Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 11
Efficient intravesical therapy of bladder cancer with cationic doxorubicin nanoassemblies
Authors Jin X, Zhang P, Luo L, Cheng H, Li Y, Du T, Zou B, Gou M
Received 11 January 2016
Accepted for publication 26 May 2016
Published 8 September 2016 Volume 2016:11 Pages 4535—4544
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S103994
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Lei Yang
Xun Jin,1 Peilan Zhang,1 Li Luo,1 Hao Cheng,1 Yunzu Li,1 Ting Du,1 Bingwen Zou,2 Maling Gou1
1State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, and Collaborative Innovation Center for Biotherapy, Chengdu, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of Thoracic Oncology, Cancer Center, West China Hospital, West China Medical School, Sichuan University, Chengdu, People’s Republic of China
Abstract: Nanoparticles have promising applications in drug delivery for cancer therapy. Herein, we prepared cationic 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium propane/methoxypoly (ethyleneglycol) (DPP) nanoparticles to deliver doxorubicin (Dox) for intravesical therapy of bladder cancer. The DPP micelles have a mean dynamic diameter of 18.65 nm and a mean zeta potential of +19.6 mV. The DPP micelles could prolong the residence of Dox in the bladder, enhance the penetration of Dox into the bladder wall, and improve cellular uptake of Dox. The encapsulation by DPP micelles significantly improved the anticancer effect of Dox against orthotopic bladder cancer in vivo. This work described a Dox-loaded DPP nanoparticle with potential applications in intravesical therapy of bladder cancer.
Keywords: bladder cancer, drug delivery, nanoparticles, intravesical therapy
Introduction
Bladder cancer is one of the most common urogenital malignancies in male. In 2015, 74,000 new cases were diagnosed and 16,000 deaths occurred in the US.1 The main therapeutic methods for bladder cancer are surgery, intravesical therapy, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.2–4 Among bladder cancers, non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) accounts for ~70%, and can progress to muscle-invasive disease.5–7 For NMIBC, a transurethral resection (TUR) of bladder tumor is followed by immediate intravesical chemotherapy. Compared to TUR alone, intravesical treatment combined with TUR shows enhanced curative effects and a prolonged TIL.8 Intravesical chemotherapy following TUR has been promoted to inhibit residual microscopic tumor cells and to reduce reimplantation.9 However, despite much progress has been made, intravesical chemotherapy for bladder cancer still remains to be improved. One problem is that drugs given by intravesical therapy could not efficiently penetrate the bladder tissue.10 Thus, developing an efficient intravesical delivery strategy for bladder cancer therapy is a pressing need.11
Doxorubicin (Dox) is one of the most effective cytotoxic drugs used in cancer therapy.12 However, cumulative cardiotoxicity and nephrotoxicity limit its clinical applications.13 Compared to systemic application, drugs given by intravesical therapy mainly reach the inside of the bladder, with little-to-no effect on other organs, such as the heart, liver, spleen, lungs, kidneys, ureters, and urethra. Intravesical chemotherapy can maximize the exposure of tumor to therapeutic agents while limiting the systemic toxicity by drug due to the cavity structure of the bladder.14
In the past few years, nanoparticle delivery systems, such as 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium propane (DOTAP) and polyethylenimine, have been widely used for cancer therapy.15–17 Nanoparticles could enhance the efficiency of drug delivery while reducing side effects due to their distinctive properties such as more active cellular uptake and more targeted localization in tumor site.18 It has also been found that nanoparticles can sustain and prolong the drug residence in the bladder by facilitating the drug penetration into the bladder mucosa.19 In our study, the cationic DOTAP was used to modify the methoxypoly (ethyleneglycol) (MPEG-PLA) nanoparticles. The prepared DOTAP-MPEG-PLA (DPP) nanoparticles were characterized by size, zeta potential, morphology, and blood compatibility. The antitumor drug Dox was encapsulated into DPP micelles to form the Dox-loaded DPP (Dox/DPP) micelles formulation. The Dox/DPP micelles formulation was further characterized by size, zeta potential, morphology, and delivery efficiency. The anticancer effect of Dox/DPP micelles formulation against bladder cancer was evaluated in vitro and in vivo. Our data suggest that Dox/DPP micelles formulation has a potential application in bladder cancer therapy.
