Back to Journals » Clinical Ophthalmology » Volume 9
Femtosecond laser-assisted implantation of complete versus incomplete rings for keratoconus treatment
Authors Hosny M , Mayah E, Sidky MK , Anis M
Received 6 September 2014
Accepted for publication 1 November 2014
Published 20 January 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 121—127
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S73855
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Mohamed Hosny, Esraa El–Mayah, Mohamed Karim Sidky, Mohamed Anis
Department of Ophthalmology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt
Purpose: To compare complete versus incomplete ring implantation for keratoconus correction.
Methods: We investigated 25 eyes of keratoconic patients, of which 15 had femtosecond-assisted MyoRing corneal implantation (Group 1) and 10 had femtosecond-assisted Keraring segments (Group 2). Uncorrected distance visual acuity (UCVA), best corrected distance visual acuity (BCVA), mean K (Km), sphere, topographic cylinder, and corneal asphericity value (Q-value) were measured in all eyes preoperatively and at 4 weeks postoperatively (1 month).
Results: In Group 1, the Km change was -6.15±2.16 D, with a mean change in sphere of 4.45±2.18 D and a mean change in refractive cylinder of 2.32±3 D. UCVA change was -0.57±0.273 logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution (LogMAR), BCVA change was -0.2±0.27 (LogMAR), and the Q-value change was 0.43±2.6. In Group 2, the Km change was -3.15±1.68 D, UCVA change was -0.48±0.37 (LogMAR), BCVA change was -0.09±0.15 (LogMAR), and the Q-value change was 0.5±0.21. Changes in the means did not significantly differ between groups, except for the Km change, which was significantly greater in Group 1 than in Group 2 (P=0.05).
Conclusion: Both complete ring and ring segment implantation are effective for improving corneal and visual parameters in keratoconus. Complete ring implantation may have a greater flattening effect on the anterior corneal surface.
Keywords: KeraRing, MyoRing, keratoconus, femtosecond
Introduction
Keratoconus is a noninflammatory ectatic disorder that usually manifests at puberty. In keratoconus, the cornea assumes a conical shape due to a gradually progressive thinning of the corneal stroma. This effect is almost always bilateral and asymmetrical. It leads to significant visual impairment, irregular astigmatism, and high myopia, and it is the leading cause of corneal transplantation in developed countries.1 Keratoconus management varies depending on the disease severity. Traditionally, incipient cases are managed with spectacles, mild-to-moderate cases with contact lenses, and severe cases can be treated with keratoplasty. Other surgical treatment options include intracorneal ring segments (ICRS), corneal cross-linking, laser procedures (such as photorefractive keratectomy [PRK], phototherapeutic keratectomy [PTK], and laser in situ keratomileusis [LASIK]), intraocular lens implants, or a combination of these procedures.2
The concept of using an intrastromal full ring as an additive refractive technique for myopia correction was first proposed in 1978.3 Such implantation is intended to minimize the spherocylindrical error by modifying the central corneal curvature and reducing the corneal higher-order aberrations by regularizing the corneal surface.4 The addition of extra material at the corneal mid-periphery induces forward displacement of the local anterior surface in this area, and a flattening of the central portion of the anterior cornea caused by the morphologic structure of the corneal lamellae (arc-shortening effect).5 The initially developed full rings were inserted through a peripheral single corneal incision into a circumferential corneal channel.6,7 However, this technique was difficult and associated with potential incision-related complications. Thus, the implants were refashioned into incomplete rings (ICRS).3
Keraring (Mediphacos Inc., Belo Horizonte, Brazil) is an ICRS that is used to treat keratoconus. It acts by regularizing the anterior corneal surface, thus decreasing the myopia and regular and irregular astigmatism. They are available in different arc lengths and are made of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA). They are triangular in cross section in contrast to other ICRS such as Ferrara rings and they have a 600 μm base and an apical diameter of 5 mm. They come in different thicknesses: 0.15, 0.20, 0.25, 0.30, and 0.35 mm.8
It has been proven that the change in the corneal biomechanics induced by any ICRS is directly proportional to its thickness and inversely proportional to its diameter.9,10
Channel creation for kerarings can be done either by a manual technique or using a femtosecond laser under topical anesthesia. The advent of the femtosecond laser has made the procedure safer, more accurate, and easier.6,11,12
Other advantages of femtosecond laser include less discomfort to the patient and better patient cooperation, precise control of tunnel depth, width, and centration.13,14
