Back to Journals » Vascular Health and Risk Management » Volume 13
Evaluation of vitamin D levels in relation to coronary CT angiographic findings in an Iranian population
Authors Moradi M, Foroutanfar A
Received 27 May 2017
Accepted for publication 14 July 2017
Published 4 October 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 361—367
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/VHRM.S142721
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takashi Kajiya
Maryam Moradi, Ali Foroutanfar
Radiology Department, Medical School, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
Background: Vitamin D deficiency, as a predisposing factor for coronary artery disease (CAD), is a subject of increasing interest. However, its role as a risk factor has not been proven. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between serum vitamin D levels and CAD.
Materials and methods: Using a cross-sectional design, 180 patients who were candidates for coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) were selected. Serum levels of vitamin D were measured and compared with the results of CCTA (including calcium score, and presence and severity of coronary artery involvement due to atherosclerotic plaques).
Results: The mean age of the participants was 60.5±10.6 years and the mean serum vitamin D level was 26.2±15.9 ng/dL (range, 3.5–83.2 ng/dL). Overall, 6.1% of the participants (n=11) had vitamin D deficiency, 56.1% (n=101) had insufficient levels of vitamin D, and 37.8% (n=68) had sufficient levels of vitamin D. The mean serum vitamin D level was significantly lower in patients with severe CAD (P=0.004). The serum vitamin D level in the “positive for CAD” group was 20.98 ng/mL, significantly lower than the level in the “negative for CAD” group (30.47 ng/mL; P<0.001). The mean calcium score among participants was 533.5±87.9. Based on the Spearman test, a significant negative correlation (–0.21) was detected between the serum vitamin D level and coronary artery calcium score (CACS) (P=0.005). Conversely, the mean CACS in the vitamin D deficient group was significantly higher than in the insufficient and sufficient vitamin D groups (P<0.001 for both comparisons).
Conclusion: Vitamin D deficiency was associated with coronary artery calcification and severity of coronary artery stenosis in Iranian patients.
Keywords: coronary artery disease, vitamin D, multidetector computed tomography, atherosclerosis, angiography
Introduction
Although vitamin D is traditionally associated with bone health because of its crucial role in bone and mineral metabolism,1 different nonskeletal functions have been proposed for this critical vitamin. Recently, a much broader role has been implicated for this unique vitamin, owing to the presence of its receptor in different tissues, including cardiovascular organs. Atherosclerosis, as a hallmark of cardiovascular disorders, is a complex process that can progress for decades before presentation.2 Inflammatory changes, osteogenesis and bone-forming mechanisms, angiogenesis, and endothelial dysfunction are examples of important issues associated with the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, which are directly or indirectly affected by vitamin D.3–8
Several studies have been performed on the association between vitamin D status and different aspects of cardiovascular disorders, including metabolic syndrome,9 hypertension,10,11 calcified atherosclerotic plaques,12,13 severity of luminal stenosis in coronary arteries,14,15 tortuosity of coronary arteries,16 and even the final outcomes or lethal events of coronary artery disease (CAD).17 In this regard, the need for increased attention has been proposed, suggesting the role of vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor for CAD. However, there remains insufficient evidence owing to controversial reports in the literature both in favor of18 and against19 this concept. However, genetic polymorphism of the vitamin D receptor could modify its role.20 Thus, differences in ethnicity, lifestyle, and geographic conditions could potentially change its effects. The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between vitamin D levels and coronary artery computed tomography (CT) angiographic findings in an Iranian population.
Materials and methods
In this cross-sectional study, we invited patients who had been referred for coronary artery CT angiography (CTA) by a cardiologist. Patients with a history of recent vitamin D intake, chronic diseases (including known hepatic, renal, endocrine, or metabolic diseases), and those with a history of a coronary stent or bypass grafting were all excluded. All subjects gave informed consent following explanation and clarification of the process.
