Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 15
Enhancing ZnO-NP Antibacterial and Osteogenesis Properties in Orthopedic Applications: A Review
Authors Li Y , Yang Y, Qing Y, Li R , Tang X , Guo D, Qin Y
Received 19 May 2020
Accepted for publication 30 July 2020
Published 20 August 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 6247—6262
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S262876
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Yuehong Li,1 Yue Yang,2 Yun’an Qing,1 Ruiyan Li,1 Xiongfeng Tang,1 Deming Guo,1 Yanguo Qin1
1Orthopaedic Medical Center, The Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of Cardiology, China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Yanguo Qin Email [email protected]
Abstract: Prosthesis-associated infections and aseptic loosening are major causes of implant failure. There is an urgent need to improve the antibacterial ability and osseointegration of orthopedic implants. Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) are a common type of zinc-containing metal oxide nanoparticles that have been widely studied in many fields, such as food packaging, pollution treatment, and biomedicine. The ZnO-NPs have low toxicity and good biological functions, as well as antibacterial, anticancer, and osteogenic capabilities. Furthermore, ZnO-NPs can be easily obtained through various methods. Among them, green preparation methods can improve the bioactivity of ZnO-NPs and strengthen their potential application in the biological field. This review discusses the antibacterial abilities of ZnO-NPs, including mechanisms and influencing factors. The toxicity and shortcomings of anticancer applications are summarized. Furthermore, osteogenic mechanisms and synergy with other materials are introduced. Green preparation methods are also briefly reviewed.
Keywords: antibacterial property, composite material, orthopedic implant, osteogenic activity, zinc oxide nanoparticles
Introduction
Pathological conditions of bones, like osteoporosis or cancer, often cause structural changes such as trabecular bone reduction and cortical bone thinning, which increase the likelihood of fractures and can lead to other bone defects. In addition to diseases, trauma is the main cause of bone defects.1–4 Although intrinsic self-healing abilities may naturally repair minor defects, therapeutic interventions are often necessary for defects larger than 6 mm.5
At present, autografting is considered the gold standard for treating critical bone defects.6 Although autografts have good histocompatibility and are non-immunogenic, the process of implantation may further harm the patient and could cause chronic pain, bleeding, and other complications.7,8 Another common treatment is the allografting of bone tissue transplanted from a donor. However, compared with autografting, it may lead to immune rejection and even serious infection.9 Artificial bone replacement is a widely accepted clinical treatment that has been used to treat bone defects for decades. However, prostheses can pose challenges such as infection and aseptic loosening.10,11 Fortunately, their biological performance can be improved by proper modifications, including the introduction of nanoparticles (NPs).
NPs are usually defined as objects with a dimension of 1–100 nm.12 These nano-scaled materials may possess different physical and chemical properties compared with the bulk ones due to their high surface area to volume ratio.13,14 NPs are widely applied in industry, cosmetics, and food products.15,16 As a trace element, zinc participates in various metabolic processes. A substantial proportion of zinc (~30%) is stored in bone, and the pathological reduction of zinc levels impairs bone growth.17–19 Zinc plays an important regulatory role in bone formation. In addition to being a component of inorganic minerals, it also activates proteins involved in bone homeostasis.20 Zinc oxide NPs (ZnO-NPs) are a common type of zinc-containing nanoparticles that have gained increasing attention in biological research because of their low toxicity, biological compatibility, bioactivity, and chemical stability.21 ZnO-NPs can accelerate bone growth and mineralization.22 In addition, they possess selective toxicity toward bacteria and normal cells.23,24 These biological properties imbue ZnO-NPs with considerable potential in orthopedic applications. In fact, studies have confirmed that implants of various materials, like metals and polymers decorated with ZnO-NPs via doping or coating, show better antibacterial and osteogenic abilities.25,26
To our knowledge, this is the first article focused on summarizing the recent progresses of ZnO-NPs in orthopedic applications. The first part is a brief review on the green preparation methods. Then, The mechanisms, influencing factors, and recent progress in antibacterial applications are discussed (Figure 1). The third section discusses the mechanisms and reducing methods of toxicity and proposes a hypothesis on the limitations of ZnO-NPs in anticancer applications. The final section highlights the osteogenic properties of ZnO-NPs. This article reviews research studies on the antibacterial, toxic, anticancer, and osteogenic properties of ZnO-NPs in orthopedics over the last 5 years. This review also sheds light on the ability of ZnO-NPs to exert both antibacterial and osteogenic effects, and their considerable potential in synergies with other co-decorated materials to enhance the biological activity of implants.
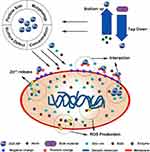 |
Figure 1 Schematic of ZnO-NP preparation strategies, antibacterial mechanisms, and influencing factors. |
Green Fabrication Process of ZnO-NPs
There are Two strategies adopted for NPs preparation: top-down and bottom-up.27,28 The top-down strategy refers to breaking bulk materials into nano-scale particles, but it produces imperfect surface structures.29 In contrast, the bottom-up strategy refers to the self-assembly process in which atoms gathered into a nucleus and finally aggregate into NPs.30 As the most widely used preparation strategy, Products obtained through bottom-up strategies usually have homogeneous chemical NPs compositions.31 ZnO-NPs can be prepared by physical, chemical, and biological methods. Physical methods often follow the top-down strategy and include: grinding, milling, thermal evaporation, pulsed laser deposition, and others.32,33 Although large quantities of ZnO-NPs can be produced in a short period of time, problems like high energy consumption, uneven size distribution, and low product nanometer rate still need to be solved.30,34 Chemical methods like electrochemistry, chemical reduction, and photochemical reduction techniques usually follow a bottom-up strategy.33 NPs produced via chemical methods are homogeneous in size.35 However, toxic chemical reagents used during synthesis often remain on NP surface, which limits their use in medical applications.23,36,37
ZnO-NP biosynthesis is mostly categorized as wet chemical synthesis involving plants or microorganisms. Biosynthesis is environmentally friendly and safe, and the obtained ZnO-NPs are usually more biocompatible since they were functionalized by biochemicals.32,38 Customized sizes and structures can be obtained by modulating extract parameters like the original source (different plants or microorganisms), pH, and concentration.32,39,40 ZnO-NPs can be obtained through plant extracts using milder solvents such as water and ethanol, and the reducing and capping agents in extracts like phenols and flavones can stabilize the NPs through electrostatic, steric, hydration, and van der Waals forces.41–44 The preparation process of plant extract-assisted biosynthesis is relatively simple and can be done in three steps (Figure 2). Generally, the first step is plant extract preparation. Next, zinc salts are added to plant extracts as precursors. During this stage, metal ions are reduced into NPs and then stabilized by reducing and capping agents. In the final step, ZnO-NPs are obtained after other synthesis processes like high temperature annealing.39,45 Wang et al45 successfully obtained spherical ZnO-NPs with a diameter of 20 nm, using the extract of Artemisia annua. Although NP sizes were relatively homogeneous, the product showed a specific aggregation phenomenon, which could lead to toxicity. Hu et al46 obtained spherical ZnO-NPs with a diameter of 8 nm from the Cucurbita pepo leaf extract using a classic mixing-stirring-annealing process. Interestingly, they claimed no aggregation occurred. This discrepancy may be explained by the different extracts and capping agents with diverse stabilizing effects.
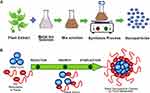 |
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of ZnO-NP preparation from plant extracts. |
Microorganisms including bacteria, fungi, and algae can also participate in ZnO-NP biosynthesis,47,48 as these microorganisms have a self-defense mechanism for heavy metal ion exposure.49 The preparation process can be divided into microorganism cultivation, biochemical activities of microorganisms, intra- and extracellular transport of metal ions, intracellular nucleation, and finally NP formation.35,49 Shamsuzzaman et al50 used a Candida albicans suspension as a reducing and capping agent, and successfully prepared quasi-spherical ZnO-NPs with a diameter of ~15–20 nm. Sanaeimehr et al51 also obtained ZnO-NPs with good anticancer effects using Sargassum muticum extract.