In 2008, the concept of an intracorneal full ring for myopia correction reappeared with an innovative implantation technique, called the corneal intrastromal implantation system (CISIS), which involves the insertion of a MyoRing flexible full-ring implant (DIOPTEX GmBH, Linz, Austria) into a corneal pocket.9 The MyoRing is currently available in a diameter range of 5–8 mm and a thickness range of 200–400 μm in 20 μm increments. The width of the ring body is 0.5 mm. The anterior surface is convex and the posterior surface is concave, with a radius of curvature of 8.0 mm. This particular shape and dimensions permit folding, which makes implantation in the pocket feasible via a small incision.6 This procedure involves the creation of an almost entirely closed intrastromal pocket, followed by placement of the complete ring within the stroma through a small incision tunnel. The intrastromal pocket is typically created using the PocketMaker (DIOPTEX GmBH), a mechanical device specifically developed for complete intrastromal corneal ring. MyoRing implantation using this mechanically guided procedure has been proven to be safe and effective in decreasing myopia, corneal steepness, and decentration of the corneal apex and for the treatment of keratoconus.5,6 However, it is well known that femtosecond laser technology allows a surgeon to program a corneal stromal dissection at a predetermined depth with an extremely high degree of accuracy, thus avoiding the potential inaccuracies of a mechanical dissection that is dependent on the surgeon’s manual skills.15,16
In this study, we evaluated the clinical results – including visual, refractive, and keratometric outcomes – after implantation of a full ring (MyoRing; DIOPTEX GmBH) versus an ICRS (Keraring; Mediphacos Inc.) by means of femtosecond laser technology in eyes with keratoconus.
Patients and methods
We conducted a prospective, nonrandomized, interventional clinical study, examining a total of 25 eyes of 22 patients who had been diagnosed with keratoconus according to standard criteria based on slit-lamp observation and corneal topography. Keratoconus cases were classified according to the Amsler–Krumeich grading system. Of the 25 investigated eyes, 15 eyes were treated with femtosecond-assisted MyoRing corneal implantation (Group 1) with a mean age of 22.4 years and 10 eyes with femtosecond assisted Keraring segments (Group 2) with a mean age of 25.5 years old. One patient underwent combined MyoRing implantation and corneal cross-linking (“Epi on” technique). Another patient underwent bilateral MyoRing implantation, having been previously treated with corneal cross-linking. Three patients underwent bilateral MyoRing implantation in the same sitting.
Inclusion criteria were reduced spectacle correction or contact lens intolerance, and a Kmax of between 42 and 65 D. Exclusion criteria were as follows: unrealistic expectations, corneal scarring, pachymetry apex <380 μm, previous corneal surgeries, other ocular pathology (eg, glaucoma or iridocyclitis), intense atopy that should have been treated previously, systemic diseases that likely affect wound healing (eg, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus), spherical equivalent of plano or hyperopia. Collagen vascular diseases, autoimmune or immunodeficiency diseases, pregnancy or nursing, ocular conditions (eg, corneal erosion syndrome or corneal dystrophies) that may predispose the patient to future complications, and use of certain medications (isotretinoin, amiodarone, or sumatriptan). No particular scotopic pupil sizes were considered inclusion or exclusion criteria. Previous corneal cross-linking was not considered an inclusion or exclusion criterion. Informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Preoperative assessment
All patients were subjected to a comprehensive preoperative examination, which included manifest refraction, slit-lamp bimicroscopy, Goldmann applanation tonometry, fundus examination, and corneal topographic analysis with the Costruzione Strumenti Oftalmici (CSO) topography system (CSO, Florence, Italy), the WaveLight® Oculyzer™, and the Topolyzer™ VARIO™ diagnostic devices. The preoperative examination also included measurements of Snellen uncorrected distance visual acuity (UCVA), best corrected distance visual acuity (BCVA), and the Q-value of the anterior corneal surface at a 6 mm diameter.
Patient preparation
The procedure was performed under topical anesthesia using benoxinate hydrochloride. This was followed by application of topical moxifloxacin (Alcon, Fort Worth, TX, USA) eye drops as a prophylaxis against infection. Povidone iodine (Betadine) 5% was used to sterilize the eye, and povidone iodine 10% was used to sterilize the eyelids and surrounding skin. A plastic sterile drape (Opsite) was applied to draw away the lashes, followed by the application of a wire speculum to separate the eyelids.
