Back to Journals » OncoTargets and Therapy » Volume 14
Expression of p16, p53, and TLR9 in HPV-Associated Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Clinicopathological Correlations and Potential Prognostic Significance
Authors Wang S, Zhuang X , Gao C, Qiao T
Received 24 November 2020
Accepted for publication 16 January 2021
Published 5 February 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 867—877
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S293163
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Gaetano Romano
Shu Wang, Xibing Zhuang, Caixia Gao, Tiankui Qiao
Center for Tumor Diagnosis and Therapy, Jinshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, 201508, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Tiankui Qiao
Center for Tumor Diagnosis and Therapy, Jinshan Hospital, Fudan University, Jinshan District, Shanghai, 201508, People’s Republic of China
Tel +86 189 3077 8786
Email [email protected]
Purpose: To investigate the association of human papillomavirus (HPV) status with p16, p53, and TLR9 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) and to evaluate these proteins as potential surrogate prognostic markers.
Methods: Expression of p16, p53, and TLR9 was assessed by immunohistochemistry, and HPV status was analyzed by in situ hybridization in 85 tumors of patients with HNSCC. Chi-square test was performed to evaluate the correlations of HPV infection with p16, p53, and TLR9 expression. Kaplan–Meier method and Cox regression analyses were applied to evaluate the associations between the expression levels of these proteins and patient outcomes.
Results: Overall, 24 of the 85 HNSCC specimens were associated with HPV infection. High expression of p16, p53, and TLR9 in tumor cells was observed in 31.76%, 61.18%, and 49.41% of the specimens, respectively. p16 showed a higher diagnostic odds ratio for the prediction of HPV DNA positivity than p53 and TLR9. Improved 5-year overall and disease-free survival correlated with HPV positivity and high p16, low p53, and low TLR9 expression. Associations with improved outcomes were also observed for marker combinations high p16/low p53 and high p16/low p53/low TLR9. In a multivariate analysis, the high p16/low p53 signature showed the lowest hazard ratio regarding death.
Conclusion: The expression of p16, p53, and TLR9 in HNSCC is associated with HPV status. High p53 and TLR9 expression may be related to poor outcomes. The two-marker signature high p16/low p53 in tumor cells is a reliable tool for patient survival prognostication in HNSCC.
Keywords: head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, human papillomavirus, p16, p53, TLR9, prognosis
Introduction
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a heterogeneous disease that includes cancers affecting the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx and is traditionally associated with smoking and alcohol consumption.1 The majority of HNSCC recurrence events or disease-specific deaths occur within the first 2 to 3 years,2 and patients are often considered cured after 5 years. Over the last 20 years, human papillomavirus (HPV) has been implicated in the progression of HNSCC, in particular, oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC).3,4 HPV-positive tumors are different from HPV-negative tumors in many characteristics such as histological appearance, differentiation, risk factors, and prognosis.5,6 Nonetheless, clinical data on the HPV infection rate among Chinese patients with HNSCC remain largely inconsistent.7–9 These discrepancies are primarily due to varied specificity of HPV-genotyping methods, the limited spectrum of HPV types analyzed, and differences among diagnostic criteria for HPV infection.10
Similar to many other oncogenic viruses, HPV integration alters cellular immune surveillance and cellular homeostasis by deregulating gene expression and facilitating epigenetic changes.11,12 The initial outcome is the augmentation of cellular proliferation, which favors viral replication and persistence. The Main players in this event are HPV oncoproteins E6 and E7, which can inhibit many cellular proteins. E6 induces rapid degradation of p53, resulting in the deregulation of a cell cycle checkpoint and the activation of S-phase re-entry. E7 binds to the cellular retinoblastoma protein (pRb) and promotes its degradation, which leads to upregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16.13,14 p16 overexpression is becoming an acceptable surrogate marker of transcriptionally active HPV in oropharyngeal carcinogenesis.15
To guarantee the persistence of HPV infection, HPVs are able to deregulate multiple immunity-related pathways to avoid recognition and clearance by the host immune system.16 TLR9 signaling pathway plays an important role in the natural immune response to the invasion of microorganisms. Historically, TLR9 has been reported to be expressed in plasmacytoid dendritic cells and B cells. On the other hand, recent studies confirmed that abnormal expression of TLR9 correlates with tumor differentiation, invasion, and metastasis.17–19 TLR signaling has been likened to a double-edged sword causing both carcinogenic effects and antitumor responses.20,21 Nevertheless, until the present study, there has been little evidence regarding the correlation between TLR9 expression in HNSCC tumors and HPV associated with HNSCC.