It is worth noting that biosynthetic methods are not perfect. The extract components may vary and some even remain unknown, which means that further purification of functional biochemicals is needed.52 In conclusion, Future explorations of biosynthesis should be focused on details of the mechanisms and purification of functional biochemicals from plants or microorganisms. Successful large-scale biosynthesis of custom-structured ZnO-NPs will enhance their application in biological fields.
Antibacterial Properties of ZnO-NPs
Antibacterial Mechanism and Influencing Factors
Prosthesis-associated infections are a major cause of implantation failure and can occur due to improper surgical performance or post-operation contamination from surrounding tissues.53 Revision of the prosthesis increases the financial burden of patients and also causes secondary injury.54 There are five stages in the development of prosthesis-associated infection: 1) reversible attachment; 2) irreversible attachment; 3) microcolony formation; 4) proliferation and maturation; and 5) matrix detachment.55 During the proliferation and maturation stage, colonies begin to form biofilms. These protective extracellular matrixes greatly enhance the resistance of bacteria against the immune system and bactericides.56–59 It is therefore essential to inhibit bacterial attachment and growth at the early stage, which could be achieved using implants with antibacterial properties.
ZnO-NPs possess good antibacterial properties; however, the specific mechanism is not clear. Antibacterial properties come from three aspects: the interaction between NPs and bacteria; the release of zinc ions (Zn2+); and the generation of reactive oxide species (ROS).24,60 Bacteria possess negative charges on their surfaces because of negatively charged cell wall components like teichoic and lipoteichoic acid.61 Conversely, ZnO-NPs are positively charged in water suspensions.62
Electrostatic attraction between bacteria and ZnO-NPs leads to the accumulation of NPs on the bacterial surface, which changes the zeta potential of the bacteria and destroys the potassium channels on cell membranes, eventually leading to lipid peroxidation and increased permeability.63,64 This membrane dysfunction also causes enhancing internalization, which finally leads to excessive intracellular ZnO-NP accumulation and altered metabolism.65 Zn2+ also plays an important role in antibacterial properties; they can combine with functional proteins, thereby changing cell membrane permeability. As the intracellular Zn2+ concentration increases, interaction with the thiol group of the enzyme is strengthened, thus affecting various bacterial enzymatic reactions, weakening glycolysis, and inducing cell death.66,67 ROS are highly reactive oxygen-containing chemical species that are involved in maintaining cellular homeostasis under normal conditions. However, high ROS levels may induce oxidative stress and toxicity.68,69 ZnO-NPs can produce ROS when subjected to light or ultraviolet irradiation because of the electron-hole pair activation, but active redox cycling on NP surfaces will still produce ROS in aqueous solutions even in darkness. Excessive ROS will directly damage bacterial lipids, proteins, and DNA, ultimately killing the bacteria.70–72
Many factors can affect ZnO-NP antibacterial performance. A smaller size corresponds to a larger specific surface area and smaller volume, thus enhancing Zn2+ dissolution, ROS generation, and abilities to adsorb and penetrate cell membranes.65,73-76 Mahamuni et al77 obtained ZnO-NPs with a diameter range of 15–100 nm through polyol synthesis. ZnO-NPs with the smallest diameter of 15 nm showed the best antibacterial effect on Staphylococcus aureus. Similarly, Wang et al78 found that bacteria are more sensitive to small-sized particles, by comparing the antibacterial properties of ZnO-NPs with diameters of 15, 50, and 90 nm.
Surface defects on particles also play an important role in mediating antibacterial properties. Physical defects like irregular protrusions and sharp edges can mechanically damage bacteria, and surface electronic states caused by chemical defects may enhance ROS production.79 In addition, antibacterial properties can be manipulated by different morphologies such as nanocombs, nanorods, nanobelts, nanowires, nanosheets, nanoflowers, and snowflakes, and such structures can be achieved by changing the preparation method.80–83 Compared with spherical particles, rod-shaped particles are more likely to penetrate the cell membrane, and thus have stronger bactericidal properties.84 Talebian et al85 compared the same volumes of ZnO-NPs in flower, rod, and ball structures and showed that flower-shaped particles had the highest specific surface area with more Zn2+ release and the strongest antibacterial properties. Various unique structures can confer many possibilities for orthopedic applications of ZnO-NPs. However, the mechanisms of ZnO-NP morphology on biological properties are not yet well understood. Therefore, more studies are needed particularly focused on specific mechanisms and optimal structures. Besides the intrinsic properties of ZnO-NPs, external environmental factors also affect antibacterial properties. Li et al86 examined the toxicity of ZnO-NPs toward S. aureus in ultrapure water, NaCl solution, minimal Davis medium (MD), and Luria–Bertani (LB) medium. They found that the solubility of ZnO-NPs in various solutions were as follows: LB, 68 mg/L; MD, 38 mg/L; NaCl, 14 mg/L; and ultrapure water, 6.9 mg/L. However, the strongest antibacterial properties were observed in ultrapure water. The difference in solubility was due to the different components of each solution. Chloride ions can form complexes with zinc ions in NaCl solution, and phosphates in other solutions can form Zn3(PO4)2 with zinc ions to accelerate dissolution. However, these reactions reduce the concentration of zinc ions, thereby reducing the antibacterial ability.
The species and metabolism of bacteria can also influence antibacterial behaviors. Gram-negative bacteria are more resistant to ZnO-NPs because lipopolysaccharides on the cell wall prevent ZnO-NP adhesion and internalization.87 Antimicrobial tests show that the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of Gram-positive compared with Gram-negative bacteria are 50%–85% lower.88 Elizabeth et al89 observed an increased Zn2+ release in the presence of bacteria. This is because bacteria lower the surrounding pH during the metabolic process, thereby accelerating dissolution.90
Antibacterial Properties of ZnO-NP-Modified Implants
ZnO-NPs modifications imbue implants with good antibacterial properties. Elizabeth et al89 covered titania nanotubes and titania nanoleaf with ZnO-NPs through precipitation. Compared with pure nano-patterned materials, the antibacterial properties of modified samples were significantly improved. Artifon et al91 mixed polyetherimide (PEI) with different concentrations of ZnO-NPs and obtained a series of ZnO/PEI scaffolds by electrospinning. The antibacterial effect increased with higher ZnO-NP content. In addition to direct toxicity toward bacteria, ZnO-NP-modified implants can also regulate the immune system and enhance antibacterial properties. Wang et al92 incorporated ZnO-NPs on the surface of a titanium substrate through magnetron sputtering to form a nano-coating. The modified samples exhibited good antibacterial properties during in vitro experiments. Interestingly, the authors reported even better antibacterial effects with in vivo experiments. Subsequently, they cultured macrophages with modified samples in vitro and found increased secretion of pro-inflammatory factors and enhanced phagocytosis ability against bacteria, indicating that immune system regulation played a considerable role in in vivo antibacterial ability.
In order to obtain materials with good antibacterial and osteogenic effects, ZnO-NPs are typically used as antibacterial agents in combination with osteogenic materials. The most common co-modified material is hydroxyapatite (HA).93–95 Maimaiti et al26 produced coatings of nano-HA (nHA) and ZnO-NPs and employed polypyrrole as a dual regulator using the pulse electrochemical deposition method. This coating exhibited good antibacterial properties while retaining mineralization functionality. Shitole et al96 obtained a series of multi-concentration gradient poly-epsiloncaprolactone (PCL)/nHA/ZnO scaffold through electrospinning by mixing PCL and nHA with ZnO-NPs in various concentrations. Although the antibacterial activity increased with higher concentration, MG-63 cell adhesion decreased on scaffolds with 15 wt% and 30 wt% ZnO-NPs, which indicated a cytotoxic effect. The final recommended concentration of ZnO-NPs was 10 wt%, which reduced the adhesion rates of S. aureus and E. coli by 80.8% and 82.1%, respectively, compared to the control group.
