Back to Journals » Journal of Blood Medicine » Volume 12
Evaluation of Hematological Parameters of Helicobacter pylori-Infected Adult Patients at Southern Ethiopia: A Comparative Cross-Sectional Study
Received 1 December 2020
Accepted for publication 11 February 2021
Published 22 February 2021 Volume 2021:12 Pages 77—84
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JBM.S294958
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Martin H Bluth
Kassahun Haile,1 Abebe Timerga2
1Department of Medical Laboratory Science, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Wolkite University, Wolkite, Ethiopia; 2Department of Biomedical Science, Wolkite University, Wolkite, Ethiopia
Correspondence: Kassahun Haile
Department of Medical Laboratory Science, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Wolkite University, P.O. Box: 07, Wolkite, Ethiopia
Tel +25-926-07-43-74
Fax +251 11 322 0041
Email [email protected]
Background: Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is a global public health problem, a higher burden of the infection was reported in developing countries including Ethiopia. It has been associated with several gastrointestinal diseases, and recently implicated in some hematological abnormalities. Despite the high prevalence of H. pylori infection in Ethiopia, there was limited data regarding the relationship between hematological parameters with H. pylori infection. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate selected hematological parameters of H. pylori-infected patients attending Wachemo University Nigist Eleni Mohammed Memorial Referral Hospital (WUNEMMRH), Hosanna, Southern, Ethiopia.
Methods and Materials: A comparative cross-sectional study was conducted from January to May 2019 among 374 (187 H. pylori-infected patients and 187controls) study participants. Data on socio-demographic characteristics were collected using a structured questionnaire. A five-milliliter venous blood sample was collected for hematological parameter analysis. Approximately two gram of stool specimen was collected to assess the presence of H. pylori antigen. Data were entered and analyzed by using SPSS version 21. Pearson correlation analysis and independent sample T-test was performed, and P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: Mean value of Hgb (p< 0.001), RBC count (p< 0.001), HCT (p< 0.001), MCV (p=0.003), MCH (p=0.008), and MCHC (p=0.006) of H. pylori-infected patients were significantly lower than control group. However, the mean value of RDW (p=0.003) in H. pylori-infected patients was significantly higher than in the control group. About 13.3%, 7%, 6.4%, and 18.2% of H. pylori-infected patients showed reduced Hgb concentration, RBC count, HCT, and MCV values, respectively.
Conclusion: The study showed a statistically significant difference in the mean value of Hgb, RBC count, HCT, MCV, MCH, MCHC, and RDW of H. pylori-infected patients and controls. Thus, hematological parameters should be considered for proper diagnosis and management of H. pylori-infected patients and eradication of this microorganism from infected patients, determination of hematological parameters for H. pylori-infected patients were recommended.
Keywords: hematological parameters, H. pylori infection, southern, Ethiopia
Introduction
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is a global public health problem affecting both developed and developing countries,1,2 with a higher burden reported from developing countries; a study showed 50.8% in developing countries as compared to 34.7% in developed countries.3 In Ethiopia,52.2% of the population were suffering from this infection.4 Besides, different studies reported 52.4%, 36.8% 60.5%, and 83.3% burden of H. pylori infection in Butajira,5 Addis Abebe,6 Dessie,7 and Hawwassa,8 respectively.