Materials and methods
Materials
MPEG-PLA (MPEG:PLA molar ratio =50:50, molecular weight =4,000 Da) was purchased from Jinan Daigang Bio-technology Co., Ltd. (Jinan, People’s Republic of China). DOTAP (chloride salt) was purchased from Avanti Polar Lipids (Alabaster, AL, USA). Dox hydrochloride was purchased from Melonepharma (Dalian, People’s Republic of China). Methanol and acetonitrile (high-performance liquid chromatography-grade) were purchased from Kermel (Tianjin, People’s Republic of China). All other chemicals were at least of analytical grade. Female C57 mice (6–8 weeks old) were purchased from Beijing HuaFukang Biological Technology Co. Ltd. (Beijing, People’s Republic of China). Mice were accustomed to the environment for at least 1 week before the experiments. All animal procedures were approved and controlled according to the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Treatment Committee of Sichuan University (approval protocol number: SYXK(CHUAN)2011-178).
Preparation of DPP micelles and Dox/DPP micelles
DPP micelles were prepared by a self-assembly method. Briefly, 98.5 mg of MPEG-PLA and 1.5 mg of DOTAP were co-dissolved in 2 mL of dichloromethane, followed by 1 hour of rotary evaporation with heat. Subsequently, 1 mL of distilled water was added followed by shaking gently in a water bath at 55°C. Finally, the prepared DPP micelles were stored at 4°C for future use. For the preparation of Dox-loaded nanoparticles, a pH-induced self-assembly method was used according to our previous report.20 Briefly, 0.1 mL of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; 10X, pH 7.4) was added into 0.1 mL of blank DPP solution (100 mg/mL). Then, 1 mg of Dox aqueous solution (1.25 mg/mL) was added into this solution under moderate stirring. After 20 minutes, the Dox/DPP micelles were obtained and stored at 4°C for future use.
Characterization of DPP micelles and Dox/DPP micelles
The size and zeta potential of DPP micelles and Dox/DPP micelles were determined at 25°C by Malvern Nano-ZS Instrument (Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK). All results were the mean of three test runs.
The morphology of DPP micelles and Dox/DPP micelles was characterized by transmission electron microscope (H-6009IV; Hitachi Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Before visualization, the nanoparticles were diluted with distilled water and placed on a copper grid covered with nitrocellulose. Samples were negatively stained with phosphotungstic acid and dried at room temperature.
High-performance liquid chromatograph (Shimadzu, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a reverse-phase C18 column (150×4.6 mm, pore size 5 μm; Scienhome, Tianjin, People’s Republic of China) was used to measure the concentration of Dox. Chromatographic separations were performed using a mobile phase consisting of methanol, acetonitrile, and water (60:25:15, v/v/v), at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. Detection was carried out at 260 nm with an ultraviolet detector. The volume of each auto-injected sample was 20 μL, and the column temperature was maintained at 25°C.
The drug loading (DL) and encapsulation efficiency (EE) of Dox in the DPP micelles were determined by centrifugation ultrafiltration as follows: 0.5 mL of Dox/DPP micelles solution was placed in a centrifuge tube (molecular weight cutoff =3 kDa; Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). The solution was then centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes to isolate the free Dox, and the concentration of free Dox was quantified by HPLC. Finally, the DL and EE of Dox/DPP micelles were calculated according to the following formulas:
|
|
|
|
In vitro drug release study
MB49 mouse urinary bladder carcinoma cell line was a generous gift from Dr Tomoko Hayashi (Moores Cancer Center, University of California, San Diego, CA, USA). The cell line was cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, penicillin (100 units/mL), and streptomycin (100 μg/mL), and maintained at 37°C in a humidified 5% CO2 incubator. In vitro drug release behaviors of Dox-loaded nanoparticles or free Dox were determined by dialysis. Briefly, 2 mL of Dox/DPP micelles solution and 2 mL of free Dox solution were placed in dialysis bags (molecular weight cutoff =3.5 kDa) separately. The dialysis bags were, respectively, incubated in 20 mL phosphate buffer of pH 7.4 and 20 mL phosphate buffer of pH 5.5 at 37°C with gentle shaking. At predetermined time points, the incubation mediums were replaced with fresh incubation mediums. The amount of released drug was quantified by HPLC.
