Back to Journals » International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease » Volume 11 » Issue 1
Efficacy and safety of tiotropium + olodaterol maintenance treatment in patients with COPD in the TONADO® and OTEMTO® studies: a subgroup analysis by age
Authors Ferguson GT , Karpel JP, Clerisme-Beaty E, Grönke L, Voß F , Buhl R
Received 18 March 2016
Accepted for publication 10 June 2016
Published 31 October 2016 Volume 2016:11(1) Pages 2701—2710
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S108758
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
Gary T Ferguson,1 Jill P Karpel,2 Emmanuelle Clerisme-Beaty,3 Lars Grönke,4 Florian Voß,4 Roland Buhl5
1Pulmonary Research Institute of Southeast Michigan, Farmington Hills, MI, 2North Shore Medical Arts LLP, Great Neck, NY, 3Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals Inc., Ridgefield, CT, USA; 4Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG, Ingelheim am Rhein, 5Pulmonary Department, Mainz University Hospital, Mainz, Germany
Background: Increasing age is associated with poor prognosis in patients with COPD.
Objective: This analysis from the replicate Phase III OTEMTO® and TONADO® studies examined the efficacy and safety of tiotropium, a long-acting anticholinergic, combined with olodaterol, a long-acting β2-agonist, compared to monotherapies and placebo in patients with COPD aged 40 years to <65 years, 65 years to <75 years, 75 years to <85 years, and ≥85 years.
Methods: In these double-blind, parallel-group, active-controlled, multicenter, randomized studies, patients received tiotropium + olodaterol 2.5/5 µg or 5/5 µg, tiotropium 5 µg or 2.5 µg (TONADO only), olodaterol 5 µg (TONADO only), or placebo (OTEMTO only). This analysis used the approved doses of tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 µg, tiotropium 5 µg, and olodaterol 5 µg. Primary end points at 12 weeks (OTEMTO) or 24 weeks (TONADO) included St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) total score, forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) area under the curve from 0 hour to 3 hours (AUC0–3) response, and trough FEV1 response.
Results: A total of 1,621 patients were randomized (40 years to <65 years, n=749; 65 years to <75 years, n=674; 75 years to <85 years, n=186; ≥85 years, n=12) in OTEMTO and 5,162 patients (40 years to <65 years, n=2,654; 65 years to <75 years, n=1,967; 75 to <85 years, n=528; ≥85 years, n=13) in TONADO. FEV1 AUC0–3 and trough FEV1 responses improved with tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 µg at 12 weeks and 24 weeks compared to monotherapies or placebo for all age groups. SGRQ scores generally improved with tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 µg after 12 weeks in OTEMTO and improved after 24 weeks in all age groups in TONADO. In all age groups receiving tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 µg compared to monotherapies or placebo, transition dyspnea index scores generally improved, while rescue medication usage improved.
Conclusion: No differences were noted in relative responses to treatment or safety when using tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 µg compared to monotherapies or placebo across all age groups.
Keywords: FEV1, SGRQ, lung function, TDI, rescue medication
Introduction
COPD is characterized by persistent, progressive airflow limitation caused by lung tissue destruction and airway inflammation.1 Age has been shown to be independently associated with poor prognosis in patients with COPD,1 and the projected aging of the world population suggests an imminent increase in the global prevalence of older patients with COPD.2
COPD is often accompanied by comorbidities,3 with 78.4% of patients reporting more than one chronic condition.4 Older patients with COPD are more likely to have such additional chronic conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and osteoporosis.5 Morbidity due to COPD has been shown to increase with age, with hospitalization due to an exacerbation more likely with older age1,6 and an increasing probability of death after hospitalization.6
Tiotropium is an established once-daily long-acting anticholinergic for COPD maintenance treatment that has been shown to provide a broad range of long-term improvements in lung function, quality of life, exacerbation risk, and exercise capacity.7–13 A newer treatment option for COPD is olodaterol, a once-daily long-acting β2-agonist with high selectivity and fast onset of action.14–17 The combination of tiotropium + olodaterol delivered via the Respimat® inhaler is approved in the US, Canada, and Europe and has been extensively studied in a large Phase III clinical trial program (TOviTO®).18
In the OTEMTO® trials – two replicate Phase III studies in patients with moderate to severe COPD – tiotropium + olodaterol was compared to tiotropium alone or placebo, and improvements in lung function and quality of life and an acceptable safety profile over 12 weeks of use were demonstrated.19 In the TONADO® trials – two large, replicate, Phase III studies – patients with moderate to very severe COPD demonstrated improvements in lung function and an acceptable safety profile with tiotropium + olodaterol compared to tiotropium and olodaterol individually over 52 weeks.20
Due to challenges that may accompany COPD in older patients with higher medical needs, it is important to examine the effects of tiotropium + olodaterol in this population. The replicate OTEMTO and TONADO studies provide a valuable opportunity to assess these end points in a large patient population followed up for up to 1 year.