To enhance the antibacterial effect of ZnO-NPs, antibiotics and other antibacterial NPs can be given in conjunction with ZnO-NPs to facilitate antibacterial synergy. Banerjee et al97 prepared ZnO-NPs by precipitation, subsequently modified them with pancreatin to obtain ZnO-NPs-PK and studied their ability to inhibit MRSA (methicillin-resistant S. aureus). They found that the MIC to inhibit 90% of MRSA isolates was 50% lower for ZnO-NPs-PK compared with bare ZnO-NPs. Furthermore, combining ZnONPs-PK with vancomycin at a concentration of 1/4 MIC almost completely inhibited MRSA growth. This phenomenon suggests that MRSA treated with low-concentration ZnO-NPs are more susceptive to certain antibiotics. However, because the antibacterial mechanism of ZnO-NPs is not fully understood, combining them with antibiotics and ZnO-NPs may not achieve a stable antibacterial effect. Alves et al98 pre-treated MRSA with low-concentration ZnO-NPs, which made MRSA develop a slight tolerance to the main antibacterial mechanism of ZnO-NPs. Subsequently, the antibacterial ability of antibiotics with different mechanisms against ZnO-NP-tolerant MRSA were tested in sub-concentrations. The authors claimed that the inhibitory effects of vancomycin and rifampicin were not obvious, indicating that the main antibacterial mechanism of ZnO-NPs in this experiment were similar to those antibiotics, which inflict RNA damage and affect cell wall synthesis. This also means that without clarifying the antibacterial effect of ZnO-NPs, the combined application with various antibiotics will have low efficiency and uncertainty and may even trigger toxicity. Combining Ag nanoparticles (AgNPs) and ZnO-NPs while modifying implants has been drawing increasing attention. AgNPs are the most widely studied antibacterial agents, with broad-spectrum antibacterial effects and no known resistant strains.99 The combined application with AgNPs enhances antibacterial ability and reduces the toxicity associated with a high concentration of a single material.100–102 Zhang et al100 mixed different proportions of AgNPs and ZnO-NPs (the total amount of these two NP concentration was10 wt%) with HA powder (90 wt%) and coated it on the surface of the titanium sheet using laser cladding. The antibacterial activity against S. aureus of coatings with only ZnO-NPs was relatively low, only 35.9%. Although the antibacterial rate of coatings with 10 wt% AgNPs reached 93%, it caused cytotoxicity in normal cells. Thus, the Ag7ZnO3HA coating (Ag/ZnO/HA = 7:3:90 wt%) was found to be the best biological coating. The antibacterial rate of S. aureus reached 85.8%, and the coating retained good biocompatibility and osteogenic effects (Figure 3).
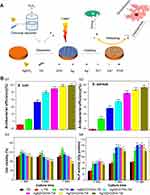 |
Figure 3 Combined application of ZnO-NPs and silver enhances antibacterial properties while reducing toxicity. |
ZnO-NPs have shown great potential for antimicrobial modification of implants, but challenges still exist. The underlying antibacterial mechanisms remain to be clarified, and the effects of combined application with antibiotics and the ability to regulate the immune system require further research.
Toxicity and Anticancer Properties
Toxicity Mechanisms and Reducing Methods
Low toxicity is a prerequisite for orthopedic implantation to minimize harm to the patient. The toxicity mechanisms of ZnO-NPs are quite similar to antibacterial mechanisms, that is, interactions between particles and cells, Zn2+ release, and ROS generation. Among these, it is generally believed that ROS generation is the main cause of eukaryotic cell death.103–106 ZnO-NPs internalized by cells may enter the mitochondria and generate excessive intracellular ROS through depolarization of mitochondrial membrane and impairing the electron transport chain. These ROS may cause oxidative stress and directly destroy the membranes of the mitochondria and other organelles to induce apoptosis.107
The US Food and Drug Administration listed ZnO-NPs as “generally regarded as safe” (GRAS) substances (21CFR182.8991). However comparing with magnesium oxide nanoparticles (MgO-NPs), which are also classified as GRAS substances (21CFR184.1431) and widely studied in the orthopedic field, ZnO-NPs show more biotoxicity.108,109 Ivask et al110 tested the toxicity of MgO-NPs and ZnO-NPs against human alveolar epithelial A549 cells, human epithelial colorectal Caco-2 cells, and the murine fibroblast cell line, Balb/c 3T3. The MgO-NPs showed non-toxicity at concentrations less than 100 µg/mL, while ZnO-NPs showed toxicity to all three cell types at concentrations higher than 30.2 µg/mL.110 Therefore, ZnO-NP applications need to be within an appropriate range of concentration.
Studies have shown that their toxicity is dose dependent. Sudhakaran et al111 obtained spherical ZnO-NPs with diameters of ~43 nm with a wet chemical method. Subsequently, ZnO-NPs were administered to healthy adult Wistar rats through intravenous and intraperitoneal routes (10 mg/kg). Although the rats had no obvious toxicity on gross examination, histological damage was found in the liver. NPs also can affect embryonic development. Yan et al112 injected ZnO-NPs into chicken embryos at a daily dose of 5 µg for 9–12 days and observed embryonic craniofacial defects. Suriyaprabha et al113 treated zebrafish embryos with different ZnO-NP concentrations and reported that only those >90 µg/mL induced abnormal embryo development. ZnO-NPs can also damage lung and reproductive functions.114,115 However, since factors like size, temperature, solvent properties, pH, and others affect ZnO-NPs toxicity, it is difficult to determine a safe concentration range. Fortunately, they are unlikely to damage organs and embryos in orthopedic applications since ZnO-NPs are incorporated or coated on the implant. However, the implants can be toxic to the peri-prothesis tissues.
Even distribution is essential when decorating implants with ZnO-NPs. Aggregation during modification may lead to high local ZnO-NP concentrations, resulting in toxicity.116 Abdulkareem et al117 coated the surface of a titanium (Ti) substrate with ZnO-NPs and HA, to create a HA/ZnO nanocomposite coated layer. The coating showed excellent antibacterial properties, but NP aggregation led to a reduction in bioactivity. Fortunately, this disadvantage can be avoided by using suitable preparation methods. Maimaiti et al26 produced an HA coating doped with ZnO-NPs by pulse electrochemical deposition. The particles were distributed uniformly, and the coating showed no toxicity while exhibiting good antibacterial and osteogenesis properties.
Besides inhibiting aggregation, decorating with materials that may reduce Zn2+ release and ROS levels is also an option. Li et al118 used atomic layer deposition to deposit the ZnO seed layer on a Ti substrate surface (Ti-ZnOs), and then the ZnO nano-rod arrays were grown with a hydrothermal method (Ti-ZnO). Subsequently, polydopamine (PDA) coating was applied (Ti-ZnO/PDA), and arginine-glycine-aspartic acid-cysteine (RGDC) peptides were immobilized to obtain the final sample (Ti-ZnO/PDA/RGDC). Ti-ZnO/PDA/RGDC exhibit good antibacterial and osteogenesis properties and less toxicity. This reduction in toxicity can be attributed to the reducibility of PDA, which consumes the ROS generated by ZnO-NPs. In addition, the covalent bonds between Zn2+ and PDA can reduce Zn2+ release, thereby further lowering toxicity and enhancing biocompatibility (Figure 4). Although the toxicity of ZnO-NPs is relatively low compared with other NPs, attention still needs to be paid to their concentration and distribution in orthopedic applications.119 Suitable implant preparation methods are needed to ensure homogeneous particle distribution, and further investigation is required to determine the mechanism of toxicity and a safe concentration range.
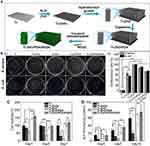 |
Figure 4 DOPA coatings reduce ZnO-NPs toxicity. |
Introducing less-toxic materials can also reduce the toxicity of ZnO-NPs. Vidic et al120 obtained ZnO/MgO mixed NPs through the combustion of zinc-magnesium alloys, and then tested the antibacterial and cytotoxic properties of ZnO-NPs, MgO-NPs, and ZnO/MgO mixed NPs against E. coli, Bacillus subtilis, and HeLa cells. Compared with MgO-NPs, ZnO-NPs exhibited better antibacterial properties against both bacterial species and stronger toxicity against HeLa cells. The antibacterial properties of the mixed NPs were better than those of MgO-NPs, while their cytotoxicity was lower than that of pure ZnO-NPs.120 This combination successfully reduced toxicity, while maintaining antibacterial properties. However, reports on the co-application of MgO-NPs and ZnO-NPs in orthopedics are few. In fact, MgO-NPs can both reduce the toxicity of ZnO-NPs and promote bone repair. The combination of ZnO-NPs and MgO-NPs may present favorable potential for orthopedic applications and requires further studies.
