Back to Journals » Infection and Drug Resistance » Volume 11
Efficacy of antifungal drugs in the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis: a Bayesian network meta-analysis
Authors Qin F, Wang Q, Zhang C, Fang C, Zhang L, Chen H, Zhang M, Cheng F
Received 28 May 2018
Accepted for publication 23 August 2018
Published 17 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1893—1901
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S175588
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Joachim Wink
Fen Qin,1,* Quan Wang,2,* Chunlian Zhang,1 Caiyun Fang,1 Liping Zhang,1 Hailin Chen,1 Mi Zhang,3 Fei Cheng3
1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, Hubei, China; 2Department of Stomatology, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, Hubei, China; 3Department of Cardiology, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, Hubei, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Purpose: Antifungal drugs are used frequently in the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC), but have shown controversial results. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of different antifungal drugs in the treatment of VVC and to provide an evidence-based reference for clinical use.
Methods: The published studies on the effectiveness of antifungal drugs in the treatment of VVC (up to April 2018) were retrieved from PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov. We sifted through the literature according to Patients, Interventions, Comparisons and Outcomes principle, extracted data on the basic characteristics of the study, and evaluated the quality of included studies. We used R software for statistical analysis.
Results: In total, 41 randomized controlled trials were included in this meta-analysis. The relative risk of VVC associated with ten drugs, including placebo, fluconazole, clotrimazole, miconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole, econazole, butoconazole, terbinafine, and terconazole, was analyzed. The following drugs appeared to show more efficacy than placebo in the treated patients: fluconazole (OR =6.45, 95% CrI 4.42–9.41), clotrimazole (OR =2.99, 95% CrI 1.61–5.55), miconazole (OR =5.96, 95% CrI 3.17–11.2), itraconazole (OR =2.29, 95% CrI 1.21–4.33), ketoconazole (OR =2.40, 95% CrI 1.55–3.71), butoconazole (OR =1.18, 95% CrI 1.06–1.31), and terconazole (OR =5.60, 95% CrI 2.78–11.3). The value of surface under the cumulative ranking curve of each drug was as follows: placebo (0.5%), fluconazole (91.5%), clotrimazole (61.8%), miconazole (33.8%), itraconazole (50.5%), ketoconazole (42.8%), econazole (46.8%), butoconazole (82.2%), terbinafine (20.9%), and terconazole (65.0%).
Conclusion: Antifungal drugs are effective in the treatment of VVC. Fluconazole appeared to be the best drug for the treatment of VVC according to our analysis.
Keywords: vulvovaginal candidiasis, antifungal drugs, randomized controlled trials, network meta-analysis
Introduction
Vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) is an infectious disease affecting the female genital tract and is caused by Candida spp. Of all the VCC cases, 80%–90% are caused by Candida albicans, and a minority are caused by Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis.1 As one of the most common infectious diseases of the female genital tract, VVC is found worldwide affecting the health of women at all levels of the society.2 With the widespread use of corticosteroids, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and immunosuppressants, as well as the emergence of AIDS, VVC is more commonly encountered in clinical practice,3,4 and the treatment of VVC has become a hot issue.
Antifungal drugs exert their effect by changing the permeability of fungal cell membrane. At present, two groups of antifungal drugs are mainly used to treat VVC: polyene antifungal drugs and pyrrole ring antifungal drugs. The former group is represented by amphotericin B. Amphotericin B has a strong antifungal activity and a wide antibacterial spectrum, but it is quite toxic. The latter group includes azoles, such as ketoconazole, fluconazole, and itraconazole. These are also most widely used and have a wide antibacterial spectrum.5,6
To evaluate the clinical efficacy of different antifungal drugs in the treatment of VVC and to provide an evidence-based reference for clinical use, we conducted a network meta-analysis based on randomized controlled trials on the efficacy of antifungal drugs in the treatment of VVC.
