Back to Journals » Patient Preference and Adherence » Volume 10
Factors influencing inpatients’ satisfaction with hospitalization service in public hospitals in Shanghai, People’s Republic of China
Authors Chen H, Li M , Wang J, Xue C, Ding T, Nong X, LIU Y, Zhang L
Received 12 October 2015
Accepted for publication 7 February 2016
Published 4 April 2016 Volume 2016:10 Pages 469—477
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S98095
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Haiping Chen,1 Meina Li,1 Jingrui Wang,1 Chen Xue,1 Tao Ding,1 Xin Nong,2 Yuan Liu,1 Lulu Zhang1
1Department of Military Health Management, College of Health Service, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, 2Department of Medical Research, Rizhao Maternity and Infant Hospital, Shandong, People’s Republic of China
Objective: The aim of this study was to observe the current status of inpatient satisfaction and analyze the possible factors influencing patient satisfaction during hospitalization.
Methods: A cross-sectional investigation was conducted to obtain basic information about inpatient satisfaction, and statistical methods were used to describe and analyze the data. A total of 878 questionnaires were included in this study. A 5-point Likert scale rating was employed to assess items related to hospitalization care. Nonparametric tests and ordinal logistic analysis were used to explore the relationship between predictors and the patients’ overall satisfaction.
Results: Among the respondents, 89.75% were satisfied overall with the service they received during hospitalization, while 0.57% reported dissatisfaction. Inpatient demographic characteristics such as sex of the patients, occupation, age, and residence had significant associations with satisfaction, while monthly income and marital status did not. Additionally, the statistical outcome indicated that doctors’ and nurses’ service attitudes, and expenditure and environment were found to have an impact on the inpatient satisfaction ratings, with odds ratio of 2.43, 3.19, and 2.72, respectively.
Conclusion: This study emphasizes the influence of sex of the patients, the service attitudes of the doctors and nurses, and expenditure and environment on inpatient satisfaction. An increase in satisfaction ratings concerning the areas of doctors’ and nurses’ service attitudes, and expenditure and environment can improve the overall satisfaction levels. Responsible health management departments should pay attention to patient satisfaction and improve the quality of relevant health services, thus ultimately enhancing inpatients’ hospitalization experiences.
Keywords: inpatients’ satisfaction, hospitalization service, influencing factors
Introduction
Patient satisfaction has been used as a tool for measuring whether the available health care supply meets patients’ health needs and expectations. This tool is widely used in the health care field around the globe. Patient satisfaction is a valuable indicator of health service quality and effectiveness, and it also has an impact on patient recovery.1–3 In recent decades, patients have become increasingly knowledgeable about health care. As a result, they have begun to require higher standards of medical effectiveness, health-staff services, expenditure, and so on.2 By using information gleaned from patient satisfaction studies, health care providers and regulatory institutions can better observe overall patient satisfaction, meet patient expectations, and discover deficits in medical service conditions, all of which would be beneficial for improving health care provision. Higher satisfaction ratings indicate fewer complaints and medical disputes, better patient recovery, and increased hospital assessment, so it is essential to conduct studies related to patient satisfaction.4,5 Because there is wide diversity in patient satisfaction among inpatients, outpatients, and emergency patients, this study focuses solely on inpatient satisfaction.
Existing studies of satisfaction have generally investigated patients’ evaluations of services, they received in order to uncover patient demands and preferences for medical projects and hospitals; they also provided information to health institutions about the areas that needed the most improvement. Previous analyses have observed that inpatient satisfaction was influenced by multiple factors, including patient factors (demographic characteristics, physical and psychological status, and expectations), health institution factors (health-staff characteristics, staff–patient interactions, health quality, treatment process, finances, medical facilities, and health organization environment including physical environment and food service), and governmental factors (social environment, health policy, medical insurance, and welfare conditions).6–12
During a retrospective literature analysis, five influencing factors (inpatient demographic characteristics, medical care, nursing care, expenditure, and the hospital environment) showed higher frequencies than other factors, so they were chosen as core research objects.13–15 Most of the previous studies have focused on inpatient satisfaction with doctors’ and nurses’ service skills, but little research has examined the service attitudes of doctors and nurses. Thus, this study was performed to investigate the current satisfaction situations of inpatients with their health services, explore whether different populations (with different sexes, occupations, ages, monthly incomes, marital status, and residences) experience different satisfaction levels with the same health services for the same issues, and define the main factors that influenced inpatient satisfaction, especially focusing on the association between the service attitudes of the medical staff (doctors and nurses) and satisfaction. As a result of this study, it was possible to posit feasible policy suggestions for the purpose of improving hospitalization service quality and increasing inpatient satisfaction levels.
