Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 9
The efficacy and safety of pemetrexed-based doublet therapy compared to pemetrexed alone for the second-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: an updated meta-analysis
Authors Zhong A, xiong X, shi M , xu H
Received 8 May 2015
Accepted for publication 18 June 2015
Published 20 July 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 3685—3693
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S88218
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Wei Duan
Anyuan Zhong,1* Xiaolu Xiong,2* Minhua Shi,1 Huajun Xu3
1Department of Respiratory Diseases, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, 2Department of Endocrinology, Drum Tower Clinical Medical College of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, 3Department of Otolaryngology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People’s Hospital, Otolaryngology Institute of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contribute equally to this work
Background: Pemetrexed is currently recommended as the second-line treatment for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, it is unclear whether pemetrexed-based doublet therapy improves treatment efficacy and safety. Thus, this meta-analysis was performed to resolve this controversial question.
Methods: Electronic databases, including PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were searched for relevant articles before April 2015. Hazard ratios (HRs) were used to estimate overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS), and odds ratios (ORs) were used to analyze the overall response rate (ORR) and grade ≥3 toxicities. Subgroup analysis, sensitivity analysis, and publication bias were also evaluated.
Results: A total of 2,519 patients from ten randomized controlled trials were included. Compared to pemetrexed alone, PFS and ORR significantly improved in the pemetrexed-based doublet group (HR, 0.86; 95% CI [confidence interval], 0.75–0.99; P=0.038; and OR, 1.98; 95% CI, 1.25–3.12; P=0.003, respectively). However, no statistically significant differences in OS were observed between groups (HR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.83–1.02; P=0.132). In addition, subgroup analyses indicated that improved OS was only observed in nonsquamous NSCLC patients who received the combination of pemetrexed and erlotinib. An increasing incidence of grade ≥3 neutropenia and thrombocytopenia was observed in the pemetrexed-based doublet group.
Conclusion: Among patients with advanced NSCLC, pemetrexed-based doublet treatment tended to be associated with improved PFS, ORR, and increased toxicity, but not OS.
Keywords: non-small-cell lung cancer, pemetrexed, second-line, meta-analysis
Introduction
Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality that accounts for 13% and 18% of all cancer-related cases and deaths, respectively, worldwide.1 Approximately, 80%–85% of lung cancer cases are non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). At the time of diagnosis, 75% of patients with NSCLC present with locally advanced or metastatic disease.2 Although surgical excision and chemotherapy are attainable in some patients with advanced NSCLC, the therapeutic options for locally advanced or metastatic disease remain limited.
Platinum-based doublets are recommended as the first-line treatment for advanced NSCLC.3 However, after cytotoxic therapy, 60%–70% of patients exhibit an initial nonresponse and the disease eventually progresses.4 Therefore, a second-line therapy is required. Docetaxel is the standard second-line treatment for advanced NSCLC.5,6 Pemetrexed, another chemotherapy drug, was also approved for the second-line treatment of advanced NSCLC, and it resulted in equivalent outcomes to docetaxel in a randomized Phase III trial.7 The use of either docetaxel or pemetrexed alone has several limitations, with a median survival time of 8 months, a 1-year survival rate of 30%, and a response rate of 10%.8 Compared to docetaxel, pemetrexed results in fewer adverse events with comparable efficacy.9 Thus, pemetrexed-based combination chemotherapy is a potential approach to combining several different agents and enhancing the antitumor effects in patients with advanced NSCLC.
Recently, several randomized controlled trials (RCTs) compared pemetrexed-based doublet therapy with pemetrexed alone as a second-line treatment for advanced NSCLC.10–19 However, the conclusion drawn from these small-sample-size studies were inconsistent. Although previous meta-analyses conducted by Qi et al20 and Sun et al21 showed that the combination of pemetrexed and chemotherapy was not superior to single-agent pemetrexed as a second-line treatment for NSCLC, these analyses only included four and five studies, respectively, which is only ~50% of the available data. In addition, subgroup and sensitivity analyses were not performed, so the results might not be robust. Therefore, we conducted a meta-analysis to solve the abovementioned deficiencies and provide a more reliable conclusion.
Materials and methods
Search strategy
Electronic databases, including PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were searched up to April 2015 using the following terms: “non-small-cell lung cancer”, “pemetrexed”, “second-line therapy”, and “randomized”. Abstracts from the annual meetings of the European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) and the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) in the past 10 years were also retrieved. The references of the included studies were also screened manually. No language limitation was applied.
