Back to Journals » International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease » Volume 11 » Issue 1
Endocan and the respiratory system: a review
Authors Kechagia M, Papassotiriou I , Gourgoulianis KI
Received 2 August 2016
Accepted for publication 20 September 2016
Published 12 December 2016 Volume 2016:11(1) Pages 3179—3187
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S118692
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
Maria Kechagia,1,2 Ioannis Papassotiriou,2 Konstantinos I Gourgoulianis1
1Respiratory Medicine Department, University of Thessaly Medical School, Larissa, 2Department of Clinical Biochemistry, Aghia Sophia Children’s Hospital, Athens, Greece
Abstract: Endocan, formerly called endothelial cell-specific molecule 1, is an endothelial cell-associated proteoglycan that is preferentially expressed by renal and pulmonary endothelium. It is upregulated by proangiogenic molecules as well as by pro-inflammatory cytokines, and since it reflects endothelial activation and dysfunction, it is regarded as a novel tissue and blood-based relevant biomarker. As such, it is increasingly being researched and evaluated in a wide spectrum of healthy and disease pathophysiological processes. Here, we review the present scientific knowledge on endocan, with emphasis on the evidence that underlines its possible clinical value as a prognostic marker in several malignant, inflammatory and obstructive disorders of the respiratory system.
Keywords: endocan, endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, respiratory disorders
Introduction
Endocan, formerly called endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (ESM-1), is a novel proteoglycan mainly, but not entirely expressed by pulmonary and renal endothelial cells. It is secreted upon stimulation by cytokines, namely tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1 and microbial lipopolysaccharide, as well as by proangiogenic factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Via its interaction with intercellular adhesion molecules, endocan exhibits a well-described inhibitory role on leukocyte binding to the vascular endothelium.1–6 These properties have highlighted its potential role as a biomarker of endothelial dysfunction and inflammation, while it has also been shown to be overexpressed in several human tumors and has, therefore, been implicated in the pathogenesis of malignancy and cancer angiogenesis.7–10
Based on its aforementioned tropism to lung endothelium and the accumulating research outcomes, despite the fact that its exact role has yet to be defined, endocan is being increasingly acknowledged as a promising agent in predicting and further understanding several inflammatory and malignant conditions of the respiratory system. In the present review, we will commence by describing endocan’s general structure followed by a brief summary of its molecular and biological properties. We will then proceed with a presentation of the current information concerning its emerging significance in the prognosis and follow-up of patients with various respiratory conditions, as well as of the evidence pointing toward a possible future role in the diagnosis and study of obstructive and inflammatory lung disorders.
Endocan: general knowledge
Structure and expression
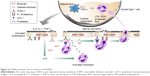
Endocan was first described and molecularly characterized in 1996 by Lassale who isolated an endothelial cell-related molecule in a human umbilical vein endothelial cell cDNA library. In humans, it is encoded by a single gene, the ESM-1 gene, localized on chromosome 5 at the position 5q11.2.1 Originally termed ESM-1, it was shown to exhibit significant cytokine-dependent functions during the inflammatory reaction and to be constitutively expressed in the endothelial cell network. Based on the latter, it was renamed accordingly, receiving its current name in 2001.4 Structurally, it is a 50 kDa soluble dermatan sulfate (DS) proteoglycan (PG) and as such comprises a protein core, covalently attached to a glycosaminoglycan (GAG)-type linear polysaccharide chain3 (Figure 1). The protein part is composed of 165 amino acids and possesses an N-terminal cysteine-rich region of 110 amino acids, which also includes an endothelial growth factor-like region, a phenylalanine-rich domain and a C-terminal region. It is linked to the GAG chain via serine 137 during posttranslational modification.1,5,6 The GAG chain contains 32 disaccharide residues consisting of an amino sugar (N-acetylglucosamine, glucosamine that is variously N-substituted, or N-acetylgalactosamine) and a uronic acid (glucuronic acid or iduronic acid with a ratio of 30/70).3
  | Figure 1 Structure of endocan. |
Unlike most chondroitin/DS-containing proteoglycans, which are either extracellular matrix (ECM) or cell membrane associated, endocan belongs to a limited category of secreted proteoglycans, but displays no clear structural linkage to any of them. First of all, its small size and single DS chain distinguishes it from most ECM PGs, which are relatively large molecules, possessing several GAG chains. In contrast to the largest class of the ECM PGs, the small leucine-rich PGs, and the hyaluronan- and lectin-binding PGs (hyalectans), endocan does not contain the conserved leucine rich repeats of the former, nor the C-type lectin domains of the latter.11,12 Furthermore, compared to the existing DS PGs, endocan’s DS chain is shorter and characterized by a higher content of non-sulfated and disulfated disaccharides.3,5,6 GAG moieties of proteoglycans are responsible for their molecular interactions and consequently their properties. Accordingly, endocan’s saccharide chain, partly due to the conformational flexibility conferred by its iduronic acid residues13 and partly due to the binding properties associated with its highly sulfated domains,6 is considered critical for the molecule’s biological functions.
