Back to Journals » OncoTargets and Therapy » Volume 7
Expression of YY1 correlates with progression and metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas
Authors Luo J, Jiang X, Cao L, Dai K, Zhang S, Ge X, Zhou X, Lu X
Received 22 April 2014
Accepted for publication 30 July 2014
Published 26 September 2014 Volume 2014:7 Pages 1753—1759
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S66667
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Faris Farassati
Judong Luo,1,* Xin Jiang,1,* LiLi Cao,2,* Kejun Dai,1 Shuyu Zhang,3,4 Xin Ge,3,4 Xifa Zhou,1 Xujing Lu1
1Department of Radiotherapy, Changzhou Tumor Hospital, Soochow University, Changzhou, People's Republic of China; 2Department of Molecular Radiobiology, Research Institute for Radiation Biology and Medicine, Hiroshima University, Hiroshima, Japan; 3School of Radiation Medicine and Protection and Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Radiation Medicine and Protection, 4Collaborative Innovation Center of Radiation Medicine of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions and School for Radiological and Interdisciplinary Sciences (RAD-X), Soochow University, Suzhou, People's Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Objective: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is one of the deadliest cancers worldwide. Yin Yang 1 (YY1) is a ubiquitous and multifunctional zinc-finger transcription factor that plays important biological functions in cell homeostasis and tumorigenesis. The purpose of this study was to investigate the expression of YY1 in different ESCC tissues and the potential relationship with clinicopathological features.
Methods: One hundred and four ESCC tissues were collected in this study. The protein levels of YY1 were measured by immunohistochemistry. TE-1 cell invasion in vitro was assessed using the Transwell assay.
Results: There were no obvious differences between expression levels in patients over age 64 and those younger than 64, and no noticeable distinction was observed between males and females. However, the YY1 protein level was significantly higher in ESCC tissues with lymph node metastasis than those without lymph node metastasis (P=0.042). Furthermore, the expression of the YY1 protein was stronger in stage III–IV patients than in stage I–II patients (P=0.002), but the protein levels between different histological grades (well, moderate, or poor) showed no statistical significance. Similarly, there was no difference in YY1 expression in patients with or without lymphatic invasion. The Transwell assay revealed that the overexpression of YY1 promoted the invasion ability of TE-1 cells and the inhibition of YY1 could reverse this promotion.
Conclusion: YY1 expression was associated with TNM stage and lymph node metastasis, suggesting that YY1 can influence human esophageal cancer progression and metastasis.
Keywords: immunohistochemistry, transwell assay, clinicopathological features, invasion
Introduction
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) ranks sixth among all cancers in mortality and is one of the deadliest cancers worldwide because of its highly aggressive nature and poor survival rate.1 The overall 5-year survival rate is only approximately 15%, and most patients die in the first year after diagnosis.2 However, the mechanisms regulating the malignancy and progression of ESCC remain under investigation, and clarifying the biological mechanisms leading to the development of esophageal tumors has become an important question in esophageal cancer research.
Transcription factors (also called sequence-specific DNA-binding factors) are specific proteins that can bind to specific DNA sequences and consequently regulate the flow of the genetic message from DNA to messenger RNA.3,4 Transcription factors have been reported to play important roles in cell growth, development, and differentiation,5 and there is substantial evidence that transcription factor dysfunction leads to detrimental outcomes, even tumorigenesis.6 Massive evidence indicates that transcription factors act as important players in human cancer development and progression, and it has been shown that the dysregulation of many transcription factors, such as Oct3/4, Sox2, KLF4, and EGR-1, is involved in the occurrence and development of esophageal cancer. For example, Oct3/4 and Sox2 overexpression leads to a poorer clinical outcome in ESCC patients.7 Although KLF4 acts as a tumor suppressor, in esophageal cancer, there is a high frequency of loss of heterozygosity of chromosome 9q31, on which KLF4 is located.8
Yin Yang 1 (YY1) is a ubiquitous and multifunctional zinc-finger transcription factor that belongs to the Polycomb group protein family. YY1 has been shown to exert important biological functions in mammals, including embryogenesis,9,10 growth, differentiation,11 proliferation, and response to genotoxic stimuli.12,13 YY1 regulates gene expression by binding to DNA directly through its C-terminal zinc-finger domain.14 YY1 activates transcription in the presence of E1A, a protein that activates the AAV P5 promoter; however, the role of YY1 is reversed when E1A is absent, converting to a transcriptional repressor.5 Furthermore, YY1 can also regulate targets independently of its DNA-binding ability by mediating protein posttranslational modifications and acting as a transcriptional cofactor.15 YY1 modulates posttranslational modification by interacting with proteins that mediate posttranslational modifications, such as histone deacetylases, p300/CBP, Ezh2, and Ezh1. Although YY1 plays an important role in normal growth, many studies have focused on its relationship with cancer. Because YY1 can regulate oncogenes and tumor suppressor expression, there is not yet a complete picture about the role of YY1 in various cancers.