Selection criteria
The relevant clinical trials were selected manually based on the following criteria: 1) trials that compared pemetrexed-based doublet with single-agent pemetrexed; 2) patients diagnosed pathologically with NSCLC and treated previously; 3) randomized Phase II and III RCTs; and 4) studies with sufficient data for extracting at least one overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), overall response rate (ORR), and grade 3 or 4 toxicities. The exclusion criteria were as follows: 1) non-RCTs, 2) truncated RCTs (since truncated RCTs could provide misleading estimates of treatment effects),22 and 3) ongoing studies. If duplicate trials were reported, only the most complete study was included.
Data extraction
Two reviewers (Zhong AY and Xiong XL) extracted the data independently. If a disagreement between reviewers occurred, a third reviewer (Xu HJ) participated, and the issue was resolved by group discussion. The data extracted from the included studies were as follows: authors, publication year, Phase, number of patients analyzed, number of patients per arm, median age, percentage of male subjects, percentage of smokers, percentage of patients with squamous carcinoma, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS). Hazard ratios (HRs) for OS and PFS, odds ratios (ORs) for ORR and grade 3 or 4 toxicities, and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were also extracted.
Quality assessment
The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias was used to evaluate the quality of the included RCTs, based on the following criteria related to random sequence generation: allocation concealment; blinding of patients, personnel, outcome assessors; incomplete outcome data; selective reporting.23
Data analysis
HRs were used to estimate OS and PFS, and ORs were used to analyze ORR and grade 3 or 4 toxicities. Interstudy heterogeneity was assessed using Cochran’s test (P<0.1). The I2 statistic was also calculated, and an I2>50% indicated significant heterogeneity across studies.24 A random-effects model was used if significant heterogeneity was seen among the trials.25 Otherwise, the results were obtained from a fixed-effects model.26 Subgroup analyses were performed according to the stratified phase, agent, and histology. Sensitivity analyses were performed by omitting one study each time. Publication bias was evaluated using subjective funnel plots and objective Begg’s and Egger’s tests.27,28 All of the data analyses were performed using STATA software (version 12.0, StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA). In addition to a special statement, P<0.05 was considered to be significant.
Results
Search results
A total of 300 potentially relevant references identified in electronic databases were reviewed, 110 were excluded because they were duplicate studies. After reviewing the titles and abstracts, another 153 studies were excluded for the following reasons: 42 were abstracts and case reports, 65 were non-RCTs, 9 were randomized Phase I trials, 15 were meta-analysis, 20 were not relevant to NSCLC, and 2 were truncated RCTs.29,30 Thus, a total of 37 potentially eligible articles were considered for further analysis. Another 27 articles were excluded because they did not compare pemetrexed-based doublet with pemetrexed alone. Finally, ten randomized trials were eligible for inclusion in this meta-analysis. A flowchart showing the study selection process is shown in Figure 1.
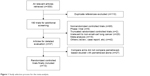  | Figure 1 Study selection process for the meta-analysis. |
Characteristics of the included studies
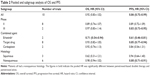
In total, ten trials that pooled 1,281 patients in the pemetrexed-based doublet arm and 1,238 patients in the pemetrexed-alone arm were included in this meta-analysis. Of the ten studies, eight were randomized Phase II trials,10–13,15,16,18,19 and the other two were randomized Phase III trials.14,17 Among these studies, two compared pemetrexed plus carboplatin with pemetrexed alone,10,15 two compared pemetrexed plus erlotinib with pemetrexed alone,16,18 one compared pemetrexed plus enzastaurin with pemetrexed alone,11 one compared pemetrexed plus bortezomib with pemetrexed alone,12 one compared pemetrexed plus matuzumab with pemetrexed alone,13 one compared pemetrexed plus vandetanib with pemetrexed alone,14 one compared pemetrexed plus nintedanib with pemetrexed alone,17 and one compared pemetrexed plus eribulin mesylate with pemetrexed alone.19 Using the Jadad scale, three trials scored 5, two scored 4, four scored 3, and one scored 2. The baseline characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 1.
  | Table 1 Baseline characteristics of the included studies |
Pooled analysis
OS and PFS
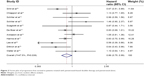
The pooled HR for OS revealed that there were no significant differences between pemetrexed-based doublet therapy and pemetrexed alone (HR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.83–1.02; P=0.137). In addition, no significant interstudy heterogeneity was found (I2=28.5%, P=0.174; Figure 2). Regarding PFS, the pooled HR demonstrated that pemetrexed-based doublet therapy was associated with a 14% reduced risk of progression compared to pemetrexed alone (HR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.75–0.99; P=0.038). There was some heterogeneity among the included studies (I2=47.5%, P=0.039; Figure 3).