Surgical procedure
Pocket formation
In all cases, the pocket for MyoRing implantation was created using the 150 kHz femtosecond technology (IntraLase, Advanced Medical Optics Inc., Santa Ana, CA, USA). After anesthetic application, IntraLase pocket creation began with fixation of a vacuum ring to the eye. The vacuum is created manually using a suction syringe attached to the vacuum ring.
The next step is to bring the sterile disposable docking cone, which mounts on the head of the laser, down onto the eye. This step has changed over time, with “soft docking” being the method of choice since it uses the smallest possible amount of applanation pressure to create the flap. This procedure has the advantages of using less pressure and creating less tension in the cornea, which minimizes significantly the incidence of opaque bubble layer creation.
This procedure results in the creation of an almost entirely closed intrastromal pocket of 9 mm in diameter and 300 μm in depth. Following pocket creation, the MyoRing was inserted into it via a temporal incision with an arc length determined according to the size of the ring (0.25 mm less than the size of the ring). Another 2 mm nasal incision was routinely made for ring adjustment. This double incision approach has not previously been described and was used for the first time in this study.
MyoRing implantation
After creation of the pocket, a space was gently formed by passing a spatula through the temporal incision between the closed flap and the bed. Then the MyoRing – selected according to the previously mentioned nomogram – was inserted into this corneal tunnel via the temporal incision. The ring was introduced using a special forceps with a groove to accommodate the ring (modified Macpherson forceps) (Figure 1). The ring was then adjusted to be centered on the corneal reflex, by pushing the ring with a sinskey hook inserted through the nasal incision. The procedure was self-sealing and no suturing was required. After MyoRing implantation, the pocket was irrigated with saline to remove air bubbles; then moxifloxacin (Alcon) was injected into the pocket. Finally, a soft contact lens was applied.
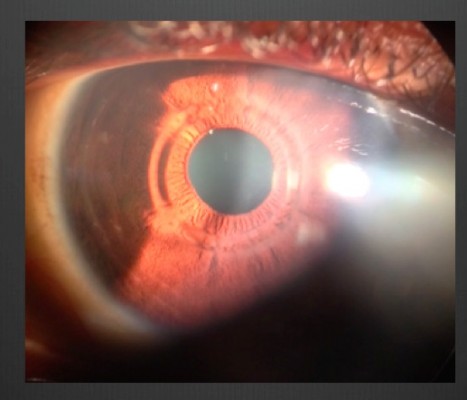
  | Figure 1 MyoRing in place 2 days postoperatively. |
Although the MyoRing is made of PMMA, its particular design allows significant compression without the risk of breakage. Therefore, the MyoRing inflates to its original preoperative circular shape once placed into the pocket. Smaller diameter and greater thickness can be used to achieve a higher corrective effect. Pupil size may be a limiting factor, but this was of less importance here than in the treatment of high myopia.
Keraring implantation
Femtosecond laser (FS 200) is used to create the tunnels. The incision is planned on the steep axis with 80% depth of the thinnest location at an optical zone 5 mm with a width of 1 mm; then the pockets are opened using a blunt sinskey and the kerarings are implanted according to the treatment nomogram.
Postoperative management
The following was prescribed for all patients: topical moxifloxacin (Alcon) eye drops, five times daily for 1 week; topical flourometholone (Allergan Inc., Irvine, CA, USA) eye drops, four times daily for 1 week; topical lubricant refresh liquigel (Allergan Inc.), four times daily for 1 month; vitamin C sachets, once daily for 1 month; Voltaren tablets for pain, as needed for the first 2 days, after meals. Postoperative visits were scheduled for the first postoperative day, and at 1 week and 1 month after surgery. On the first postoperative day, UCVA measurement and slit-lamp examination (MyoRing position and corneal integrity) were performed. At 1 week after surgery, the treatment was adjusted. At 1 month after surgery, the preoperative examinations were performed again. The main outcome measures of the study included UCVA, BCVA, manifest refraction, K readings, corneal thickness, and the Q-value of the anterior corneal surface at a 6 mm diameter.
Statistical analysis
Microsoft Excel 2010 and MedCalc were used for statistical analysis. For all data, normality was first checked using the Kolmogorov Smirnov test. When parametric analysis was possible, the Student’s t-test for paired data was performed for all parameter comparisons between preoperative and postoperative examinations. When parametric analysis was not possible, the Wilcoxon rank-sum test was applied to assess the significance of differences between preoperative and postoperative data. Differences were considered significant when P<0.05. Correlation coefficients (Pearson or Spearman, depending on whether normality could be assumed) were used to assess the correlation between different clinical variables. When reviewing the outcomes of the statistical analysis, it should be considered that the sample size was small, and therefore, there was only limited statistical power.