Methods
Search strategy
The published studies on the effectiveness of antifungal drugs in the treatment of oral candidiasis (up to April 2018) were retrieved from PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov, with keywords including “Vulvovaginal Candidiases” [MeSH] OR “Vulvovaginal Candidiasis” [MeSH] OR “Vulvovaginal Moniliases” [MeSH] OR “Vulvovaginal Moniliasis” [MeSH] OR “Vaginal Yeast Infections” [MeSH] OR “Genital Vulvovaginal Candidiasis” [MeSH] OR “Genital Vulvovaginal Candidiases” [MeSH] OR “Genital Candidiases” [MeSH] OR “Genital Candidiasis” [MeSH] OR “Monilial Vaginitides” [MeSH] OR “Monilial Vaginitis” [MeSH] AND “Antifungal Agents” [MeSH] OR “Itraconazole” [MeSH] OR “Miconazole” [MeSH] OR “Clotrimazole” [MeSH] OR “Fluconazole” [MeSH] OR “Ketoconazole” [MeSH] OR “Econazole” [MeSH] OR “Butoconazole” [MeSH] OR “Terbinafine” [MeSH] OR “Terconazole” [MeSH] AND “Randomized Controlled Trials” [MeSH] OR “RCT” [MeSH].
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
We included randomized controlled trials written in English, regardless of whether or not specific random allocation methods and blind data hiding scheme are mentioned and the timing of publication. Study subjects were females with typical clinical symptoms and signs of VVC confirmed by mycological examination.
We imported the literature retrieved from the database into EndNote and eliminated duplicates. We screened the titles and abstracts according to the Patients, Interventions, Comparisons and Outcomes principle, and then read the full text of the eligible articles. The data were extracted and evaluated by two reviewers. Any differences in opinion were discussed and resolved by the reviewers. The following data were extracted: first author of the study, publication time, sample size, age, and intervention measures. Quality evaluation was performed using Cochrane risk-of-bias assessment tool.
Statistical analysis
We conducted a network meta-analysis (Bayesian approach) which included both direct and indirect evidence in the network. Direct comparison was performed using Stata14.0 software for statistical analysis. The risk of vulvovaginal candidiasis in each group was compared using the OR. Before the combined data were analyzed by meta-analysis, the heterogeneity of each group was tested. If there was no heterogeneity (P≥0.05 or I2≤50%), the combined statistics were calculated by fixed-effect model analysis. If there was significant heterogeneity among the groups (P<0.05 or I2>50%), the source of heterogeneity was analyzed, and a subgroup analysis of the factors leading to heterogeneity was carried out. Indirect comparison was made using R software to draw a mesh diagram. Drugs were ranked based on the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) values. A drug was considered more preferable than another if it had a larger SUCRA value.
Results
Literature search results
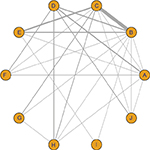
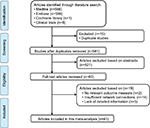
A total of 566 studies from Medline, 596 studies from Embase, one study from Cochrane Library, and eight studies from ClinicalTrials.gov were selected. After removing duplicates, 581 studies remained. After reviewing their titles and abstracts, 521 citations were excluded. The remaining 60 citations were assessed in more detail for eligibility by reading the full text. Among them, two were excluded due to lack of relevant outcome measure, 14 were excluded due to insufficient network connections, and three were excluded due to lack of detailed information. Finally, 41 studies were used for the final data synthesis.5,7–46 The flowchart of literature search is presented in Figure 1. The risk of bias of the 41 studies included in this meta-analysis is summarized in Figure 2. The characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 1. The pattern of evidence within the network is displayed in Figure 3.