As already mentioned, endocan is secreted by activated endothelial cells, preferentially of the lung and less intensively of the renal vasculature, including tumor endothelial cells.1,10 Nevertheless, its expression is not entirely restricted to the endothelium. More recent studies have demonstrated its active synthesis by several normal, actively proliferative tissues, as well as by tissues undergoing neogenesis.7,8,14 Endocan overexpression has also been clearly demonstrated in malignant tissues such as melanoma, glioblastoma, renal and lung carcinoma, with the level of expression directly correlating to the severity of the disease.3 Tissue activity seems to be a prerequisite for endocan expression as it has not yet been described in quiescent tissues such as major vessels or the spleen.14
Binding properties
Being a proteoglycan, the multifunctionality of endocan arises from its structure and involves intercellular interactions, which to a large extent depend on the interaction of the GAG chain and the protein core with various ligands. The latter has been well documented to bind to the β2 integrin CD11a/CD18, known as lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1). LFA-1 is expressed in leukocytes and is important in the migration of neutrophils, monocytes and lymphocytes through its binding to the cellular adhesion molecules (CAMs) 1 and 2 that are expressed on vascular endothelium in inflammatory sites.15 Through its interaction with LFA-1, endocan inhibits the aforementioned binding and consequently the LFA-1/intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1)-dependent leukocyte adhesion that normally occurs during inflammatory processes.2
As far as the GAG chain is concerned, it has been shown to mediate several biological functions with iduronic acid being fundamental in the protein binding properties of the molecule.10,16 One of these functions is the promotion of the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-dependent proliferation of endothelial cells, a process that is implicated in angiogenesis, tumorigenesis and tumor progression.4,6,17 Taking into consideration the binding properties exhibited by the DS moiety, possible interactions of endocan with several other proteins cannot be excluded.18,19
Regulation
Consistent with endocan’s role in inflammation and endothelial activation, cytokines that provide activation signals for the functional potentiation of integrins and their conversion from low- to high-affinity state on leukocytes have been shown to induce its expression in vitro. Such cytokines are TNF-α and IL-1, which seem to increase not only the molecule’s m-RNA content of HUVEC cells but also its secretion.20 Endocan m-RNA and its protein expression are also induced by VEGF,21 while transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 and fibroblast growth factor-2 in vitro stimulate its release in endothelial cells and tumor cell lines.22 At the same time, others such as interferon-γ (IFNγ) and IL-4 seem to play an inhibitory and no role at all, respectively. IFNγ, in particular, interestingly exhibits a stronger inhibitory effect on endocan expression when combined with TNF-α, despite their usual synergistic effect on the expression of various pro-inflammatory factors and adhesion molecules.1,20
Pathophysiological significance
Due to its involvement in the regulation of cellular behavior and in an attempt to explore its potential significance as a biomarker, endocan’s role is increasingly being studied in a spectrum of healthy and disease pathophysiological processes.
Despite a certain controversy in literature in cases of low-grade inflammation, endocan’s blood levels have been found elevated in septic patients with increasing severity of illness as well as in immunocompromised patients with complicating bacterial infections. This underlines a possible future role in the differential diagnosis of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome and a predictive value in terms of clinical outcome.9,20,23 Such findings are, as expected, consistent with the reported higher levels of ICAM-1 and P-selectin in relation to the degree of the syndrome’s severity.24–26 Given the endothelium’s central role in its pathogenesis, endocan has also been studied in relation to Behcet’s-Adamantiades disease and has been found potentially significant as a biomarker.27
The molecule was also recently investigated in relation to essential hypertension, as the pathogenesis of the latter is characterized by inflammation and interactions between the vasculature and circulating leukocytes, and its levels were found to be directly related to the blood pressure values.28 It should be mentioned that hypertensive patients also exhibit elevated serum levels of E-selectin, P-selectin and ICAM-1 compared to normotensive individuals. This evidence is supportive of a protective role against complications, for instance atherosclerosis, through endocan’s competitive affinity for LFA-1 and provides a basis for further investigation in other conditions with underlying endothelial dysfunctions such as cardiovascular diseases and diabetes mellitus. Surprisingly though, despite the fact that obesity is a state of low-grade inflammation and is associated with enhanced release of adipokines and adhesion molecules, namely ICAM-1, circulating levels of endocan are decreased in obese individuals.7,29
