and collagen I. In light of these results, we are assured that CDDO-Me could effectively act in vivo and have a therapeutic effect in radiation induced lung inflammation.
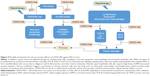
Because CDDO-Me was effective at reducing early inflammation and expression of profibrotic genes (Figure 9), we subsequently checked whether early treatment with CDDO-Me would prevent late development of lung fibrosis. Fibronectin is a key effector in fibrosis because it is involved in cell adhesion and migration, and in binding to integrins, collagen, and other matrix proteins, thus contributing to the overall fibrotic milieu.73–76 Fibronectin is an important component of the extracellular matrix that has been demonstrated to play an active role in the pathogenesis of RILI. Fibronectin directly mediates and enhances migration of small airway and alveolar epithelial cells, and also enhances proliferation of resident lung epithelial cells and airway smooth muscle cells. The function of fibronectin is multifaceted and includes regulation of embryogenesis, mesoderm formation, tissue repair, cell migration, differentiation, and cell growth, as well as certain pathological disorders such as fibrosis, tumor development, and atherosclerosis.77–80 Fibronectin is secreted by cells as a soluble dimer which is then assembled into an insoluble network of fibers. The binding of fibronectin to cell surface integrins initiates conformational changes in the fibronectin molecule that expose self-association sites and formation of an insoluble fibronectin matrix in the extracellular space.79,80 Any stimulus that promote fibrillogenesis will inhibit the turnover, endocytosis, and intracellular degradation of fibronectin. α-SMA is a marker of myofibroblast differentiation and is a sensitive indicator of the presence of fibrogenic cells in lung tissue.81 α-SMA is released in response to myofibroblast activation and confers strong contractile properties. Therefore, fibronectin, α-SMA, and collagen I were selected as biomarkers to estimate the extent of lung fibrosis. Masson’s trichrome staining and hydroxyproline content measurement were also used in the evaluation. It was observed that CDDO-Me significantly decreased mRNA levels of fibronectin, α-SMA, and collagen I, as well as the hydroxyproline content in lung tissue. The amount of lung collagen visualized by Masson’s trichrome staining after irradiation was also substantially suppressed in CDDO-Me-treated mice, as indicated by the Ashcroft score.42 These findings indicate that early administration of CDDO-Me has long-lasting effects on the radiation-induced lung fibrosis process.
There are several limitations to the present study. First, the dose-dependent effect of CDDO-Me was not clearly defined. Thus, the optimal dosage of CDDO-Me in the treatment of RILI needs further investigations. Second, although the anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects of CDDO-Me were identified in this study, the precise biochemical mechanisms of these effects are unclear. Previous studies have shown that oxidative damage and NF-κB play critical roles in the pathogenesis of RILI.18–20,26,27 Accumulating data demonstrate that CDDO-Me is an effective antioxidant agent and that it can blunt activation of NF-κB, which is a central mediator of the inflammatory response and can induce expression of inflammatory cytokines.33 Thus, activating Nrf2 and blunting NF-κB may contribute to the therapeutic effect of CDDO-Me in RILI. However, other Nrf2-independent radioprotective mechanisms for CDDO-Me cannot be excluded, so further mechanistic studies are warranted.