H. pylori infection is one of the most common bacterial infections in humans and possesses several mechanisms to colonize the host; flagella-mediated motility, surviving in an acidic stomach environment, attaching to host receptors by adhesions, and causing tissue damage by releasing toxin.9,10 It causes gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, gastroduodenal ulcer, atrophic gastritis, gastric cancers, and dyspeptic symptom.11,12 A study conducted in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, reported a significant number of gastric cancer cases in Ethiopia.13 Furthermore, H. pylori infection has been implicated in some hematological manifestations such as anemia and micronutrient deficiency (iron, and vitamin B12).14,15
Red blood cell synthesis is regulated by many factors, like erythropoietin, iron, vitamin B12, folic acid, and vitamin C. Iron and vitamin B12 are especially important for hemoglobin synthesis and maturation of red blood cells, lack of any of the nutrients resulted in alteration of RBC parameter.16–18 However, different studies indicated H. pylori infection was independently associated with vitamin B12 deficiency,17,19 iron deficiency,20,21 and iron-deficiency anemia,22 and the presence of H. pylori infection is associated with a poorer response to oral iron therapy.23,24 It has been suggested that H. pylori eradication therapy in addition to iron therapy, might show improvements in ferritin and hemoglobin levels in infected patients.23,25
H. pylori infection is related to iron deficiency and iron-deficiency anemia by impairing iron absorption as a result of chronic gastritis which causes gastric hypochlorhydria, leading to impair reduction of the dietary iron from the ferric to ferrous form.26 Because most dietary iron is in the ferric form, needs acidic intra-gastric pH and ascorbic acid to reduce into ferrous form for absorption.27 Hence, H. pylori is a major cause of chronic superficial gastritis leading to atrophy of gastric glands, resulting in reducing gastric acid secretion.28,29
H. pylori impair iron uptake which can compete with the host,30 and increased hepcidin production secondary to H. pylori infection decreases the release of iron from macrophages of the reticuloendothelial system and entrecote, which impairs hemoglobin synthesis.26 Because hepcidin acts as an acute phase reactant in response to the inflammation produced in the gastric mucosa.14 Hemorrhagic gastritis and active bleeding peptic ulcers were other possible ways for iron loss.31
Also, H. pylori infection causes the deficiency of vitamin B12 by producing chronic gastritis and atrophic gastritis;32 H. pylori infection causes hypochlorhydria, which leads to increased bacterial colonization. Bacteria compete with the host for vitamin B12. Gastric acid in the stomach and pepsin was required to release protein bounded vitamin B12 from food; thereby vitamin B12 cannot bind to R-protein and then with intrinsic factor, lead to malabsorption of vitamin B12. Also, decreased production of an intrinsic factor due to atrophic gastritis may result in vitamin B12 deficiency and anemia.31–33
H. pylori infection diagnosis was performed by invasive (rapid urease test, culture, endoscopy, and endoscopic biopsy for histopathology) and non-invasive (urea breath tests, stool antigen test, and serological tests) methods.34 However, the choice of diagnostic methods general depends on population prevalence of infection, differences in test performance, availability, affordability, and clinical situation.35
Several epidemiological studies reported a higher burden of H.pylori infection in Africa including Ethiopia.1,4 Despite the high prevalence of H.pylori infection in Ethiopia, data regarding the association of hematological parameters with H.pylori infection is scarce, evaluating the relationship between hematological parameters with H.pylori infection was important to aid effective intervention measures to reduce its public health burden and related complication in adult patients. Also, it aids in the proper diagnosis and management of H. pylori-infected patients. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the effect of H. pylori infection on selected hematological parameters in Southern Ethiopia.
Methods and Materials
Study Design, Period, and Area
A comparative cross-sectional study was conducted among adults patient from January 1, to May 30, 2019, at Wachemo University Nigist Eleni Mohammed Memorial Referral Hospital (WUNEMMRH), Hosanna town, Hadiya Zone, Southern Ethiopia. The town is located about 232 km far from the capital city of Ethiopia, Addis Ababa. WUNEMMRH is the largest public referral hospital in the Hadiya Zone, as a teaching hospital, it plays an important role in providing teaching, research, and community service and provides services for more than 3.2 million inhabitants. All adult patients (≥18years) who visited the hospital with signs and symptoms suggestive of H.pylori infections were considered as a source population for the H. pylori-infected group.
Study Participants
A total of 374 study participants; 187 H. pylori-infected patients (94 females and 93 males) and 187 control groups (94 females and 93 males) were included in the study. Control groups were age and sex-matched healthy individuals who had no previous history of chronic diseases that affect hematological parameters. Also, the control groups were negative for H.pylori infection. Control groups were WUNEMMRH staff, patient’s relatives or guardians, and Wachemo University students.