Associations between HPV infection and HNSCC have been observed worldwide, although they have been investigated almost exclusively in economically developed countries.22–25 The aim of this study was to evaluate the correlations and prognostic significance of p16, p53, and TLR9 in HPV-associated HNSCC in the Chinese population and to identify potential molecular and immunological markers of HNSCC.
Materials and Methods
Case Selection
Our study involved 85 cases of HNSCC resection selected at Jinshan Hospital of Fudan University. The diagnosis was made according to the World Health Organization criteria. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) the pathological type is squamous cell carcinoma; (2) the location includes a palatine tonsil, soft palate, tongue root, and the posterior wall of oropharynx, larynx, hypopharynx, oral cavity; (3) tumor specimens for all cases were obtained during a surgical procedure or diagnostic biopsy, and one representative paraffin block was selected for each case; (4) there is no other primary cancer or distant metastasis at the same time. Pathological staging was performed using the 7th edition of the AJCC/UICC TNM classification system (2010).
All specimens underwent HPV DNA detection and p16, p53, and TLR9 protein detection; the study population included 69 males and 16 females, aged 23 to 81 years, with a median age of 62 years. The tumor location was the oropharynx (35 cases), larynx (30 cases), hypopharynx (14 cases), and oral cavity (6 cases). There were 10.59% of patients at stage I, 12.94% at stage II, 16.47% at stage III, and 60% at stage IV (see Table 1).
 |
Table 1 Baseline Clinicopathological Data of Patients with HNSCC and Expression of p53 and TLR9 in Relation to HPV and p16 Status |
Clinicopathological data, including age, sex, tumor location, histological grade, TNM stage, and smoking and drinking history, were obtained from medical charts and pathology reports. The patients were followed for at least 2 years or until death. This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study protocol was approved by (and performed in accordance with the guidelines of) the ethics committee of Jinshan Hospital of Fudan University (Shanghai, China), with the confirmation that all patients whose tissues were analyzed provided written informed consent.
HPV DNA Detection by in situ Hybridization (ISH)
The ISH assay for high-risk-HPV DNA was performed using a Ventana BenchMark automated slide staining system (Ventana Medical System, Inc., Tucson, AZ) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The probes for the detection of 12 oncogenic HPV types were provided by Ventana Medical Systems. Visualization of hybridized DNA was performed with Ventana Red Counterstain II. Blue nuclear dots were designated as positive signals of hybridization. Any definitive nuclear staining was considered positive. Specimens were classified in a binary manner as either test-positive or -negative. The ISH slides were independently reviewed, and the conclusions were agreed on by two pathologists.
Analysis of p16, p53, and TLR9 Expression by Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
Tissue specimens were fixed in 10% neutral formalin, embedded in paraffin, and cut into sections of 4-µm thickness. The sections were deparaffinized and hydrated, followed by microwave treatment in EDTA (pH6.0) for antigen retrieval. Endogenous peroxidase was inactivated using 3% hydrogen peroxide. After three washes with phosphate-buffered saline, the sections were blocked with 10% rabbit serum (DAKO, Hamburg, Germany) for 20 min. Primary antibodies (a rabbit anti-p53 monoclonal antibody, 1:50 dilution, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, USA; rabbit anti-p16 monoclonal antibody, 1:50; and rabbit anti-TLR9 monoclonal antibody, 1:100, Abcam, Cambridge, UK) were incubated with the slides overnight at 4 °C in a humidified chamber, followed by probing with a horseradish peroxidase–conjugated secondary antibody for 30 min at room temperature. The sections were treated at room temperature with a diaminobenzidine solution for color development.