The sample comprised 180 patients. Initially, the age and sex of each patient was recorded, as well as any family history of CAD and cigarette smoking. Patients were introduced to a constant laboratory environment at our hospital on the same day of CTA. Blood samples were taken and analyzed, and serum levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) were measured using high-performance liquid chromatography. Based on the levels of vitamin D measured, patients were categorized into four groups as follows: vitamin D deficiency (<10 ng/mL), insufficient level of vitamin D (10–30 ng/mL), sufficient level of vitamin D (31–100 ng/mL), and toxic level of vitamin D (>100 ng/mL).21 Noncontrast followed by contrast-enhanced coronary CTA were performed for all the participants using a 64-slice scanner system (Lightspeed VCT 64; GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences Corp., Piscataway, NJ, USA). The coronary artery calcium score (CACS) was measured using the Agatston scoring method (Smart Score software) and was recorded for each patient. Patients were categorized into five groups based on their scores as follows (based on Rumberger’s guidelines):22 normal (CACS =0), minimal (CACS =1–10), mild (CACS =11–100), moderate (CACS =101–400), and severe (CACS >400). A retrospective electrocardiogram-gated technique was used. The scan delay was calculated using the test bolus technique. A bolus of 85 mL of the iodinated contrast (Visipaque [GE Healthcare], Omnipaque [GE Healthcare], or Scanlux [Sanochemia, Vienna, Austria]) was injected, followed by saline, intravenously at a flow rate of 4–6 mL/s. The scan parameters were: collimation, 64 × 0.625 mm; tube current, 400–600 mA; tube voltage, 120 kV; and gantry rotation time, 350 ms.
First, the source images were reconstructed at 75% of the R-R interval to serve as default images; however, other phase locations were available and reviewed if necessary. Both thin-slice maximum intensity projections and curved multiplanar reconstructions were utilized. Coronary artery stenosis was assessed, and the severity of stenosis was estimated (as the ratio of the luminal diameter of the most stenotic area over that of the unaffected distal portion) and assumed as significant if it was 50% or more. All scans were independently reviewed by a cardiologist and a radiologist experienced in coronary CTA. Accordingly, patients were categorized into five groups: normal (no plaque), nonsignificant (presence of plaque with less than 50% stenosis), single-vessel, double-vessel, and triple-vessel disease (significant plaque in one, two, or three major coronary arteries, respectively). We also divided patients into two larger groups, the “negative for CAD” group that included those who were normal and nonsignificant and “positive for CAD” that included the other three groups. All data about participants were analyzed using the SPSS software (v20; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Quantitative variables and qualitative variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation, and proportions were expressed as percentages. The data were analyzed using the chi-squared test, paired t-test, Spearman correlation coefficient, and linear regression analysis. A two-sided α level of 0.05 was used to assess the statistical significance. This study (research project number 394823) was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Isfahan University of Medical Sciences.
Results
The most common reason for patient referral was atypical chest pain or chest discomfort (59%). Typical chest pain, arrhythmia, and unexplained reduced ejection fraction were among the other indications. The mean age of participants was 60.5±10.6 years (range 30-80 years) and the age distribution was as follows: 16.7% (n=30) were less than 50 years of age; 26.1% (n=47) were between 50 and 59 years; 30.6% (n=55) were between 60 and 69 years; and 26.7% (n=40) were older than 70 years. About 57% (n=102) were male, 33% (n=60) were smokers, and 21.7% (n=39) had a positive family history of CAD in first-degree relatives. The distribution of serum vitamin D levels, calcium scores, and demographic variables at different stages of CAD is shown in Table 1.
  | Table 1 Demographic variables, serum vitamin D levels, and coronary artery calcium score according to severity of coronary artery disease |
The CT angiographic findings among participants were as follows: 22.2% (n=40) had normal CTA; 32.8% (n=59) had nonsignificant findings; 11.7% (n=21) had single-vessel disease (SVD); 8.3% (n=15) had double-vessel disease (DVD); and 25% (n=45) had triple-vessel disease (TVD). We also divided patients into two larger groups, the “negative for CAD” (n=99, 55%) and “positive for CAD” (n=81, 45%) groups. Positive CAD was more prevalent in males and smokers (P=0.005). Negative CTA was more prevalent in those with a negative family history; however, this difference was not significant (P=0.1).
The mean calcium score among participants was 533.5±87.9; 8.3% (n=15), 5% (n=9), 20.6% (n=37), 29.4% (n=53), and 36.7% (n=66) had normal, minimal, mild, moderate, and severe calcium scores, respectively. As expected, the mean calcium score was significantly higher in patients with severe CAD (P<0.001). According to the Spearman test, a significant negative correlation coefficient (–0.21) was detected between serum vitamin D levels and CACS (P=0.005) (Figure 1). Conversely, the mean CACS in the vitamin D deficient group was significantly higher than in the vitamin D insufficient and sufficient groups (P<0.001) (Figure 2).