From those patients with presumptive signs and symptoms suggestive of H.pylori infections, stool antigen confirmed consecutive H.pylori infected patients were taken as H. pylori-infected groups. H. pylori-infected patients who took treatment within the last three months, who had previous stomach or small bowel surgery, donate blood within the last three months and on treatment for anemia before data collection, bleeding manifestations, pregnant women, severely ill and who had other chronic diseases were excluded from the study.
Sample Size Determination and Sampling Technique
Two population mean formulae were used to calculate the sample size using G-power, version 3.1, by considering the following assumptions: 95% confidence interval (two-sided), 80% power and the ratio of cases to control group was 1:1. Taking the mean and standard deviation (SD) of RBC for H.pylori infected patients and control group from the previous study,5 4.63 and 0.59 for H.pylori infected patients and 4.83 and 0.72 for the control group. We got a total sample size of 374 with 187 for each group. All consecutively identified controls and H. pylori-infected cases were included in the study.
Data Collection and Laboratory Method
Data on socio-demographic characteristics were collected using a structured questionnaire by trained nurses.
Blood Sample Collection and Analysis
A five-milliliter venous blood sample was collected from each study participant by laboratory technologists for hematological parameter analysis. Hematological parameters (RBC, Hgb, HCT, MCV, MCH, MCHC, and RDW) were determined using Mindray BC-3000 plus (Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics, China) automated blood analyzer. Hematological parameters (RBC, Hgb, HCT, MCV, MCH, MCHC, and RDW) were categorized into low, normal, and high based on the hematological reference range conducted in adults in Ethiopia.36
Stool Specimen Collection and Analysis
After explaining how to collect representative stool specimens clean cupped plastic container was given to the participants. Approximately two gram of stool specimen was collected from each study participant and checked for the presence of H. pylori antigen by wondfo one step H. pylori feces test (Guangzhou Wondfo Biotech, China).
From all study participants; (height, weight, and blood pressure) were measured and body mass index (BMI) was calculated as weight in kilogram divided by the square of height in meter and categorized into four groups; BMI<18.5 kg/m2 as underweight, BMI = 18.5–24.9 kg/m2 as normal weight, BMI = 25–29.9 kg/m2 as overweight, and BMI ≥ 30 kg/m 2as obese.
Data Management and Quality Assurance
To ensure the quality of data, all laboratory tests were done by following the standard operating procedures and manufacturer instructions, reagents and test kits were checked for their expiry date, half-day training was given to data collectors and completeness of each questionnaire was checked regularly. The performance of the hematology analyzer was checked before running the patients’ samples by performing normal, low, and high blood controls.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Data were entered and analyzed by using SPSS version 21 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). Frequency tables and descriptive summaries like mean and standard deviation (SD) were used to describe the study variables. Data were tested for the normality of its distribution by Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. The difference in the mean (SD) values of RBC parameters between H. pylori-infected and control groups were explored using an independent sample T-test. Pearson correlation analysis was performed. A P-value, < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Socio-Demographic Characteristics of Study Participants
A total of 374 study participants; 187 H. pylori-infected patients and 187 control groups were included in this study. The mean age of H. pylori-infected patients was 31.89 with a standard deviation of ±7.8 years. There was no statistically significant difference between the mean age (p=0.29) of the H. pylori-infected patient and the control group. Among the study participants, 93 (49.7%) and 94 (50.3%) were males and females in both groups respectively. More than half of the study participants; 109 (58.3%) in the H. pylori-infected group and 107 (57.2%) in the control group were rural dwellers (Table 1). Among H. pylori-infected study participants 7(3.5%),151 (80.7%), and 29 (15.5%) had underweight, normal weight and overweight, respectively.