Results
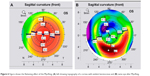
In Group 1, the mean K (Km) change was −6.15±2.16 D (P=0.0004), with a mean change in sphere of 4.45±2.18 D (P=0.0003) and a mean change in refractive cylinder of 2.32±3 D (P=0.0043). The average preoperative UCVA (LogMAR [logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution]) is 1.21±0.26, while the average postoperative UCVA (LogMAR) is 0.63±0.27, with an UCVA change of −0.57±0.273 (LogMAR). The average preoperative BCVA (LogMAR) is 0.47±0.23, while the average postoperative BCVA (LogMAR) is 0.27±0.24, with a change in the BCVA of −0.2 (LogMAR), and the Q-value change was 0.43±2.6. In Group 2, the Km change was −3.15±1.68 D, and the mean change in the sphere was 2.5±6 D, while the mean change in the refractive cylinder was 0.9±3.8. The average preoperative UCVA (LogMAR) is 0.89±0.46, while the average postoperative UCVA (LogMAR) is 0.55±0.21, with a change in the UCVA of −0.48±0.37 (LogMAR). The average preoperative BCVA (LogMAR) is 0.36±0.14, while the average postoperative BCVA (LogMAR) is 0.28±0.1, with a change of −0.09±0.15 (LogMAR), and the Q-value change was 0.5±0.21. The means did not significantly differ between the two groups, except for the Km change, which was significantly greater in Group 1 than in Group 2 (P=0.05). Detailed results of Group 1 and a table of the descriptive statistics of Group 2 are given as Figures 2–6.
  | Figure 2 Changes in UCVA in both groups (LogMAR). |
  | Figure 3 Changes in BCVA in both groups (LogMAR). |
  | Figure 4 Changes in keratometry mean in both groups. |
  | Figure 5 Changes in Q-value in both groups. |
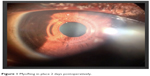
  | Figure 6 Figure shows the flattening effect of the MyoRing, (A) left showing topography of a cornea with evident keratoconus and (B) same eye after MyoRing. |
Discussion
In this study, we evaluated the visual, refractive, and pachymetric outcomes after MyoRing implantation in eyes with keratoconus, using the femtosecond laser technology for intrastromal pocket creation. At 1 month after surgery, we observed statistically significant reductions in myopia and cylinder. The changes were of large magnitude, with a mean change in sphere of 4.45 D and a mean change in refractive cylinder of 2.32 D. These levels of refractive change were consistent with those previously reported after MyoRing implantation with mechanical dissection.6,9 They were also close to those reported by Alio et al8 who analyzed 12 eyes following MyoRing implantation using femtosecond laser, and reported a mean change in sphere of 4.62 D and a mean change in cylinder of 4.47 D.
The mean change in sphere reported by Alio et al12 after Intacs implantation in advanced keratoconus was of similar magnitude (4.06 D). It should be noted that the ring segments implanted in eyes in previous studies of ICRS were even larger than those used in this study. Therefore, it seems that compared to ICRS, MyoRing implants have a greater potential for myopic and astigmatic correction in keratoconus, probably because of the more substantial arc-shortening effect achieved with a completely circular mid-peripheral implant. This is a topic that should be addressed in the future through a randomized comparative study.
As expected, the significant level of refractive correction achieved with MyoRing implants in our study was accompanied with a significant improvement in UCVA. The mean change UCVA (ΔUCVA) improvement was 6 lines of logMAR, and ΔUCVA was −0.57 (standard deviation, 0.27). Mahmood et al6 previously reported a UCVA improvement of 7 lines, and Daxer et al9 demonstrated a UCVA improvement of 10 lines. In these two previous studies, MyoRing implants were also used for keratoconus management, but mainly in grade II and III cases, while our sample included a substantial number of keratoconus grade IV cases. Alio et al12 reported a mean change in UCVA of 7 lines. With regard to BCVA, we observed an improvement by 2 lines of logMAR, which is in concordance with previous study results.
With regard to corneal topography, we observed a significant central flattening after surgery, which was consistent with the refractive change induced. The mean change in Km was 6.13 D (standard deviation, 4.37 D). This flattening effect is comparable to that reported by (mean change in maximum keratometry of 9.60 D) after Ferrara ring segment implantation in severe keratoconus. It was also comparable to those reported by Mahmood et al,6 Daxer et al,9 and Alio et al11 who also used the MyoRing in keratoconus. The large flattening effect achieved by Coskunseven et al17 with Ferrara ring segments was probably due to the use of thicker implants and reduced diameters, which are proven to be related to more substantial flattening.