Evaluation of the IHC Data
Known p16- and p53-expressing HNSCC cases served as positive controls. p16 staining was nuclear and cytoplasmic, but p53 staining was solely nuclear. The p16 IHC signals were defined as strong when more than 70% of tumor cells stained.26 For p53, staining was graded—according to the percentage of p53-positive cells—as either low (staining of <25% of all nuclei) or high (staining of ≥25% of all nuclei) nuclear staining.27 For TLR9, the proportion of stained tumor cells was graded as follows: 0 (no stained tumor cells), 1 (<10% of stained tumor cells), 2 (10–50% of stained tumor cells), and 3 (>50% of stained tumor cells). The staining intensity was recorded on a four-point scale: 0 (no staining), 1 (weak staining, light yellow), 2 (moderate staining, yellowish brown), and 3 (strong staining, brown). The staining index was calculated as follows: staining index=staining intensity + score of stained tumor cells. A staining index of ≥4 was defined as high expression of TLR9, and a staining index of <4 as low expression of TLR9.18
Statistical Analyses
The statistical analyses were performed in PASW Statistics 22.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and GraphPad Prism6 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). Correlations of HPV status and the expression of p16, p53, and TLR9 with various clinicopathological findings were evaluated by the Chi-square test. Overall survival (OS) was defined as the time from diagnosis to the date of death or last follow-up; disease-free survival (DFS) was defined as the time from diagnosis to the date of the first recurrence (local, regional, or distant). OS and DFS curves were constructed by the Kaplan–Meier method, and differences were identified with the log rank test. Univariate and multivariate analyses were carried out via the Cox proportional hazards regression model to verify independent risk factors. Data with a P value of <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
HPV Status and p16 Expression
Tumor tissues from 85 patients were tested for the presence of HPV using ISH. The results of HPV ISH and IHC staining with antibodies against p16, p53, and TLR9 are presented in Figure 1A–H. Table 1 shows associations of HPV status and p16 expression with clinicopathological characteristics of the patients with HNSCC. We found that 24 (28.24%) tumors were HPV positive (HPV16: 23 and HPV18: 1), and 61 (71.76%) were HPV negative. Similar to prior reports, 75% (18/24) of HPV-positive tumors were located in the oropharynx. HPV positivity was higher in young patients (P=0.023), in regionally advanced metastatic (N2–3) disease (P=0.033), and when tumor cell differentiation was poor (P=0.006). HPV infection and other clinicopathological characteristics such as sex and clinical stage did not correlate significantly. In addition, the staining of p16 revealed 27 (31.76%) p16-positive and 58 (68.24%) p16-negative tumors. Significantly higher p16 expression in the tumor was also detected in young patients (P=0.003), in regionally advanced metastatic (N2–3) disease (P=0.032), and when tumor cell differentiation was poor (P=0.008). Notably, p16 positivity strongly correlated with HPV16 infection in this cohort (P<0.01).
Protein Expression of P53 and TLR9
We next evaluated p53 and TLR9 protein expression in the tissue cores of 85 HNSCC specimens. Table 2 indicates that p53 and TLR9 immunoreactivity was high in 61.18% (52/85) and 49.41% (42/85) of the HNSCC specimens, respectively. Of note, the expression of p53 and TLR9 in HPV-positive tumors was significantly lower than that in HPV-negative tumors. Only 12.5% (3/24) of the HPV-positive HNSCC tumors featured p53 expression (P<0.001). Similarly, the HPV-negative HNSCC cases had a higher TLR9 positivity rate than that of the HPV-positive group (P=0.019). We also found that p53 and TLR9 expression was significantly lower in p16-positive tumors (Table 1, P<0.05). The high p16/low p53 signature of tumor cells was present in 25.88% (22/85) of the HNSCC cases. Nearly 20% (17/85) of the HNSCC tumors had the high p16/low p53/low TLR9 signature.