Methods
The study sample consisted of inpatients from ten public hospitals in Shanghai. The inclusion criteria were as follows for the inpatients: aged 18 years or older; able to make decisions independently; able to speak, read, and write Chinese; and able to understand and complete the questionnaires independently. The procedure of this study was approved by the ethics committee of the Second Military Medical University (approval number 2013LL058). All participants were given an explanation of the aims and objectives of the study, following oral consent the survey was conducted. Simple random sampling was performed to identify the potential participants to whom the questionnaires were administered after verification. The inquiry continued for 2 months, from July to September 2013. A total of 950 questionnaires were distributed, 916 were recovered, and 878 met eligibility standards. The response rate was 92.42% (878/950). The self-administered questionnaire was designed by our research group based on a retrospective literature analysis and was standardized through the work of three relevant specialists. The specialists examined the questionnaire and ensured that it included all of the content to be measured for this study. Then, a pilot study (of 50 cases) was conducted using data from inpatients at Shanghai Hospitals to obtain the response rate (92.00%) and the average time required to complete a questionnaire (within 10 minutes). The results revealed that this questionnaire had good feasibility. In addition, it was revealed that inpatients did not understand the question about daily doctors’ ward rounds; thus, the statement “the time of daily doctors’ ward rounds” was changed to “the duration of daily doctors’ ward rounds”. The questionnaire’s structure was also assessed regarding construct validity, which a principal component analysis (PCA) demonstrated to be good. The Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin value was 0.89, and the results of Bartlett’s test were significant (normal approximate =6,445.64, P<0.01). Cronbach’s α for the total questionnaire was 0.71, and the standardized Cronbach’s α was 0.81.
The questionnaire included 17 closed-ended items, which were classified into two sections. Section 1 was about inpatients’ demographic variables (sex of the patient, occupation, age, monthly income, marital status, and residence). Section 2 was composed of items that related to hospitalization care: 1) overall satisfaction with service received during hospitalization, 2) frequency of a daily nurses’ ward rounds, 3) nurses’ service attitudes when providing physical examinations, 4) nurses’ service attitudes when providing injections, 5) nurses’ total service attitudes, 6) duration of daily doctors’ ward rounds, 7) doctors’ service attitudes when addressing concerns, 8) doctors’ service attitudes when providing information, 9) doctors’ total service attitudes, 10) expenditures, and 11) hospital environment. These eleven items were assessed on a 5-point Likert scale rating (completely dissatisfied =1, dissatisfied =2, neutral =3, satisfied =4, and completely satisfied =5).
The basic data were double-input into Epidata 3.0 and were sorted out using Excel. Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (Version 17.0) was used for data analysis. The survey adopted a two-sided significance level of 5%. As for ordinal and nonnormally distributed data, we utilized nonparametric tests for comparative analysis between inpatients with six kinds of demographic characteristics. The basic data were arranged into contingency tables. Sex of the patient, occupation, marital status, and residence belong to a one-orientation contingency table; therefore, a rank sum test was used. Age stage and monthly income belong to a double-orientation contingency table with different attributes in rows and lines; therefore, Spearman’s rank correlation was used. With regard to the rank sum test, Wilcoxon rank sum test (for sex) and the Kruskal–Wallis test (for occupation, marital status, and residence) were applied depending on the number of involved groups. Overall satisfaction with service received during hospitalization was considered to be the dependent variable, and the other 16 items acted as the independent variables. PCA and ordinal logistic analysis were applied to establish the regression equations between possible factors and overall inpatient satisfaction ratings.