Safety and delivery efficacy of DPP micelles
Hematoxylin-and-eosin staining
Six- to 8-week-old mice were anesthetized with chloral hydrate (5 mg/100 mL); the dosage used was 5 mL/kg per mouse. One hundred microliters of DPP solution (10 mg/mL) was intravesically administered into the bladder and kept anesthetized for 1 hour on day 0. The mice were sacrificed, and the bladder was harvested on day 2 for hematoxylin-and-eosin staining.
Erythrocytes aggregation in vitro
Fresh blood from Sprague Dawley rats was collected in heparinized tubes by drawing blood from rat tail. The blood was washed with normal saline (NS) until the supernatant was colorless. One hundred microliters of erythrocytes (4%) was treated with 100 μL of samples (NS, MPEG-PLA nanoparticles, or DPP micelles) in 24-well plates. After culturing for 2 hours at 37°C, images of erythrocytes were taken with an optical microscope.
Hemolytic test in vitro
The hemolytic test of DPP micelles was carried out in vitro. Briefly, 10 mg of MPEG-PLA or DPP micelles was diluted with 1 mL of NS, and 0.5 mL of this solution was added with 0.5 mL of rat erythrocyte suspension (4%) in NS at 37°C. NS and distilled water were employed as negative and positive control, respectively. Three hours later, the erythrocyte suspension was centrifuged (1,800 rpm, 3 minutes), and the color of supernatant was compared with negative control. Absolute achromatic supernatant solution implies that there is no hemolysis. In contrast, red supernatant solution indicates hemolysis.
Determination of the delivery efficiency
The delivery efficiency of DPP micelles was determined in vivo. Nine female C57 mice (8 weeks old) were used to evaluate the distribution of the cargo. Nine mice were randomly divided into three groups. Coumarin-6-loaded MPEG-PLA (PP-C) nanoparticles, coumarin-6-loaded DPP (DPP-C) nanoparticles (80 μL), or NS was intravesically administered into 8-week-old female C57 mice. At different time points (1, 4, and 6 hours) after administration, mice were killed by cervical vertebra dislocation, and their bladders were immediately harvested and imaged by Bio-Real in vivo imaging system (Bio-Real Quick View 3000; Geneway International, Salzburg, Austria) using a blue filter (excitation wavelength 460–490 nm, emission 470 nm).
Frozen section
Frozen section was used to determine the capacity of DPP micelles to enhance the permeability of instilled drugs. Coumarin-6 was encapsulated in DPP micelles as model drug. Six female C57 mice (8 weeks old) were divided into two groups, which were intravesically administered with 80 μL of PP-C or DPP-C nanoparticles. Two hours later, the mice were killed, and the bladders were harvested. The bladders were then washed with NS, followed by frozen sectioning.21 The fluorescence in the bladder section was examined using a Zeiss MocBio fluorescence microscope (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany).
Cellular uptake of fluorescent nanoparticles
MB49 bladder cancer cells were cultured on plates for 24 hours to achieve 60% confluence. Free coumarin-6, PP-C nanoparticles, or DPP-C nanoparticles (DL =0.5%) were added into the former plates. The concentration of coumarin-6 used was 10 ng/mL. After incubation of 2 hours, the cells were collected for measurement of coumarin-6-derived green fluorescent signal by flow cytometer.