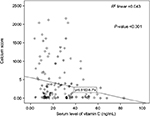  | Figure 1 Spearman correlation between vitamin D levels in serum and the coronary artery calcium score. |
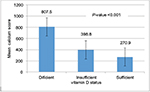  | Figure 2 Mean calcium score in different groups based on vitamin D level. |
The mean vitamin D serum level was 26.2±15.9 ng/dL with a range of 3.5–83.2 ng/dL. Based on the results of vitamin D serum levels, 6.1% of all participants (n=11) had vitamin D deficiency, 56.1% (n=101) had insufficient levels of vitamin D, and 37.8% (n=68) had sufficient levels of vitamin D. The mean vitamin D serum levels in males and females were 20.78±9.9 and 33.28±19.3 ng/dL, respectively, and this difference was statistically significant (P<0.001). The mean serum vitamin D level declined remarkably (P=0.004) as the severity of CAD increased (from normal to nonsignificant status, to single-, double-, and triple-vessel stenosis), as shown in Figure 3. The distribution of serum vitamin D (median, 25th and 75th percentile) at different stages of CAD is also shown in Figure 4. The serum vitamin D level in the “positive for CAD” group was 20.98 ng/mL, a value that was significantly lower than that (30.47 ng/mL) in the “negative for CAD” group (P<0.001). Logistic regression analysis (the backward conditional method) showed that sex, cigarette smoking, and calcium score played significant roles in CAD. The odds ratios (OR) for males, cigarette smoking, and calcium score were 4.4 (P=0.002), 4.5 (P=0.002), and 1.006 (P<0.001), respectively. According to this analysis, family history and vitamin D levels played no significant roles in modifying the risk of coronary artery involvement.
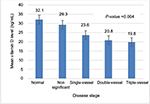  | Figure 3 Mean vitamin D levels in different coronary artery disease groups. |
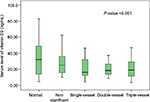  | Figure 4 Median 25th and 75th percentile of vitamin D in different coronary artery disease groups. |
Discussion
Vitamin D deficiency is a major global health challenge, particularly in developing countries such as Iran, which has a high prevalence of the condition.23,24 In the present study, ~6.1% of all patients had vitamin D deficiency (below 10 ng/mL), and 56.1% had insufficient levels of vitamin D (below 30 ng/mL). Recent studies have used a cutoff point of 20 ng/mL to define deficiency and a range of 21–30 ng/mL to define insufficiency.25 However, we used a limit of 10 ng/mL because it has been the value that is consistently used in the reporting sheet of our referral laboratory. If we assume, however, a value of 30 ng/mL as the cutoff point for normal versus abnormal levels, the abnormal vitamin D levels in our study (62%) would be similar to those of previous Iranian reports.26,27
The role of vitamin D deficiency in various disorders, including CAD, has been evaluated, but with conflicting results. However, genetic polymorphisms in the vitamin D receptor suggest that ethnicity-related differences might affect the incidence of vitamin D deficiency. These findings motivated the present evaluation among the Iranian population. Our study demonstrated that there is indeed a relationship between serum vitamin D levels and severity of CAD. These results are contrary to those of Ho et al;28 however, this disparity could be attributed to differences in geographic location and ethnicity, as well as a lower CAD prevalence in that study and the absence of female participants. Furthermore, the relatively small sample in the present study was also a contributing factor. Other studies that have focused on this issue in Iran29,30 have consistently found a relationship between coronary artery-related disorders and vitamin D deficiency, but they have not focused directly on detailed angiographic data. However, the present study showed a significant relationship between increased CACS and the severity of vitamin D abnormalities (deficiency or insufficiency). Considering the important and proven role of the CACS in predicting the plaque burden of coronary arteries, its significant relationship with low vitamin D levels (in the present study) could support the idea of a meaningful relationship between CAD severity and abnormal vitamin D levels. In addition, the average CACS in different CAD groups were compared and found to be in agreement with the findings of another study in a similar population.31
In a recently published study by Manousaki et al, genetically reduced 25(OH)D levels were not associated with an increased risk of CAD, suggesting that a possible relationship between vitamin D levels and CAD might either be confounded or due to reverse causation.19 Vitamin D deficiency is associated with various conditions, including obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.9,10,32 Significant relationships also exist between vitamin D-associated abnormalities and major cardiovascular events, such as heart failure, myocardial infarction, sudden cardiac death, stroke, atrial fibrillation, and peripheral vascular disease.17,33
The pathophysiology of these relationships is not clearly understood; however, hyperactivity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system seems to play an important role,34 and vitamin D regulates the renin-angiotensin axis by directly suppressing the expression of the renin gene. Vascular smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells express receptors for vitamin D, and the vascular effects of vitamin D include modulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation, inflammation, and thrombosis.35 However, vitamin D deficiency can lead to secondary hyperparathyroidism. Parathyroid hormone can cause myocyte hypertrophy and vascular remodeling, and has proinflammatory effects that increase cytokine release from vascular smooth muscle cells.36,37 In addition, inflammation of epicardial adipose tissue, which has been considered in pathogenesis of CAD, is enhanced by vitamin D deficiency.38
Although we demonstrated a significant relationship between vitamin D deficiency and CAD, some limitations remain. We must acknowledge that CAD is a chronic process that usually begins during childhood; however, we only had a single laboratory report of vitamin D levels that could not have been representative of past or lifelong vitamin D status. Vitamin D levels can also change, depending on the season, and this was not evaluated in the present study. However, our sampling almost evenly covered all the four seasons, to reduce the effects of seasonal fluctuations. We also relied on patient memory regarding the avoidance of supplements around the time of sampling; thus, memory bias could not have been eliminated. Many studies support the relationship between hypertension and vitamin D deficiency, and considering the relationship between hypertension and CAD, this condition could represent a confounding variable. Further studies devoid of these limiting factors and including larger samples are needed for clarification of this hypothesis.