Results
Sample demographic data
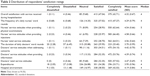
The basic information concerning the 878 respondents’ demographic characteristics is shown in Table 1. More than half (64.37%) were between the ages of 20 and 59 years, 58.43% were located in Shanghai, and the male–female ratio was 1:1.14. Respondents’ occupations were as follows: retirees (28.70%), factory workers (20.50%), and farmers (12.53%). Among the participating inpatients, 45.10% earned between 303.41 and 758.37 US$ (2,000 and 4,999 RMB [RenMinBi Yuan]) per month, and 22.32% earned between 0.15 and 303.26 US$ (1 and 1,999 RMB). The percentages of married and single inpatients were 80.41% and 16.06%, respectively.
Satisfaction with hospitalization care
Respondents’ current reported satisfaction situations are displayed in Table 2. The mean rating for inpatients’ overall satisfaction during hospitalization ranged from 3.65 to 4.99, and the proportion of satisfied and completely satisfied together was 89.75%. This is obviously higher than the proportion of dissatisfied and completely dissatisfied among all items related to hospitalization care. Inpatient satisfaction was highest in terms of nurses’ service attitudes when they were providing injections, with mean scores of 4.58 (standard deviation [SD] =0.66). The percentages of satisfied and completely satisfied responses together were 92.37. The patients experienced the most dissatisfaction with the duration of daily doctors’ ward rounds, with mean scores of 3.70 (SD =0.99). The percentage of satisfied and completely satisfied responses together was 55.35. In general, people were more satisfied with nurses than they were with doctors, especially concerning the amount of time doctors took to complete their ward rounds. Inpatients showed lower satisfaction scores in the areas of expenditure and hospital environment, with mean scores of <4.20, and the percentage of satisfied and completely satisfied together was <80.00.
  | Table 2 Distribution of respondents’ satisfaction ratings |
Difference between demographic characteristics and satisfaction
Of the six demographic characteristics, only sex was statistically significantly associated with overall satisfaction with hospitalization service (χ2=11.38, P<0.01) and satisfaction with the length of doctors’ daily ward rounds (χ2=7.01, P=0.01). As seen in Table 3, sex of the patient, occupation, and residence influenced inpatients’ satisfaction with the durations of nurses’ ward rounds (P=0.01, P=0.01, and P=0.04, respectively). In terms of inpatient satisfaction with doctors’ service attitudes when addressing concerns: sex, occupation, and marital status were influencing factors, with P-values of 0.03, <0.01, and 0.02, respectively. The Kruskal–Wallis test (Table 3) revealed that inpatient satisfaction with doctors’ total service attitudes had a statistically significant relationship with sex (P=0.01), occupation (P=0.04), and marital status (P=0.04). In addition, differences in occupation and residence affected the level of satisfaction with expenditure (P<0.05). In addition, sex (P=0.01) and marital status (P=0.03) were significant predictors of inpatient satisfaction with the hospital environment.
The association between age and overall satisfaction during hospitalization (rS=0.03, P=0.45) was not significant, but age was significantly associated with the duration of nurses’ daily ward rounds (P<0.01), nurses’ service attitudes when providing physical examinations (P<0.01), nurses’ service attitudes when providing injections (P<0.01), nurses’ total service attitudes (P=0.03), doctors’ service attitudes when addressing concerns (P<0.01), doctors’ service attitudes when providing information (P<0.01), and doctors’ total service attitudes (P<0.01). Furthermore, rS (0.08≤rS≤0.16) was positive, which indicates that inpatient satisfaction ratings increase along with age.
The outcome of Spearman’s rank correlation showed that there was no significant relationship between inpatient satisfaction and monthly income for any of the eleven items (P>0.05).