MTT assay for anticancer efficacy of Dox/DPP
The anticancer efficacy of Dox/DPP micelles formulation against MB49 cells was determined with MTT assay. Dox or Dox-loaded cationic nanoparticle solutions used in the cytotoxicity assays were prepared in 0.01 M PBS. The concentrations of Dox and nanoparticles formulation were maintained in the same range throughout the cytotoxicity studies. 3,500 MB49 cells were seeded into the wells of 96-well plates. The cells were allowed to attach to the surface for 12 hours and then exposed to 100 μL of diluted formulations ranging from 0.03125 to 8 μg/mL. After 24 hours of incubation, 20 μL of MTT solution (5 mg/mL) was added into the wells. Three hours later, the produced formazan crystals were dissolved by adding 100 μL dimethyl sulfoxide. Optical densities were read at 570 nm using a microplate reader.
Anticancer effects of Dox/DPP micelles on subcutaneous tumor model
Subcutaneous tumor model was generated via subcutaneous injection of MB49 bladder cancer cells. Six- to 8-week-old female C57 mice were injected with 106 cells on day 0. When the tumor diameter was 5 mm, 20 μL solution of NS, free Dox, Dox-loaded MPEG-PLA (Dox/PP), and Dox/DPP (Dox 1 mg/mL) was intratumorally injected every 2 days. On day 23, six mice in each group were sacrificed, and tumors were harvested.
Anticancer effects of Dox/DPP micelles on orthotopic bladder cancer model
Orthotopic bladder tumors were generated via injection of MB49 cells between the bladder wall and mucous layer. Briefly, 6-week-old C57 female mice were anesthetized with chloral hydrate (0.25 mg/kg). The laparotomy was performed under aseptic condition. After exposure of the bladder, 20 μL cell suspension with 4×105 cells was injected into the space between the bladder wall and mucous membrane. The tumor-bearing mice were then randomly divided into four groups. They were intravesically administered with 100 μL solution of NS, free Dox, Dox/PP nanoparticles, or Dox/DPP micelles (Dox 1 mg/mL) into the bladder, respectively, and kept anesthetized for 1 hour on day 0. At day 3, six mice in each group were sacrificed, and their bladders were harvested for the further evaluation.
Statistical analysis
All experiments were performed at least three times. Results are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean and were analyzed by a two-tailed Student’s t-test. P-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant. The analysis was conducted using GraphPad software (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA).
Results
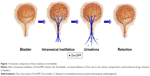
Dox is a potential anticancer drug; however, cumulative cardiotoxicity and nephrotoxicity limit its clinical applications. Intravesical therapy is one of the main treatments for bladder cancer which delivers drugs into the bladder via a catheter with minimal systemic effects.17 In an attempt to extend the retention time of drug in the bladder, we designed the cationic DPP micelles to encapsulate anticancer drug Dox to treat bladder cancer. The scheme is presented in Figure 1. Free Dox could not remain in the bladder to establish the effective drug concentration, while the Dox/DPP micelles could adhere to the bladder wall to prolong the drug retention because of the positive surface charge of nanoparticles. In this work, we developed the DPP drug delivery system which could effectively deliver Dox for intravesical treatment of bladder cancer.
Preparation and characterization of DPP micelles
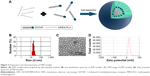
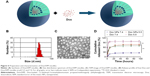
To prepare the DPP nanoparticles, a self-assembly method was used as shown in Figure 2A. MPEG-PLA diblock copolymer has an amphiphilic structure with a hydrophilic MPEG segment and a hydrophobic PLA segment. Also, DOTAP is amphiphilic with a hydrophilic cationic head and a hydrophobic carbochain. Thus, self-assembly of MPEG-PLA and DOTAP in water allowed formation of the core–shell-structured nanoparticles. The physicochemical properties of the DPP micelles were characterized in detail. According to dynamic light-scattering results, the DPP micelles were uniform in size with a mean particle size of 18.65 nm and a polydispersity index of 0.297 (Figure 2B). The transmission electron micrographs of DPP micelles are shown in Figure 2C, which demonstrated that DPP micelles had a spherical morphology. The mean zeta potential was 19.6 mV (Figure 2D).