As far as endocan’s aforementioned potential role in tumor development and growth is concerned, it has motivated ongoing scientific activity with the majority of studies exploring its future use as a relevant biomarker. Recent studies indicate that endocan not only is upregulated in the presence of proangiogenic factors such as VEGF,21 but that it in turn enhances their mitogenic activity.30 Furthermore, increased vascular expression of endocan has been demonstrated by its immunoreactivity within endothelial cells, and association with intra-tumoral microvascular density has been reported in studies involving glioblastoma, bladder, clear renal cell, colorectal and hepatocellular carcinoma as well as in malignant melanoma cases.22,31–36 Therefore, it is possibly involved in neoangiogenesis with its levels correlating with tumor aggressiveness and progression and could be valuable in monitoring treatment with antiangiogenic agents in cancer patients. This hypothesis is strengthened by the confirmation of its expression and specificity to endothelial tip cells.37 Tip cells are a subpopulation of endothelial cells that are known to mediate vascular growth and to play an important role in neoangiogenesis. The recent identification of endocan’s expression and active secretion by tumor cells, which tend to express endothelial cell-associated genes, also suggests its possible pro-tumorigenic role, with higher degrees of expression being associated with increased tumor invasiveness.22,38 Not surprisingly, given the biological significance of the molecule’s DS, only fully glycanated endocan promotes tumorigenesis, although not without the contribution of its polypeptide.38,39
Besides solid tumors, the molecule might also have a clinical impact in hematological malignancies, as suggested by recent attempts to evaluate it as a prognostic marker in acute myeloid and lymphoid leukemia.40,41 According to the results, its serum levels, as well as its cytoplasmic expression in bone marrow blasts, were associated with chemotherapy outcome, a finding which is again in consistence with VEGF’s reported role in leukemia-associated angiogenesis.42 This rapidly expanding research activity surrounding endocan is facilitated by the relatively simple laboratory methods developed for such purposes, including sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, immunohistochemistry and immunoprecipitation. Sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays are commercially available for diagnostic purposes as well; can be applied in cell culture supernatants, serum or plasma; and could provide a useful tool for quick quantification of endocan levels in various clinical settings.
Endocan and the respiratory system
A considerable spectrum of lung diseases, ranging from atopic asthma and COPD to lung cancers, is invariably characterized by different degrees of endothelial damage and microvascular inflammation with accompanying upregulation of adhesion molecules, the expression of which mediates leukocyte trafficking and adherence to the endothelium. ICAM-1 and LFA-1 are thought to play a crucial role in airway inflammation and lung tumors with certain studies clearly demonstrating their upregulation, while others present with more or less conflicting results.43–50 Considering endocan’s selective expression in activated pulmonary endothelial cells and interaction with LFA-1, its role in lung disorders with underlying endothelial dysfunction is of particular interest as it could reflect the severity of such pathophysiological conditions. Nevertheless, data about the molecule’s role are just emerging since it has, surprisingly, not been studied extensively in clinical settings of the respiratory system (Table 1).
Lung neoplasms
As already mentioned in the previous section, the majority of existing endocan-centered studies have investigated it in relation to tumorigenesis. Taking into consideration the fact that endothelial endocan expression is stimulated by VEGF production by neoplastic cells, these two molecules are strictly connected. Nevertheless, in contrast to the abundant literature assessing VEGF expression and serum levels,51,52 presently only two studies have investigated endocan in relation to primary lung cancer.38,53
In the study conducted by Scherpereel et al,38 the sera of patients with various lung cancers were collected upon diagnosis and prior to specific treatment. The revealed elevated endocan concentrations, directly correlating with the tumoral size, provided the first indication of the molecule’s possible use in the evaluation of the overall prognosis of such cases. The subsequent clinical study by Grigoriu et al53 evaluated endocan’s expression in lung in specimens of 24 non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) patients undergoing surgery, as well as in 30 previously untreated ones, and demonstrated a VEGF-dependent overexpression of both the molecules’ m-RNA and protein in the tumoral, but not in the distal, healthy lung tissue. This study also suggested a close relationship between the elevated serum endocan levels and poor survival, with the cutoff level between survivors and non-survivors being 1.3 ng/mL. Lung biopsy molecular profiling studies, like the one conducted by Borczuk et al,54 which supports the use of gene expression profiles as predictive information about clinical outcome and has identified the ESM-1 gene among the ones associated with high risk of death within 1 year, represent an attractive future approach.
Acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome
In addition to lung neoplasms, endocan has also been studied in relation to acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) with more or less contradictory outcomes. These two conditions are characterized by acute onset, alveolar and endothelial injury, pulmonary edema and severe hypoxemia and are major complications of either pulmonary or extra-pulmonary insults.55 Clinical conditions that exert their effects directly on lung cells include diffuse pulmonary infection, aspiration and, less commonly, injurious ventilation, pulmonary contusion and toxic inhalation. On the other hand, indirect lung injury can be the result of sepsis, severe extrathoracic trauma, multiple blood transfusions, as well as several other causes of an acute systemic inflammatory response.56
Irrespective of the noxious agent’s nature, it triggers an intense pulmonary inflammatory response with accumulation of pro-inflammatory mediators originating from activated platelets, alveolar macrophages, migrating leukocytes as well as injured tissues.57,58 Such mediators include thromboxane A2, TNF-β, VEGF and TNF-α and initiate a cascade of events leading to the disruption of the pulmonary endothelial functional and structural integrity that characterizes the condition.59 The upregulation of CAMs in particular, with subsequent enhancement of leukocyte and platelet recruitment and aggregation, is of key significance. The adherent platelets further release mediators that lead to endothelial activation, promoting its procoagulant properties, while leukocytes, particularly neutrophils, through their ICAM-1 interaction release reactive oxygen species, which induce oxidative injury.59,60 Studies emphasizing the role of markers denoting pulmonary endothelial dysfunction have been performed in an attempt to investigate the aforementioned pathogenetic mechanisms and have reported, despite a relative confliction, higher levels of VEGF, P-selectin, ICAM-1 and vWF in ALI patients.61–65
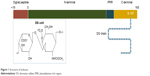
Based on the aforementioned pathophysiological processes, endocan has been investigated as a predictive biomarker for the development of ALI or ARDS originating from severe sepsis in a 72-hour prospective study of 21 intensive care unit patients and nine healthy controls.66 Although significantly increased in the severe sepsis and septic shock patients versus the individuals belonging to the controls’ group, the molecule’s levels were found to be lower than expected in those patients who developed either ALI or ARDS at 48 and 72 hours compared to the ones that did not at the same time points. Despite the pathophysiological and clinical differences between ALI of traumatic and non-traumatic etiology, these findings are in accordance with another recent study attempting to associate endocan’s serum levels to the development of ALI triggered by major trauma.67,68 The outcome from both studies supports the hypothesis that endocan-mediated inhibition of leukocyte recruitment may exhibit a protective role against the development of ALI and ARDS (Figure 2) and if further verified, it could represent a future therapeutic approach. The results, at a molecular level, could be further explained by either a reduced release of endocan from pulmonary endothelial cells, or an increase of its proteolysis by neutrophil serine proteases.69
By contrast, significantly elevated plasma endocan levels were observed by Tang et al70 in pneumonia patients developing ARDS compared with ones that did not, and were further associated with an increased incidence of multiple organ dysfunction in these patients. The proposed responsible mechanism is the induction of the molecule’s synthesis by bacterial endotoxins as well as by pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and TNF-α.70
The compromise of the pulmonary endothelial cell barrier in response to ALI is also strongly dependent on cytoskeletal remodeling, resulting in the disruption of the cytoskeleton network. These complex mechanisms involved in endothelial cell permeability are not fully explored. Nevertheless, they seem to include signal transduction pathways that involve, among others, protein kinase C, myosin light chain kinase, Rho and p38 kinase signaling, resulting in the phosphorylation of several cytoskeletal proteins.71 Endocan’s role in the aforementioned processes could be an attractive topic for future research. Its regulation by VEGF and the fact that the latter has been shown to stimulate the reorganization of endothelial actin and the formation of stress fibers72 could also be of relevance and should be taken into consideration.
Other clinical settings
At this point, it is worth mentioning that endocan has also been studied in less critical lower respiratory infections. In their study, Kao et al attempted to evaluate endocan’s usefulness in differentiating healthy individuals from patients with pulmonary infections.73 More specifically, endocan levels were measured in 82 hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) and compared to those of healthy controls. The molecule’s levels were found to directly correlate to illness severity and response to antibiotic treatment in a more specific manner than to C-reactive protein concentrations or white blood cell counts.
Based on the association of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and endothelial dysfunction, endocan was also very recently investigated in a prospective study by Altintas et al.74 The effect of the condition on the molecule’s levels was assessed in moderate-to-severe OSA patients, at baseline and following 3 months of continuous positive airway pressure treatment. According to the results, not only was endocan able to distinguish patients with OSA from individuals with suspected, though not confirmed, diagnosis but also further correlated with the severity of the condition, measured by the apnea-hypopnea index and the therapeutic response. Such data are supportive of OSA having an endothelium-dependent pathology, as well as of endocan’s potential role as a biomarker in the diagnosis and monitoring of affected individuals.
Finally, in a study of patients admitted with pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE), endocan levels demonstrated a significant difference not only between patients and controls but also between the patients’ clinical subclasses according to right ventricular dilatation.75 Endocan clearly showed a positive correlation with the latter and was significantly higher in the submassive and massive PTE cases than in the non-massive ones. As expected, since the molecule reflects endothelial integrity, the results are indicative not only of its possible value as a biomarker in such events but also in the determination of their severity.75
Future perspectives in inflammatory and obstructive lung disorders
Endocan’s properties provide enough ground for further investigation in search of information about its possible value as a marker of several respiratory conditions. For instance, it has been reported that TGF-β and VEGF levels are elevated in complicated parapneumonic effusions and empyemas, with the latter exhibiting a predictive value for the development of residual pleural thickening.76–78 As both growth factors1,30 induce endocan’s expression we postulate that endocan correlates with parapneumonic effusions as well, but this hypothesis may warrant further investigation. Furthermore, although the demonstration of a causal relationship between endothelial dysfunction and chronic airway disease is challenging, there is accumulating evidence supporting an association between endothelial dysfunction, COPD and asthma.