Limitations of Anticancer Effects in Orthopedic Applications
The anti-cancer properties of ZnO-NPs are a research hot spot aimed at improved bio-applications. The mechanism is the same as for toxicity. Many studies have reported ZnO-NP anti-cancer effects on multiple cancer cell lines, including bladder, breast, lung, and others.121–124 However, very few reports have focused on ZnO-NP treatment for bone tumors. After tumor resection, bone defects need to be filled with implants that can assist in the elimination of remaining cancer cells and enhance bone healing.125
Highly proliferative cells are more sensitive to ZnO-NPs and the strong toxicity of ZnO-NPs against rapidly proliferating cells may delay the healing process.126 Taccola et al127 examined the response of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) and differentiated osteoblasts to ZnO-NPs. At a concentration of 20 µg/mL, BMSCs with strong proliferating potential are significantly inhibited, while ZnO-NPs have little effect on osteoblasts with lower proliferation abilities. Kim et al128 suggested that ZnO-NPs participate in mitochondrial dysfunction and lead to BMSC apoptosis. These findings suggest that ZnO-NPs with anti-cancer effects may damage normal cell proliferation and may not suitable for treating bone cancer.
Osteogenic and Chondrogenic Abilities of ZnO-NPs
Osteogenic Mechanism of ZnO-NPs
The osteogenic properties of ZnO-NPs are due to Zn2+ release. As an essential trace element, Zn2+ participates in various enzyme catalytic activation reactions.22 Furthermore, Zn2+ can promote bone growth, mineralization, and formation.129,130 ZnO-NPs produce Zn-OH groups when in contact with water molecules that act as apatite nuclei and accelerate mineralization.131 In addition, Zn2+ can activate the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, which promotes expression of the osteocalcin gene region. Moreover, cells exposed to excessive Zn2+ may up-regulate the expression of Zn2+ transporters such as ZIP1, and its overexpression can enhance Runx2 expression, thus enhancing bone formation.132,133
Yamaguchi et al134 demonstrated that 10–250 µmol/L Zn2+ inhibited osteoclast differentiation. They pointed out that Zn2+ suppresses nuclear factor-κB signaling by reducing levels of tumor necrosis factor-α in vivo. This inhibitory effect decreases osteoclast generation and enhances the proliferation of osteoblasts, with a net effect of greatly enhanced osteogenesis. Park et al135 studied the upstream signaling pathway of RUNX2 and found that Zn2+ can activate protein kinase A signaling, by up-regulating cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), and thus enhancing nuclear translocation of phosphorylated cAMP response element-binding protein and upregulated RUNX2 expression.
ZnO-NPs can improve the activity and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and osteoblasts on the implant surface. These properties are ascribed to the larger modified implant surface area, which may possess more active sites that tend to absorb more proteins.136 Furthermore, studies have shown that physical properties of the scaffold are very important and can affect bone regeneration.137–140 These physical properties can also be optimized by ZnO-NPs modifications. Sahmani et al93 mixed different proportions of ZnO-NPs with HA, then sintered the mixed materials, and coated the resulting scaffolds with gelatin-ibuprofen. They found that the higher the ZnO-NP weight fraction, the higher the rate of degradation. Li et al141 proposed that doping ZnO-NPs into beta-phase poly (vinylidene fluoride) can produce a scaffold with a bone-like Young’s modulus, which can promote bone repair in vivo. However, several studies reported that doping ZnO-NPs would increase the water contact angle and reduce the material’s hydrophilicity, impairing osteoblast adhesion.96,142
Osteogenic Properties of ZnO-NP-Modified Implants
Wang et al45 found that ZnO-NP osteogenic ability is concentration dependent (Figure 5). They reported that the expressions of alkaline phosphatase and collagen significantly increased in MG63 cells cultured with 10 µg/mL ZnO-NPs compared to 5 µg/mL. They proposed that more ZnO-NPs produce a better osteogenic effect within the non-toxic concentration range. Shen et al143 applied a ZnO coating onto a micrometer-scale patterned Ti substrate using a hydrothermal method. The ZnO-NP-containing samples promoted osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. Furthermore, quantitative tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) activity analysis of RAW264.7 cells was performed, and the ZnO-NPs modified samples had the lowest TRAP activity, indicating the inhibition of osteoclast differentiation.143 The results of subsequent animal experiments corroborated the in vitro results that ZnO-NP modification could efficiently promote new bone tissue formation after implantation for 4 and 12 weeks.
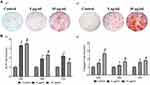 |
Figure 5 Effect of ZnO-NP concentration on osteogenesis activity. |
The combination of HA and ZnO-NPs is very common in orthopedic experiments and can promote osteogenesis via multiple mechanisms. Shitole et al96 incorporated nano-HA and ZnO-NPs into the PCL scaffold, which greatly improved its osteogenic effect. Maimaiti et al26 proposed that the HA/Zn coating achieved better osteogenic performance for bone formation compared to the pure HA coating. Gnaneshwar et al144 firstly doped ZnO-NPs into HA particles to obtain ZnO/HA particles, and then incorporated them to poly (L-lactic acid)-co-PCL and silk fibroin nanofibrous scaffolds. They found that scaffolds doped with ZnO/HA particles possessed stronger osteogenesis effects than scaffolds doped with the same quantities of ZnO-NPs and nHA. This result could guide the development of new co-modification strategies with various NPs in the future. AgNPs, As a strong antibiotic, also have the ability to promote bone formation.99 Interestingly, AgNPs and ZnNPs may act synergistically to promote osteogenesis.100,101 In the study of Deng et al,101 AgNPs and ZnNPs were uniformly doped on the surface of sulfonated polyetheretherketone (PEEK), using a layer-by-layer technique. Compared to PEEK doped with pure silver or ZnO-NPs, the hydrophilicity of ZnO/Ag/PEEK was reduced, cell adhesion was impaired in the early stage, and the number of MG-63 cells on ZnO/Ag/PEEK were the highest on day 5. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction of cells co-cultured with the sample on day 14, showed significantly higher expression of osteogenic genes with ZnO/Ag/PEEK compared with Ag/PEEK and ZnO/PEEK (Figure 6). Although the synergistic mechanism of AgNPs and ZnO-NPs is not clear, their combined application has considerable potential for osteogenesis.
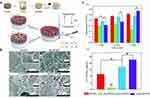 |
Figure 6 Combined application of ZnO-NPs and silver exerts a synergistic osteogenesis effect. |
Interestingly, ZnO-NPs can promote cartilage formation at lower concentrations. Khader et al25 prepared ZnO/PCL scaffolds with a concentration gradient of 1–10 wt% ZnO-NPs with an electrospinning technique. They found that under concentrations of 1–2.5wt%, the expression of cartilage markers such as SOX-9 and collagen type II were significantly increased in MSCs. Moreover, the scaffold with 10 wt% ZnO-NPs promoted osteogenic properties rather than chondrogenic differentiation, which is consistent with the findings of a previous study.145
Mirza et al145 studied the chondrogenic effects of 1% ZnO-NPs decorated with poly (octanediol citrate) polymer, and found that they improved chondrocyte viability, upregulated the expression of cartilage matrix-specific genes (COL2A1 and ACAN), and inhibited the expression of the matrix degradation gene (MMP-13).This cartilage-promoting ability could be attributed to Zn2+ release. Some studies claim that Zn2+ can enhance chondrocyte proliferation, while also preventing cartilage loss by activating the P13/Akt pathway.146,147 However, the mechanism by which ZnO-NPs promote cartilage growth is not clear, and further in vitro and in vivo experiments are needed.