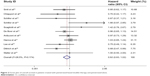  | Figure 2 Forest plot of overall survival in patients treated with pemetrexed-based doublet therapy and pemetrexed alone. |
Subgroup analysis
As shown in Table 2, subgroup analyses were performed according to trial phase, agents and trial histology. Compared to pemetrexed alone, an improved PFS was observed in Phase III trials (HR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.73–0.95; P=0.005) in those that received a combination with erlotinib (HR, 0.61; 95% CI, 0.46–0.81; P=0.001), treated with targeted drug (HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.77–0.94; P=0.001), and with a non-squamous histology (HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.71–0.91; P=0.001). Regarding OS, a prolonged survival time was observed in nonsquamous NSCLC patients who received the combination of pemetrexed and erlotinib (HR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.54–0.94; P=0.02). No statistically significant differences were observed in other subgroup analyses.
Overall response rate
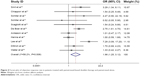
As shown in Figure 4, pemetrexed-based doublet therapy significantly improved ORR in patients with advanced NSCLC compared with pemetrexed alone (OR, 1.98; 95% CI, 1.25–3.12; P=0.003). Moderate heterogeneity was noted among studies (I2=58.2%, P=0.008).
Safety
There were significantly higher incidences of grade 3–4 neutropenia and thrombocytopenia in the pemetrexed-based doublet arm compared with the single-agent pemetrexed arm. However, there were no significant differences in the incidence of grade 3–4 anemia, fatigue, or leukopenia between groups (Table 3). Except for the grade 3–4 anemia and leukopenia, no significant interstudy heterogeneity was observed.
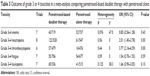  | Table 3 Outcome of grade 3 or 4 toxicities in a meta-analysis comparing pemetrexed-based doublet therapy with pemetrexed alone |
Sensitivity analyses
Sensitivity analyses were performed to assess the stability of this meta-analysis by omitting individual trials sequentially. No single trial significantly altered the pooled results for OS (HRs ranged from 0.88 to 0.95), PFS (HRs ranged from 0.83 to 0.88), and ORR (ORs ranged from 1.65 to 2.06).
Publication bias
No significant asymmetry was observed in funnel plots (data not shown). In addition, Begg’s and Egger’s linear regression tests revealed an absence of publication bias (OS: P=0.50 and 0.62; PFS: P=0.67 and 0.74; and ORR: P=0.76 and 0.87, respectively).
Discussion
In this meta-analysis, data from 10 RCTs including 2,519 patients with advanced NSCLC were pooled, and the efficacy and safety of pemetrexed-based doublet therapy and pemetrexed alone were compared. Overall, the pooled analysis demonstrated that pemetrexed-based doublet treatment increased ORR and PFS compared to pemetrexed alone. However, there was no difference in OS between the two arms. Regarding toxicity, a higher frequency of drug-related grade 3–4 neutropenia and thrombocytopenia was observed in the pemetrexed-based doublet arm.