This analysis examines the effects of tiotropium + olodaterol on lung function, safety, and health-related quality of life compared to monotherapies and placebo in patients with COPD stratified by age from the OTEMTO and TONADO trials.
Methods
Study design
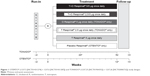
Detailed methodologies of OTEMTO (1237.5+1237.6) and TONADO (1237.25+1237.26) have been previously published.19,20 Briefly, these trials were two pairs of replicate, double-blind, parallel-group, active-controlled, multicenter, randomized, Phase III studies (registered with ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01431274 [Study 1237.5], NCT01431287 [Study 1237.6], NCT01964352 [Study 1237.25], and NCT02006732 [Study 1237.26]). The OTEMTO studies were placebo-controlled and comparator-controlled trials, and patients were randomized to receive tiotropium + olodaterol 2.5/5 μg or 5/5 μg, tiotropium 5 μg, or placebo for 12 weeks (Figure 1). The TONADO studies did not have a placebo-control arm, and patients received tiotropium + olodaterol 2.5/5 μg or 5/5 μg, tiotropium 2.5 μg or 5 μg, or olodaterol 5 μg over 52 weeks (Figure 1). This analysis focuses on the approved doses of tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg, tiotropium 5 μg, and olodaterol 5 μg. All treatments were administered once daily via the Respimat inhaler (Boehringer Ingelheim, Ingelheim am Rhein, Germany). Salbutamol (albuterol) was provided as rescue medication for all study participants and use was recorded in a diary. Patients were permitted to continue use of inhaled corticosteroids, if previously prescribed, provided the dose was stabilized for 6 weeks prior to the screening visit.
The studies included in this post hoc analysis were approved by the review boards of the coordinating institutions (TONADO: University Hospital Mainz, Mainz, Germany; OTEMTO: National Research Ethics Service Committee, Manchester, UK) as well as each relevant national, regional, or independent ethics committee or institutional review board and conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and Good Clinical Practice guidelines. Patients provided written informed consent.
Study outcomes and assessments
Primary end points, measured at 12 weeks (OTEMTO) or 24 weeks (TONADO), included St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) total score, forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) area under the curve from 0 hour to 3 hours (AUC0–3) response (change from baseline), and trough FEV1 response. Secondary end points included the transition dyspnea index (TDI) focal score, also measured at 12 weeks (OTEMTO) or 24 weeks (TONADO). Further end points included SGRQ responder analysis (responders defined as having a decrease in SGRQ total score ≥4.0 units, based on the proposed minimum clinically important difference for active treatment versus placebo21) and TDI responder analysis (responders defined as patients with a value ≥1.0 unit at the time of analysis, ie, improvement from baseline dyspnea index of ≥1.0 unit, considered the threshold of clinical relevance22).
Analyses were performed on pooled data for the OTEMTO studies and pooled data for the TONADO studies. This age subgroup analysis, including age cutoffs, was preplanned for FEV1 AUC0–3 and trough FEV1 for the individual OTEMTO and TONADO trials and pooled TONADO trials. Age subgroup analysis was not prespecified in the pooled OTEMTO trials.
Patients
The main inclusion criteria were: outpatients aged ≥40 years with a history of moderate to severe (OTEMTO) or moderate to very severe (TONADO) COPD; postbronchodilator FEV1 <80% of predicted normal (lower limit ≥30% in OTEMTO; no lower limit in TONADO); postbronchodilator FEV1/forced vital capacity <70%; and current or ex-smokers with a smoking history of >10 pack-years. The main exclusion factors were: presence of a significant disease other than COPD; clinically relevant abnormal baseline laboratory parameters or a history of asthma; or regular use of daytime oxygen if patients were unable to abstain during clinic visits. Non-long-acting β2-agonist or non-long-acting muscarinic antagonist concomitant respiratory medications were allowed in all studies, with further details presented elsewhere.19,20
For the prespecified analysis of FEV1 AUC0–3 and trough FEV1 in each study, patients were divided into the following age groups: 40 years to <65 years, 65 years to <75 years, 75 years to <85 years, and ≥85 years. The prespecified categorization from the single studies was used throughout all analyses performed. Predicted FEV1 values were used according to those calculated for adults (aged 18–70 years) by the European Community for Steel and Coal/European Respiratory Society, and interpolated for those patients aged >70 years.23 Further details of statistical analyses are contained in the Supplementary materials.