Perspectives and Conclusion
Enhancing osseointegration and preventing post-implant prosthesis infections are major clinical challenges. ZnO-NP utilization may be one solution for these issues. This article summarized the preparation methods of ZnO-NPs, as well as the mechanisms, influencing factors, and the latest research progress into understanding their toxicity and osteogenic and antibacterial effects. However, several problems still remain. First, the specific mechanisms of antibacterial and toxicity are not yet well understood, so an effective non-toxic concentration range integrating multiple influencing factors cannot currently be determined. Second, ZnO-NPs exert synergistic antibacterial and osteogenic effects in combinations with other materials, and the specific mechanisms and optimal composition details need to be determined. Third, ZnO-NPs may promote cartilage formation, although this requires further exploration. Future research directions should focus on expanding non-toxic preparations (such as large-scale green preparations), reducing toxicity, clarifying specific mechanisms of antibacterial and osteogenic abilities, and determine how to enhance beneficial effects.
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
1. El-Rashidy AA, Roether JA, Harhaus L, Kneser U, Boccaccini AR. Regenerating bone with bioactive glass scaffolds: a review of in vivo studies in bone defect models. Acta Biomater. 2017;62:1–28. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2017.08.030
2. Vidal L, Kampleitner C, Brennan MA, Hoornaert A, Layrolle P. Reconstruction of large skeletal defects: current clinical therapeutic strategies and future directions using 3D printing. Front Bioeng Biotech. 2020;8:61. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2020.00061
3. Miyakoshi N. Effects of parathyroid hormone on cancellous bone mass and structure in osteoporosis. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(21):2615–2627. doi:10.2174/1381612043383737
4. Paterson AH. Evaluating bone mass and bone quality in patients with breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 2005;5(2):S41–45. doi:10.3816/CBC.2005.s.003
5. Schemitsch EH. Size matters: defining critical in bone defect size! J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(Suppl 5):S20–S22. doi:10.1097/BOT.0000000000000978
6. Dimitriou R, Jones E, McGonagle D, Giannoudis PV. Bone regeneration: current concepts and future directions. BMC Med. 2011;9(1):66. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-9-66
7. Amini AR, Laurencin CT, Nukavarapu SP. Bone tissue engineering: recent advances and challenges. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2012;40(5):363–408. doi:10.1615/CritRevBiomedEng.v40.i5.10
8. Zhang L, Ning C, Zhou T, et al. Polymeric nanoarchitectures on Ti-based implants for antibacterial applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(20):17323–17345. doi:10.1021/am5045604
9. Delloye C, Cornu O, Druez V, Barbier O. Bone allografts: what they can offer and what they cannot. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89(5):574–579. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.89B5.19039
10. Bose S, Sarkar N. Natural medicinal compounds in bone tissue engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2019.
11. Agarwal R, Garcia AJ. Biomaterial strategies for engineering implants for enhanced osseointegration and bone repair. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;94:53–62. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2015.03.013
12. Teow Y, Asharani PV, Hande MP, Valiyaveettil S. Health impact and safety of engineered nanomaterials. Chem Commun (Camb). 2011;47(25):7025–7038. doi:10.1039/c0cc05271j
13. Heng BC, Zhao X, Tan EC, et al. Evaluation of the cytotoxic and inflammatory potential of differentially shaped zinc oxide nanoparticles. Arch Toxicol. 2011;85(12):1517–1528. doi:10.1007/s00204-011-0722-1
14. Patil RM, Thorat ND, Shete PB, et al. Comprehensive cytotoxicity studies of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2018;13:63–72. doi:10.1016/j.bbrep.2017.12.002
15. Colvin VL. The potential environmental impact of engineered nanomaterials. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21(10):1166–1170. doi:10.1038/nbt875
16. Abdelkarem HM, Fadda LH, El-Sayed EM, Radwan OK. Potential role of L-arginine and vitamin E against bone loss induced by nano-zinc oxide in rats. J Diet Suppl. 2018;15(3):300–310. doi:10.1080/19390211.2017.1343889
17. Kambe T, Tsuji T, Hashimoto A, Itsumura N. The physiological, biochemical, and molecular roles of zinc transporters in zinc homeostasis and metabolism. Physiol Rev. 2015;95(3):749–784. doi:10.1152/physrev.00035.2014
18. Yamaguchi M. Role of nutritional zinc in the prevention of osteoporosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010;338(1–2):241–254. doi:10.1007/s11010-009-0358-0
19. Huang T, Yan G, Guan M. Zinc homeostasis in bone: zinc transporters and bone diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4).
20. Lin W, Li D. Zinc and zinc transporters: novel regulators of ventricular myocardial development. Pediatr Cardiol. 2018;39(5):1042–1051. doi:10.1007/s00246-018-1859-y
21. Teow SY, Wong MM, Yap HY, Peh SC, Shameli K. Bactericidal properties of plants-derived metal and metal oxide nanoparticles (NPs). Molecules. 2018;23(6):1366. doi:10.3390/molecules23061366
22. Zhang T, Liu J, Fellner M, Zhang C, Sui D, Hu J. Crystal structures of a ZIP zinc transporter reveal a binuclear metal center in the transport pathway. Sci Adv. 2017;3(8):e1700344. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1700344
23. Hanley C, Layne J, Punnoose A, et al. Preferential killing of cancer cells and activated human T cells using ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotechnology. 2008;19(29):295103. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/19/29/295103
24. Krol A, Pomastowski P, Rafinska K, Railean-Plugaru V, Buszewski B. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, antiseptic activity and toxicity mechanism. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;249:37–52. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2017.07.033
25. Khader A, Arinzeh TL. Biodegradable zinc oxide composite scaffolds promote osteochondral differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2020;117(1):194–209. doi:10.1002/bit.27173
26. Maimaiti B, Zhang N, Yan L, et al. Stable ZnO-doped hydroxyapatite nanocoating for anti-infection and osteogenic on titanium. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;186:110731. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110731
27. Mukherjee P, Roy M, Mandal BP, et al. Green synthesis of highly stabilized nanocrystalline silver particles by a non-pathogenic and agriculturally important fungus T. asperellum. Nanotechnology. 2008;19(7):075103. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/19/7/075103
28. Ahmed S, Ahmad M, Swami BL, Ikram S. A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: a green expertise. J Adv Res. 2016;7(1):17–28. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2015.02.007
29. Huang CC, Aronstam RS, Chen DR, Huang YW. Oxidative stress, calcium homeostasis, and altered gene expression in human lung epithelial cells exposed to ZnO nanoparticles. Toxicol in Vitro. 2010;24(1):45–55. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2009.09.007
30. Shedbalkar U, Singh R, Wadhwani S, Gaidhani S, Chopade BA. Microbial synthesis of gold nanoparticles: current status and future prospects. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2014;209:40–48. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2013.12.011
31. Shankar SS, Rai A, Ankamwar B, Singh A, Ahmad A, Sastry M. Biological synthesis of triangular gold nanoprisms. Nat Mater. 2004;3(7):482–488. doi:10.1038/nmat1152
32. Gahlawat G, Choudhury AR. A review on the biosynthesis of metal and metal salt nanoparticles by microbes. RSC Adv. 2019;9(23):12944–12967. doi:10.1039/C8RA10483B
33. Ahmed S, Annu CSA, Ikram S. A review on biogenic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using plant extracts and microbes: a prospect towards green chemistry. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017;166:272–284. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.12.011
34. Kalpana VN, Rajeswari VD. A review on green synthesis, biomedical applications, and toxicity studies of ZnO NPs. Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2018;2018:1–12. doi:10.1155/2018/3569758
35. Mirzaei H, Darroudi M. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: biological synthesis and biomedical applications. Ceram Int. 2017;43(1):907–914. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.10.051
36. Rasmussen JW, Martinez E, Louka P, Wingett DG. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for selective destruction of tumor cells and potential for drug delivery applications. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2010;7(9):1063–1077. doi:10.1517/17425247.2010.502560
37. Darroudi M, Sabouri Z, Oskuee RK, Zak AK, Kargar H, Abd Hamid MHN. Green chemistry approach for the synthesis of ZnO nanopowders and their cytotoxic effects. Ceram Int. 2014;40(3):4827–4831. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.09.032
38. Dukhinova MS, Prilepskii AY, Shtil AA, Vinogradov VV. Metal oxide nanoparticles in therapeutic regulation of macrophage functions. Nanomaterials. 2019;9(11).