Factors associated with inpatient satisfaction
Spearman’s rank correlation was used to observe the possible correlation between overall satisfaction during hospitalization and the remaining 16 items. The results indicated that sex of the patient, frequency of nurses’ daily ward rounds, nurses’ service attitudes when providing physical examinations and injections, nurses’ total service attitudes, duration of doctors’ daily ward rounds, doctors’ service attitudes when addressing concerns or providing information, doctors’ total service attitudes, expenditures, and hospital environment have a relationship (P<0.05) with overall satisfaction during hospitalization. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients (rS) ranged from −0.14 to 0.57. The other five variables (occupation, age stage, monthly income, marital status, and residence) showed no statistical association with overall satisfaction. Thus, we selected the eleven related items for the subsequent analyses.
Utilizing PCA and varimax rotation method, the Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin value =0.91 and the results of Bartlett’s test were significant (normal approximate χ2=5,457.72, P<0.01). The construct validity result revealed that it is proper to conduct PCA. The components in which an Eigenvalue was greater than or approaching one were considered important, and the number of components was adjusted by the specialists. Consequently, four principal factors were extracted from the eleven items, and the cumulative percentage of variance was 77.96%. Factor 1, labeled as nurses’ service attitudes, accounted for 51.47% of the variance. This factor consisted of four items that were mainly related to nursing care. Factor 1, which expressed a salient nurse influence on inpatient satisfaction, accounted for the largest proportion. Factor 2, labeled as doctors’ service attitudes, which contained four items mainly related to doctors’ care, accounted for 9.71% of the variance. Factor 3, labeled as expenditure and environment, included two items that accounted for 8.99% of the variance. Factor 4, labeled as sex, mainly referred to one item that accounted for 7.79% of the variance (Table 4).
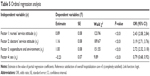
PCA eliminated the existence of multicollinearity. The result of PCA showed overall inpatient satisfaction is affected by four principal factors, namely nurses’ service attitudes, doctors’ service attitudes, expenditures and environment, and sex of the patient. Considering the four principal factors as independent variables (xi for i=1–4) and establishing overall inpatient satisfaction as the dependent variable (Y) that belongs to the ordinal variables (ranging from completely dissatisfied =1 to completely satisfied =5). Ordinal logistic analysis was applied to explore the correlation between predictors and the response variable. The likelihood ratio test for model χ2=470.70, df=4, P<0.01 indicated that the regression equations were significant. The goodness-of-fit operation showed a good model fit through the following measures: Pearson χ2=3,311.42 (P<0.01), Cox and Snell R2=0.42, and Nagelkerke R2=0.48. Finally, four regression equations were established as:
logit(P)(Y ≤1) =−8.38+0.89x1 +1.16x2 +1.00x3 −0.23x4 | (1) |
logit(P)(Y ≤2) =−6.77+0.89x1 +1.16x2 +1.00x3 −0.23x4 | (2) |
logit(P)(Y ≤3) =−3.30+0.89x1 +1.16x2 +1.00x3 −0.23x4 | (3) |
logit(P)(Y ≤4) =0.58+0.89x1 +1.16x2 +1.00x3 −0.23x4 | (4) |
where Y is the level of overall inpatient satisfaction (Y ≤ j, for j=1–4). The values of −8.38, −6.77, −3.30, and 0.58 are the estimated values of the constant terms (β0j, for j=1–4) for each of the four equations, respectively, which means that when all the independent variables are equal to 0, P(Y ≤ j) = eβ0 j/(1 + eβ0 j). Concerning the independent variables (xi for i=1–4), x1 represents nurses’ service attitudes, x2 represents doctors’ service attitudes, x3 represents expenditure and environment, and x4 represents sex.
The outcome of ordinal logistic analysis shows all four independent predictors (sex of the patient, nurses’ service attitudes, doctors’ service attitudes, and expenditure and environment) and had significant impacts on dependent variables, with odds ratios of 0.79, 2.43, 3.19, and 2.72, respectively (Table 5). Male inpatients, inpatients who were more satisfied with nurses’ service attitudes, inpatients who were more satisfied with doctors’ service attitudes, and inpatients with higher satisfaction scores of expenditure and environment were more likely to be satisfied with overall hospitalization care.