  | Figure 1 Flow diagram of the study selection process. |
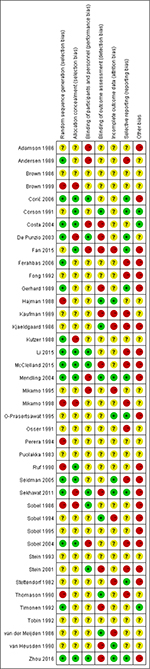  | Figure 2 Risk of bias of the included randomized controlled trials (review authors’ judgments about each risk-of-bias item for each included study). Note: +, low risk; −, high risk; ?, unclear risk. |
  | Table 1 Characteristics of the included studies |
Results of pairwise meta-analysis
Table 2 displays the results produced by pairwise meta-analysis. The following drugs appeared to show more efficacy than placebo in the treated patients: fluconazole (OR =6.45, 95% CrI 4.42–9.41), clotrimazole (OR =2.99, 95% CrI 1.61–5.55), miconazole (OR =5.96, 95% CrI 3.17–11.2), itraconazole (OR =2.29, 95% CrI 1.21–4.33), ketoconazole (OR =2.40, 95% CrI 1.55–3.71), butoconazole (OR =1.18, 95% CrI 1.06–1.31), and terconazole (OR =5.60, 95% CrI 2.78–11.3). Moreover, there was no significant heterogeneity among the studies for the above results (P-heterogeneity >0.05 and I2<50%).
  | Table 2 Summary ORs of antifungal drugs and heterogeneity of each direct comparison |
Network meta-analysis
Table 3 displays the results produced by network meta-analysis. The following nine drugs appeared to show more efficacy than placebo in the treated patients: fluconazole (OR =26.0, 95% CrI 14.0–50.0), clotrimazole (OR =17.0, 95% CrI 8.70–34.0), miconazole (OR =12.0, 95% CrI 6.30–22.0), itraconazole (OR =14.0, 95% CrI 6.40–32.0), ketoconazole (OR =13.0, 95% CrI 6.10–27.0), econazole (OR =14.0, 95% CrI 5.10–38.0), butoconazole (OR =25.0, 95% CrI 12.0–56.0), terbinafine (OR =5.20, 95% CrI 1.70–35.0), and terconazole (OR =18.0, 95% CrI 7.80–43.0).
  | Table 3 Network meta-analysis comparisons |
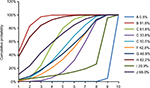
The corresponding SUCRA values of the drugs were as follows: placebo (0.5%), fluconazole (91.5%), clotrimazole (61.8%), miconazole (33.8%), itraconazole (50.5%), ketoconazole (42.8%), econazole (46.8%), butoconazole (82.2%), terbinafine (20.9%), and terconazole (65.0%) (Figure 4). Incorporating adjuvants particularly fluconazole appeared to be the best strategy for the treatment of oral candidiasis.
Publication bias
The results of the comparison-adjusted funnel plots did not reveal any evidence of apparent asymmetry (Figure 5). No significant publication bias was observed.
Discussion
VVC has a high incidence and recurrence rate, but its pathogenesis is not yet clear.47 At present, it is believed that the pathogenesis and recurrence of VVC are related to many factors, such as the increasing resistance of Candida, the local immune response of host against Candida, and the change of virulence factor of Candida.48,49 Available data show that 75% of women have VVC at least once in their lifetime, and 50% of women with VVC have recurrent infections, with the highest incidence found among women of reproductive age.50 VVC is the most common cause of vaginal infections, second only to bacterial vaginitis. Candida has a high rate of intravaginal colonization; it can be isolated from the vagina of about 20% of healthy asymptomatic women and 30% of pregnant women.51
Candida, as a part of normal flora, can be found on the surface of the skin, digestive tract, and genitourinary tract; however, the mechanism of colonization and pathogenicity of Candida are unclear. The pathogens of VVC include C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis, Candida krusei, and C. glabrata.52 C. albicans is the main pathogen of VVC, and accounts for 73.8%–95.0% of all Candida spp. isolated from the vagina. The most common non-albicans species is C. glabrata, which accounts for 10%–20% of all VVC pathogens.53 VVC causes increased leucorrhea, vulva itching, burning pain, urinal pain, and intercourse pain, and seriously affects the physical and mental health of the majority of women. Therefore, there is an urgent need for most suitable drugs for the treatment of VVC.