39. Thema FT, Manikandan E, Dhlamini MS, Maaza M. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles via agathosma betulina natural extract. Mater Lett. 2015;161:124–127. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2015.08.052
40. Rich IN, Worthington-White D, Garden OA, Musk P. Apoptosis of leukemic cells accompanies reduction in intracellular pH after targeted inhibition of the Na+/H+ exchanger. Blood. 2000;95(4):1427–1434. doi:10.1182/blood.V95.4.1427.004k48_1427_1434
41. Mohamad NAN, Arham NA, Jai J, Hadi A. Plant extract as reducing agent in synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: a review. In: Mamat MH, Khusaimi Z, Bakar SA, Nor AM, Soga T, Mahmood MR, editors. Nanoscience, Nanotechnology and Nanoengineering. Vol. 832. 2014:350–355.
42. Roopan SM, Rajeswari VD, Kalpana VN, Elango G. Biotechnology and pharmacological evaluation of Indian vegetable crop Lagenaria siceraria: an overview. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;100(3):1153–1162. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-7190-0
43. Makarov VV, Love AJ, Sinitsyna OV, et al. “Green” nanotechnologies: synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Acta Naturae. 2014;6(1):35–44. doi:10.32607/20758251-2014-6-1-35-44
44. Ajitha B, Reddy YAK, Reddy PS, Jeon H-J, Ahn CW. Role of capping agents in controlling silver nanoparticles size, antibacterial activity and potential application as optical hydrogen peroxide sensor. RSC Adv. 2016;6(42):36171–36179. doi:10.1039/C6RA03766F
45. Wang D, Cui L, Chang X, Guan D. Biosynthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Artemisia annua and investigate their effect on proliferation, osteogenic differentiation and mineralization in human osteoblast-like MG-63 Cells. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2020;202:111652. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111652
46. Hu D, Si W, Qin W, et al. Cucurbita pepo leaf extract induced synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles, characterization for the treatment of femoral fracture. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2019;195:12–16. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.04.001
47. Kundu D, Hazra C, Chatterjee A, Chaudhari A, Mishra S. Extracellular biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using rhodococcus pyridinivorans NT2: multifunctional textile finishing, biosafety evaluation and in vitro drug delivery in colon carcinoma. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2014;140:194–204. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.08.001
48. Azizi S, Ahmad MB, Namvar F, Mohamad R. Green biosynthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using brown marine macroalga sargassum muticum aqueous extract. Mater Lett. 2014;116:275–277. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2013.11.038
49. Iravani S. Bacteria in nanoparticle synthesis: current status and future prospects. Int Sch Res Notices. 2014;2014:359316. doi:10.1155/2014/608739
50. Shamsuzzaman MA, Khanam H, Aljawfi RN. Biological synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using C. albicans and studying their catalytic performance in the synthesis of steroidal pyrazolines. Arab J Chem. 2017;10:S1530–S1536. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.05.004
51. Sanaeimehr Z, Javadi I, Namvar F. Antiangiogenic and antiapoptotic effects of green-synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using sargassum muticum algae extraction. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2018;9(1):3. doi:10.1186/s12645-018-0037-5
52. Bharde A, Rautaray D, Bansal V, et al. Extracellular biosynthesis of magnetite using fungi. Small. 2006;2(1):135–141. doi:10.1002/smll.200500180
53. Feng WC, Geng Z, Li ZY, et al. Controlled release behaviour and antibacterial effects of antibiotic-loaded titania nanotubes. Mat Sci Eng C Mater. 2016;62:105–112. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2016.01.046
54. Abad CL, Haleem A. Prosthetic joint infections: an update. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2018;20(7):15. doi:10.1007/s11908-018-0622-0
55. Kostakioti M, Hadjifrangiskou M, Hultgren SJ. Bacterial biofilms: development, dispersal, and therapeutic strategies in the dawn of the postantibiotic era. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2013;3(4):a010306–a010306. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a010306
56. Chen M, Yu Q, Sun H. Novel strategies for the prevention and treatment of biofilm related infections. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(9):18488–18501. doi:10.3390/ijms140918488
57. Peng Z, Ni J, Zheng K, et al. Dual effects and mechanism of TiO2 nanotube arrays in reducing bacterial colonization and enhancing C3H10T1/2 cell adhesion. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:3093–3105. doi:10.2147/IJN.S48084
58. Jacqueline C, Caillon J. Impact of bacterial biofilm on the treatment of prosthetic joint infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014;69(suppl 1):37–40. doi:10.1093/jac/dku254
59. Rabin N, Zheng Y, Opoku-Temeng C, Du YX, Bonsu E, Sintim HO. Biofilm formation mechanisms and targets for developing antibiofilm agents (vol 7, pg 493, 2015). Future Med Chem. 2015;7(10):1362. doi:10.4155/fmc.15.6
60. Ostomel TA, Shi Q, Stoimenov PK, Stucky GD. Metal oxide surface charge mediated hemostasis. Langmuir. 2007;23(22):11233–11238. doi:10.1021/la701281t
61. Ivanova EP, Truong VK, Wang JY, et al. Impact of nanoscale roughness of titanium thin film surfaces on bacterial retention. Langmuir. 2010;26(3):1973–1982. doi:10.1021/la902623c
62. Stoimenov PK, Klinger RL, Marchin GL, Klabunde KJ. Metal oxide nanoparticles as bactericidal agents. Langmuir. 2002;18(17):6679–6686. doi:10.1021/la0202374
63. Warren EAK, Payne CK. Cellular binding of nanoparticles disrupts the membrane potential. RSC Adv. 2015;5(18):13660–13666. doi:10.1039/C4RA15727C
64. Halder S, Yadav KK, Sarkar R, et al. Alteration of zeta potential and membrane permeability in bacteria: a study with cationic agents. Springerplus. 2015;4.
65. Sirelkhatim A, Mahmud S, Seeni A, et al. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015;7(3):219–242. doi:10.1007/s40820-015-0040-x
66. Choi E-K, Lee -H-H, Kang M-S, et al. Potentiation of bacterial killing activity of zinc chloride by pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate. J Microbiol. 2010;48(1):40–43. doi:10.1007/s12275-009-0049-2
67. Happy A, Soumya M, Venkat Kumar S, Rajeshkumar S. Mechanistic study on antibacterial action of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using green route. Chem Biol Interact. 2018;286:60–70. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2018.03.008
68. Akhtar MJ, Ahamed M, Alhadlaq HA, Alshamsan A. Mechanism of ROS scavenging and antioxidant signalling by redox metallic and fullerene nanomaterials: potential implications in ROS associated degenerative disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2017;1861(4):802–813. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.01.018
69. Ng CT, Ong CN, Yu LE, Bay BH, Baeg GH. Toxicity study of zinc oxide nanoparticles in cell culture and in drosophila melanogaster. J Vis Exp. 2019;(151). doi:10.3791/59510.
70. Premanathan M, Karthikeyan K, Jeyasubramanian K, Manivannan G. Selective toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles toward Gram-positive bacteria and cancer cells by apoptosis through lipid peroxidation. Nanomed Nanotechnol. 2011;7(2):184–192. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2010.10.001
71. Su Y, Wu D, Xia H, et al. Metallic nanoparticles induced antibiotic resistance genes attenuation of leachate culturable microbiota: the combined roles of growth inhibition, ion dissolution and oxidative stress. Environ Int. 2019;128:407–416. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2019.05.007
72. Hirota K, Sugimoto M, Kato M, Tsukagoshi K, Tanigawa T, Sugimoto H. Preparation of zinc oxide ceramics with a sustainable antibacterial activity under dark conditions. Ceram Int. 2010;36(2):497–506. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2009.09.026
73. Padmavathy N, Vijayaraghavan R. Enhanced bioactivity of ZnO nanoparticles-an antimicrobial study. Sci Technol Adv Mat. 2008;9(3):035004. doi:10.1088/1468-6996/9/3/035004
74. Khan HA, Shanker R. Toxicity of Nanomaterials. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:521014. doi:10.1155/2015/521014
75. Scown TM, van Aerle R, Tyler CR. Review: do engineered nanoparticles pose a significant threat to the aquatic environment? Crit Rev Toxicol. 2010;40(7):653–670. doi:10.3109/10408444.2010.494174
76. Pasquet J, Chevalier Y, Pelletier J, Couval E, Bouvier D, Bolzinger M-A. The contribution of zinc ions to the antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide. Colloids Surf A. 2014;457:263–274.