It is reported that YY1 is overexpressed in many tumors, such as prostate,16,17 ovarian,18,19 breast,20,21 colon,22,23 liver,24,25 lung26,27 cancers, melanoma28 and leukemia.29 In a recent study, we found that YY1 was significantly increased in ESCC tissues compared with normal esophageal tissues or adjacent tumor tissues.30 However, it remains unclear whether there are differences between various ESCC patients and whether YY1 has a relationship with the development and progression of ESCC. In this study, we investigated the protein levels of YY1 in different ESCC tissue samples, and we discuss the relationship of YY1 expression with clinicopathological factors.
Materials and methods
Patients and tissues
All of 104 ESCC samples were collected from patients who underwent surgical treatment in Changzhou Tumor Hospital (Changzhou, People’s Republic of China). These patients consisted of 73 males and 31 females; their median age was 59 years, ranging from 32 to 76 years old. None of the patients accepted any chemotherapy or radiotherapy prior to surgery. All patients provided signed, informed consent for their tissues to be used for scientific research, and ethical approval for the study was obtained from Changzhou Tumor Hospital. All diagnoses were based on pathological and/or cytological evidence. The histological features of the samples were evaluated by a senior pathologist according to the classification criteria of the World Health Organization.31
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
An IHC analysis was performed as reported previously.30 The tissue samples were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin and embedded in paraffin. Three-micrometer-thick paraffin sections were deparaffinized, dehydrated, and heat-treated with citrate buffer (pH 6.0) for 15 minutes as an epitope retrieval protocol. The endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked with 3% hydrogen peroxide for 30 minutes, and the nonspecific binding sites were blocked with 4% skim milk powder for 30 minutes. After three washes in phosphate-buffered saline, the sections were incubated with a YY1 antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA; dilution 1:200) overnight at 4°C. The sections were mixed with 2% skim milk powder to reduce nonspecific staining, and a biotinylated secondary antibody was added for 30 minutes. Avidin–biotin–peroxidase complex (Dako LSAB2 system; DAKO Co, Carpinteria, CA, USA) was added, and the color was developed using 3-3′-diaminobenzidine. Counterstaining was performed with hematoxylin. All steps were carried out at room temperature.
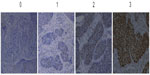
The following standards were used to score the stained sections: negative (0), <10% of the entire tissue section stained positive; weakly positive (+1), 10%–25% of the entire tissue section stained positive; moderately positive (+2), 25%–75% of the entire tissue section stained positive; and strongly positive (+3), >75% of the tissue section stained positive.
Cell culture and transfection
The human ESCC cell line TE-1 was maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and antibiotics (100 units/mL penicillin G, 100 units/mL streptomycin sulfate; Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA). The cells were grown in a 37°C incubator with 5% CO2. For transfection, the cells were transfected with plasmids using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), as reported previously.30
Tumor cell invasion assay
TE-1 cell invasion was evaluated in vitro using a Transwell system (Corning, Tewksbury, MA, USA). The Transwell chamber includes a polycarbonate filter membrane with a pore size of 8 μm. Matrigel (12.5 μg; Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) was diluted with 50 μL phosphate-buffered saline on ice and then added to the filter. After the gel formed a thin layer, TE-1 cells were suspended in 100 μL serum-free DMEM and added to the upper chamber of the Transwell insert. The lower chamber was filled with 500 μL DMEM plus 20% fetal bovine serum. After 24 hours of incubation at 37°C, the cells on the upper surface of the filter were removed using a cotton swab. The cells that adhered to the lower surface of the filter were fixed with methanol and then stained with hematoxylin. The cells were counted under a microscope.
Statistical analysis
A correlation analysis between the YY1 IHC staining score and clinicopathological factors was carried out using χ2 tests and the Mann–Whitney U-test when only two groups were compared or the Kruskal–Wallis test when more than two groups were compared. The statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS software (Release 19.0, IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA), and a P-value <0.05 was considered to be significant.