Results
In total, 1,621 patients were randomized (40 years to <65 years, n=749; 65 years to <75 years, n=674; 75 years to <85 years, n=186; ≥85 years, n=12) in the OTEMTO trials. In the TONADO trials, 5,162 patients were randomized to treatment (40 years to <65 years, n=2,654; 65 years to <75 years, n=1,967; 75 years to <85 years, n=528; ≥85 years, n=13). There were very few patients in the ≥85 years group, so this group was excluded from further analysis. The majority of patients were in their 60s, with an average age of 64.7±8.4 years in OTEMTO and 64.0±8.3 years in TONADO (Figure S1).
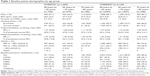
Baseline patient demographics were similar between studies, although TONADO included a greater percentage of male patients compared to OTEMTO (Table 1). Mean duration of COPD and percentage of current smokers were slightly higher for all age groups in OTEMTO compared to TONADO. OTEMTO patients also tended to have slightly higher baseline lung function values, reflecting the exclusion of patients with very severe COPD.
Across both studies, there were fewer men in the youngest age group (40 years to <65 years) compared to the older age groups. In the older age groups in both OTEMTO and TONADO, absolute lung function at baseline (mean FEV1 postbronchodilator) was lower, although the relative severity as a percent of predicted FEV1 was similar across age groups. There was a trend toward fewer current smokers in the older patient groups. The majority of patients in both studies had COPD classified as Global initiative for chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2, and fewer patients in the 40 years to <65 years group were receiving pulmonary medications at baseline compared to older groups.
Lung function response
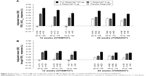
In OTEMTO and TONADO, FEV1 AUC0–3 response improved in patients across all age groups receiving tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg compared to monotherapies or placebo after 12 weeks and 24 weeks, respectively (Figure 2A). Trough FEV1 response was also greater with tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg compared to monotherapies or placebo in all age groups (Figure 2B). In both studies, the change in adjusted mean FEV1 AUC0–3 response with tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg versus monotherapy or placebo was most pronounced in individuals aged 40 years to <65 years, with a lesser effect in individuals aged 75 years to <85 years (Figure 3A), but in general similar effects with widely overlapping 95% confidence intervals were observed.
Similarly, in TONADO, the difference in trough FEV1 response between tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg and tiotropium 5 μg was less pronounced in those aged 75 years to <85 years than in the other age groups (Figure 3B). The differences in trough FEV1 response between tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg and olodaterol 5 μg in TONADO and between tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg and tiotropium 5 μg or placebo in OTEMTO were relatively consistent across the three age groups. The smaller treatment difference observed in the oldest age group might be in part due to the small sample size in this age group, reflected by the wide 95% confidence interval.
Health status outcomes (SGRQ total scores and TDI focal scores)
After 12 weeks in OTEMTO, SGRQ total score improved in the 40 years to <65 years and 65 years to <75 years groups receiving tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg compared to tiotropium 5 μg and placebo; in the 75 years to <85 years group, a numerical improvement was observed in the tiotropium 5 μg group compared to tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg, but 95% confidence intervals were still overlapping (Table S1; Figure S2). In TONADO, SGRQ total scores generally improved after 24 weeks across all age groups with tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg compared to olodaterol 5 μg and tiotropium 5 μg (Table S1). Treatment effects seemed to be similar, with widely overlapping 95% confidence intervals across all age groups (Figure S2).
In OTEMTO, more patients receiving tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg were SGRQ responders compared to patients receiving tiotropium 5 μg or placebo in all age groups (Table S1; Figure S3). In TONADO, the percentage of patients classified as SGRQ responders was highest with tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg in all age groups compared to monotherapies (Table S1; Figure S3).
After 12 weeks in the OTEMTO studies, mean TDI focal scores were higher in patients receiving tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg compared to placebo in all age groups, and compared to tiotropium 5 μg in the 40 years to <65 years and 65 years to <75 years groups (Table S2). There seemed to be some heterogeneity across the age groups in OTEMTO (Figure S4). All age groups in TONADO demonstrated an improvement in TDI focal scores with tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg compared to monotherapies. Improvements in TDI focal score were most pronounced in the 65 years to <75 years group (Table S2), but 95% confidence intervals were widely overlapping and the treatment effects seemed to be homogeneous across age groups in TONADO (Figure S4).