 |
Table 2 Associations Between p16, p53, and TLR9 Protein Expression and HPV Status |
Associations of p16, p53, and TLR9 Protein Expression with HPV Status
We then estimated the association of p16, p53, and TLR9 protein expression with HPV status (Table 2). The results showed that HPV-positive HNSCC tumors tested positive for p16, p53, and TLR9 in 95.83% (23/24), 12.5% (3/24), and 29.17% (7/24) of the cases, respectively. There was a strong association between HPV positivity and high p16 expression. In addition, HPV positivity correlated with low p53 and low TLR9 expression. There was also a strong association between HPV positivity and both two-marker signatures high p16/low p53 and high p16/low TLR9 and the three-marker signature high p16/low p53/low TLR9 (P<0.001). High p16 expression alone manifested the highest sensitivity (95.83%) and negative predictive value (98.28%) for HPV status prediction. In contrast, the three-marker signature showed the highest specificity (98.36%) and positive predictive value (94.12%). To directly compare the performance of individual protein markers and multimarker signatures on the detection of HPV-positive HNSCC, diagnostic odds ratios (DORs) were calculated. The DOR ranges from 0 to infinity, with higher values indicating better discriminatory test performance. The highest DOR belonged to high p16 expression as an individual marker.
Associations of p16, p53, and TLR9 Protein Expression with Survival
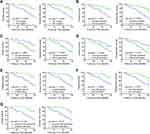
We also assessed the association of p16, p53 and TLR9 protein expression with survival of HNSCC patients. Kaplan–Meier analysis indicated that both improved OS and DFS among the patients with HNSCC were associated with HPV positivity and high p16, low p53, and low TLR9 expression in tumor cells (Figure 2A–D). The two-marker signatures high p16/low p53 and high p16/low TLR9 and the three-marker signature high p16/low p53/low TLR9 were also associated with better 5-year OS and DFS (Figure 2E–G). Furthermore, univariate Cox regression analysis revealed lower overall risk of death for patients with HNSCC with HPV positivity and high p16 expression in the tumor (Table 3). By contrast, hazard ratios were higher in HNSCC cases with high p53 or high TLR9 expression. The 5-year OS rates corresponding to high p53 or high TLR9 expression in the tumor were 46.2% and 45.2%, respectively. The multimarker signatures high p16/low p53, high p16/low TLR9, and high p16/low p53/low TLR9 were associated with reduced overall risk of death.
 |
Table 3 Univariate and Multivariate Cox Regression Analyses of OS Among the 85 Patients with HNSCC |
Comparable results were obtained for the probability of DFS, which was evaluated as a secondary endpoint (Table 4). Low p53 expression was associated with favorable 5-year DFS; the 5-year DFS rate corresponding to low p53 was 63.6%. TLR9 expression statistically significantly correlated with the 5-year DFS rate too. Patients with tumors underexpressing TLR9 exhibited better DFS. The 5-year DFS rate corresponding to low TLR9 was 60.5%.
 |
Table 4 Univariate and Multivariate Cox Regression Analyses of DFS Among the 85 Patients with HNSCC |
Besides, we used Cox proportional hazards models adjusted for age, smoking history, alcohol intake, T stage, and N stage to evaluate and compare the prognostic significance of the various parameters. In the multivariate analysis of all 85 patients, advanced regional metastasis (N2–N3) turned out to be an independent risk factor for poor OS and DFS (Tables 3 and 4). High p16 expression combined with low p53 levels was found to be an independent predictive factor of favorable OS and DFS. For TLR9 and alcohol history, the overall P value remained nonsignificant, though differences were found between subgroups.