At present, pyrrole ring drugs are mainly used to treat VVC in clinical practice. Pyrrole ring drugs such as imidazoles and triazoles are related to the inhibition of ergosterol synthesis in fungi and thus destroy the integrity of fungal cell membrane and achieve the antifungal effect.54 The most common drugs represented by imidazoles are clotrimazole, ketoconazole, and miconazole. Triazoles are represented by fluconazole and itraconazole. Triazole antifungal drugs have a high bioavailability and strong antifungal effect, and the associated liver toxicity is relatively small.55
This network meta-analysis attempted to analyze the effectiveness of different antifungal drugs in the treatment of VVC and to provide an evidence-based reference for clinical use. Our analysis suggested that antifungal drugs are effective in the treatment of VVC, and fluconazole appeared to be best drug for the treatment of VVC. The American and European guidelines for the treatment of VVC, based on a large number of evidence-based clinical practice, recommended the use of fluconazole (150 mg) for the treatment of moderate-to-severe VVC, which is consistent with our results.
Fluconazole is a triazole antifungal drug that can inhibit or kill fungi by competitively inhibiting the synthesis of ergosterol. It has shown a significant effect in the treatment of deep fungal infections, especially those caused by C. albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans.56 Since it was launched in 1988, fluconazole has been widely used in clinical practice because of its excellent pharmacokinetic properties, such as broad antifungal spectrum, low hepatotoxicity, good oral absorption, high bioavailability, and wide tissue distribution.57 Designated by the WHO as the first choice for the treatment of systemic fungal infections, fluconazole is effective for various human and animal fungal infections, such as Candida infection (including systemic candidiasis in normal or immune-impaired people and animals), new cryptococcus infection (including intracranial infection), Malassezia, Microsporum, and Trichophyton infections, psoriasis, dermatitis, and rougherosporum (including intracranial infection). The antibacterial activity of fluconazole in vitro was found to be significantly lower than that of ketoconazole, but the antifungal activity of this drug was significantly higher than ketoconazole in vitro.57
This meta-analysis also has some limitations. The results of statistical heterogeneity analysis of the antifungal drugs are limited in randomized controlled trials. In addition, the limited evidence of a dose-dependent association between antifungal drugs and VVC treatment provides limited confidence in the study findings. Second, there is no record for a standardized treatment of VVC, which leads to difference in results between the trials; therefore, these results should be carefully interpreted with caution. Third, the study durations were short in these randomized controlled trials and patients included in these trials might be different from patients in the real life. Fourth, these findings may not be generalizable to a specific group of patients because randomized controlled trials tended to exclude participants. Fifth, most of the including studies have not enough detail in their reports, such as the absence of a random allocation method, the implementation of the allocation concealment, or the implementation of the blind law, which leads to existence of varying degrees of bias and risk.
Our findings underscore the notion that antifungal drugs are effective in the treatment of VVC, and fluconazole appeared to be the best drug for the treatment of VC according to our analysis. However, due to the low quality of the included studies, this conclusion needs to be further confirmed by high-quality research with a large sample.