In both the OTEMTO and TONADO studies, more patients receiving tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg were TDI responders compared to patients receiving monotherapies or placebo in the 40 years to <65 years and 65 years to <75 years groups. In the 75 years to <85 years groups in both studies, a greater percentage of patients receiving tiotropium 5 μg achieved TDI responder status compared to patients receiving tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg, olodaterol 5 μg, or placebo (Table S2), but more patients in the tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg arm were TDI responders than in the olodaterol 5 μg and placebo arms. The 65 years to <75 years group in patients receiving tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg had the greatest percentage of TDI responders compared to other age groups and treatments in both studies (Table S2; Figure S5).
Rescue medication use
Daytime and nighttime rescue medication use was reduced in patients receiving tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg compared to patients receiving monotherapies or placebo across all age groups (Tables S3 and S4).
Safety
The percentage of patients experiencing any adverse event increased slightly with age in the TONADO and OTEMTO studies (Table 2). In all age groups in TONADO, the system organ classes with the highest reported adverse events were: respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders; infections and infestations; and gastrointestinal disorders. In OTEMTO, the most commonly reported adverse events were within the system organ classes of: respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders; infections and infestations; and musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders.
The same trend was seen with serious adverse events, with a slight increase with age seen in all treatment groups in both studies. Across all age groups and treatment groups in both studies, COPD was the most common serious adverse event reported.
Discussion
OTEMTO and TONADO were two replicate, large-scale paired studies assessing the efficacy and safety of the combination of tiotropium + olodaterol for the treatment of COPD compared to the monotherapies and placebo (OTEMTO only). Overall, there were some differences in response to treatment between the patient groups, but tiotropium + olodaterol was effective irrespective of age, as noted by improvements in lung function, SGRQ scores, TDI focal scores, and rescue medication use in all the age groups. A trend toward smaller improvements was seen in patients aged 75 years to <85 years for some end points. Although we did not see a difference in percent predicted FEV1 across the age groups in this study, there was lower absolute pre- and postbronchodilator FEV1 at baseline in older patients, which could be one explanation for the smaller improvements in this population. Lower baseline lung function has been reported in older individuals,24 and smaller improvements in lung function were observed in older patients receiving tiotropium alone in a previous study.25 In addition, it is possible that the aging lung may have less capacity for improvement following bronchodilator treatment.
We observed greater variation in the lung function response in older patients indicated by wider confidence intervals in the 75 years to <85 years group. This is, in part, due to there being fewer patients in this group; however, we cannot exclude the possibility that greater variation may be due to reduced compliance and/or increased difficulty in performing spirometry maneuvers in this age group.
Importantly, the analysis did not suggest any safety concerns in older patients using tiotropium + olodaterol compared to monotherapies or placebo, similar to previous findings for tiotropium alone (once daily via Respimat 5 μg or HandiHaler® [Boehringer Ingelheim] 18 μg for >4 weeks) in Japanese patients ≥80 years old.25
By assessing both the 12-week OTEMTO and 24-week TONADO studies, it was possible to investigate the effects of tiotropium + olodaterol in patients with moderate to very severe COPD, including those on other respiratory medications, providing a more “real-world” assessment of the relatively broad range of patients who are likely to need maintenance treatment for COPD symptom management in clinical practice.
The prevalence of COPD has been shown to increase significantly with increasing age, with the highest prevalence seen in men and women >70 years of age.26 However, most COPD clinical trials have not specifically assessed the effects of maintenance treatment in patients aged >70 years. As there was no upper age limit for inclusion in this study, the safety and efficacy of tiotropium + olodaterol in this older age group could be assessed.
There are a number of issues that must be considered when managing COPD in elderly patients. COPD is associated with many serious chronic conditions, notably diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.27 Elderly patients with COPD have a more than twofold increase in prevalence of frailty compared to those without COPD,28 and older patients with COPD have also been found to be at risk of greater loss of bone mineral density29 and community-acquired pneumonia than healthy older populations, often accompanied by worse clinical outcomes.30,31 However, treatment with an inhaled bronchodilator may be beneficial in older patients with comorbidities. In patients aged 50 years to 85 years, β2-agonist treatment has been shown to reduce lung hyperinflation, with improvements in right cardiac chamber compliance indices and contractility.32
Advanced age coupled with serious comorbidities may also affect a patient’s ability to properly use an inhaler, although in the investigators’ experience, this trial demonstrated no issues with handling of the Respimat inhaler, regardless of age. Clinical guidelines recommend that a health-care professional should regularly assess patients’ inhaler technique.33,34 These factors may require additional vigilance in elderly populations to evaluate potential impact on treatment response.