Discussion
HPV-positive tumor cells overexpress the p16 protein in a diffuse manner. This overexpression is directly related to the molecular process involved in carcinogenesis induced by major HPV oncoproteins (E6 and E7). The p16 protein is both a key element of the negative feedback mechanism of mitosis, and is a regulator of a cell growth factor.13,14 The 8th edition TNM classification for HNSCC distinguishes between OPSCC with and without HPV infection and recommends p16 immunostaining for the identification of tumors with positive HPV status. This is because p16 overexpression is crucial for cell survival in HPV-positive tumors, whereas p16 overexpression is frequently absent in HPV-negative tumors. These data make p16 overexpression a reliable surrogate marker of transcriptionally active HPV.28 Nonetheless, p16 expression alone as a biomarker of positive HPV status may have limitations due to HPV-independent mechanisms of p16 upregulation.29 Our study is suggestive of an additional potential mechanism, the one involving lower p53 and TLR9 expression in HPV-positive HNSCC.
Some investigators have evaluated the relation between p53 and HPV in HNSCC.30,31 The most comprehensive integrative genomic analysis of HNSCCs in The Cancer Genome Atlas (http://gdac.broadinstitute.org/) has confirmed that p53 is the most frequently mutated gene in HNSCC. Moreover, tumors of the larynx and hypopharynx have the highest p53 mutation rate, tumors of the tongue and oral cavity have an intermediate p53 mutation rate, and tumors of the oropharynx (including the tonsils) and of the base of tongue have the lowest p53 mutation rate. The finding that the lowest p53 mutation rate is characteristic of tumors of the oropharynx and tonsils is not surprising given that the vast majority of oropharyngeal cancers are associated with HPV. In our study, among the 24 cases of HPV-associated OPSCC, only 3 primary tumors were p53 positive. One possible explanation for this phenomenon is that HPV-associated OPSCC does not carry p53 gene mutations and expresses only a small amount of the wild-type p53 protein with shorter half-life.32 Another possibility is that the HPV16 E6 protein promotes the degradation of accumulated mutant p53 proteins by ubiquitination or other pathways.33
HNSCC is commonly recognized as an immunosuppressive disease due to the HPV activity that can abrogate the initial steps of an innate immune response involving Toll-like receptor signaling, thus compromising the immune response to an invasive agent. The expression of TLR9 is reported to be altered during HPV infection. In cervical cancer, HPV16 E7 oncoprotein induces a transcriptional repressive complex that suppresses TLR9 expression and induces epigenetic changes.34 In addition, TLR9 expression is downregulated by other oncogenic viruses.35–37 On the other hand, TLR9 was reported to be overexpressed in high-grade cervical cancer owing to compensation for TLR deficiency or via mechanisms of the host immune defense system against tumor cells.38–41 TLR9 expression has also been assessed in oral squamous cell carcinoma, and in that study, Toll-like receptors were to have higher expression levels, which were associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation.42 Whether the increased level of TLR9 is related to malignant transformation or to a reaction of the host immune system to tumor cells is still not clear. In our study, TLR9 was more often underexpressed in HPV-positive HNSCC tumors (P=0.019) and was associated with OS (P=0.028) and DFS (P=0.011).
Likewise, our findings indicate that HPV infection and high p16 expression significantly correlate with several patient and disease characteristics, including younger age, nonsmoking status, poor differentiation, regionally advanced N class, and tumor site. HPV infection and high p16 expression in oropharynx tumors were different from those in the larynx and hypopharynx tumors. The p16 positivity of oropharynx tumors (57.14%) was significantly higher (P=0.001) than that of other cancers: laryngeal (13.33%), hypopharyngeal (16.67%), and oral-cavity tumors (16.67%). Additionally, high p16 staining showed the strongest association with HPV infection when evaluated as a single marker (sensitivity 95.83%, specificity 93.44%). Besides, we observed that specificity of the two-marker signature high p16/low TLR9 and of the three-marker signature high p16/low p53/low TLR9 was higher, but sensitivity was lower. According to the DOR as a performance metric, high p16 expression alone was the best surrogate marker of HPV infection. The addition of proteins p53 and TLR9 did not significantly increase the diagnostic performance of p16 as a single marker.