Author contributions
Fei Cheng was responsible for the concept and design of the review, the acquisition of data, the analysis and interpretation of data, and for the preparation of the manuscript. Fen Qin was responsible for the acquisition of data and for the preparation of the manuscript. Quan Wang was responsible for the analysis and interpretation of data and for the preparation of the manuscript. Chunlian Zhang and Caiyun Fang was responsible for the acquisition of data. Liping Zhang and Hailin Chen was responsible for the analysis and interpretation of data and for the preparation of the manuscript. Mi Zhang was responsible for the preparation of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript. All authors contributed to data analysis, drafting and revising the article, gave final approval of the version to be published, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Martin Lopez JE. Candidiasis (vulvovaginal). BMJ Clin Evid. 2015;16. | ||
Nwadioha SI, Nwokedi EO, Egesie J, Enejuo H. Vaginal candidiasis and its risk factors among women attending a Nigerian teaching hospital. Niger Postgrad Med J. 2013;20(1):20–23. | ||
Rathod SD, Buffler PA. Highly-cited estimates of the cumulative incidence and recurrence of vulvovaginal candidiasis are inadequately documented. BMC Womens Health. 2014;14(1):1472–6874. | ||
Gonçalves B, Ferreira C, Alves CT, Henriques M, Azeredo J, Silva S. Vulvovaginal candidiasis: Epidemiology, microbiology and risk factors. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2016;42(6):905–927. | ||
Mikamo H, Kawazoe K, Sato Y, Hayasaki Y, Tamaya T. Comparative study on the effectiveness of antifungal agents in different regimens against vaginal candidiasis. Chemotherapy. 1998;44(5):364–368. | ||
Dovnik A, Golle A, Novak D, Arko D, Takač I. Treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis: a review of the literature. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2015;24(1):5–7. | ||
A comparison of single-dose oral fluconazole with 3-day intravaginal clotrimazole in the treatment of vaginal candidiasis. Report of an international multicentre trial. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1989;96(2):226–232. | ||
Corić M, Barisić D, Lovrić H. Fluconazole versus 3-day clotrimazole in the treatment of sporadic and recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2006;95(2):171–172. | ||
Costa M, Passos XS, Miranda AT, de Araújo RS, Paula CR, Silva MR. Correlation of in vitro itraconazole and fluconazole susceptibility with clinical outcome for patients with vulvovaginal candidiasis. Mycopathologia. 2004;157(1):43–47. | ||
de Punzio C, Garutti P, Mollica G, Nappi C, Piccoli R, Genazzani AR. Fluconazole 150 mg single dose versus itraconazole 200 mg per day for 3 days in the treatment of acute vaginal candidiasis: a double-blind randomized study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2003;106(2):193–197. | ||
Fan S, Liu X, Liang Y. Miconazole nitrate vaginal suppository 1,200 mg versus oral fluconazole 150 mg in treating severe vulvovaginal candidiasis. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2015;80(2):113–118. | ||
Ferahbas A, Koc AN, Uksal U, Aygen E, Mistik S, Yildiz S. Terbinafine versus itraconazole and fluconazole in the treatment of Vulvovaginal candidiasis. Am J Ther. 2006;13(4):332–336. | ||
Li T, Zhu Y, Fan S, Liu X, Xu H, Liang Y. A randomized clinical trial of the efficacy and safety of terconazole vaginal suppository versus oral fluconazole for treating severe vulvovaginal candidiasis. Med Mycol. 2015;53(5):455–461. | ||
Mcclelland RS, Balkus JE, Lee J, et al. Randomized trial of periodic presumptive treatment with high-dose intravaginal metronidazole and miconazole to prevent vaginal infections in HIV-negative women. J Infect Dis. 2015;211(12):1875–1882. | ||
Mendling W, Krauss C, Fladung B. A clinical multicenter study comparing efficacy and tolerability of topical combination therapy with clotrimazole (Canesten, two formats) with oral single dose fluconazole (Diflucan) in vulvovaginal mycoses. Mycoses. 2004;47(3-4):136–142. | ||