Pemetrexed, a novel multitargeted agent, inhibits a series of folate-requiring enzymes (including thymidylate synthase, dihydrofolate reductase, and glycinamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase) and prevents tumor cell growth.31 It is now recommended as a second-line treatment for patients with advanced NSCLC; however, the ORR is low and the survival time is limited in these patients.8 One of the traditional strategies to enhance the antitumor effects is combination chemotherapy. However, the results of RCTs conducted to evaluate and compare the efficacy of pemetrexed-based doublet with pemetrexed alone for the treatment of advanced NSCLC are inconsistent; therefore, whether pemetrexed alone or pemetrexed-based doublet is the optimal second-line treatment for advanced NSCLC remains controversial. These inconsistent results could be explained by several factors. First, different chemotherapy regimens were used for the first-line treatment in the different randomized trials, which might influence subsequent treatments. Second, the drugs added to pemetrexed in the combination arm varied, namely, carboplatin,10,15 enzastauri,11 bortezomib,12 matuzumab,13 vandetanib,14 erlotinib,16,18 nintedanib,17 and eribulin19 were used. Finally, different histological types of NSCLC might affect the results because some RCTs only included nonsquamous tumors,16–19 whereas others included all histological carcinomas.10–15
This meta-analysis was performed to resolve this controversial question. Our results showed that pemetrexed-based doublet therapy significantly improved PFS and ORR. However, with respect to survival outcomes, the improvement in PFS failed to translate into OS benefits. This was mostly due to the confounding effects from subsequent treatments. For example, in a Phase II trial,13 of patients in the pemetrexed plus weekly matuzumab group, 37% received further chemotherapy (any) and 20% continued with an anti-EGFR treatment comprised of any EGFR TKI (tyrosine-kinase inhibitor) as subsequent therapy, compared with 20% and 30% in the pemetrexed alone group, compared with and 26% and 11% patients in the pemetrexed plus matuzumab every 3 weeks group. Additionally, in a randomized, double-blind Phase III trial,14 ~50% of patients received some form of subsequent cancer therapy in this study, differences in response to postprogression therapy between treatment groups may have influenced the OS outcome. Since more and more active agents are emerging for the treatment of NSCLC, a PFS advantage is rarely associated with an OS advantage.32,33 More work is still required to demonstrate the impact of PFS on OS.
Toxicity is particularly noteworthy in the second-line therapy of advanced NSCLC because most patients with NSCLC have suffered a long period of increasing frailty. In addition, toxicity could have a negative effect on quality of life. Regarding grade 3–4 toxicity profiles, the current meta-analysis demonstrated that there were more incidences of grade 3–4 neutropenia (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.45–2.78; P<0.001) and thrombocytopenia (OR, 3.77; 95% CI, 2.16–6.59; P<0.001) in the pemetrexed-based doublet treatment group compared to pemetrexed alone. Thus, more toxic effects were observed in patients with advanced NSCLC when more chemotherapy agents were administered.
Significant statistical interstudy heterogeneity was observed in PFS and ORR. The primary source of heterogeneity might arise from confounding factors among studies, including different baseline populations, study design, and data sources. Therefore, we performed a subsequent subgroup analysis stratified according to phase, agent, and histology, and the results showed that the heterogeneity disappeared in PFS subgroups according to randomized Phase III trials, combination treatment with erlotinib, and nonsquamous NSCLC, suggesting that phase, the combination agent used, and the histology might be sources of heterogeneity for PFS. However, none of abovementioned factors could explain the heterogeneity in ORR (data not shown). Interestingly, a prolonged survival time was observed in nonsquamous patients with advanced NSCLC who received the combination of pemetrexed and erlotinib. However, this conclusion is not definitive because only two RCTs were pooled.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the most comprehensive meta-analysis pooling well-designed RCTs, performed to date, to compare the efficacy and safety of pemetrexed-based doublet treatment versus pemetrexed alone in advanced NSCLC, using adequate methodology. It is noteworthy that no publication bias was detected in this meta-analysis, and no single study altered the results. All of the abovementioned statistical analyses showed that the results were robust. Nevertheless, several limitations still need to be addressed. First, some potentially relevant studies were excluded due to missing or unavailable data. Second, the total sample size included in this meta-analysis was relatively small. Finally, the treatment schedules and drugs added to the standard second-line chemotherapy in the combination arm differed.
In conclusion, the treatment of advanced NSCLC patients using pemetrexed-based doublet therapy improved PFS and ORR, but not OS, and it also increased toxicity. Thus, the use of pemetrexed-based combination chemotherapy as second-line treatment for NSCLC patients should be considered carefully. Additional RCTs with larger samples are warranted to confirm these findings. The effectiveness of other chemotherapy drugs in combination with pemextred needs to be evaluated for the treatment of NSCLC.