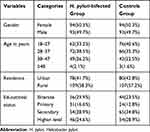 |
Table 1 Socio-Demographic Variables Distribution of H. pylori-Infected Patients and Controls at Wachemo University Nigist Eleni Mohammed Memorial Referral Hospital, 2019 |
Comparisons of RBC Parameters in Study Participants
The mean (SD) of the parameters related to red blood cells were also compared between H.pylori infected and the control group. Accordingly statistically significant lower mean value of Hgb (p<0.001), RBC (p<0.001), HCT (p<0.001), MCV (p=0.003), MCH (p=0.008), and MCHC (p=0.006) were observed in H. pylori-infected patients compared to control group. However, the mean value of RDW in H. pylori-infected patients was higher than the control group, which was also statistically significant (p=0.003) (Table 2).
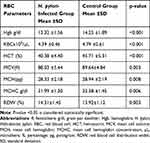 |
Table 2 Comparisons of Mean Values of RBC Parameters of H. pylori-Infected Patients and Controls at Wachemo University Nigist Eleni Mohammed Memorial Referral Hospital, 2019 |
Hematologic Abnormalities in H. pylori-Infected Patients
Among 187 H.pylori infected patients; about 13.3%, 7%, 6.4% and 18.2% of patients showed reduced Hgb concentration, RBC count, HCT, and MCV values, respectively (Table 3).
 |
Table 3 The Proportion of H. pylori-Infected Patients (n=187) with Low, Normal, and High Values of RBC Parameters at Wachemo University Nigist Eleni Mohammed Memorial Referral Hospital, 2019 |
Correlation Analysis of RBC Parameters with Predictors Among H. pylori-Infected Patients
Haemoglobin concentration showed statistically positive correlation with systolic blood pressure (r: 0.14, p: 0.006), and negative correlation with residence (r: −0.12, p=0.01). In addition HCT shows negative correlation with residence (r: −0.11, p: 0.002) and positive correlation with gender (r: 0.15, p: 0.003) (Table 4).
 |
Table 4 Correlation Analysis of RBC Parameters with Predictors Among H. pylori-Infected Patients at Wachemo University Nigist Eleni Mohammed Memorial Referral Hospital, 2019 |
Discussion
H. pylori infection is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide2. More than 50% of the global population is estimated to be infected.1,37 It causes chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer, gastric adenocarcinoma, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma.12 Different studies suggested that H. pylori infection was associated with some hematological abnormalities.17 Therefore, the current study aimed to assess the relation between RBC parameters and H. pylori infection in adult patients at WUNEMMRH.
Alteration of RBC parameters in H. pylori-infected adult patients associated with different mechanisms; consumption of iron by the H. pylori30 decreased iron absorption secondary to chronic gastritis,20 iron loss via hemorrhagic gastritis, and active bleeding peptic ulcers, deficiency of iron and vitamin B12 secondary to chronic and atrophic gastritis,27 which might contribute to the alteration of RBC parameters in H. pylori-infected patients as compared to control.
Besides, H. pylori infection is associated with deficiency of iron and vitaminB12,20,21,30 which was important micronutrients for hemoglobin synthesis and maturation of red blood cells; their deficiency may result in variation in size and shapes of RBC, and defects in hemoglobin maturation. Consequently may contribute to the alteration of RBC parameters.
This study revealed a significant decrement of mean hemoglobin concentration (p<0.001) of H. pylori-infected patients as compared to the control. This finding was in line with other similar studies conducted in Palestine in adult H. pylori-infected patients,17 in Egypt22 and Karachi.38 Consumption of iron by the H. pylori,30 decreased iron absorption secondary to chronic gastritis,20 iron loss via hemorrhagic gastritis, and active bleeding peptic ulcers,27 which might contribute to decrement of blood hemoglobin concentration in H. pylori-infected patients. Several studies reported that depletion of iron in H. pylori-infected patients,30 and eradication of H. pylori infection shows improvements in blood hemoglobin concentration.22,23 However, our finding contradicts the study conducted in Dhaka, Bangladesh,39 which reported there was no significant difference in hemoglobin concentration between the two groups. This might be due to a difference in sample size and methodology.
The mean values of RBC count were lower in H. pylori-infected patients compared to the control group in our study, which was statistically significant. This finding is supported by previous studies conducted in Turkey,40 Palestine17 and Sudan.41 The decrement of RBC count among H. pylori-infected patients might be because of blood loss due to chronic erosive gastritis and active bleeding peptic ulcers.