Results
Patient demographics for the IHC analysis
To detect the expression of YY1, we collected a total of 104 ESCC tissues. The demographic features of the tissue samples are summarized in Table 1. For the total ESCC group, there were 15 cases at stage I, nine males and six females, with a median age of 62.8 years, ranging from 55 to 69; there were 52 cases at stage II, 37 males and 15 females, with a median age of 59.21 years, ranging from 33 to 76; there were 33 cases at stage III, 23 males and 10 females, with a median age of 56.53 years, ranging from 32 to 75; and there were four cases at stage IV, four males and zero females, with a median age of 66 years, ranging from 52 to 67.
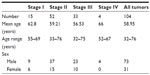  | Table 1 Patient demographics for the immunohistochemistry analysis |
Association of YY1 protein expression with clinicopathological factors
To study the relationship between the YY1 expression level and clinicopathological characteristics of the patients, including age, sex, histological grade, lymph node metastasis, TNM stage, and lymphatic invasion, IHC staining was performed on the 104 paraffin-embedded ESCC tissue samples.
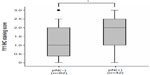
In the IHC analysis, 55.7% (58 cases) of samples were positive for YY1 expression, and 44.3% (46 cases) were negative. Representative IHC staining of YY1 in ESCC tissues is shown in Figure 1. The relationship between YY1 expression and clinicopathological features is shown in Table 2. There were no obvious differences between age greater than 64 or less than 64 (P=0.286), and also no notable distinction between the males and females (P=0.255). Conversely, the protein level of YY1 was significantly higher in ESCC tissues with lymph node metastasis than in those without lymph node metastasis (P=0.042, Figure 2). Furthermore, YY1 protein expression was stronger in the stage III–IV patients than in the stage I–II patients (P=0.002, Figure 3), though the protein levels between the different histological grades (well, moderate, or poor) exhibited no statistical significance (P=0.752). Similarly, the expression of YY1 showed no differences in patients with or without lymphatic invasion (P=0.141). Taken together, YY1 expression was associated with TNM stage and lymph node metastasis but had no statistical correlation with age, sex, histological grade, and lymphatic invasion.
YY1 promotes the invasion of ESCC cells
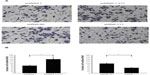
It was found that the protein level of YY1 was significantly higher in ESCC tissues with lymph node metastasis than those without lymph node metastasis. As it remains unclear whether YY1 affects ESCC cell invasion, a classical Transwell system was used to investigate the effect of YY1 in esophageal cancer cell invasion. The results showed that the number of TE-1 cells migrating through the membrane increased after transfection with a YY1 overexpression vector, and significantly decreased after silencing with small hairpin RNA, indicating that YY1 increased the invasive ability of TE-1 cells and the inhibition of YY1 could reverse this promotion (Figure 4).
Discussion
YY1, a ubiquitously expressed transcription factor, has complex and diverse biological functions. YY1 can either activate or repress gene transcription depending on the stimuli received by the cells and the association with other cellular factors. YY1 belongs to the Polycomb group protein family, a group of homeobox gene receptors that play a key role in hematopoiesis and cell cycle regulation. YY1 was initially found simultaneously by two independent groups in 199132,33 and is located on the telomere region of human chromosome 14 at the segment q32.2.34 The human YY1 gene produces eight different transcripts (named a, b, c, d, e, f, g, and h) generated by alternative splicing, encoding eight different putative protein isoforms. However, the functional significance of these different isoforms remains unknown.35
YY1 has been reported to be overexpressed in multiple types of tumors, and it is known that YY1 overexpression may affect the clinical behavior of cancers.36,37 Thomassen et al found that YY1 is upregulated in metastatic breast cancer,38 and YY1 overexpression strongly correlates with the malignancy degree of osteosarcoma.39 Chinnappan et al reported that the YY1 expression level was more marked in poorly differentiated tumors than in moderately or well-differentiated colon carcinomas.40 To understand whether differences in YY1 expression levels occur in different clinicopathological ESCC, IHC staining was used to detect the protein levels of YY1 in 104 ESCC tissue samples. We found that the level of YY1 protein was higher in ESCC tissues with lymph node metastasis than in those without lymph node metastasis and was also higher in ESCC tissues of stage III–IV versus stage I–II. Thus, YY1 expression is associated with TNM stage and lymph node metastasis.