77. Mahamuni PP, Patil PM, Dhanavade MJ, et al. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles by using polyol chemistry for their antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2019;17:71–80. doi:10.1016/j.bbrep.2018.11.007
78. Wang S, Gao M, Ma B, Xi M, Kong F. Size-dependent effects of ZnO nanoparticles on performance, microbial enzymatic activity and extracellular polymeric substances in sequencing batch reactor. Environ Pollut. 2020;257:113596. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113596
79. Persaud I, Raghavendra AJ, Paruthi A, et al. Defect-induced electronic states amplify the cellular toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology. 2020;14(2):145–161. doi:10.1080/17435390.2019.1668067
80. Pan X, Liu X, Bermak A, Fan Z. Self-gating effect induced large performance improvement of ZnO nanocomb gas sensors. ACS Nano. 2013;7(10):9318–9324. doi:10.1021/nn4040074
81. Tan KH, Lim FS, Toh AZY, et al. Tunable spectrum selectivity for multiphoton absorption with enhanced visible light trapping in ZnO nanorods. Small. 2018;14(20):e1704053. doi:10.1002/smll.201704053
82. Yang YC, Wang GF, Li XD. Water molecule-induced stiffening in ZnO nanobelts. Nano Lett. 2011;11(7):2845–2848. doi:10.1021/nl201237x
83. Jin SE, Jin HE. Synthesis, characterization, and three-dimensional structure generation of zinc oxide-based nanomedicine for biomedical applications. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11(11):575. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics11110575
84. Yang H, Liu C, Yang D, Zhang H, Xi Z. Comparative study of cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and genotoxicity induced by four typical nanomaterials: the role of particle size, shape and composition. J Appl Toxicol. 2009;29(1):69–78. doi:10.1002/jat.1385
85. Talebian N, Amininezhad SM, Doudi M. Controllable synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their morphology-dependent antibacterial and optical properties. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2013;120:66–73. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2013.01.004
86. Li M, Zhu L, Lin D. Toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles to escherichia coli: mechanism and the influence of medium components. Environ Sci Technol. 2011;45(5):1977–1983. doi:10.1021/es102624t
87. Yu J, Zhang W, Li Y, et al. Synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial activity and mechanism of a novel hydroxyapatite whisker/nano zinc oxide biomaterial. Biomed Mater. 2015;10(1). doi:10.1088/1748-6041/10/1/015022.
88. Liu C, Jin H, Yu Y, et al. The improvement of nanoemulsion stability and antioxidation via protein-chlorogenic acid-dextran conjugates as emulsifiers. Nanomaterials. 2020;10(6). doi:10.3390/nano10061094.
89. Elizabeth E, Baranwal G, Krishnan AG, Menon D, Nair M. ZnO nanoparticle incorporated nanostructured metallic titanium for increased mesenchymal stem cell response and antibacterial activity. Nanotechnology. 2014;25(11):115101. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/25/11/115101
90. Qian W, Yan C, He DF, et al. pH-triggered charge-reversible of glycol chitosan conjugated carboxyl graphene for enhancing photothermal ablation of focal infection. Acta Biomater. 2018;69:256–264. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2018.01.022
91. Artifon W, Pasini SM, Valerio A, Gonzalez SYG, de Arruda Guelli Ulson de Souza SM, de Souza AAU. Harsh environment resistant - antibacterial zinc oxide/polyetherimide electrospun composite scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;103:109859. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2019.109859
92. Wang J, Zhou H, Guo G, et al. Enhanced anti-infective efficacy of ZnO nanoreservoirs through a combination of intrinsic anti-biofilm activity and reinforced innate defense. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(39):33609–33623. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b08864
93. Sahmani S, Saber-Samandari S, Shahali M, et al. Mechanical and biological performance of axially loaded novel bio-nanocomposite sandwich plate-type implant coated by biological polymer thin film. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;88:238–250. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.08.030
94. Dittler ML, Unalan I, Grunewald A, et al. Bioactive glass (45S5)-based 3D scaffolds coated with magnesium and zinc-loaded hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for tissue engineering applications. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;182:110346. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110346
95. Bhowmick A, Banerjee SL, Pramanik N, et al. Organically modified clay supported chitosan/hydroxyapatite-zinc oxide nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical and biological properties for the application in bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;106:11–19. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.07.168
96. Shitole AA, Raut PW, Sharma N, Giram P, Khandwekar AP, Garnaik B. Electrospun polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite/ZnO nanofibers as potential biomaterials for bone tissue regeneration. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(5):51. doi:10.1007/s10856-019-6255-5
97. Banerjee S, Vishakha K, Das S, et al. Antibacterial, anti-biofilm activity and mechanism of action of pancreatin doped zinc oxide nanoparticles against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;190:110921. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.110921
98. Alves MM, Bouchami O, Tavares A, et al. New insights into antibiofilm effect of a nanosized ZnO coating against the pathogenic methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(34):28157–28167. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b02320
99. Qing YA, Cheng L, Li RY, et al. Potential antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and the optimization of orthopedic implants by advanced modification technologies. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:3311–3327. doi:10.2147/IJN.S165125
100. Zhang Y, Liu X, Li Z, et al. Nano Ag/ZnO-incorporated hydroxyapatite composite coatings: highly effective infection prevention and excellent osteointegration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(1):1266–1277. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b17351
101. Deng Y, Yang L, Huang X, et al. Dual Ag/ZnO-decorated micro-/nanoporous sulfonated polyetheretherketone with superior antibacterial capability and biocompatibility via layer-by-layer self-assembly strategy. Macromol Biosci. 2018;18(7):e1800028. doi:10.1002/mabi.201800028
102. Roguska A, Belcarz A, Pisarek M, Ginalska G, Lewandowska M. TiO2 nanotube composite layers as delivery system for ZnO and Ag nanoparticles - an unexpected overdose effect decreasing their antibacterial efficacy. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;51:158–166. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2015.02.046
103. Li F, Song L, Yang X, et al. Anticancer and genotoxicity effect of (clausena lansium (lour.) skeels) peel ZnONPs on neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) cells through the modulation of autophagy mechanism. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2020;203:111748. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111748
104. Cheng J, Wang X, Qiu L, et al. Green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles regulates the apoptotic expression in bone cancer cells MG-63 cells. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2020;202:111644. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111644
105. R. MA, B. G, M.S. MJ, G. A, N. S. Anticancer potential of zinc oxide nanoparticles against cervical carcinoma cells synthesized via biogenic route using aqueous extract of gracilaria edulis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;103:109840. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2019.109840
106. Akhtar MJ, Ahamed M, Kumar S, Khan MM, Ahmad J, Alrokayan SA. Zinc oxide nanoparticles selectively induce apoptosis in human cancer cells through reactive oxygen species. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:845–857. doi:10.2147/IJN.S29129
107. Hameed S, Iqbal J, Ali M, et al. Green synthesis of zinc nanoparticles through plant extracts: establishing a novel era in cancer theranostics. Mater Res Express. 2019;6(10):102005. doi:10.1088/2053-1591/ab40df
108. Sahmani S, Saber-Samandari S, Khandan A, Aghdam MM. Influence of MgO nanoparticles on the mechanical properties of coated hydroxyapatite nanocomposite scaffolds produced via space holder technique: fabrication, characterization and simulation. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019;95:76–88. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2019.03.014
109. Horie M, Shimizu K, Tabei Y. Validation of metallothionein, interleukin-8, and heme oxygenase-1 as markers for the evaluation of cytotoxicity caused by metal oxide nanoparticles. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2018;28(8):630–638. doi:10.1080/15376516.2018.1486931
110. Ivask A, Titma T, Visnapuu M, et al. Toxicity of 11 metal oxide nanoparticles to three mammalian cell types in vitro. Curr Top Med Chem. 2015;15(18):1914–1929. doi:10.2174/1568026615666150506150109
111. Sudhakaran S, Athira SS, Varma HK, Mohanan PV. Determination of the bioavailability of zinc oxide nanoparticles using ICP-AES and associated toxicity. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;188:110767. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110767
112. Yan Y, Wang G, Huang J, et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticles exposure-induced oxidative stress restricts cranial neural crest development during chicken embryogenesis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020;194:110415. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110415
113. Suriyaprabha R, Balu KS, Karthik S, et al. A sensitive refining of in vitro and in vivo toxicological behavior of green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles from the shells of Jatropha curcas for multifunctional biomaterials development. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019;184:109621. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109621
114. Pinho AR, Rebelo S, Pereira ML. The impact of zinc oxide nanoparticles on male (in)fertility. Materials. 2020;13(4). doi:10.3390/ma13040849
115. Wang P, Zhang L, Liao Y, et al. Effect of intratracheal instillation of ZnO nanoparticles on acute lung inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharides in mice. Toxicol Sci. 2020;173(2):373–386. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfz234
116. Sehgal RR, Carvalho E, Banerjee R. Mechanically stiff, zinc cross-linked nanocomposite scaffolds with improved osteostimulation and antibacterial properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(22):13735–13747. doi:10.1021/acsami.6b02740
117. Abdulkareem EH, Memarzadeh K, Allaker RP, Huang J, Pratten J, Spratt D. Anti-biofilm activity of zinc oxide and hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as dental implant coating materials. J Dent. 2015;43(12):1462–1469. doi:10.1016/j.jdent.2015.10.010
118. Li J, Tan L, Liu XM, et al. Balancing bacteria-osteoblast competition through selective physical puncture and biofunctionalization of ZnO/polydopamine/arginine-glycine-aspartic acid-cysteine nanorods. Acs Nano. 2017;11(11):11250–11263. doi:10.1021/acsnano.7b05620
119. Vicario-Pares U, Castanaga L, Maria Lacave J, et al. Comparative toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles (CuO, ZnO and TiO2) to developing zebrafish embryos. J Nanopart Res. 2014;16(8). doi:10.1007/s11051-014-2550-8.