A key limitation of these trials was the exclusion of patients who had severe conditions other than COPD that could have affected the outcome of a patient, influenced the results of the studies, or caused concern regarding a patient’s ability to participate. However, TONADO did allow the inclusion of patients with significant cardiovascular comorbidities, including patients on β-blockers. This could mean that these studies may not reflect the whole spectrum of older patients with COPD and higher risk comorbidities in a real-world setting; furthermore, we did not directly assess whether the impact of therapy was affected by the presence of comorbidities. The findings of this analysis also cannot be applied to the oldest of patients, as there were too few patients in the >85 years group to be included in the analysis. These patients may require special consideration that needs further investigation.
Conclusion
This analysis shows that the combination of once-daily tiotropium + olodaterol demonstrated significant improvements from baseline for lung function and symptomatic response in all groups, which were improved versus monotherapies or placebo in most age subgroups. The combination of tiotropium + olodaterol was also well tolerated in older patients, with a similar safety profile to that of the overall patient population.
Acknowledgments
The reported studies were supported by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG. The authors received no compensation related to the development of the manuscript. Medical writing assistance was provided by Laura Badtke, PhD, on behalf of Complete HealthVizion, which was contracted and compensated by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Author contributions
The authors meet the criteria for authorship as recommended by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. All authors contributed towards data analysis, drafting and critically revising the paper, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. They take full responsibility for the scope, direction, content, and editorial decisions relating to the manuscript, were involved at all stages of development, and have approved the submitted manuscript.
Disclosure
GTF has received consulting and advisory board fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Pearl Therapeutics, Novartis, Forest, Sunovion, and Verona, consulting fees from Receptos, speaker fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Pearl Therapeutics, Forest, and Sunovion, and is in receipt of research grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Pearl Therapeutics, Sunovion, Novartis, Theravance, Sanofi, Forest, and GlaxoSmithKline. JPK discloses no conflicts of interest. ECB, LG, and FV are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim. RB reports grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, and the German Research Foundation. RB also reports consulting, Speaker Bureau, and advisory committee fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Grifols, Novartis, Roche, and Takeda. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease [homepage on the Internet]. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Updated 2016. Available from: http://www.goldcopd.org/. Accessed April 27, 2016. | ||
Feenstra TL, van Genugten MLL, Hoogenveen RT, Wouters EF, Rutten-van Mölken MPH. The impact of aging and smoking on the future burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a model analysis in the Netherlands. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164(4):590–596. | ||
Barnes PJ, Celli BR. Systemic manifestations and comorbidities of COPD. Eur Respir J. 2009;33(5):1165–1185. | ||
Roberts MH, Mapel DW, Thomson HN. The impact of chronic pain on direct medical utilization and costs in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2015;7:173–184. | ||
Anecchino C, Rossi E, Fanizza C, et al. Prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and pattern of comorbidities in a general population. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2007;2(4):567–574. | ||
Hoogendoorn M, Hoogenveen RT, Rutten-van Mölken MP, Vestbo J, Feenstra TL. Case fatality of COPD exacerbations: a meta-analysis and statistical modelling approach. Eur Respir J. 2011;37(3):508–515. | ||
Casaburi R, Mahler DA, Jones PW, et al. A long-term evaluation of once-daily inhaled tiotropium in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J. 2002;19(2):217–224. | ||
O’Donnell DE, Flüge T, Gerken F, et al. Effects of tiotropium on lung hyperinflation, dyspnoea and exercise tolerance in COPD. Eur Respir J. 2004;23(6):832–840. | ||
Maltais F, Hamilton A, Marciniuk D, et al. Improvements in symptom-limited exercise performance over 8 h with once-daily tiotropium in patients with COPD. Chest. 2005;128(3):1168–1178. | ||