Both systemic and bronchial inflammation with the observed elevated levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8 and adhesion molecules and the increased bronchial leukocyte counts could be responsible for the atherosclerotic lesions that characterize many of the cardiovascular comorbidities of COPD patients.49,79 The airway vasculature has been assessed in such patients, and findings of altered small airway wall vascularity and reactivity are consistent with endothelial dysfunction, possibly linking bronchial obstruction to the functional changes of the endothelial arterial wall.80,81 In addition, as heightened systemic inflammation is associated with recurrent exacerbations, the inflammatory changes observed during the course of such episodes, including the levels of markers such as TNF-α and IL-6, have been shown to be of potential value in the exacerbation pattern prediction.82–84 As far as asthma is concerned, possibly due to inflammation, the airway circulation in such patients has been shown to be characterized by microvascular hyperpermeability, vascular remodeling that involves the whole bronchial tree, increase in subepithelial blood flow and endothelial dysfunction.85–88
Taking into consideration endocan’s upregulation both in settings of endothelial dysfunction and in inflammatory processes of similar molecular patterns, there is adequate ground for future investigation of its role in the natural history of obstructive pulmonary diseases as well as in the follow-up of affected patients. The relationship of the molecule’s levels and the clinical outcomes of patients could be of importance, possibly in line with recent findings supporting an inverse relation between serum levels of VEGF and disease severity89,90 and is a potentially interesting field for further exploration. Endocan could furthermore provide information about the endothelial function of patients with different exacerbation phenotypes, not only contributing in the ongoing research of a possible causal relationship between endothelial dysfunction and COPD exacerbation pattern, but also in the determination of an optimal and individualized therapeutic approach.
Conclusion
Endocan is a promising novel marker of endothelial dysfunction with recent developments pointing toward possible future applications in the prognosis and staging of several inflammatory and malignant clinical conditions. The identification of its overexpression in NSCLC tissues, paired with the emerging evidence of a key role in respiratory disorders characterized by inflammatory response, underlines the fact that endocan could be considered as a biomarker of pulmonary-activated endothelial cells with promising potential applications. These could include, among others, its adoption as a biomarker in the severity assessment of CAP and PTE, the prediction of development of ALI, the phenotypic classification of COPD patients, as well as its use as possible therapeutic target for these conditions. Endocan could also improve the prognostic evaluation of cancer patients and the identification of those with high-risk tumors, as well as the selection of appropriate chemotherapeutic regimens. Furthermore, it could not only aid the early detection and study of neoangiogenesis but also provide a new target for antiangiogenic therapies. Nevertheless, despite the solid pathophysiological basis, it has not been adequately studied nor evaluated, particularly in non-neoplastic lung diseases. At the moment, this represents, in our opinion, the biggest limitation in its use as a relevant biomarker. Therefore, further investigations are required in order to clarify its exact role in the aforementioned processes and to fully assess its suitability and consistency as a biomarker of respiratory diseases characterized by microvascular inflammation and endothelial damage.
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank Dr Giorgos Ntatsis for his valuable help with graphic designing.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Lassalle P, Molet S, Janin A, et al. ESM-1 is a novel human endothelial cell-specific molecule expressed in lung and regulated by cytokines. J Biol Chem. 1996;271(34):20458–20464. | ||
Béchard D, Scherpereel A, Hammad H, et al. Human endothelial-cell specific molecule-1 binds directly to the integrin CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1) and blocks binding to intercellular adhesion molecule-1.J Immunol. 2001;167(6):3099–3106. | ||
Delehedde M, Devenyns L, Maurage CA, Vivès RR. Endocan in cancers: a lesson from a circulating dermatan sulfate proteoglycan. Int J Cell Biol. 2013;2013:705027. | ||
Béchard D, Gentina T, Delehedde M, et al. Endocan is a novel chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate proteoglycan that promotes hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor mitogenic activity. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(51):48341–48349. | ||
Bishop JR, Schuksz M, Esko JD. Heparan sulphate proteoglycans fine-tune mammalian physiology. Nature. 2007;446(7139):1030–1037. | ||
Sarrazin S, Lyon M, Deakin JA, et al. Characterization and binding activity of the chondroitin/dermatan sulfate chain from endocan, a soluble endothelial proteoglycan. Glycobiology. 2010;20(11):1380–1388. | ||