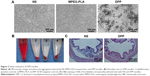
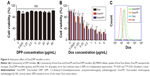
To further characterize the DPP micelles, we conducted the erythrocyte aggregation and hemolysis analysis to investigate the blood compatibility of MPEG-PLA and DPP micelles. As shown in Figure 3A, MPEG-PLA nanoparticles did not induce obvious erythrocyte aggregation, but DPP micelles could cause appreciable erythrocyte aggregation, indicating that cationic DPP micelles were limited in intravenous administration. Our data also showed that both MPEG-PLA and DPP micelles did not induce hemolysis (Figure 3B). In addition, the bladder did not show any symptom of edema or inflammatory reaction after treating with DPP micelles (Figure 3C). Thus, these results demonstrated a good biocompatibility of DPP micelles in the bladder.
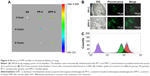
Then, the capability of DPP micelles to deliver drugs to the bladder was evaluated in vivo. Coumarin-6 was used as a fluorescent model drug to be encapsulated in MPEG-PLA or DPP micelles as described previously. As shown in Figure 4A, PP-C nanoparticles could not remain in the bladder for a long time (6 hours); in contrast, DPP-C nanoparticles exhibited intense fluorescent signal over 6 hours, suggesting that DPP nanoparticles were able to prolong the residence of delivered drug in the bladder. This may be attributed to the ability of cationic nanoparticles to improve the drug retention in the bladder. In line with this finding, the frozen sections of the bladders administered with DPP-C showed stronger fluorescent signal than that of PP-C. In addition, compared to MPEG-PLA nanoparticles, DPP micelles efficiently enhanced the drug permeability into the bladder (Figure 4B) due to the positive charge that is capable of enhancing the cellular uptake and tissue absorption of nanoparticles.22 Furthermore, we compared the tumor cellular uptake of DPP-C micelles with that of free coumarin-6 or PP-C nanoparticles in vitro. As show in Figure 4C, MB49 bladder cancer cells preferred to uptake DPP-C rather than PP-C or free coumarin-6, implicating that the cationic surface improved the cellular uptake of nanoparticles. Thus, we conclude that the DPP nanoparticle is a potential delivery system for intravesical drug delivery.
Preparation and characterization of Dox/DPP micelles formulation
Because DPP nanoparticle has been demonstrated to be a promising carrier for intravesical drug delivery, and Dox is a clinical drug for the treatment of bladder cancer, we made further efforts to develop Dox/DPP micelles for the treatment of bladder cancer. Dox was loaded into the blank DPP micelles by a pH-induced self-assembly method. To our knowledge, the solubility of Dox in distilled water is high, while Dox cannot be well dissolved in PBS. Therefore, when Dox aqueous solution was dropped into DPP micelles in PBS (pH 7.4) under stirring, the Dox became hydrophobic and self-assembled into the hydrophobic cores of DPP micelles (Figure 5A). We found that Dox could be encapsulated into DPP micelles efficiently with a drug encapsulation efficiency of ~89.75% and a drug loading of ~8.47%. This method of preparing Dox/DPP micelles was simple and easy to scale up, implying its advantage in practical application.