Tashkin DP, Celli B, Senn S, et al. A 4-year trial of tiotropium in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(15):1543–1554. | ||
Bateman ED, Tashkin D, Siafakas N, et al. A one-year trial of tiotropium Respimat® plus usual therapy in COPD patients. Respir Med. 2010;104(10):1460–1472. | ||
Yohannes AM, Willgoss TG, Vestbo J. Tiotropium for treatment of stable COPD: a meta-analysis of clinically relevant outcomes. Respir Care. 2011;56(4):477–487. | ||
Vogelmeier C, Hederer B, Glaab T, et al. Tiotropium versus salmeterol for the prevention of exacerbations of COPD. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(12):1093–1103. | ||
Ferguson GT, Feldman GJ, Hofbauer P, et al. Efficacy and safety of olodaterol once daily delivered via Respimat® in patients with GOLD 2–4 COPD: results from two replicate 48-week studies. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2014;9:629–645. | ||
Koch A, Pizzichini E, Hamilton A, et al. Lung function efficacy and symptomatic benefit of olodaterol once daily delivered via Respimat® versus placebo and formoterol twice daily in patients with GOLD 2–4 COPD: results from two replicate 48-week studies. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2014;9:697–714. | ||
Feldman GJ, Bernstein JA, Hamilton A, Nivens MC, Korducki L, LaForce C. The 24-h FEV1 time profile of olodaterol once daily via Respimat® and formoterol twice daily via Aerolizer® in patients with GOLD 2–4 COPD: results from two 6-week crossover studies. Springerplus. 2014;3:419. | ||
Lange P, Aumann J-L, Hamilton A, Tetzlaff K, Ting N, Derom E. The 24 hour lung function time profile of olodaterol once daily versus placebo and tiotropium in patients with moderate to very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Pulm Respir Med. 2014;4:196. | ||
Cazzola M, Rogliani P, Ora J, Matera MG. Olodaterol + tiotropium bromide for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2015;8(5):529–539. | ||
Singh D, Ferguson GT, Bolitschek J, et al. Tiotropium + olodaterol shows clinically meaningful improvements in quality of life. Respir Med. 2015;109(10):1312–1319. | ||
Buhl R, Maltais F, Abrahams R, et al. Tiotropium and olodaterol fixed-dose combination versus mono-components in COPD (GOLD 2–4). Eur Respir J. 2015;45(4):969–979. | ||
Jones PW. Estimation and application of the minimum clinically important difference in COPD. Lancet Respir Med. 2014;2(3):167–169. | ||
Witek TJ Jr, Mahler DA. Minimal important difference of the transition dyspnoea index in a multinational clinical trial. Eur Respir J. 2003;21(2):267–272. | ||
Quanjer PH, Tammeling GJ, Cotes JE, Pedersen OF, Peslin R, Yernault J-C. Lung volumes and forced ventilatory flows. Eur Respir J. 1993;6(suppl 16):5–40. | ||
Pride NB. Ageing and changes in lung mechanics. Eur Respir J. 2005;26(4):563–565. | ||
Satoh H, Kagohashi K, Ohara G, et al. Use of tiotropium in patients with COPD aged 80 years and older. Exp Ther Med. 2013;5(4):997–1000. | ||
Schirnhofer L, Lamprecht B, Vollmer WM, et al. COPD prevalence in Salzburg, Austria: results from the Burden of Obstructive Lung Disease (BOLD) Study. Chest. 2007;131(1):29–36. | ||
Mannino DM, Thorn D, Swensen A, Holguin F. Prevalence and outcomes of diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular disease in COPD. Eur Respir J. 2008;32(4):962–969. | ||
Lahousse L, Ziere G, Verlinden VJA, et al. Risk of frailty in elderly with COPD: a population-based study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2016;71(5):689–695. | ||
Scanlon PD, Connett JE, Wise RA, et al. Loss of bone density with inhaled triamcinolone in Lung Health Study II. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;170(12):1302–1309. | ||
Mannino DM, Davis KJ, Kiri VA. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and hospitalizations for pneumonia in a US cohort. Respir Med. 2009;103(2):224–229. | ||
Molinos L, Clemente MG, Miranda B, et al. Community-acquired pneumonia in patients with and without chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Infect. 2009;58(6):417–424. | ||
Santus P, Radovanovic D, Di Marco S, et al. Effect of indacaterol on lung deflation improves cardiac performance in hyperinflated COPD patients: an interventional, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:1917–1923. | ||
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence [webpage on the Internet]. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in over 16s: Diagnosis and Management. Clinical Guideline. NICE Guidelines [CG101]; 2010. Available from: http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg101/resources/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-in-over-16s-diagnosis-and-management-35109323931589. Accessed November 18, 2015. | ||
American Medical Directors Association (AMDA). COPD Management in the Long-Term Care Setting. Columbia: AMDA; 2010. |
 © 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.