Conclusion
Vitamin D levels were associated with the CACS and severity of luminal stenosis due to atherosclerotic plaques. Based on the relatively high incidence of cardiovascular disease and vitamin D deficiency in the screening population, treatment with vitamin D supplements could be beneficial.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Holick MF. The role of vitamin D for bone health and fracture prevention [review]. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2006;4(3):96–102. | ||
Otsuka F, Sakakura K, Yahagi K, Joner M, Virmani R. Has our understanding of calcification in human coronary atherosclerosis progressed? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34(4):724–736. | ||
Leszczynska A, O’Doherty A, Farrell E, et al. Differentiation of vascular stem cells contributes to ectopic calcification of atherosclerotic plaque. Stem Cells. 2016;34(4):913–923. | ||
Pillar R, G Lopes MG, Rocha LA, et al. Severe hypovitaminosis D in chronic kidney disease: association with blood pressure and coronary artery calcification. Hypertens Res. 2013;36(5):428–432. | ||
Shioi A. [Mechanism of vascular calcification]. Clin Calcium. 2004;14(1):133–139. Japanese. | ||
Mantell D, Owens P, Bundred N, Mawer E, Canfield A. 1α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Circ Res. 2000;87(3):214–220. | ||
Al Mheid I, Patel R, Murrow J, et al. Vitamin D status is associated with arterial stiffness and vascular dysfunction in healthy humans. J Am Coll of Cardiol. 2011;58(2):186–192. | ||
Menezes AR, Lamb MC, Lavie CJ, DiNicolantonio JJ. Vitamin D and atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2014;29(6):571–577. | ||
Sung KC, Chang Y, Ryu S, Chung HK. High levels of serum vitamin D are associated with a decreased risk of metabolic diseases in both men and women, but an increased risk for coronary artery calcification in Korean men. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2016;15(1):112. | ||
Chen S, Sun Y, Agrawal DK. Vitamin D deficiency and essential hypertension. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2015;9(11):885–901. | ||
Akbari R, Adelani B, Ghadimi R. Serum vitamin D in hypertensive patients versus healthy controls is there an association? Caspian J Intern Med. 2016;7(3):168–172. | ||
Lee S, Ahuja V, Masaki K, et al. A significant positive association of vitamin D deficiency with coronary artery calcification among middle-aged men: for the ERA JUMP study. J Am Coll Nutr. 2016;35(7):614–620. | ||
Lai S, Fishman EK, Gerstenblith G, et al. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with coronary artery calcification in cardiovascularly asymptomatic African Americans with HIV infection. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2013;9:493–500. | ||
Wu Z, Wang T, Zhu S, Li L. Effect of vitamin D supplementation as an adjuvant therapy in coronary artery disease patients. Scand Cardiovasc J. 2016;50(1):9–16. | ||
Alsancak Y, Cengel A, Akyel A, et al. Relationship between serum vitamin D levels and angiographic severity and extent of coronary artery disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 2015;45(9):940–948. | ||
Oz F, Cizgici AY, Topuz M, et al. Vitamin D insufficiency is associated with coronary artery tortuosity. Kardiol Pol. 2017;75(2):174–180. | ||
Naesgaard PA, León de la Fuente RA, Nilsen ST, et al. Suggested cut-off values for vitamin D as a risk marker for total and cardiac death in patients with suspected acute coronary syndrome. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2016;3:4. | ||
Sogomonian R, Alkhawam H, Jolly J, et al. Serum vitamin D levels correlate to coronary artery disease severity: a retrospective chart analysis. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2016;14(8):977–982. | ||
Manousaki D, Mokry LE, Ross S, Goltzman D, Richards JB. Mendelian randomization studies do not support a role for vitamin D in coronary artery disease. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2016;9(4):349–356. | ||