We characterized physicochemical properties of Dox/DPP micelles. According to dynamic light-scattering results, the Dox/DPP micelles were monodispersed with a mean particle size of 18.71 nm (Figure 5B), suggesting no obvious changes in size and morphology caused by Dox loading. The transmission electron micrographs of Dox/DPP micelles are shown in Figure 5C. Additionally, we investigated the release profile of Dox from Dox/DPP micelles in vitro by dialysis. As shown in Figure 5D, the nanoparticles obviously slowed down the release of Dox. Similar to Tomar et al’s report,23 the mechanism of Dox release from the DPP micelles can be divided into two phases: a burst-release phase and a controlled-release phase. The burst release corresponded to the Dox adsorbed or attached by weak bonding onto the surface of the nanoparticles, while the controlled release was due to the entrapment of nanoparticles. Meanwhile, we found that Dox was released faster in a condition of pH 5.5 than pH 7.4 (Figure 5D). The protonation of the amino group of Dox at lower pH might account for the pH-dependent releasing behavior.24 Therefore, it was anticipated that Dox could achieve slow release in plasma under normal physiological condition (pH 7.4) but quick release at the slightly acidic tumor site (pH 5.5).
Anticancer effect of Dox/DPP micelles
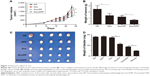
To study the cytotoxicity of Dox/DPP micelles in bladder cancer cells, we first examined whether drugs can be delivered into living cells by DPP micelles using flow cytometry. Next, we investigated the cytotoxicity of Dox/DPP micelles in MB49 bladder cancer cells. As expected, blank DPP micelles had no obvious cytotoxicity against MB49 cells even at relatively high concentrations (Figure 6A), whereas Dox/DPP micelles markedly inhibited cell viability (Figure 6B) with a relative low IC50 value of 0.281 μg/mL, compared with free Dox (IC50 0.815 μg/mL) or Dox/PP nanoparticles (IC50 0.638 μg/mL) result from the enhanced drug uptake (Figure 6C). Next, we used mouse subcutaneous tumor model to evaluate the anticancer effect of Dox/DPP micelles in vivo. As shown in Figure 7A and B, compared with Dox administration alone, treatment of Dox/DPP micelles inhibited bladder tumor growth as evidenced by reduced tumor volume and decreased tumor weight.
To corroborate the anticancer effect of Dox/DPP micelles in vivo, we established the orthotopic bladder cancer model by injecting MB49 bladder cancer cells and administered Dox/DPP micelles intravesically. Our results indicated that blank DPP micelles and free Dox showed no apparent influence on the bladder tumor growth; this may be indicating that free Dox is unable to permeate into the bladder mucosa to kill the tumor cells. In contrast, Dox loaded on DPP micelles showed significant inhibition of tumor size and repression of tumor weight (Figure 7C and D). Taken together, our results suggested that DPP micelles can effectively deliver Dox into the bladder for the treatment of bladder cancer.
Discussion
In this work, we prepared the cationic DPP nanoparticles to encapsulate the antitumor drug Dox to form the Dox/DPP nanoassemblies formulation. This study suggested that Dox may have potential applications in bladder cancer therapy and the Dox/DPP formulation may represent a candidate for intravesical therapy of bladder cancer.
Cationic nanoparticles has called much attention for their wide application as delivery system.25,26 For example, Wang et al tried to co-deliver paclitaxel and an interleukin-12-encoded plasmid by cationic core–shell nanoparticles to suppress the cancer growth;27 Liu et al used an amphiphilic peptide to prepare cationic nanoparticles that acted as an efficient antimicrobial agent.28 Despite extensive applications as delivery system, the development of cationic nanoparticles is still challenged by the fast elimination by reticuloendothelial system. Intravesical administration of cationic nanoparticles has shows significant potency in NMIBC treatment, since the topical administration minimizes the risk of erythrocytes aggregation and protects the cationic nanoparticles from being cleared away by the reticuloendothelial system. Hence, we developed the cationic DPP micelles for intravesical delivery of Dox to treat bladder cancer. The hybrid nanoparticles had a size of 20 nm and a surface charge of 20 mV. These physical characters were preferred by cells or tissues compared to large neural or negative nanoparticles, resulting in an enhanced cellular uptake of nanoparticles. Moreover, our results indicated that the cationic nanoparticles could help improve the retention and penetration of drugs. Thus, the cationic DDP nanoparticles could serve as an efficient delivery system for intravesical drug delivery.