In addition to visual, refractive, and corneal topography outcomes, we also evaluated changes in anterior corneal asphericity. We observed an increase in Q-value (measured at 6 mm diameter), rendering the corneal surface less prolate, but it was statistically insignificant (paired t-test P-value =0.497). Analyzing the correlation between changes of Q-value and changes of BCVA revealed that the Pearson correlation coefficient was negative (r=−0.5138), which was statistically insignificant (P-value =0.0501). As expected, analyzing the correlation between change in Km and change in BCVA revealed a statistically significant correlation between change in Km and change in BCVA (r=0.5451, P-value =0.0356). There was also a statistically significant correlation between change in cylinder and change in BCVA (r=−0.6542, P-value =0.0082). The correlation between the change in BCVA and sphere was statistically insignificant (r=−0.06343, P-value =0.8223).
One limiting factor in this study was the small number of cases. Despite this limitation, improvements were statistically significant in all statistical tests. However, the small number of cases may be relevant with respect to the probable occurrence of complications. A second limiting factor seems to be the “mixture” of eyes that did and did not undergo corneal cross linking.
In conclusion, we found that the implantation of MyoRings and Kerarings by means of femtosecond technology in cases of keratoconus significantly reduced the myopic spherical error due to central corneal flattening. The CISIS provides a new option for keratoconus management. The technique appears to be effective for decreasing myopia, corneal steepness, and decentration of the corneal apex, and it is also potentially reversible. Additionally, corneal intralstromal rings can be combined with corneal cross linking. Complete ring implantation may have a more flattening effect on the anterior corneal surface.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Rabinowitz YS. Keratoconus. Surv Ophthalmol. 1998;42(4):297–319. | ||
Romero-Jimenez M, Santodomingo-Rubido J, Wolffsohn JS. Keratoconus: a review. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2010;33:157–166. | ||
Piñero DP, Alio JL. Intracorneal ring segments in ectatic corneal disease–a review. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010;38:154–167. | ||
Patel S, Marshall J, Fitzke FW III. Model for deriving the optical performance of the myopic eye corrected with an intracorneal ring. J Refract Surg. 1995;11:248–252. | ||
Daxer A. Adjustable intracorneal ring in a lamellar pocket for keratoconus. J Refract Surg. 2010;26:217–221. | ||
Mahmood H, Venkateswaran RS, Daxer A. Implantation of complete corneal ring in an intrastromal pocket for keratoconus. J Refract Surg. 2011;27:63–68. | ||
Piñero DP, Alio JL, El Kady B, et al. Refractive and aberrometric outcomes of intracorneal ring segments for keratoconus: mechanical versus femtosecond-assisted procedures. Ophthalmology. 2009;116:1675–1687. | ||
Burris TE. Intrastromal corneal ring technology: results and indications. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1998;9:9–14. | ||
Daxer A, Mahmoud H, Venkateswaran RS. Intracorneal continuous ring implantation for keratoconus: one-year follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36:1296–1302. | ||
Daxer A. Corneal intrastromal implantation surgery for the treatment of moderate and high myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008;34:194–198. | ||
Alio JL, Piñero DP, Daxer A. Clinical outcomes after complete ring implantation in corneal ectasia using the femtosecond technology. Ophthalmology. 2011;118:1282–1287. | ||
Alio JL, Shabayek MH. Intracorneal ring segments (INTACS) for keratoconus correction: long term follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006;32:978–985. | ||
Ertan A, Ozkilic E. Effect of age on outcomes in patients with keratoconus treated by intacs using a femtosecond laser. J Refract Surg. 2008;24(7):690–695. | ||
El-Raggal TM, Abdel Fattah AA. Sequential Intacts and Verisyse phakic intraocular lens for refractive improvement in keratoconic eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007;33:966–970. | ||
Pokroy R, Levinger S. Intacs adjustment surgery for keratoconus. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006;36(6):986–992. | ||
Buratto L, Belloni S, Valeri R. Excimer laser lamellar keratoplasty of augmented thickness for keratoconus. J Refract Surg. 1998;14:517–525. | ||
Coskunseven E, Onder M, Kymionis GD, Diakonis VF, Arslan E, Tsiklis N, et al. Combined intacts and posterior chamber toric implantable collamer lens omplantation for keratoconic patients with extrememyopia. Am J Opthalmol. 2007;144:387–389. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