Discussion
In terms of inpatient satisfaction, the results of the People’s Republic of China’s Fifth National Health Services Survey showed that among the 24,740 hospitalization questionnaire respondents, the overall proportion of inpatients satisfied with hospitalization was 67.20% and the overall proportion of inpatients dissatisfied with hospitalization was 4.40%.16 The proportion of satisfied and completely satisfied responses concerning overall satisfaction during hospitalization was relatively high in this study compared to the reported nationwide satisfaction level, but inpatients’ satisfaction ratings with the duration of doctors’ daily ward rounds were the lowest among all the survey items (Table 2), which should pique the attention of health leaders and providers.17 The length of time it took for doctors to complete their daily ward rounds did not meet inpatients’ expectations. This finding is in line with those of earlier papers, which reported that the duration of doctors’ ward rounds influenced medical quality and impacted patient satisfaction,18 so it is crucial for hospitals to adjust the doctors’ ward round system to provide enough ward round time to their patients.
According to an ordinal regression analysis, sex of the patient, nurses’ service attitudes, doctors’ service attitudes, and expenditure and environment were significantly associated with overall satisfaction during hospitalization (P<0.05, Table 5). Nurses’ service attitudes were the most powerful factor with the largest odds ratio, followed by doctors’ service attitudes, expenditure and environment, and sex. This finding is similar to the results of previous studies, in which staff attitude was the most important factor in patient satisfaction.19 The second most influential factor was staff technology skill, and the third was staff–patient communication and expenditure.19
This study emphasized the importance of nurses’ service attitudes to inpatient satisfaction levels. The more satisfied a patient was with a nurse’s attitude, the more likely that patient was to have more overall satisfaction while hospitalized. This is in accordance with the results of previous studies that noted how nurses’ behaviors directly affect patient satisfaction. Allowing for more nursing time is, therefore, vital to improving nursing care, and increasing training for nurses can enhance the satisfaction ratings.20,21 In addition, comparing the density of the health workforce per 10,000 people (the data come from the World Health Statistics 2014 and the Chinese Health Statistics Yearbook 2014), the ratio of physician-to-nurse density in Shanghai in 2013 (40.5/47.4) was lower than that of the international ratio (14.1/29.2). The numbers and structures of nursing staff members are inadequate to meet patient needs, and this should arouse the attention of health departments worldwide. To maintain a more reasonable physician-to-nurse density, it is necessary to increase supervision and administration to enhance nurses’ service quality.22
Similar to nurses, doctors play a major role in inpatient satisfaction. Doctors’ service attitudes can greatly affect inpatient satisfaction with them. Those patients who are less satisfied with their doctors’ service attitudes will have lower levels of overall satisfaction. Similar findings were reported by Tung and Chang,19 who found that doctors’ care has a prominent impact on patient satisfaction, and doctors’ characteristics, including technical and interpersonal skills, can influence patient attitudes or medical outcomes.