Apart from the advantage of efficient delivery, it has been demonstrated that cationic DPP micelles are safe for intravesical administration. The DDP nanoparticles comprise biocompatible materials namely MPEG-PLA and DOTAP, both of which were approved by the US Food and Drug Administration as therapeutic agents. In addition, the results of both hemolysis analysis and hematoxylin-and-eosin staining indicated their safety, since the DPP micelles did not cause hemolysis, inflammation, edema, or other adverse reaction.
In the present study, DPP micelles were employed for intravesical delivery of Dox, which is a highly potent antitumor drug approved for clinical use against bladder cancer. However, the long-term clinical use of Dox is compromised by its severe toxicity, the most serious being irreversible cardiomyopathy and subsequent congestive heart failure.29 Fortunately, the strategies involving nanoparticles and topical administration could play a positive role in limiting the cardiac toxicity of Dox. By topical administration of Dox/DPP micelles to the bladder, the Dox level was increased in the bladder, and meanwhile, the cardiotoxicity of Dox was shunned (data not shown). Moreover, the drug release profile showed that Dox/DPP micelles were capable of sustaining the drug concentration in the tumor site, while the free Dox exhibited a robust release. Additionally, our in vivo results showed that Dox/DPP micelles could suppress the growth of bladder cancer. Our results were also supported by Bilensoy et al’s research, in which the cationic nanoparticles delivered mitomycin C to bladder tumor site and improved the therapeutic effect of mitomycin C in the bladder.30 Therefore, the Dox/DPP micelles formulation shows a promising application in intravesical treatment of bladder cancer.
Conclusion
We prepared cationic DPP nanoparticles for intravesical drug delivery. These nanoparticles can improve the retention, penetration, and intracellular uptake of cargos. Then encapsulation of Dox in DPP micelles significantly enhanced its anticancer effect against bladder cancer in vitro and in vivo. The DPP micelle-encapsulated Dox might have potential applications in intravesical therapy of bladder cancer.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (81572990, 81422025, 81301907), the Foundation for Distinguished Young Scientists of Sichuan Province (2016JQ0020), and the Outstanding Young Scholars Research Fund of Sichuan University (2014SCU04A12). The authors would like to express their great thanks to Zhouli Cheng, Yuping Yang, Yujiao Wu, Tianyi Kang, and Ke Men. The authors thank Dr Tomoko Hayashi (Cancer Center, University of California, San Diego, CA, USA) for providing MB49 cells.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(1):5–29. | ||
van Kessel KE, Zuiverloon TC, Alberts AR, Boormans JL, Zwarthoff EC. Targeted therapies in bladder cancer: an overview of in vivo research. Nat Rev Urol. 2015;12(12):681–694. | ||
Thariat J, Aluwini S, Pan Q, et al. Image-guided radiation therapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 2012;9(1):23–29. | ||
Oosterlinck W. Chemotherapy: electromotive mitomycin in superficial bladder cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;8(11):633–634. | ||
Babjuk M, Burger M, Zigeuner R, et al. EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2013. Eur Urol. 2013;64(4):639–653. | ||
Anastasiadis A, de Reijke TM. Best practice in the treatment of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer. Ther Adv Urol. 2012;4(1):13–32. | ||
Knowles MA, Hurst CD. Molecular biology of bladder cancer: new insights into pathogenesis and clinical diversity. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15(1):25–41. | ||
Sanchez A, Wszolek MF. Bladder cancer: quality of life in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 2015;12(4):186–188. | ||
Sexton WJ, Wiegand LR, Correa JJ, Politis C, Dickinson SI, Kang LC. Bladder cancer: a review of non-muscle invasive disease. Cancer Control. 2010;17(4):256–268. | ||