Mikamo H, Izumi K, Ito K, Tamaya T. Comparative study of the effectiveness of oral fluconazole and intravaginal clotrimazole in the treatment of vaginal candidiasis. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 1995;3(1):7–11. | ||
O-Prasertsawat P, Bourlert A. Comparative study of fluconazole and clotrimazole for the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis. Sex Transm Dis. 1995;22(4):228–230. | ||
Osser S, Haglund A, Weström L. Treatment of candidal vaginitis. A prospective randomized investigator-blind multicenter study comparing topically applied econazole with oral fluconazole. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1991;70(1):73–78. | ||
Seidman LS, Skokos CK. An evaluation of butoconazole nitrate 2% site release vaginal cream (Gynazole-1) compared to fluconazole 150 mg tablets (Diflucan) in the time to relief of symptoms in patients with vulvovaginal candidiasis. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 2005;13(4):197–206. | ||
Sekhavat L, Tabatabaii A, Tezerjani FZ. Oral fluconazole 150 mg single dose versus intra-vaginal clotrimazole treatment of acute vulvovaginal candidiasis. J Infect Public Health. 2011;4(4):195–199. | ||
Sobel JD, Brooker D, Stein GE, et al. Single oral dose fluconazole compared with conventional clotrimazole topical therapy of Candida vaginitis. Fluconazole Vaginitis Study Group. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995;172(4 Pt 1):1263–1268. | ||
Sobel JD, Wiesenfeld HC, Martens M, et al. Maintenance fluconazole therapy for recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(9):876–883. | ||
Stein GE, Christensen S, Mummaw N. Comparative study of fluconazole and clotrimazole in the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis. DICP. 1991;25(6):582–585. | ||
Stein GE, Mummaw N. Placebo-controlled trial of itraconazole for treatment of acute vaginal candidiasis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993;37(1):89–92. | ||
Timonen H. Shorter treatment for vaginal candidosis: comparison between single-dose oral fluconazole and three-day treatment with local miconazole. Mycoses. 1992;35(11-12):317–320. | ||
Tobin JM, Loo P, Granger SE. Treatment of vaginal candidosis: a comparative study of the efficacy and acceptability of itraconazole and clotrimazole. Genitourin Med. 1992;68(1):36–38. | ||
van Heusden AM, Merkus HM, Corbeij RS, et al. Single-dose oral fluconazole versus single-dose topical miconazole for the treatment of acute vulvovaginal candidosis. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1990;69(5):417–422. | ||
Zhou X, Li T, Fan S, et al. The efficacy and safety of clotrimazole vaginal tablet vs. oral fluconazole in treating severe vulvovaginal candidiasis. Mycoses. 2016;59(7):419–428. | ||
Fong IW. The value of chronic suppressive therapy with itraconazole versus clotrimazole in women with recurrent vaginal candidiasis. Genitourin Med. 1992;68(6):374–377. | ||
Puolakka J, Tuimala R. Comparison between oral ketoconazole and topical miconazole in the treatment of vaginal candidiasis. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1983;62(6):575–577. | ||
Corson SL, Kapikian RR, Nehring R. Terconazole and miconazole cream for treating vulvovaginal candidiasis. A comparison. J Reprod Med. 1991;36(8):561–567. | ||
Thomason JL, Gelbart SM, Kellett AV, Scaglione NJ, Gotwalt KT, Broekhuizen FF. Terconazole for the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis. J Reprod Med. 1990;35(11):992–994. | ||
Brown D, Henzl MR, Lepage ME, et al. Butoconazole vaginal cream in the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis. Comparison with miconazole nitrate and placebo. J Reprod Med. 1986;31(11):1045–1048. | ||
Adamson GD, Brown D, Standard JV, Henzl MR. Three-day treatment with butoconazole vaginal suppositories for vulvovaginal candidiasis. J Reprod Med. 1986;31(2):131–132. | ||
Stettendorf S, Benijts G, Vignali M, Kreysing W. Three-day therapy of vaginal candidiasis with clotrimazole vaginal tablets and econazole ovules: a multicenter comparative study. Chemotherapy. 1982;28 Suppl 1:87–91. | ||
Perera J, Seneviratne HR. Econazole and clotrimazole in the treatment of vaginal candidiasis: a double blind comparative study. Ceylon Med J. 1994;39(3):132–134. | ||