Some research articles suggested that HPV DNA detection alone, combined detection of HPV DNA and protein p16, the analysis of p16 protein expression alone, or HPV E6/E7 mRNA expression identify patients with HNSCC with favorable prognosis.43–45 In our study, the Kaplan–Meier method and univariate analysis revealed that improved outcomes were associated with high p16, low p53, and low TLR9 expression. Furthermore, the multimarker signatures high p16/low p53, high p16/low TLR9, and high p16/low p53/low TLR9 were associated with reduced risks of death and of disease recurrence and progression. The parameter high p16/low p53 retained prognostic significance in multivariate analyses. Our results indicate that high p16/low p53 expression provides consistent prognostic information and may therefore serve as a reliable surrogate marker of favorable prognosis.
In our study, we utilized HPV DNA positivity by ISH as the gold standard for HPV infection detection. ISH even has the advantage of direct visualization of HPV in nuclei, indicative of HPV integration, and is used as a more practical tool by diagnostic pathologists; HPV E6/E7 mRNA detection is also considered the best marker of biologically relevant HPV infection. Moreover, because the sample size here is modest, stratification by multivariate analysis failed to uncover an association with other parameters, except for advanced regional metastasis (N2–N3) and high p16/low p53. Consequently, we could not draw firm conclusions concerning the survival results.
Conclusion
Our results show that the expression of p16, p53, and TLR9 in HNSCC is associated with HPV status in the tumor tissue. High p53 and TLR9 expression may be related to poor outcomes. The two-marker signature high p16/low p53 expression in tumor cells is a reliable tool for patient survival prognostication in HNSCC.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Jinshan Health Planning Committee Fund (grant number JSKJ-KTMS-2018-06).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Solomon B, Young RJ, Rischin D. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: genomics and emerging biomarkers for immunomodulatory cancer treatments. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018;52(Pt 2):228–240. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2018.01.008
2. Hoffman HT, Karnell LH, Funk GF, Robinson RA, Menck HR. The national cancer data base report on cancer of the head and neck. Arch Otolaryngol. 1998;124(9):951–962. doi:10.1001/archotol.124.9.951
3. Taberna M, Mena M, Pavon MA, Alemany L, Gillison ML, Mesia R. Human papillomavirus-related oropharyngeal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(10):2386–2398. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdx304
4. de Martel C, Plummer M, Vignat J, Franceschi S. Worldwide burden of cancer attributable to HPV by site, country and HPV type. Int J Cancer. 2017;141(4):664–670. doi:10.1002/ijc.30716
5. Krump NA, Liu W, You J. Mechanisms of persistence by small DNA tumor viruses. Curr Opin Virol. 2018;32:71–79. doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2018.09.002
6. Emmett S, Whiteman DC, Panizza BJ, Antonsson A. An update on cellular microRNA expression in human papillomavirus-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncology. 2018;95(4):193–201. doi:10.1159/000489786
7. Wei W, Shi Q, Guo F, et al. The distribution of human papillomavirus in tissues from patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2012;28(5):1750–1756. doi:10.3892/or.2012.1990
8. Wang Z, Xia RH, Ye DX, Li J. Human papillomavirus 16 infection and TP53 mutation: two distinct pathogeneses for oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma in an eastern chinese population. PLoS One. 2016;11(10):e0164491. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0164491
9. Xu T, Shen C, Wei Y, et al. Human papillomavirus (HPV) in Chinese oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC): a strong predilection for the tonsil. Cancer Med. 2020;9:6556–6564. doi:10.1002/cam4.3339
10. Bukhari N, Joseph JP, Hussain SS, et al. Prevalence of human papilloma virus sub genotypes following head and neck squamous cell carcinomas in asian continent, a systematic review article. Asian Pac J Cancer Preven. 2019;20(11):3269–3277. doi:10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.11.3269