Janke J, Engeli S, Gorzelniak K, et al. Adipose tissue and circulating endothelial cell specific molecule-1 in human obesity. Horm Metab Res. 2006;38(1):28–33. | ||
Wellner M, Herse F, Janke J, et al. Endothelial cell specific molecule-1 – a newly identified protein in adipocytes. Horm Metab Res. 2004;35(4):217–221. | ||
Paulus P, Jennewein C, Zacharowski K. Biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction: can they help us deciphering systemic inflammation and sepsis? Biomarkers. 2011;16(suppl 1):S11–S21. | ||
Sarrazin S, Adam E, Lyon M, et al. Endocan or endothelial cell specific molecule-1 (ESM-1): a potential novel endothelial cell marker and a new target for cancer therapy.Biochim Biophy Acta. 2006;1765(1):25–37. | ||
Iozzo RV, Schaefer L. Proteoglycan form and function: a comprehensive nomenclature of proteoglycans. Matrix Biol. 2015;42:11–55. | ||
Iozzo RV. Matrix proteoglycans: from molecular design to cellular function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:609–652. | ||
Casu B, Petitou M, Provasoli M, Sinay P. Conformational flexibility: a new concept for explaining binding and biological properties of iduronic acid-containing glycosaminoglycans. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988;13(6):221–225. | ||
Zhang SM, Zuo L, Zhou Q, et al. Expression and distribution of endocan in human tissues. Biotech Histochem. 2012;87(3):172–178. | ||
Long EO. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1): getting a grip on leukocyte adhesion. J Immunol. 2011;186(9):5021–5023. | ||
Lyon M, Deakin JA, Rahmoune H, Fernig DG, Nakamura T, Gallagher JT. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor binds with high affinity to dermatan sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(1):271–278. | ||
Bhowmick NA, Neilson EG, Moses HL. Stromal fibroblasts in cancer initiation and progression. Nature. 2004;432(7015):332–337. | ||
Maimone MM, Tollefsen DM. Structure of a dermatan sulfate hexasaccharide that binds to heparin cofactor II with high affinity. J Biol Chem. 1990;265(30):18263–18271. | ||
Merle B, Durussel L, Delmas PD, Clezardin P. Decorin inhibits cell migration through a process requiring its glycosaminoglycan side chain. J Cell Biochem. 1999;75(3):538–546. | ||
Bechard D, Meignin V, Scherpereel A, et al. Characterization of the secreted form of endothelial-cell-specific molecule 1 by specific monoclonal antibodies. J Vasc Res. 2000;37(5):417–425. | ||
Rennel E, Mellberg S, Dimberg A, et al. Endocan is a VEGFA and PI3K regulated gene with increased expression in human renal cancer. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313(7):1285–1294. | ||
Maurage CA, Adam E, Minéo JF, et al. Endocan expression and localization in human glioblastomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2009;68(6):633–641. | ||
Scherpereel A, Depontieu F, Grigoriu B, et al. Endocan, a new endothelial marker in human sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2006;34(2):532–537. | ||
Sessler CN, Windsor AC, Schwartz M, et al. Circulating ICAM-1 is increased in septic shock. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;151(5):1420–1427. | ||
Kayal S, Jaïs JP, Aguini N, Chaudière J, Labrousse J. Elevated circulating E-selectin, intercellular adhesion molecule 1, and von Willebrand factor in patients with severe infection.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157(3 Pt 1):776–784. | ||
Endo S, Inada K, Kasai T, et al. Levels of soluble adhesion molecules and cytokines in patients with septic multiple organ failure. J Inflamm. 1995;46(4):212–219. | ||
Balta I, Balta S, Koryurek OM, et al. Serum endocan levels as a marker of disease activity in patients with Behçet disease. J Am Acad of Dermatol. 2014;70(2):291–296. | ||
Tadzic R, Mihalj M, Vcev A, Ennen J, Tadzic A, Drenjancevic I. The effects of arterial blood pressure reduction on endocan and soluble endothelial cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) and CAMs ligands expression in hypertensive patients on Ca-channel blocker therapy. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2013;37(2–3):103–115. | ||
Fain JN. Release of inflammatory mediators by human adipose tissue is enhanced in obesity and primarily by the nonfat cells: a review. Mediators Inflamm. 2010;2010:513948. | ||
Shin JW, Huggenberger R, Detmar M. Transcriptional profiling of VEGF-A and VEGF-C target genes in lymphatic endothelium reveals endothelial-specific molecule-1 as a novel mediator of lymphangiogenesis. Blood. 2008;112(6):2318–2326. | ||
Zuo L, Zhang SM, Hu RL, et al. Correlation between expression and differentiation of endocan in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(28):4562–4568. | ||
Kim JH, Park MY, Kim CN, et al. Expression of endothelial cell-specific molecule-1 regulated by hypoxia inducible factor-1α in human colon carcinoma: impact of ESM-1 on prognosis and its correlation with clinicopathological features. Oncol Rep. 2012;28(5):1701–1708. | ||
Chen LY, Liu X, Wang SL, Qin CY. Over-expression of the endocan gene in endothelial cells from hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with angiogenesis and tumour invasion. J Int Med Res. 2010;38(2):498–510. | ||
Huang GW, Tao YM, Ding X. Endocan expression correlated with poor survival in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 2009;54(2):389–394. | ||