Shen Z, Shen T, Wientjes MG, O’Donnell MA, Au JL. Intravesical treatments of bladder cancer: review. Pharm Res. 2008;25(7):1500–1510. | ||
Soloway MS. Bladder cancer: lack of progress in bladder cancer–what are the obstacles? Nat Rev Urol. 2013;10(1):5–6. | ||
Rocha VC, Franca LS, de Araujo CF, et al. Protective effects of mito-TEMPO against doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016;77(3):659–662. | ||
Hershman DL, McBride RB, Eisenberger A, Tsai WY, Grann VR, Jacobson JS. Doxorubicin, cardiac risk factors, and cardiac toxicity in elderly patients with diffuse B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(19):3159–3165. | ||
Hadaschik BA, ter Borg MG, Jackson J, et al. Paclitaxel and cisplatin as intravesical agents against non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2008;101(11):1347–1355. | ||
Gou M, Men K, Zhang J, et al. Efficient inhibition of C-26 colon carcinoma by VSVMP gene delivered by biodegradable cationic nanogel derived from polyethyleneimine. ACS Nano. 2010;4(10):5573–5584. | ||
Duan X, Wang P, Men K, et al. Treating colon cancer with a suicide gene delivered by self-assembled cationic MPEG-PCL micelles. Nanoscale. 2012;4(7):2400–2407. | ||
Men K, Liu W, Li L, et al. Delivering instilled hydrophobic drug to the bladder by a cationic nanoparticle and thermo-sensitive hydrogel composite system. Nanoscale. 2012;4(20):6425–6433. | ||
Davis ME, Chen ZG, Shin DM. Nanoparticle therapeutics: an emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7(9):771–782. | ||
Kerec M, Bogataj M, Veranic P, Mrhar A. Permeability of pig urinary bladder wall: the effect of chitosan and the role of calcium. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2005;25(1):113–121. | ||
Gou M, Shi H, Guo G, et al. Improving anticancer activity and reducing systemic toxicity of doxorubicin by self-assembled polymeric micelles. Nanotechnology. 2011;22(9):095102. | ||
Wert KJ, Mahajan VB, Zhang L, et al. Neuroretinal hypoxic signaling in a new preclinical murine model for proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Signal transduction and targeted therapy. 2016;1. | ||
Kim B, Han G, Toley BJ, Kim CK, Rotello VM, Forbes NS. Tuning payload delivery in tumour cylindroids using gold nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol. 2010;5(6):465–472. | ||
Tomar L, Tyagi C, Kumar M, et al. In vivo evaluation of a conjugated poly(lactide-ethylene glycol) nanoparticle depot formulation for prolonged insulin delivery in the diabetic rabbit model. Int J Nanomed. 2013;8:505–520. | ||
Shuai X, Ai H, Nasongkla N, Kim S, Gao J. Micellar carriers based on block copolymers of poly(epsilon-caprolactone) and poly(ethylene glycol) for doxorubicin delivery. J Control Release. 2004;98(3):415–426. | ||
Kojima C, Hirano Y, Yuba E, Harada A, Kono K. Preparation and characterization of complexes of liposomes with gold nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2008;66(2):246–252. | ||
Panda JJ, Varshney A, Chauhan VS. Self-assembled nanoparticles based on modified cationic dipeptides and DNA: novel systems for gene delivery. J Nanobiotechnol. 2013;11:18. | ||
Wang Y, Gao S, Ye WH, Yoon HS, Yang YY. Co-delivery of drugs and DNA from cationic core-shell nanoparticles self-assembled from a biodegradable copolymer. Nat Mater. 2006;5(10):791–796. | ||
Liu L, Xu K, Wang H, et al. Self-assembled cationic peptide nanoparticles as an efficient antimicrobial agent. Nat Nanotechnol. 2009;4(7):457–463. | ||
Park J, Fong PM, Lu J, et al. PEGylated PLGA nanoparticles for the improved delivery of doxorubicin. Nanomedicine. 2009;5(4):410–418. | ||
Bilensoy E, Sarisozen C, Esendagli G, et al. Intravesical cationic nanoparticles of chitosan and polycaprolactone for the delivery of Mitomycin C to bladder tumors. Int J Pharm. 2009;371(1–2):170–176. |
 © 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.