The role of YY1 in cancer progression is still a matter of heated debate and may depend on the type of tumor or other still-unknown factors. In a previous study, using the human ESCC TE-1 cell line, we found that YY1 could inhibit TE-1 cell proliferation by enhancing the binding of P21 to Cyclin D1 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 4, a protein complex known to mediate cell cycle progression. We also found that YY1 upregulated heme oxygenase 1 expression, which also inhibited ESCC proliferation.30 This evidence demonstrates that YY1 may act as a tumor suppressor in ESCC, at least in ESCC-derived TE-1 cells. In the present study, we found that YY1 promoted the invasion of ESCC cells and the inhibition of YY1 could reverse this promotion. Esophageal carcinoma normally metastasizes to the lymph nodes, and lymph node metastases and clinical stage are correlated with the prognosis of patients.41,42 In our study, which encompassed a relatively large number of ESCC patients, higher YY1 expression was associated with tumors with an advanced lymph node metastatic status (P=0.042) and tumors with a later TNM stage (P=0.002). Therefore, YY1 may be responsible for human esophageal cancer metastasis.
So, as in other types of cancer, many genes and pathways are involved in ESCC progression. YY1 is one of those genes that can inhibit ESCC proliferation and promotes the metastasis of ESCC. And these data suggest that the examination of YY1 expression might be helpful in guiding clinical management. However, the functional role and mechanisms of YY1 in esophageal cancer are still unclear and require further investigation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the expression of YY1 is correlated with tumor stage and pN, and these findings suggest that YY1 plays a role in ESCC progression and metastasis.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81402518;81472920), the Jiangsu Provincial Special Program of Medical Science (BL2012046), the Changzhou Scientific Project (CE20125026; CE20135050; ZD201315; CY20130017), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60(5):277–300. | |
Polednak AP. Trends in survival for both histologic types of esophageal cancer in US surveillance, epidemiology and end results areas. Int J Cancer. 2003;105(1):98–100. | |
Latchman DS. Transcription factors: an overview. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997;29(12):1305–1312. | |
Karin M. Too many transcription factors: positive and negative interactions. New Biol. 1990;2(2):126–131. | |
Shi Y, Lee JS, Galvin KM. Everything you have ever wanted to know about Yin Yang 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1332(2):F49–F66. | |
Darnell JE Jr. Transcription factors as targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(10):740–749. | |
Wang Q, He W, Lu C, et al. Oct3/4 and Sox2 are significantly associated with an unfavorable clinical outcome in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2009;29(4):1233–1241. | |
Wei D, Kanai M, Huang S, Xie K. Emerging role of KLF4 in human gastrointestinal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27(1):23–31. | |
Donohoe ME, Zhang X, McGinnis L, Biggers J, Li E, Shi Y. Targeted disruption of mouse Yin Yang 1 transcription factor results in peri-implantation lethality. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19(10):7237–7244. | |
Morgan MJ, Woltering JM, In der Rieden PM, Durston AJ, Thiery JP. YY1 regulates the neural crest-associated slug gene in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(45):46826–46834. | |
Kurisaki K, Kurisaki A, Valcourt U, et al. Nuclear factor YY1 inhibits transforming growth factor beta- and bone morphogenetic protein-induced cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(13):4494–4510. | |
Oei SL, Shi Y. Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of transcription factor Yin Yang 1 under conditions of DNA damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;285(1):27–31. | |
Oei SL, Shi Y. Transcription factor Yin Yang 1 stimulates poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation and DNA repair. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001; 284(2):450–454. | |
Yant SR, Zhu W, Millinoff D, Slightom JL, Goodman M, Gumucio DL. High affinity YY1 binding motifs: identification of two core types (ACAT and CCAT) and distribution of potential binding sites within the human beta globin cluster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995;23(21):4353–4362. | |
Deng Z, Cao P, Wan MM, Sui G. Yin Yang 1: a multifaceted protein beyond a transcription factor. Transcription. 2010;1(2):81–84. | |
Singh D, Febbo PG, Ross K, et al. Gene expression correlates of clinical prostate cancer behavior. Cancer Cell. 2002;1(2):203–209. | |
Vanaja DK, Cheville JC, Iturria SJ, Young CY. Transcriptional silencing of zinc finger protein 185 identified by expression profiling is associated with prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2003;63(14):3877–3882. | |