120. Vidic J, Stankic S, Haque F, et al. Selective antibacterial effects of mixed ZnMgO nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res. 2013;15(5):1595. doi:10.1007/s11051-013-1595-4
121. Zhang T, Du E, Liu Y, et al. Anticancer effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles through altering the methylation status of histone on bladder cancer cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:1457–1468. doi:10.2147/IJN.S228839
122. Saravanakumar K, Jeevithan E, Hu X, Chelliah R, Oh DH, Wang MH. Enhanced anti-lung carcinoma and anti-biofilm activity of fungal molecules mediated biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles conjugated with beta-D-glucan from barley. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2020;203:111728. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111728
123. Kim YJ, Perumalsamy H, Castro-Aceituno V, et al. Photoluminescent and self-assembled hyaluronic acid-zinc oxide-ginsenoside Rh2 nanoparticles and their potential caspase-9 apoptotic mechanism towards cancer cell lines. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:8195–8208. doi:10.2147/IJN.S221328
124. Shobha N, Nanda N, Giresha AS, et al. Synthesis and characterization of Zinc oxide nanoparticles utilizing seed source of ricinus communis and study of its antioxidant, antifungal and anticancer activity. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;97:842–850. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2018.12.023
125. Marques C, Ferreira JM, Andronescu E, Ficai D, Sonmez M, Ficai A. Multifunctional materials for bone cancer treatment. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:2713–2725. doi:10.2147/IJN.S55943
126. Hobman JL, Crossman LC. Bacterial antimicrobial metal ion resistance. J Med Microbiol. 2015;64(Pt 5):471–497. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.023036-0
127. Taccola L, Raffa V, Riggio C, et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticles as selective killers of proliferating cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6.
128. Kim DY, Kim JH, Lee JC, et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticles exhibit both cyclooxygenase- and lipoxygenase-mediated apoptosis in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Toxicol Res. 2019;35(1):83–91. doi:10.5487/TR.2019.35.1.083
129. Choi S, Liu X, Pan Z. Zinc deficiency and cellular oxidative stress: prognostic implications in cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39(7):1120–1132. doi:10.1038/aps.2018.25
130. Moonga BS, Dempster DW. Zinc is a potent inhibitor of osteoclastic bone resorption in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 1995;10(3):453–457. doi:10.1002/jbmr.5650100317
131. Suh KS, Lee YS, Seo SH, Kim YS, Choi EM. Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the function of MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2013;155(2):287–294. doi:10.1007/s12011-013-9772-y
132. Qiao Y, Zhang W, Tian P, et al. Stimulation of bone growth following zinc incorporation into biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2014;35(25):6882–6897. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.04.101
133. Chen J, Zhang X, Cai H, et al. Osteogenic activity and antibacterial effect of zinc oxide/carboxylated graphene oxide nanocomposites: preparation and in vitro evaluation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016;147:397–407. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.08.023
134. Yamaguchi M, Weitzmann MN. Zinc stimulates osteoblastogenesis and suppresses osteoclastogenesis by antagonizing NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;355(1–2):179–186. doi:10.1007/s11010-011-0852-z
135. Park KH, Choi Y, Yoon DS, Lee KM, Kim D, Lee JW. Zinc promotes osteoblast differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells via activation of the cAMP-PKA-CREB signaling pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2018;27(16):1125–1135. doi:10.1089/scd.2018.0023
136. Colon G, Ward BC, Webster TJ. Increased osteoblast and decreased Staphylococcus epidermidis functions on nanophase ZnO and TiO2. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;78A(3):595–604. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.30789
137. Aghdam HA, Sanatizadeh E, Motififard M, et al. Effect of calcium silicate nanoparticle on surface feature of calcium phosphates hybrid bio-nanocomposite using for bone substitute application. Powder Technol. 2020;361:917–929. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2019.10.111
138. Farazin A, Aghdam HA, Motififard M, et al. A polycaprolactone bio-nanocomposite bone substitute fabricated for femoral fracture approaches: molecular dynamic and micro-mechanical Investigation. J Nanoanalysis. 2019;6(3):172–184.
139. Sahmani S, Khandan A, Esmaeili S, Saber-Samandari S, Nejad MG, Aghdam MM. Calcium phosphate-PLA scaffolds fabricated by fused deposition modeling technique for bone tissue applications: fabrication, characterization and simulation. Ceram Int. 2020;46(2):2447–2456. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.238
140. Amiryaghoubi N, Fathi M, Pesyan NN, Samiei M, Barar J, Omidi Y. Bioactive polymeric scaffolds for osteogenic repair and bone regenerative medicine. Med Res Rev. 2020. doi:10.1002/med.21672
141. Li Y, Sun L, Webster TJ. The investigation of ZnO/poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites with improved mechanical, piezoelectric, and antimicrobial properties for orthopedic applications. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2018;14(3):536–545. doi:10.1166/jbn.2018.2519
142. Prado-Prone G, Silva-Bermudez P, Bazzar M, et al. Antibacterial composite membranes of polycaprolactone/gelatin loaded with zinc oxide nanoparticles for guided tissue regeneration. Biomed Mater. 2020;15(3):035006. doi:10.1088/1748-605X/ab70ef
143. Shen X, Hu Y, Xu G, et al. Regulation of the biological functions of osteoblasts and bone formation by zn-incorporated coating on microrough titanium. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(18):16426–16440. doi:10.1021/am5049338
144. Gnaneshwar PV, Sudakaran SV, Abisegapriyan S, et al. Ramification of zinc oxide doped hydroxyapatite biocomposites for the mineralization of osteoblasts. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;96:337–346. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.033
145. Mirza EH, Pan-Pan C, Wan Ibrahim WM, Djordjevic I, Pingguan-Murphy B. Chondroprotective effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles in conjunction with hypoxia on bovine cartilage-matrix synthesis. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(11):3554–3563. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.35495
146. Huang TC, Chang WT, Hu YC, et al. Zinc protects articular chondrocytes through changes in Nrf2-mediated antioxidants, cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases. Nutrients. 2018;10(4):471. doi:10.3390/nu10040471
147. Apostu D, Lucaciu O, Mester A, et al. Systemic drugs with impact on osteoarthritis. Drug Metab Rev. 2019;51(4):498–523. doi:10.1080/03602532.2019.1687511
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