Abu El Maaty MA, Hassanein SI, Gad MZ. Genetic variation in vitamin D receptor gene (Fok1:rs2228570) is associated with risk of coronary artery disease. Biomarkers. 2016;21(1):68–72. | ||
Gallagher JC, Sai AJ. Vitamin D insufficiency, deficiency, and bone health. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(6):2630–2633. | ||
Rumberger JA, Kaufman L. A rosetta stone for coronary calcium risk stratification: agatston, volume, and mass scores in 11,490 individuals. Am J Roentgenol. 2003;181(3):743–748. | ||
Palacios C, Gonzalez L. Is vitamin D deficiency a major global public health problem? J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014;144(Pt A):138–145. | ||
Hossein-Nezhad A, Khoshniat N, Maghbooli M, et al. Relationship between serum vitamin D concentration and metabolic syndrome among Iranian adults population. DARU J Pharm Sci. 2015;17(1):1–5. | ||
Ross AC, Manson JE, Abrams SA, et al. The 2011 report on dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D from the Institute of Medicine: what clinicians need to know. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2011;96(1):53–58. | ||
Rahnavard Z, Eybpoosh S, Homami MR, et.al. Vitamin D deficiency in healthy male population: results of the Iranian multi-center osteoporosis study. Iran J Public Health. 2010;39(3):45–52. | ||
Ardeshir Larijani F, Kalantar Motamedi SM, Keshtkar AA, et.al. The Relation between serum vitamin D levels and blood pressure: a population-based study. Acta Med Iran. 2014;52(4):290–297. | ||
Ho JS, Cannaday JJ, Barlow CE, Reinhardt DB, Wade WA, Ellis JR. Low 25-OH vitamin D levels are not associated with coronary artery calcium or obstructive stenoses. Coron Artery Dis. 2015;26(6):521–525. | ||
Mahdavi K, Amirajam Z, Yazdankhah S, et.al. The prevalence and prognostic role of vitamin D deficiency in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a single centre study in South-West of Iran. Heart Lung Circ. 2013;22:346–351. | ||
Siadat ZD, Kiani K, Sadeghi M, Shariat AS, Farajzadegan Z, Kheirmand M. Association of vitamin D deficiency and coronary artery disease with cardiovascular risk factors. J Res Med Sci. 2012;17(11):1052–1055. | ||
Moradi M, Nouri Sh, Nourozi Ali, Golbidi D. Prognostic value of coronary artery calcium score for determination of presence and severity of coronary artery disease. Pol J of Radiol. 2017;82:165–169. | ||
Anderson JL, May HT, Horne BD, et al. Relation of vitamin D deficiency to cardiovascular risk factors, disease status, and incident events in a general healthcare population. Am J Cardiol. 2010;106(7):963–968. | ||
Muscogiuri G, Annweiler C, Duval G, et.al. Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease: from atherosclerosis to myocardial infarction and stroke. Int J Cardiol. 2017;230:577–584. | ||
McMullan CJ, Borgi L, Curhan GC, Fisher N, Forman JP. The effect of vitamin D on renin-angiotensin system activation and blood pressure: a randomized control trial. J Hypertens. 2017;35(4):822–829. | ||
Aihara K, Azuma H, Akaike M, et al. Disruption of nuclear vitamin D receptor gene causes enhanced thrombogenicity in mice. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(34):35798–35802. | ||
Perkovic V, Hewitson TD, Kelynack KJ, Martic M, Tait MG, Becker GJ. Parathyroid hormone has a prosclerotic effect on vascular smooth muscle cells. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2003;26(1):27–33. | ||
Martín-Ventura JL, Ortego M, Esbrit P, Hernández-Presa MA, Ortega L, Egido J. Possible role of parathyroid hormone-related protein as a proinflammatory cytokine in atherosclerosis. Stroke. 2003;34(7):1783–1789. | ||
Chen S, Swier VJ, Boosani CS, Radwan MM, Agrawal DK. Vitamin D deficiency accelerates coronary artery disease progression in swine. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016;36(8):1651–1659. |
 © 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