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81272610 to MH Shi).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. | ||
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. | ||
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, et al. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:92–98. | ||
Stinchcombe TE, Socinski MA. Current treatments for advanced stage non-small cell lung cancer. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2009;6:233–241. | ||
Shepherd FA, Dancey J, Ramlau R, et al. Prospective randomized trial of docetaxel versus best supportive care in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:2095–2103. | ||
Marinis F, Grossib F. Clinical evidence for second- and third-line treatment options in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Oncologist. 2008;13:14–20. | ||
Hanna N, Shepherd FA, Fossella FV, et al. Randomized phase III trial of pemetrexed versus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1589–1597. | ||
Arrieta O, Villarreal-Garza C, Pachuca D, et al. High response of second-line chemotherapy with pemetrexed or gemcitabine combined with carboplatin in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer experiencing progression following 6 months after concluding platinum-based chemotherapy. Med Oncol. 2011;8:300–306. | ||
Barlési F, Jacot W, Astoul P, Pujol JL. Second-line treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review. Lung Cancer. 2006;51:159–172. | ||
Smit EF, Burgers SA, Biesma B, et al. Randomized phase II and pharmacogenetic study of pemetrexed compared with pemetrexed plus carboplatin in pretreated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:2038–2045. | ||
Chiappori A, Bepler G, Barlesi F, et al. Phase II, double-blinded, randomized study of enzastaurin plus pemetrexed as second-line therapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5:369–375. | ||
Scagliotti GV, Germonpré P, Bosquée L, et al. A randomized phase II study of bortezomib and pemetrexed, in combination or alone, in patients with previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2010;68:420–426. | ||
Schiller JH, von Pawel J, Schütt P, et al. Pemetrexed with or without matuzumab as second-line treatment for patients with stage IIIB/IV non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5:1977–1985. | ||
De Boer RH, Arrieta Ó, Yang CH, et al. Vandetanib plus pemetrexed for the second-line treatment of advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer: a randomized, double-blind phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1067–1074. | ||
Ardizzoni A, Tiseo M, Boni L, et al. Pemetrexed versus pemetrexed and carboplatin as second-line chemotherapy in advanced non–small-cell lung cancer: results of the GOIRC 02-2006 randomized phase II study and pooled analysis with the NVALT7 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:4501–4507. | ||
Lee DH, Lee JS, Kim SW, et al. Three-arm randomised controlled phase 2 study comparing pemetrexed and erlotinib to either pemetrexed or erlotinib alone as second-line treatment for never-smokers with non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49:3111–3312. | ||
Hanna NH, Kaiser R, Sullivan RN, et al. Lume-lung 2: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, phase III study of nintedanib plus pemetrexed versus placebo plus pemetrexed in patients with advanced nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) after failure of first-line chemotherapy [Abstract 8034]. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31. | ||
Dittrich C, Szekely ZP, Vinolas N, et al. A randomised phase II study of pemetrexed versus pemetrexed + erlotinib as second-line treatment for locally advanced or metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:1571–1580. | ||
Waller CF, Vynnychenko I, Bondarenko I, et al. An open-label, multicenter, randomized phase Ib/II study of eribulin mesylate administered in combination with pemetrexed versus pemetrexed alone as second-line therapy in patients with advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2015;16(2):92–99. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2014.10.001. | ||
Qi WX, Tang LN, He AN, Shen Z, Yao Y. Effectiveness and safety of pemetrexed-based doublet versus pemetrexed alone as second-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138:745–751. | ||
Sun CT, Xu X, Sheng W, Wang XW, Wen SL, Han JQ. A meta-analysis of pemetrexed-based doublet compared with pemetrexed alone for the second-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2014;115:233–237. | ||
Bassler D, Briel M, Montori VM, et al. Early termination of clinical trials may overestimate treatment effects. JAMA. 2010;303:1180–1187. | ||
Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, et al. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta-analyses? Lancet. 1998;352:609–613. | ||
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–560. | ||
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7:177–188. | ||
Mantel N, Haenszel W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959;22:719–748. | ||
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315:629–634. | ||
Stuck AE, Rubenstein LZ, Wieland D. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Asymmetry detected in funnel plot was probably due to true heterogeneity. BMJ. 1998;316:469–470. | ||
Rudin CM, Brahmer JR, Juergens RA, et al. Phase 2 study of pemetrexed and itraconazole as second-line therapy for metastatic nonsquamous non–small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013;8:619–623. | ||
Heist RS, Wang X, Hodgson L, et al. A randomized phase II study to assess the effiacy of pemetrexed or sunitinib or pemetrexed plus sunitinib in the second-line treatment of advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9:214–221. | ||
Adjei AA. Pemetrexed (Alimta): a novel multitargeted antifolate agent. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2003;3:145–156. | ||
Soria JC, Massard C, Le Chevalier T. Should progression-free survival be the primary measure of efficacy for advanced NSCLC therapy? Ann Oncol. 2010;21:2324–2332. | ||
Hotta K, Suzuki E, Di Maio M, et al. Progression-free survival and overall survival in phase III trials of molecular-targeted agents in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2013;79:20–26. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.