Leroy X, Aubert S, Zini L, et al. Vascular endocan (ESM-1) is markedly overexpressed in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Histopathology. 2010;56(2):180–187. | ||
Roudnicky F, Poyet C, Wild P, et al. Endocan is upregulated on tumor vessels in invasive bladder cancer where it mediates VEGF-A-induced angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2013;73(3):1097–1106. | ||
Strasser GA, Kaminker JS, Tessier-Lavigne M. Microarray analysis of retinal endothelial tip cells identifies CXCR4 as a mediator of tip cell morphology and branching. Blood. 2010;115(24):5102–5110. | ||
Scherpereel A, Gentina T, Grigoriu B, et al. Overexpression of endocan induces tumor formation. Cancer Res. 2003;63(18):6084–6089. | ||
Depontieu F, Grigoriu BD, Scherpereel A, et al. Loss of endocan tumorigenic properties after alternative splicing of exon 2. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:14. | ||
Xu Z, Zhang S, Zhou Q, Wang Y, Xia R. Endocan, a potential prognostic and diagnostic biomarker of acute leukemia. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;395(1–2):117–123. | ||
Hatfield KJ, Lassalle P, Leiva RA, Lindås R, Wendelboe Ø, Bruserud Ø. Serum levels of endothelium-derived endocan are increased in patients with untreated acute myeloid leukemia. Hematology. 2011;16(6):351–356. | ||
Wegiel B, Ekberg J, Talasila KM, Jalili S, Persson JL. The role of VEGF and a functional link between VEGF and p27Kip1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2009;23(2):251–261. | ||
Popper HH, Pailer S, Wurzinger G, Feldner H, Hesse C, Eber E. Expression of adhesion molecules in allergic lung diseases. Virchows Arch. 2002;440(2):172–180. | ||
Corry DB, Kheradmand F. Asthma. In: Zander DS, Popper HH, Jagirdar J, Haque AK, Cagle PT, Barrios R, editors. Molecular Pathology of Lung Diseases. New York: Springer; 2010:549–576. | ||
Jiang Z, Woda BA, Savas L, Fraire AE. Expression of ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and LFA-1 in adenocarcinoma of the lung with observations on the expression of these adhesion molecules in non-neoplastic lung tissue. Mod Pathol. 1998;11(12):1189–1192. | ||
Jahnz-Rózyk K, Chciałowski A, Pirozyńska E, Rogalewska A. Expression of adhesion molecules LFA-1 (CD11a and ICAM-1 (CD54) on lymphocytes and chemokines IL-8 and MCP-1 concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavage of patients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2000;9(52):649–652. | ||
Di Stefano A, Maestrelli P, Roggeri A, et al. Upregulation of adhesion molecules in the bronchial mucosa of subjects with chronic obstructive bronchitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;149(3 Pt 1):803–810. | ||
Vignola AM, Campbell AM, Chanez P, et al. HLA-DR and ICAM-1 expression on bronchial epithelial cells in asthma and chronic bronchitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993;148(3):689–694. | ||
Lopez-Campos JL, Calero C, Arellano-Orden E, et al. Increased levels of soluble ICAM-1 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and resistant smokers are related to active smoking. Biomark Med. 2012;6(6):805–811. | ||
Tsoutsou PG, Gourgoulianis KI, Petinaki E, et al. ICAM-1, ICAM-2 and ICAM-3 in the sera of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Inflammation. 2004;28(6):359–364. | ||
Yuan A, Yu CJ, Chen WJ, et al. Correlation of total VEGF mRNA and protein expression with histologic type, tumor angiogenesis, patient survival and timing of relapse in non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 2000;89(6):475–483. | ||
Papaioannou AI, Kostikas K, Kollia P, Gourgoulianis KI. Clinical implications for vascular endothelial growth factor in the lung: friend or foe? Respir Res. 2006;7(1):128. | ||
Grigoriu BD, Depontieu F, Scherpereel A, et al. Endocan expression and relationship with survival in human non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(15):4575–4582. | ||
Borczuk AC, Shah L, Pearson GD, et al. Molecular signatures in biopsy specimens of lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;170(2):167–174. | ||
Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, et al. The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;149(3 Pt 1):818–824. | ||
Atabai K, Matthay MA. The pulmonary physician in critical care. 5: acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: definitions and epidemiology. Thorax. 2002;57:452–458. | ||
Hasleton PS, Roberts TE. Adult respiratory distress syndrome-an update. Histopathology. 1999;34(4):285–294. | ||
Ware LB. Pathophysiology of acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;27(4):337–349. | ||
Maniatis NA, Orfanos SE. The endothelium in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2008;14(1):22–30. | ||
Albelda SM, Smith CW, Ward PA. Adhesion molecules and inflammatory injury. FASEB J. 1994;8(8):504–512. | ||
Thickett DR, Armstrong L, Christie SJ, Millar AB. Vascular endothelial growth factor may contribute to increased vascular permeability in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164(9):1601–1605. | ||
Rubin DB, Wiener-Kronish JP, Murray JF, et al. Elevated von Willebrand factor antigen is an early plasma predictor of acute lung injury in nonpulmonary sepsis syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1990;86(2):474–480. | ||