Expenditure and environment also significantly influence the overall inpatient satisfaction. Previous papers have reported that medical expenditure was significantly associated with patient satisfaction.23 According to the People’s Republic of China’s Fifth National Health Services Survey, high expenditure is the most important reason for inpatient dissatisfaction. Additionally, regarding the question of inpatient opinions on hospitalization expenditures, among the 24,740 respondents, 36.00% of inpatients considered hospitalization to be expensive, and 22.90% considered it to be inexpensive.16 Therefore, hospitals should insist on clarity in expenditure, informing patients in a timely manner about their medical costs and bills, and adjusting the prices and structures of medical costs to reduce patients’ financial burdens to some extent.24 In terms of residents listed in the Shanghai household register, current hospitalization expenditures are mainly paid by medical insurance and out of the inpatients’ own pockets, depending on a certain payment proportion. The commercial insurance and health care subsidies system was created as a supplemental tool for health care payments. By the end of 2010, among the residents listed in the Shanghai household register, coverage for all types of basic medical insurance exceeded 97.00%. However, the basic medical insurance does not cover all hospitalization costs, and financing from medical insurance has decreased significantly in recent years, leading to markedly great fiscal pressures on individuals. Additionally, for inhabitants not listed on the Shanghai household register, the compensatory proportion of medical insurance is relatively low, or they do not have medical insurance, so the burden of health care-associated charges is heavy on these patients.25,26
A convenient and comfortable environment will increase inpatient satisfaction.27 In this study, the hospital environment was found to have a positive impact on patient satisfaction ratings. Similar conclusions were reached by Abdellah et al concerning hospital environment and patient feelings. The hospital environment usually comprises the physical environment and food service.28 The rational planning of buildings would increase hospital safety and security and reduce infection rates. Crowded and noisy surroundings reduce inpatient satisfaction scores. Keeping the hospital environment clean and neat is helpful for making the inpatients feel comfortable.29,30 In addition, Rasmussen et al noted that patients’ nutritional status is related to recent food intake,12 and therefore the quality of hospital food is related to patient malnutrition status during hospitalization. Choosing high-quality primary materials, providing a menu adapted to inpatient preferences, and ensuring the quality of hospital food service (eg, maintaining staff cleanliness and friendliness) will be helpful for improving inpatients’ appetites and satisfaction levels.11,31 Thus, hospitals and related health institutions will need to improve the quality of their environment.
Sex of the patient is an influencing factor for satisfaction. Male inpatients tend to be more satisfied with the frequency of daily nurses’ ward rounds, the length of time doctors take for completing their ward rounds, doctors’ service attitudes when addressing concerns and providing information, doctors’ total service attitudes, and hospital environments, so male inpatients have a higher overall satisfaction with hospitalization care. This finding is similar to that of Aiello et al32 regarding the difference between males and females in regards to the areas of medical expenditure, privacy protection, and medical requirements, whereas Binsalih et al34 and Cleary and McNeil33 noted that the sex of the patient had no clear association with satisfaction.35 Considering the differences in physical and psychological status between men and women, it is necessary for hospitals to study the possible relationship between the sex of the patient and satisfaction, as it would be helpful for ensuring more humane medical care.
Inpatients’ occupation, age, and marital status also influenced patient satisfaction for partial survey items. The difference between occupation and satisfaction was significant. Age had a positive correlation with inpatient satisfaction in the areas of nursing and doctors’ care, and the marital status affected the inpatient satisfaction in the aspects of doctors’ care and hospital environment. This is similar to the findings of Hall and Dornan36 and Aiello et al,32 who found that patients who have different occupations have remarkably different satisfaction ratings, and older patients and those who are married tend to have higher satisfaction levels. Because of these individual differences, hospitals and health-staff members should consider inpatients’ individual characteristics when offering hospitalization care to different populations.
This study had several limitations. First, according to patients’ existing mobility abilities, patients may be influenced by preference, disease severity, and hospital reputation, and they are more likely to choose hospitals in different regions.37,38 The survey hospitals were all located in Shanghai, and Shanghai’s health service care is better than that of other developing regions in the People’s Republic of China. Inpatients who move to Shanghai’s hospitals have different characteristics than those who choose local hospitals; however, this study did not perform an in-depth analysis to evaluate the difference. Further studies should compare the characteristics of patients who choose local hospitals from those who move to hospitals in foreign regions. Second, the study’s inclusion criteria included only inpatients who were able to speak, read, and write Chinese and who were able to understand and complete the questionnaires independently. Due to illiteracy and Alzheimer’s disease, some elderly patients may have had difficulties in completing the questionnaire independently. Thus, there was a possible selection bias in this study.
Although this study is not without limitations, it is beneficial for health departments to observe the actual practice of medical care within a hospital, uncover the factors influencing inpatients’ satisfaction, analyze the possible deficiencies, and design corresponding strategies. Further studies and policy changes will need to regularly measure inpatient satisfaction with hospital care and monitor and adjust health projects according to the varied demands of inpatients.