In the current study, the mean level of HCT was showed a statistically significant difference between H. pylori-infected patients and control groups. A similar observation was reported from Butajira, Ethiopia,5 Sudan,41 and Turkey.40 Change in hematological parameters might be due to H. pylori infection. Different studies also reported that eradication of H. pylori infection shows improvements in hematological parameters.22,25
The mean cell volume value was significantly lower in H. pylori-infected patients as compared to the control group in this study. This finding is supported by a study conducted in Sudan,16 Turkey,40 Dhaka, Bangladesh,39 Butajira, Ethiopia.5 Whereas, another similar study done in Palestine17 and Sudan41 was reported no significant difference in MCV value between H. pylori-infected patients and the control group. The observed difference may be due to the variation in the sample size between studies.
Statistically, a significant mean difference in MCH value was observed between H. pylori-infected patients and the control group in our study. This finding is in agreement with a study conducted in Butajira, Ethiopia,5 Kosti Teaching Hospital, Sudan,16 and Bangladesh.39 However, a study conducted in Palestine17 and Sudan41 reported no significant differences were found in the MCH value, which was contradicting our finding. Several studies indicated that H. pylori infection was associated with impairments of micronutrients essential for hemoglobin synthesis,17,22,30 which may contribute to the observed difference.
In the current study, the mean level of MCHC was showed a statistically significant difference between H. pylori-infected patients and control groups. Contrary results were reported from Sudan,16,41 but the supporting observation was reported from Ethiopia.5
H. pylori infection is associated with deficiency of iron and vitaminB12,20,21,30 which was important micronutrients for hemoglobin synthesis and maturation of red blood cells; their deficiency may result in variation in size and shapes of RBC. A significantly higher mean value of RDW was found in H. pylori-infected patients as compared to the control group in this study. This finding is supported by a study conducted in Palestine.17 This is might be due to fact that high RDW indicates impairment of erythropoiesis, reflecting chronic inflammation and deficiency of micronutrients, both of which are significant signs of H. pylori infection that result in the RBC size variation.
In the current study about 13.3%, 7%, 6.4%, and 18.2% of H. pylori-infected patients showed reduced blood Hgb concentration, RBC count, HCT, and MCV values respectively. Reduction in hematological indices might be due to blood loss via hemorrhagic gastritis and active bleeding peptic ulcers, impairing iron absorption as a result of chronic gastritis, deficiency of iron and vitamin B12 secondary to chronic and atrophic gastritis.
Concerning the correlation of hematological indices, RBC count and hemoglobin level showed a statistically positive correlation with systolic blood pressure. A similar observation was reported from Ethiopia,42 China,43 and Netherland.44
Conclusion
In this study, the mean value of Hgb, RBC count, HCT, MCV, MCH, and MCHC were showed significant decrements in H. pylori-infected patients compared to the control group. However, the mean value of RDW in H. pylori-infected patients was significantly higher than in the control group. Therefore, hematological parameters showed a significant difference should be considered for proper diagnosis and management of H. pylori-infected patients, and eradication of this microorganism from infected patients, determination of hematological parameters for the patients who had H. pylori infection, prevention and control of this infection, and performing large longitudinal community-based studies were recommended.
Limitation of the Study
The limitation of this study is it does not show a cause-effect relationship between variables and H. pylori infection because of the cross-sectional nature of the study design. We had not assessed micronutrient level and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet lymphocyte ratio due to logistic constraints.
Data Sharing Statements
The original data for this study is available from the corresponding author on a reasonable request.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical clearance was obtained from Wolkite University Ethical Review Board. A letter of cooperation was written to WUNEMMRH and permission was obtained from the hospital administration. Written informed consent was obtained from each study participant after explaining the purpose and procedures of the study. The data were kept confidential by using codes rather than any personal identifier, and the results were communicated to the physicians for proper management. The study was carried out following the Declaration of Helsinki.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Wachemo University Nigist Eleni Mohammed Memorial Referral Hospital staff for their support during data collection. We are also grateful to all the study participants for their collaboration.