11. Speel EJ. HPV integration in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: cause and consequence. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2017;206:57–72. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-43580-0_4
12. Anayannis NV, Schlecht NF, Belbin TJ. Epigenetic mechanisms of human papillomavirus-associated head and neck cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2015;139(11):1373–1378. doi:10.5858/arpa.2014-0554-RA
13. Tomaic V. Functional roles of E6 and E7 oncoproteins in HPV-induced malignancies at diverse anatomical sites. Cancers. 2016;8:95. doi:10.3390/cancers8100095
14. Hoppe-Seyler K, Bossler F, Braun JA, Herrmann AL, Hoppe-Seyler F. The HPV E6/E7 oncogenes: key factors for viral carcinogenesis and therapeutic targets. Trends Microbiol. 2018;26(2):158–168. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2017.07.007
15. Kim Y, Joo YH, Kim MS, Lee YS. Prevalence of high-risk human papillomavirus and its genotype distribution in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(5):411–418. doi:10.4132/jptm.2020.06.22
16. Grabowska AK, Riemer AB. The invisible enemy - how human papillomaviruses avoid recognition and clearance by the host immune system. Open Virol J. 2012;6:249–256. doi:10.2174/1874357901206010249
17. Samara KD, Antoniou KM, Karagiannis K, et al. Expression profiles of Toll-like receptors in non-small cell lung cancer and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Oncol. 2012;40(5):1397–1404. doi:10.3892/ijo.2012.1374
18. Gao C, Qiao T, Zhang B, Yuan S, Zhuang X, Luo Y. TLR9 signaling activation at different stages in colorectal cancer and NF-kappaB expression. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:5963–5971. doi:10.2147/OTT.S174274
19. Tuomela J, Sandholm J, Karihtala P, et al. Low TLR9 expression defines an aggressive subtype of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;135(2):481–493. doi:10.1007/s10549-012-2181-7
20. Rich AM, Hussaini HM, Parachuru VP, Seymour GJ. Toll-like receptors and cancer, particularly oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front Immunol. 2014;5:464. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00464
21. Basith S, Manavalan B, Yoo TH, Kim SG, Choi S. Roles of toll-like receptors in cancer: a double-edged sword for defense and offense. Arch Pharm Res. 2012;35(8):1297–1316. doi:10.1007/s12272-012-0802-7
22. Chaturvedi AK, Anderson WF, Lortet-Tieulent J, et al. Worldwide trends in incidence rates for oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancers. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(36):4550–4559. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.50.3870
23. Ang KK, Harris J, Wheeler R, et al. Human papillomavirus and survival of patients with oropharyngeal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(1):24–35. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0912217
24. Castellsague X, Alemany L, Quer M, et al. HPV involvement in head and neck cancers: comprehensive assessment of biomarkers in 3680 patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016;108(6):djv403. doi:10.1093/jnci/djv403
25. Bulane A, Goedhals D, Seedat RY, Goedhals J, Burt F. Human papillomavirus DNA in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas in the Free State, South Africa. J Med Virol. 2020;92(2):227–233. doi:10.1002/jmv.25556
26. Singhi AD, Westra WH. Comparison of human papillomavirus in situ hybridization and p16 immunohistochemistry in the detection of human papillomavirus-associated head and neck cancer based on a prospective clinical experience. Cancer. 2010;116(9):2166–2173. doi:10.1002/cncr.25033
27. Cruz I, Snijders PJ, Van Houten V, Vosjan M, Van der Waal I, Meijer CJ. Specific p53 immunostaining patterns are associated with smoking habits in patients with oral squamous cell carcinomas. J Clin Pathol. 2002;55(11):834–840. doi:10.1136/jcp.55.11.834
28. Ndiaye C, Mena M, Alemany L, et al. HPV DNA, E6/E7 mRNA, and p16INK4a detection in head and neck cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(12):1319–1331. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70471-1
29. Sekee TR, Burt FJ, Goedhals D, Goedhals J, Munsamy Y, Seedat RY. Human papillomavirus in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas in a South African cohort. Papillomavirus Res. 2018;6:58–62. doi:10.1016/j.pvr.2018.10.006