Conclusion
In conclusion, inpatients’ overall satisfaction during hospitalization was affected by four predictors (sex, nurses’ service attitudes, doctors’ service attitudes, and expenditures and environment). Nurses’ service attitudes were most influential, followed by doctors’ service attitudes, expenditure and environment, and the sex of the patient. Male inpatients or those satisfied with nurses’ or doctors’ service attitudes and expenditure and environment tended to report higher overall satisfaction with hospital care. In addition, occupation, age, and marital status had an impact on inpatient satisfaction, whereas there was no statistical association between monthly income, residence, and inpatient satisfaction.
Acknowledgments
Meina Li and Jingrui Wang are co-first authors. This project was supported by the Major Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (71233008), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (71303248), Training Program of the Major Research Plan of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91224005), and Major Program of Military Logistic Science and Technology during the Twelfth Five-Year Guideline (AWS12J002).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Sun BC, Adams JG, Burstin HR. Validating a model of patient satisfaction with emergency care. Ann Emerg Med. 2001;38(5):527–532. | ||
Sahin B, Yilmaz F, Lee K-H. Factors affecting inpatient satisfaction: structural equation modeling. J Med Syst. 2007;31(1):9–16. | ||
Zendjidjian X-Y, Baumstarck K, Auquier P, Loundou A, Lançon C, Boyer L. Satisfaction of hospitalized psychiatry patients: why should clinicians care? Patient Prefer Adherence. 2014;8:575. | ||
Gong C, Xinzheng J. Investigation on the satisfaction of the in- and out-patients. Med Soc. 2005;18(6):12–15. | ||
Mittal V, Huppertz JW, Khare A. Customer complaining: the role of tie strength and information control. J Retailing. 2008;84(2):195–204. | ||
Kuosmanen L, Hätönen H, Jyrkinen AR, Katajisto J, Välimäki M. Patient satisfaction with psychiatric inpatient care. J Adv Nurs. 2006;55(6):655–663. | ||
Birhanu Z, Assefa T, Woldie M, Morankar S. Determinants of satisfaction with health care provider interactions at health centres in central Ethiopia: a cross sectional study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2010;10(1):78. | ||
Ameryoun A, Pourtaghi G, Yahaghi E, et al. Outpatient and inpatient services satisfaction in Iranian military hospitals. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2013;15(9):843. | ||
Gupta D, Rodeghier M, Lis CG. Patient satisfaction with service quality as a predictor of survival outcomes in breast cancer. Support Care Cancer. 2014;22(1):129–134. | ||
Liu W, Li R, Wang L. Research of hospital patient satisfaction and influencing factors based on SEM. Soft Sci. 2014;28(1):140–144. [In Chinese]. | ||
Messina G, Fenucci R, Vencia F, Niccolini F, Quercioli C, Nante N. Patients’ evaluation of hospital foodservice quality in Italy: what do patients really value? Public Health Nutr. 2013;16(04):730–737. | ||
Rasmussen HH, Holst M, Kondrup J. Measuring nutritional risk in hospitals. Clin Epidemiol. 2010;2:209. | ||
Thi PLN, Briancon S, Empereur F, Guillemin F. Factors determining inpatient satisfaction with care. Soc Sci Med. 2002;54(4):493–504. | ||
Danforth RM, Pitt HA, Flanagan ME, Brewster BD, Brand EW, Frankel RM. Surgical inpatient satisfaction: what are the real drivers? Surgery. 2014;156(2):328–335. | ||
Lan G, Ji T, Gao S. Analysis of the influencing factors on inpatient satisfaction level in a hospital. Chin Health Qual Manag. 2014;21(6):68–70. [In Chinese]. | ||
Ling X, Qun M. The fifth national health service survey. Chin J Health Inform Manag. 2014;11(2):104–105. | ||