Moss M, Ackerson L, Gillespie MK, Moore FA, Moore EE, Parsons PE. Von Willebrand factor antigen levels are not predictive for the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;151(1):15–20. | ||
Sakamaki F, Ishizaka A, Handa M, et al. Soluble form of P-selectin in plasma is elevated in acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;151(6):1821–1826. | ||
Moss M, Gillespie MK, Ackerson L, Moore FA, Moore EE, Parsons PE. Endothelial cell activity varies in patients at risk for the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 1996;24(11):1782–1786. | ||
Lassalle P. Methods and kits for predicting the risk of respiratory failure, renal failure or thrombopenia in a septic patient by measuring endocan levels in blood. Lille, France; 2012. | ||
Calfee CS, Eisner MD, Ware LB, et al. Trauma-associated lung injury differs clinically and biologically from acute lung injury due to other clinical disorders. Crit Care Med. 2007;35(10):2243–2250. | ||
Mikkelsen ME, Shah CV, Scherpereel A, et al. Lower serum endocan levels are associated with the development of acute lung injury after major trauma. J Crit Care. 2012;27(5):522. | ||
De Freitas Caires N, Legendre B, Parmentier E, et al. Identification of a 14 kDa endocan fragment generated by cathepsin G, a novel circulating biomarker in patients with sepsis. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013;78–79:45–51. | ||
Tang L, Zhao Y, Wang D, et al. Endocan levels in peripheral blood predict outcomes of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:625180. | ||
Kása A, Csortos C, Verin AD. Cytoskeletal mechanisms regulating vascular endothelial barrier function in response to acute lung injury. Tissue Barriers. 2015;3(1–2):e974448. | ||
Morales-Ruiz M, Fulton D, Sowa G, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-stimulated actin reorganization and migration of endothelial cells is regulated via the serine/threonine kinase Akt. Circ Res. 2000;86(8):892–896. | ||
Kao SJ, Chuang CY, Tang CH, et al. Plasma endothelial cell-specific molecule-1 (ESM-1) in management of community-acquired pneumonia. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2014;52(3):445–451. | ||
Altintas N, Mutlu LC, Akkoyun DC, et al. Effect of CPAP on new endothelial dysfunction marker, endocan, in people with obstructive sleep apnea. Angiology. 2016;67(4):364–374. | ||
Güzel A, Duran L, Köksal N, et al. Evaluation of serum endothelial cell specific molecule-1 (endocan) levels as a biomarker in patients with pulmonary thromboembolism. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2014;25(3):272–276. | ||
Cheng D, Lee YC, Rogers JT, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor level correlates with transforming growth factor-β isoform levels in pleural effusions. Chest. 2000;118(6):1747–1753. | ||
Thickett DR, Armstrong L, Millar AB. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in inflammatory and malignant pleural effusions. Thorax. 1999;54(8):707–710. | ||
Papaioannou AI, Kostikas K, Tsopa P, et al. Residual pleural thickening is related to vascular endothelial growth factor levels in parapneumonic pleural effusions. Respiration. 2010;80(6):472–479. | ||
Maclay JD, McAllister DA, Mills NL, et al. Vascular dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180(6):513–520. | ||
Hashimoto M, Tanaka H, Shoshaku A. Quantitative analysis of bronchial wall vascularity in the medium and small airways of patients with asthma and COPD. Chest. 2005;127(3):965–972. | ||
Moro L, Pedone C, Scarlata S, Malafarina V, Fimognari F, Antonelli-Incalzi R. Endothelial dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Angiology. 2008;59(3):357–364. | ||
Perera WR, Hurst JR, Wilkinson TM, et al. Inflammatory changes, recovery and recurrence at COPD exacerbation. Eur Respir J. 2007;29(3):527–534. | ||
Pinto-Plata VM, Livnat G, Girish M, et al. Systemic cytokines, clinical and physiological changes in patients hospitalized for exacerbation of COPD. Chest. 2007;131(1):37–43. | ||
Koutsokera A, Kiropoulos TS, Nikoulis DJ, et al. Clinical, functional and biochemical changes during recovery from COPD exacerbations. Respir Med. 2009;103(6):919–926. | ||
Kumar SD, Emery MJ, Atkins ND, Danta I, Wanner A. Airway mucosal blood flow in bronchial asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;158(1):153–156. | ||
Li X, Wilson JW. Increased vascularity of the bronchial mucosa in mild asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;156(1):229–233. | ||
Green FHY, Butt JC, James AL, Carroll NG. Abnormalities of the bronchial arteries in asthma. Chest. 2006;130(4):1025–1033. | ||
Wanner A, Mendes ES. Airway endothelial dysfunction in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A challenge for future research. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;182(11):1344–1351. | ||
Pinto-Plata V, Casanova C, Müllerova H, et al. Inflammatory and repair serum biomarker pattern. Association to clinical outcomes in COPD. Respir Res. 2012;13(1):71. | ||
Tuder RM, Yoshida T, Arap W, Pasqualini R, Petrache I. State of the art. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of alveolar destruction in emphysema: an evolutionary perspective. Prac Am Thorac Soc. 2006;3(6):503–510. |
 © 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.