Welsh JB, Zarrinkar PP, Sapinoso LM, et al. Analysis of gene expression profiles in normal and neoplastic ovarian tissue samples identifies candidate molecular markers of epithelial ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(3):1176–1181. | |
Hendrix ND, Wu R, Kuick R, Schwartz DR, Fearon ER, Cho KR. Fibroblast growth factor 9 has oncogenic activity and is a downstream target of Wnt signaling in ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 2006;66(3):1354–1362. | |
Richardson AL, Wang ZC, De Nicolo A, et al. X chromosomal abnormalities in basal-like human breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2006;9(2):121–132. | |
Turashvili G, Bouchal J, Baumforth K, et al. Novel markers for differentiation of lobular and ductal invasive breast carcinomas by laser microdissection and microarray analysis. BMC Cancer. 2007;7:55. | |
Notterman DA, Alon U, Sierk AJ, Levine AJ. Transcriptional gene expression profiles of colorectal adenoma, adenocarcinoma, and normal tissue examined by oligonucleotide arrays. Cancer Res. 2001;61(7):3124–3130. | |
Ki DH, Jeung HC, Park CH, et al. Whole genome analysis for liver metastasis gene signatures in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007;121(9):2005–2012. | |
Chen X, Cheung ST, So S, et al. Gene expression patterns in human liver cancers. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(6):1929–1939. | |
Wurmbach E, Chen YB, Khitrov G, et al. Genome-wide molecular profiles of HCV-induced dysplasia and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2007;45(4):938–947. | |
Bhattacharjee A, Richards WG, Staunton J, et al. Classification of human lung carcinomas by mRNA expression profiling reveals distinct adenocarcinoma subclasses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(24):13790–13795. | |
Stearman RS, Dwyer-Nield L, Zerbe L, et al. Analysis of orthologous gene expression between human pulmonary adenocarcinoma and a carcinogen-induced murine model. Am J Pathol. 2005;167(6):1763–1775. | |
Hoek KS, Schlegel NC, Brafford P, et al. Metastatic potential of melanomas defined by specific gene expression profiles with no BRAF signature. Pigment Cell Res. 2006;19(4):290–302. | |
Andersson A, Ritz C, Lindgren D, et al. Microarray-based classification of a consecutive series of 121 childhood acute leukemias: prediction of leukemic and genetic subtype as well as of minimal residual disease status. Leukemia. 2007;21(6):1198–1203. | |
Luo J, Zhou X, Ge X, et al. Upregulation of Ying Yang 1 (YY1) suppresses esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development through heme oxygenase-1. Cancer Sci. 2013;104(11):1544–1551. | |
UICC International Union Against Cancer. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. 6th ed. Sobin LH, Wittekind C, editors. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons; 2002. | |
Shi Y, Seto E, Chang LS, Shenk T. Transcriptional repression by YY1, a human GLI-Krüppel-related protein, and relief of repression by adenovirus E1A protein. Cell. 1991;67(2):377–388. | |
Park K, Atchison ML. Isolation of a candidate repressor/activator, NF-E1 (YY-1, delta), that binds to the immunoglobulin kappa 3′ enhancer and the immunoglobulin heavy-chain mu E1 site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88(21):9804–9808. | |
Yao YL, Dupont BR, Ghosh S, Fang Y, Leach RJ, Seto E. Cloning, chromosomal localization and promoter analysis of the human transcription factor YY1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998;26(16):3776–3783. | |
Gordon S, Akopyan G, Garban H, Bonavida B. Transcription factor YY1: structure, function, and therapeutic implications in cancer biology. Oncogene. 2006;25(8):1125–1142. | |
Castellano G, Torrisi E, Ligresti G, et al. The involvement of the transcription factor Yin Yang 1 in cancer development and progression. Cell Cycle. 2009;8(9):1367–1372. | |
Zaravinos A, Spandidos DA. Yin Yang 1 as a prognostic factor. Cell Cycle. 2009;8(9):1305–1307. | |
Thomassen M, Tan Q, Kruse TA. Gene expression meta-analysis identifies metastatic pathways and transcription factors in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:394. | |
de Nigris F, Botti C, de Chiara A, et al. Expression of transcription factor Yin Yang 1 in human osteosarcomas. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42(15):2420–2424. | |
Chinnappan D, Xiao D, Ratnasari A, Andry C, King TC, Weber HC. Transcription factor YY1 expression in human gastrointestinal cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2009;34(5):1417–1423. | |
Wilson M, Rosato EL, Chojnacki KA, et al. Prognostic significance of lymph node metastases and ratio in esophageal cancer. J Surg Res. 2008;146(1):11–15. | |
Aurello P, D’Angelo F, Nigri G, et al. Comparison between site N-category and number N-category for nodal staging in carcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction: our experience and literature review. Am Surg. 2006;72(2):118–123. |
 © 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.