In summary, we provide experimental evidence demonstrating that administration of CDDO-Me during the period of exposure to radiation protects against RILI and suggesting that this compound may represent a new therapeutic strategy to minimize the adverse effects of radiotherapy in patients with cancer, especially thoracic cancer.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81460477) and a research grant from Ningxia Medical University (XM201317).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Kong FM, Zhao L, Hayman JA. The role of radiation therapy in thoracic tumors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006;20(2):363–400. | ||
Rodrigues G, Movsas B. Future directions in palliative thoracic radiotherapy. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2012;6(1):91–96. | ||
Videtic GM. The role of radiation therapy in small cell lung cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2013;15(4):405–410. | ||
Delaney G, Jacob S, Featherstone C, Barton M. The role of radiotherapy in cancer treatment: estimating optimal utilization from a review of evidence-based clinical guidelines. Cancer. 2005;104(6):1129–1137. | ||
Marks LB, Yu X, Vujaskovic Z, Small W Jr, Folz R, Anscher MS. Radiation-induced lung injury. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2003;13(3):333–345. | ||
Madani I, De Ruyck K, Goeminne H, De Neve W, Thierens H, Van Meerbeeck J. Predicting risk of radiation-induced lung injury. J Thorac Oncol. 2007;2(9):864–874. | ||
Williams JP. Assessment of radiation-induced lung disease. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2011;9(2):160–162. | ||
Benveniste MF, Welsh J, Godoy MC, Betancourt SL, Mawlawi OR, Munden RF. New era of radiotherapy: an update in radiation-induced lung disease. Clin Radiol. 2013;68(6):e275–e290. | ||
Ding NH, Li JJ, Sun LQ. Molecular mechanisms and treatment of radiation-induced lung fibrosis. Curr Drug Targets. 2013;14(11):1347–1356. | ||
Chargari C, Riet F, Mazevet M, Morel E, Lepechoux C, Deutsch E. [Complications of thoracic radiotherapy]. Presse Med. 2013;42(9 Pt 2):e342–e351. French. | ||
Robnett TJ, Machtay M, Vines EF, McKenna MG, Algazy KM, McKenna WG. Factors predicting severe radiation pneumonitis in patients receiving definitive chemoradiation for lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;48(1):89–94. | ||
Marks LB, Fan M, Clough R, et al. Radiation-induced pulmonary injury: symptomatic versus subclinical endpoints. Int J Radiat Biol. 2000;76(4):469–475. | ||
Zhao W, Robbins ME. Inflammation and chronic oxidative stress in radiation-induced late normal tissue injury: therapeutic implications. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(2):130–143. | ||
Graves PR, Siddiqui F, Anscher MS, Movsas B. Radiation pulmonary toxicity: from mechanisms to management. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2010;20(3):201–207. | ||
Nieder C, Jeremic B, Astner S, Molls M. Radiotherapy-induced lung toxicity: risk factors and prevention strategies. Anticancer Res. 2003;23(6D):4991–4998. | ||
Brush J, Lipnick SL, Phillips T, Sitko J, McDonald JT, McBride WH. Molecular mechanisms of late normal tissue injury. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2007;17(2):121–130. | ||
Kunwar A, Haston CK. Basal levels of glutathione peroxidase correlate with onset of radiation induced lung disease in inbred mouse strains. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014;307(8):L597–L604. | ||
Robbins ME, Zhao W. Chronic oxidative stress and radiation-induced late normal tissue injury: a review. Int J Radiat Biol. 2004;80(4):251–259. | ||
Terasaki Y, Ohsawa I, Terasaki M, et al. Hydrogen therapy attenuates irradiation-induced lung damage by reducing oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011;301(4):L415–L426. | ||
Rabbani ZN, Mi J, Zhang Y, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor 1a signaling in fractionated radiation-induced lung injury: role of oxidative stress and tissue hypoxia. Radiat Res. 2010;173(2):165–174. | ||
Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Shared principles in NF-kB signaling. Cell. 2008;132(3):344–362. | ||
Hayden MS, Ghosh S. NF-kB, the first quarter-century: remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes Dev. 2012;26(3):203–234. | ||
Alvira CM. Nuclear factor-kB signaling in lung development and disease: one pathway, numerous functions. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2014;100(3):202–216. | ||
Kelly C, Shields MD, Elborn JS, Schock BC. A20 regulation of nuclear factor-kB: perspectives for inflammatory lung disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011;44(6):743–748. | ||
Yao H, Yang SR, Kode A, et al. Redox regulation of lung inflammation: role of NADPH oxidase and NF-kB signalling. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007;35(Pt 5):1151–1155. | ||
Chen MF, Keng PC, Lin PY, Yang CT, Liao SK, Chen WC. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester decreases acute pneumonitis after irradiation in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer. 2005;5:158. | ||