Author Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Disclosure
The authors declared that they have no competing interests.
References
1. Hooi JKY, Lai WY, Ng WK, et al. Global Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection: systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World J of Gastroenterology. 2017;153(2):420–429. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.04.022
2. Sjomina O, Pavlova J, Niv Y, Leja M. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. John Wiley. 2018;13:6–11.
3. Zamani M, Alizadeh- WHMR. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the worldwide prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;868–876.
4. Melese A, Genet C, Zeleke B, Andualem T. Helicobacter pylori infections in Ethiopia; prevalence and associated factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019;19(8):1–15.
5. Kibru D, Gelaw B, Alemu A, Addis Z. Helicobacter pylori infection and its association with anemia among adult dyspeptic patients attending Butajira Hospital, Ethiopia. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14:1–7.
6. Shiferaw G, Abera D. Magnitude of Helicobacter pylori and associated risk factors among symptomatic patients attending at Jasmin internal medicine and pediatrics specialized private clinic in Addis Ababa city, Ethiopia. BMC Infect Dis. 2019;5:1–6.
7. Seid A, Demsiss W. Feco-prevalence and risk factors of Helicobacter pylori infection among symptomatic patients at Dessie Referral. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18:1–9.
8. Tadesse E, Daka D, Yemane D, Shimelis T. Seroprevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection and its related risk factors in symptomatic patients in southern Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. 2014;7(1):1–5.
9. Kao C, Sheu B, Wu J. Helicobacter pylori infection: an overview of bacterial virulence factors and pathogenesis. Biomed J. 2016;39(1):14–23.
10. Camilo V, Sugiyama T, Touati E. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. John Wiley. 2017;22:1–6.
11. Chmiela M, Kupcinskas J. Review: pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. John Wiley. 2019;24:1–5.
12. De BBB, Antônio F, Soares AS, et al. Pathogenesis and clinical management of Helicobacter pylori gastric infection. World J Gastroenterology. 2019;25(37):5578–5589.
13. Gebresillasse HW, Tamrat G, Abule T. Gastric cancer features and outcomes at a tertiary teaching hospital in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: a 5-year retrospective study. East Cent Afr J Surg. 2019;24(2):105–109.
14. Augusto J, Díaz U, Regino WO, Zuleta MG. Helicobacter pylori and hematologic diseases. Rev Col Gastroenterol. 2013;28(4):323–331.
15. Campuzano-Maya G. Hematologic manifestations of Helicobacter pylori infection. World J Gastroenterology. 2014;20(36):12818–12838.
16. Ali E, Elamin I, Suliman MA, et al. Effect of helicobacter pylori infection on haematological parameters in kosti teaching hospital, sudan. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2018;20(2):1–6.
17. Mwafy SN, Afana WM. Hematological parameters, serum iron, and vitamin B 12 levels in hospitalized Palestinian adult patients infected with Helicobacter pylori. Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2018;40(2):160–165.
18. Victor Hoffbrand A. Daniel Catovsky, Edward GD Tuddenham ARG. Postgraduate Haematology.
19. Humeida AT, Abdalla MHA. Association of helicobacter Pylori Infection and Vitamin B 12 Level among Sudanese Patients. IOSR J Dent Med Sci. 2017;16(3):12–14.
20. Jasem MA, Al-ubaidi AA, Daood NM, Muhsin JA. Iron deficiency in Helicobacter pylori-infected patients in Baghdad. J Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011;1(3):114–117.
21. Fraser AG, Scragg R, Schaaf D, Metcalf P, Grant CC. Helicobacter pylori infection and iron deficiency in teenage females in New Zealand. J New Zeal Med Assoc. 2010;123(1313):38–45.
22. Abdel Y, Abdel L, Mohamed R, Mohamed R, Ahmed M. Helicobacter pylori and its hematological effect. Egypt J Intern Med. 2019;31:332–342.
23. Huang X, Qu X, Yan W, et al. Iron deficiency anemia can be improved after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Postgrad Med J. 2010;86:272–278.