Papsdorf I, Hannich H, Tost F. Information oder Verwirrung Eine formal-quantitative Analyse augenärztlicher Visitengespräche. [Information or confusion. A formal quantitative analysis of ophthalmology ward rounds]. Ophthalmologe. 2009;106(10):905–912. German. | ||
Veigel S, Schmid A, Kollmar O, et al. Arbeitszeitkonformes Visitenmodell und Patientenzufriedenheit. Zentralbl Chir [Reduced time-frame for ward rounds and patient satisfaction]. Zentralbl Chir. 2012;137(2):187–195. German. | ||
Tung Y-C, Chang G-M. Patient satisfaction with and recommendation of a primary care provider: associations of perceived quality and patient education. Int J Qual Health Care. 2009;21(3):206–213. | ||
Wagner D, Bear M. Patient satisfaction with nursing care: a concept analysis within a nursing framework. J Adv Nurs. 2009;65(3):692–701. | ||
Merkouris A, Papathanassoglou ED, Lemonidou C. Evaluation of patient satisfaction with nursing care: quantitative or qualitative approach? Int J Nurs Stud. 2004;41(4):355–367. | ||
Price K, Patterson E, Hegney D. Being strategic: utilising consumer views to better promote an expanded role for nurses in Australian general practice. Collegian. 2006;13(4):16–21. | ||
Vanhoof K, Pauwels P, Dombi J, Brijs T, Wets G. Penalty-Reward Analysis with Uninorms: A Study of Customer (Dis) Satisfaction. Intelligent Data Mining. Heidelberg: Springer; 2005:237–252. | ||
Zhang X, Dai Q, Liu L. Survey of status quo of satisfaction of inpatients under hospital hosted mode. Chin Nurs Res. 2013;27(5):1326–1328. [In Chinese]. | ||
Chen M, Zhao Y, Si L. Who pays for health care in China? The case of Heilongjiang province. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e108867. | ||
Siming N, Hong X, Zhenyao G, Junshan C, Yi Z, Hong L. Constantly improve the medical security system to achieve universal coverage. Chin J Hosp Admin. 2011;27(7):523–526. | ||
Kavadas V, Barham C, Finch-Jones M, et al. Assessment of satisfaction with care after inpatient treatment for oesophageal and gastric cancer. Br J Surg. 2004;91(6):719–723. | ||
Andrade C, Lima ML, Fornara F, Bonaiuto M. Users’ views of hospital environmental quality: validation of the perceived hospital environment quality indicators (PHEQIs). J Environ Psychol. 2012;32(2):97–111. | ||
Abdellah FG, Levine E, Levine BS. Better Patient Care Through Nursing Research. New York, NY: MacMillan Publishing Company; 1986. | ||
Bruyneel L, Li B, Ausserhofer D, et al. Organization of hospital nursing, provision of nursing care, and patient experiences with care in Europe. Med Care Res Rev. 2015;72(6):643–664. | ||
Naithani S, Whelan K, Thomas J, Gulliford MC, Morgan M. Hospital inpatients’ experiences of access to food: a qualitative interview and observational study. Health Expect. 2008;11(3):294–303. | ||
Aiello A, Garman A, Morris SB. Patient satisfaction with nursing care: a multilevel analysis. Qual Manag Healthcare. 2003;12(3):187–190. | ||
Cleary PD, McNeil BJ. Patient satisfaction as an indicator of quality care. Inquiry. 1988;25:25–36. | ||
Binsalih SA, Waness AO, Tamim HM, Harakati MS, Al Sayyari AA. Inpatients’ care experience and satisfaction study. J Fam Commun Med. 2011;18(3):111. | ||
Lyu H, Wick EC, Housman M, Freischlag JA, Makary MA. Patient satisfaction as a possible indicator of quality surgical care. JAMA Surg. 2013;148(4):362–367. | ||
Hall JA, Dornan MC. Patient sociodemographic characteristics as predictors of satisfaction with medical care: a meta-analysis. Soc Sci Med. 1990;30(7):811–818. | ||
Messina G, Forni S, Collini F, Quercioli C, Nante N. Patient mobility for cardiac problems: a risk-adjusted analysis in Italy. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13(1):56. | ||
Glinos IA, Baeten R, Helble M, Maarse H. A typology of cross-border patient mobility. Health Place. 2010;16(6):1145–1155. |
 © 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.