Haase MG, Klawitter A, Geyer P, et al. Sustained elevation of NF-kB DNA binding activity in radiation-induced lung damage in rats. Int J Radiat Biol. 2003;79(11):863–877. | ||
Ostrau C, Hulsenbeck J, Herzog M, et al. Lovastatin attenuates ionizing radiation-induced normal tissue damage in vivo. Radiother Oncol. 2009;92(3):492–499. | ||
Yang HJ, Youn H, Seong KM, et al. Psoralidin, a dual inhibitor of COX-2 and 5-LOX, regulates ionizing radiation (IR)-induced pulmonary inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011;82(5):524–534. | ||
Johnston CJ, Williams JP, Okunieff P, Finkelstein JN. Radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis: examination of chemokine and chemokine receptor families. Radiat Res. 2002;157(3):256–265. | ||
Huang MT, Ho CT, Wang ZY, et al. Inhibition of skin tumorigenesis by rosemary and its constituents carnosol and ursolic acid. Cancer Res. 1994;54(3):701–708. | ||
Nishino H, Nishino A, Takayasu J, et al. Inhibition of the tumor-promoting action of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate by some oleanane-type triterpenoid compounds. Cancer Res. 1988;48(18):5210–5215. | ||
Liby KT, Sporn MB. Synthetic oleanane triterpenoids: multifunctional drugs with a broad range of applications for prevention and treatment of chronic disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2012;64(4):972–1003. | ||
Wang YY, Zhe H, Zhao R. Preclinical evidences toward the use of triterpenoid CDDO-Me for solid cancer prevention and treatment. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:30. | ||
Dinkova-Kostova AT, Liby KT, Stephenson KK, et al. Extremely potent triterpenoid inducers of the phase 2 response: correlations of protection against oxidant and inflammatory stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(12):4584–4589. | ||
Ahmad R, Raina D, Meyer C, Kharbanda S, Kufe D. Triterpenoid CDDO-Me blocks the NF-kB pathway by direct inhibition of IKKb on Cys-179. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(47):35764–35769. | ||
Eskiocak U, Kim SB, Roig AI, et al. CDDO-Me protects against space radiation-induced transformation of human colon epithelial cells. Radiat Res. 2010;174(1):27–36. | ||
Kim SB, Pandita RK, Eskiocak U, et al. Targeting of Nrf2 induces DNA damage signaling and protects colonic epithelial cells from ionizing radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(43):E2949–E2955. | ||
Kim SB, Ly P, Kaisani A, Zhang L, Wright WE, Shay JW. Mitigation of radiation-induced damage by targeting EGFR in noncancerous human epithelial cells. Radiat Res. 2013;180(3):259–267. | ||
Kulkarni AA, Thatcher TH, Hsiao HM, et al. The triterpenoid CDDO-Me inhibits bleomycin-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e63798. | ||
Eldh T, Heinzelmann F, Velalakan A, Budach W, Belka C, Jendrossek V. Radiation-induced changes in breathing frequency and lung histology of C57BL/6J mice are time- and dose-dependent. Strahlenther Onkol. 2012;188(3):274–281. | ||
Woessner JF Jr. The determination of hydroxyproline in tissue and protein samples containing small proportions of this imino acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961;93:440–447. | ||
Cho YJ, Yi CO, Jeon BT, et al. Curcumin attenuates radiation-induced inflammation and fibrosis in rat lungs. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013;17(4):267–274. | ||
Costabel U, Guzman J, Bonella F, Oshimo S. Bronchoalveolar lavage in other interstitial lung diseases. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;28(5):514–524. | ||
Yang X, Walton W, Cook DN, et al. The chemokine, CCL3, and its receptor, CCR1, mediate thoracic radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011;45(1):127–135. | ||
Cappuccini F, Eldh T, Bruder D, et al. New insights into the molecular pathology of radiation-induced pneumopathy. Radiother Oncol. 2011;101(1):86–92. | ||
Ashcroft T, Simpson JM, Timbrell V. Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J Clin Pathol. 1988;41(4):467–470. | ||
Park S, Ahn JY, Lim MJ, et al. Sustained expression of NADPH oxidase 4 by p38 MAPK-Akt signaling potentiates radiation-induced differentiation of lung fibroblasts. J Mol Med (Berl). 2010;88(8):807–816. | ||
Nagarajan D, Melo T, Deng Z, Almeida C, Zhao W. ERK/GSK3beta/Snail signaling mediates radiation-induced alveolar epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012;52(6):983–992. | ||
Jung JW, Hwang SY, Hwang JS, Oh ES, Park S, Han IO. Ionising radiation induces changes associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation and increased cell motility of A549 lung epithelial cells. Eur J Cancer. 2007;43(7):1214–1224. | ||
Wirsdorfer F, Cappuccini F, Niazman M, et al. Thorax irradiation triggers a local and systemic accumulation of immunosuppressive CD4+ FoxP3+ regulatory T cells. Radiat Oncol. 2014;9:98. | ||