24. Demerdash DME, Ibrahim H, Hassan DM, Moustafa H, Tawfik NM. Helicobacter pylori-associated to unexplained or refractory iron deficiency anemia: an Egyptian single-center experience. Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2018;40(3):219–225.
25. Hudak L, Jaraisy A, Haj S, Muhsen K. An updated systematic review and meta-analysis on the association between Helicobacter pylori infection and iron deficiency anemia. Wiley. 2017;22:1–16.
26. Sato Y, Yoneyama O, Azumaya M, Takeuchi M, Sasaki S. The relationship between iron deficiency in patients with helicobacter pylori -infected nodular gastritis and the serum prohepcidin level. John Wiley. 2014;20:11–18.
27. Miguel A. Hematological Extradigestive Manifestations of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Childhood. InTech. 2016;76–110.
28. Ansari S, Yamaoka Y. Survival of Helicobacter pylori in the gastric acidic territory. HHS Public Access. 2018;22(4):1–25.
29. Mitchell H, Dipped H, Katelaris P, Frcp F. Epidemiology, clinical impacts and current clinical management of Helicobacter pylori infection. Med J Aust. 2016;204(10):376–386.
30. Ciacci C, Sabbatini F, Cavallaro R, et al. Helicobacter pylori impairs iron absorption in infected individuals. Dig Liver Dis. 2004;36:455–460.
31. Campuzano-Maya G. Helicobacter pylori and Hematologic Diseases. InTech. 2016;33–52.
32. Tsay F, Hsu P. H. pylori infection and extra-gastroduodenal diseases. J Biomed Sci. 2018;1–8.
33. Campuzano-Maya G. Helicobacter pylori and Hematologic Diseases. World J Gastroenterology. 2016;33–39.
34. Kalali B, Formichella L, Gerhard M. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori: changes towards the Future. Open-Access Dis. 2015;3:122–135.
35. Hunt RH, France FM. Helicobacter pylori in developing countries. world gastroenterology organisation global guideline. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2011;20(3):299–304.
36. Yalew A, Terefe B, Alem M, Enawgaw B. Hematological reference intervals determination in adults at Gondar university hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. 2016;9(483):1–9.
37. Eusebi LH, Zagari RM, Bazzoli F. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori Infection. John Wiley. 2014;19:1–5.
38. Zuberi BF, Afsar S, Qadeer R, Baloch I. Muhammad Saeed Quraishy AK, and NA. hemoglobin, ferritin, vitamin B12, and helicobacter pylori infection: a study in patients who underwent upper gi endoscopy at civil hospital Karachi. JCPSP. 2007;17(9):546–549.
39. Rahman A, Karim ME, Saeed A, Siddique AR, Sadat SMA. Association between helicobacter pylori infection and iron deficiency anemia: a cross-sectional study. J Bangladesh Coll Phys Surg. 2020;38(2):68–78.
40. Saler T, Özgür F, Ke G, Sibel KJ, Ahbab S. L GO. H. pylori may not be associated with iron deficiency anemia in patients with normal gastrointestinal tract endoscopy results. Hindawi Publ Corp Adv Hematol. 2015;1–5.
41. Abass A, Mohamed KO, Yosif AA, Fatima A, Elfadil M. Evaluation of serum vitamin B12 and ferritin levels in h. pylori- associated gastritis. IOSR J Pharm Biol Sci. 2016;11(1):1–5.
42. Enawgaw B, Adane N, Terefe B, Asrie F, Melku M. A comparative cross-sectional study of some hematological parameters of hypertensive and normotensive individuals at the University of Gondar hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Hematol. 2017;17:1–7.
43. Yan X, Junli Zuo SZ. Association of hemoglobin and blood pressure in a chinese community-dwelling population. Pulse. 2018;6:154–160.
44. Atsma F, Veldhuizen I, De KW, Van KM, Jong PP, Deinum J. Hemoglobin level is positively associated with blood pressure in a large cohort of healthy individuals. Hypertension. 2012;60:936–941.
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