Kaufman RH, Henzl MR, Brown D, et al. Comparison of three-day butoconazole treatment with seven-day miconazole treatment for vulvovaginal candidiasis. J Reprod Med. 1989;34(7):479–483. | ||
Hajman AJ. Vulvovaginal candidosis: comparison of 3-day treatment with 2% butoconazole nitrate cream and 6-day treatment with 1% clotrimazole cream. J Int Med Res. 1988;16(5):367–375. | ||
Brown D, Henzl MR, Kaufman RH. Butoconazole nitrate 2% for vulvovaginal candidiasis. New, single-dose vaginal cream formulation vs. seven-day treatment with miconazole nitrate. Gynazole 1 Study Group. J Reprod Med. 1999;44(11):933–938. | ||
Ruf H, Vitse M. A comparison of butoconazole nitrate cream with econazole nitrate cream for the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis. J Int Med Res. 1990;18(5):389–399. | ||
Rohde-Werner H. Topical tioconazole versus systemic ketoconazole treatment of vaginal candidiasis. J Int Med Res. 1984;12(5):298–302. | ||
Sobel JD, Schmitt C, Stein G, Mummaw N, Christensen S, Meriwether C. Initial management of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis with oral ketoconazole and topical clotrimazole. J Reprod Med. 1994;39(7):517–520. | ||
Gerhard I, Ohlhorst D, Eggert-Kruse W, Runnebaum B. Topical one-time therapy with ketoconazole: a double-blind randomized study in vaginal mycosis. Mycoses. 1989;32(5):253–265. | ||
Sobel JD. Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. A prospective study of the efficacy of maintenance ketoconazole therapy. N Engl J Med. 1986;315(23):1455–1458. | ||
van der Meijden WI, van der Hoek JC, Staal HJ, van Joost T, Stolz E. Double-blind comparison of 200-mg ketoconazole oral tablets and 1200-mg miconazole vaginal capsule in the treatment of vaginal candidosis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1986;22(3):133–138. | ||
Kutzer E, Oittner R, Leodolter S, Brammer KW. A comparison of fluconazole and ketoconazole in the oral treatment of vaginal candidiasis; report of a double-blind multicentre trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1988;29(4):305–313. | ||
Hong E, Dixit S, Fidel PL, Bradford J, Fischer G. Vulvovaginal candidiasis as a chronic disease: diagnostic criteria and definition. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2014;18(1):31–38. | ||
Zhang JY, Liu JH, Liu FD, et al. Vulvovaginal candidiasis: species distribution, fluconazole resistance and drug efflux pump gene overexpression. Mycoses. 2014;57(10):584–591. | ||
Foxman B, Muraglia R, Dietz JP, Sobel JD, Wagner J. Prevalence of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis in 5 European countries and the United States: results from an internet panel survey. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2013;17(3):340–345. | ||
Fardiazar Z, Ronaci F, Torab R, Goldust M. Vulvovaginitis candidiasis recurrence during pregnancy. Pak J Biol Sci. 2012;15(8):399–402. | ||
Goldacre MJ, Watt B, Loudon N, Milne LJ, Loudon JD, Vessey MP. Vaginal microbial flora in normal young women. Br Med J. 1979;1(6176):1450–1455. | ||
Guzel AB, Ilkit M, Akar T, Burgut R, Demir SC. Evaluation of risk factors in patients with vulvovaginal candidiasis and the value of chromID Candida agar versus CHROMagar Candida for recovery and presumptive identification of vaginal yeast species. Med Mycol. 2011;49(1):16–25. | ||
Workowski KA, Bolan GA, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2015;64(RR-03):1–137. | ||
Lalla RV, Dongari-Bagtzoglou A. Antifungal medications or disinfectants for denture stomatitis. Evid Based Dent. 2014;15(2):61–62. | ||
Peyton LR, Gallagher S, Hashemzadeh M. Triazole antifungals: a review. Drugs Today. 2015;51(12):705–718. | ||
Eschenauer GA, Nguyen MH, Clancy CJ. Is fluconazole or an echinocandin the agent of choice for candidemia. Ann Pharmacother. 2015;49(9):1068–1074. | ||
Wildfeuer A, Laufen H, Schmalreck AF, Yeates RA, Zimmermann T. Fluconazole: comparison of pharmacokinetics, therapy and in vitro susceptibility. Mycoses. 1997;40(7–8):259–265. | ||
Kjaeldgaard A. Comparison of terconazole and clotrimazole vaginal tablets in the treatment of vulvovaginal candidosis. Pharmatherapeutica. 1986;4(8):525–531. |
 © 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.