Kim KS, Choi KJ, Bae S. Interferon-g enhances radiation-induced cell death via downregulation of Chk1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012;13(11):1018–1025. | ||
Anscher MS, Thrasher B, Zgonjanin L, et al. Small molecular inhibitor of transforming growth factor-b protects against development of radiation-induced lung injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;71(3):829–837. | ||
Abid SH, Malhotra V, Perry MC. Radiation-induced and chemotherapy-induced pulmonary injury. Curr Opin Oncol. 2001;13(4):242–248. | ||
Provatopoulou X, Athanasiou E, Gounaris A. Predictive markers of radiation pneumonitis. Anticancer Res. 2008;28(4C):2421–2432. | ||
Kong FM, Ao X, Wang L, Lawrence TS. The use of blood biomarkers to predict radiation lung toxicity: a potential strategy to individualize thoracic radiation therapy. Cancer Control. 2008;15(2):140–150. | ||
Ghafoori P, Marks LB, Vujaskovic Z, Kelsey CR. Radiation-induced lung injury. Assessment, management, and prevention. Oncology (Williston Park). 2008;22(1):37–47; discussion 52–33. | ||
Pohlers D, Brenmoehl J, Loffler I, et al. TGF-b and fibrosis in different organs – molecular pathway imprints. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1792(8):746–756. | ||
Kim de R, Laurence B, Jan VM, Wilfried de N, Hubert T. Association of TGFb1 polymorphisms involved in radiation toxicity with TGFb1 secretion in vitro. Cytokine. 2010;50(1):37–41. | ||
Chai Y, Lam RK, Calaf GM, Zhou H, Amundson S, Hei TK. Radiation-induced non-targeted response in vivo: role of the TGFb-TGFBR1-COX-2 signalling pathway. Br J Cancer. 2013;108(5):1106–1112. | ||
Li MO, Flavell RA. TGF-b: a master of all T cell trades. Cell. 2008;134(3):392–404. | ||
Almeida C, Nagarajan D, Tian J, et al. The role of alveolar epithelium in radiation-induced lung injury. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53628. | ||
Hawrylowicz CM, O’Garra A. Potential role of interleukin-10-secreting regulatory T cells in allergy and asthma. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5(4):271–283. | ||
Lloyd CM, Hessel EM. Functions of T cells in asthma: more than just TH2 cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10(12):838–848. | ||
Waldmann TA. The biology of interleukin-2 and interleukin-15: implications for cancer therapy and vaccine design. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(8):595–601. | ||
Schoenborn JR, Wilson CB. Regulation of interferon-g during innate and adaptive immune responses. Adv Immunol. 2007;96:41–101. | ||
Locksley RM, Killeen N, Lenardo MJ. The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell. 2001;104(4):487–501. | ||
Mills CD. M1 and M2 macrophages: oracles of health and disease. Crit Rev Immunol. 2012;32(6):463–488. | ||
Mukaida N. Pathophysiological roles of interleukin-8/CXCL8 in pulmonary diseases. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003;284(4):L566–L577. | ||
Fox J, Haston CK. CXC receptor 1 and 2 and neutrophil elastase inhibitors alter radiation-induced lung disease in the mouse. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;85(1):215–222. | ||
Shimbo T, Inomata T, Takahashi M, et al. Effects of sivelestat sodium hydrate on the reduction of radiation pneumonitis. Int J Mol Med. 2007;20(6):817–822. | ||
Yoshikawa N, Inomata T, Okada Y, et al. Sivelestat sodium hydrate reduces radiation-induced lung injury in mice by inhibiting neutrophil elastase. Mol Med Rep. 2013;7(4):1091–1095. | ||
Lim MJ, Ahn J, Yi JY, et al. Induction of galectin-1 by TGF-b1 accelerates fibrosis through enhancing nuclear retention of Smad2. Exp Cell Res. 2014;326(1):125–135. | ||
Fernandes DJ, Bonacci JV, Stewart AG. Extracellular matrix, integrins, and mesenchymal cell function in the airways. Curr Drug Targets. 2006;7(5):567–577. | ||
Gomperts BN, Strieter RM. Fibrocytes in lung disease. J Leukoc Biol. 2007;82(3):449–456. | ||
Oikonomidi S, Kostikas K, Tsilioni I, Tanou K, Gourgoulianis KI, Kiropoulos TS. Matrix metalloproteinases in respiratory diseases: from pathogenesis to potential clinical implications. Curr Med Chem. 2009; 16(10):1214–1228. | ||
Crosby LM, Waters CM. Epithelial repair mechanisms in the lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010;298(6):L715–L731. | ||
Hsu E, Yasuoka H, Feghali-Bostwick CA. Gene expression in pulmonary fibrosis. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2008;18(1):47–56. | ||
Kadler KE, Hill A, Canty-Laird EG. Collagen fibrillogenesis: fibronectin, integrins, and minor collagens as organizers and nucleators. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008;20(5):495–501. | ||
Wight TN, Potter-Perigo S. The extracellular matrix: an active or passive player in fibrosis? Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011;301(6):G950–G955. | ||
Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, Galli A, Bochaton-Piallat ML, Gabbiani G. The myofibroblast: one function, multiple origins. Am J Pathol. 2007;170(6):1807–1816. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.