30. Hong A, Zhang X, Jones D, et al. Relationships between p53 mutation, HPV status and outcome in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Radiother Oncol. 2016;118(2):342–349. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2016.02.009
31. Caicedo-Granados E, Lin R, Fujisawa C, Yueh B, Sangwan V, Saluja A. Wild-type p53 reactivation by small-molecule Minnelide in human papillomavirus (HPV)-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2014;50(12):1149–1156. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2014.09.013
32. Westra WH, Taube JM, Poeta ML, Begum S, Sidransky D, Koch WM. Inverse relationship between human papillomavirus-16 infection and disruptive p53 gene mutations in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(2):366–369. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1402
33. Scheffner M, Huibregtse JM, Vierstra RD, Howley PM. The HPV-16 E6 and E6-AP complex functions as a ubiquitin-protein ligase in the ubiquitination of p53. Cell. 1993;75(3):495–505. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90384-3
34. Hasan UA, Zannetti C, Parroche P, et al. The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein induces a transcriptional repressor complex on the toll-like receptor 9 promoter. J Exp Med. 2013;210(7):1369–1387. doi:10.1084/jem.20122394
35. van Gent M, Griffin BD, Berkhoff EG, et al. EBV lytic-phase protein BGLF5 contributes to TLR9 downregulation during productive infection. J Immunol. 2011;186(3):1694–1702. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0903120
36. Vincent IE, Zannetti C, Lucifora J, et al. Hepatitis B virus impairs TLR9 expression and function in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26315. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026315
37. Shahzad N, Shuda M, Gheit T, et al. The T antigen locus of Merkel cell polyomavirus downregulates human Toll-like receptor 9 expression. J Virol. 2013;87(23):13009–13019. doi:10.1128/JVI.01786-13
38. Aggarwal R, Misra S, Guleria C, et al. Characterization of toll-like receptor transcriptome in squamous cell carcinoma of cervix: a case-control study. Gynecol Oncol. 2015;138(2):358–362. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2015.05.029
39. DeCarlo CA, Rosa B, Jackson R, Niccoli S, Escott NG, Zehbe I. Toll-like receptor transcriptome in the HPV-positive cervical cancer microenvironment. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:785825. doi:10.1155/2012/785825
40. Hasimu A, Ge L, Li QZ, Zhang RP, Guo X. Expressions of Toll-like receptors 3, 4, 7, and 9 in cervical lesions and their correlation with HPV16 infection in Uighur women. Chin J Cancer. 2011;30(5):344–350. doi:10.5732/cjc.010.10456
41. Ghosh A, Dasgupta A, Bandyopadhyay A, et al. A study of the expression and localization of toll-like receptors 2 and 9 in different grades of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol. 2015;99(3):720–724. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2015.11.015
42. Min R, Siyi L, Wenjun Y, et al. Toll-like receptor-9 agonists increase cyclin D1 expression partly through activation of activator protein-1 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci. 2012;103(11):1938–1945. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02394.x
43. Schache AG, Liloglou T, Risk JM, et al. Evaluation of human papilloma virus diagnostic testing in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: sensitivity, specificity, and prognostic discrimination. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(19):6262–6271. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0388
44. Ukpo OC, Flanagan JJ, Ma XJ, Luo Y, Thorstad WL, Lewis JS. High-risk human papillomavirus E6/E7 mRNA detection by a novel in situ hybridization assay strongly correlates with p16 expression and patient outcomes in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35(9):1343–1350. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e318220e59d
45. Ni G, Huang K, Luan Y, et al. Human papillomavirus infection among head and neck squamous cell carcinomas in southern China. PLoS One. 2019;14(9):e0221045. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0221045
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.