Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 15
Dual-Ligand Functionalized Core-Shell Chitosan-Based Nanocarrier for Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Targeted Drug Delivery
Authors Hefnawy A , Khalil IH , Arafa K , Emara M , El-Sherbiny IM
Received 28 November 2019
Accepted for publication 15 January 2020
Published 5 February 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 821—837
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S240359
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
Amr Hefnawy,1 Islam H Khalil,1,2 Kholoud Arafa,3 Marwan Emara,3 Ibrahim M El-Sherbiny1
1Nanomaterials Lab, Center of Material Science (CMS), Zewail City of Science and Technology, Giza 12578, Egypt; 2Department of Pharmaceutics, College of Pharmacy and Drug Manufacturing, Misr University of Science and Technology (MUST), Giza 12566, Egypt; 3Center for Aging and Associated Diseases, Zewail City of Science and Technology, Giza 12578, Egypt
Correspondence: Ibrahim M El-Sherbiny
Zewail City for Science and Technology, Ahmed Zewail Road, October Gardens, 6th of October City, Giza, Egypt
Tel +20 238540407
Fax +20 238517181
Email [email protected]
Introduction: Hepatocellular carcinoma represents a major health problem with the related death numbers still increasing. Active targeting is considered an attractive choice for the development of selective therapeutics with limited side effects and improved efficiency. In this study, we report the design, development and evaluation of a novel dual-ligand functionalized core-shell chitosan-based nanocarrier for the selective delivery of doxorubicin (DOX) for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: Following factorial design experiments, DOX was initially complexed with negatively charged carboxymethyl chitosan-g-poly(acrylate) and then the complex was coated with a positively charged dual-ligand (lactobionic acid and glycyrrhetinic acid)-conjugated chitosan. The developed active targeting system was then tested in vitro on Hep-G2 cells using flow cytometry and fluorescence imaging.
Results: The obtained results proved the ability of the dual-ligand system to enhance the intracellular uptake of the drug by 4-fold and 8-fold after 4 hrs and 24 hrs of incubation, respectively. The efficiency of the dual-ligand functionalized nanoparticles was also tested in vivo on Wistar rats with induced liver tumors. Testing of serum biomarkers (albumin, creatinine, urea, alpha fetoprotein, ALT, AST and ALP) in addition to histopathological microscopic examination of liver, kidney and heart tissues confirmed the enhanced safety of the developed targeted nanocarrier system compared to the conventional DOX.
Discussion: The developed targeted system showed improved intracellular drug delivery and uptake as well as enhanced safety profile. The nanoparticles were formed based on electrostatic interactions providing the flexibility that allows their use as a model for delivery of other drugs and other targets.
Keywords: liver cancer, dual targeting, doxorubicin, core-shell nanoparticles
Introduction
Liver cancer remains among the challenging health problems with no satisfactory treatments available till now. According to the cancer statistics published in 2016, liver cancer is the 5th deadliest type of tumors in males. The death rate caused by liver cancer is even increasing despite the fact that cancer-related deaths have dropped by 23% in the period between 1991 and 2012.1 Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) is actually the highest for incidence and mortality among primary tumors.2 These numbers indicate the need for more convenient and efficient therapeutic approaches for the treatment of liver cancer. According to the American Cancer Society, most of the liver tumors are metastatic from other parts of the body, while some others are primary tumors originating initially in the liver. Besides, the American Cancer Society classifies liver tumors into intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, angiosarcoma and hemangiosarcoma, hepatoblastoma and HCC, with the latter being the most common type.
There are several treatment options for liver cancer including chemotherapy, surgery, radiation and immunotherapy. One of the most commonly used chemotherapeutic agents in liver cancer treatment is doxorubicin (DOX) which acts by DNA intercalation. The drug has a potent anticancer activity and is approved for the treatment of various types of tumors including bladder, breast, stomach, lung, ovaries, thyroid, soft tissue sarcoma and multiple myeloma.3 However, the use of the drug is limited by its severe side effects including alopecia, vomiting, diarrhea and fatal cardiotoxicity.4 Accordingly, it is highly desired to load DOX into a carrier system that is able to maintain or improve its therapeutic efficiency while avoiding its side effects. Doxil is a Dox-loaded pegylated liposomes that received FDA approval and became available for clinical use in 1995 making it the first nanomedicine to reach the market.5 This formulation provided sustained duration of action and reduced the incidence of cardiomyopathy that can occur as a side effect for the use of DOX, however the nature of the liposomes resulted in its accumulation in the skin and so it is mainly indicated for certain forms of skin cancer. Additionally, its accumulation in the skin results in increased risk for other side effects as mucositis, stomatitis and palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia.6 However, Doxil would have limited use for the treatment of liver cancer due to its distribution profile in addition to its inability to actively target cancer cells.
Loading DOX is a challenging step since the drug is highly hydrophilic with a relatively high molecular weight. Additionally, the drug has two acidic phenolic groups and a basic amino group making it highly sensitive to changes in the medium pH during the loading process. These factors commonly result in very low entrapment efficiency when DOX is loaded through conventional methods in nanoparticles (NPs). In our previously published study, we developed a method to load DOX in alginate/chitosan NPs based on counter ion complexation. This method allowed improving the entrapment efficiency from 4% at slightly acidic media to more than 80% and sustaining the release of the loaded DOX to more than 20 days. Formulations based on ionic interactions generally require simpler procedures compared to covalent conjugation since the ionic interactions are spontaneous and need only adjustment of the pH of the medium.7
Targeting of chemotherapeutic agents selectively to tumors can be achieved using various approaches including passive targeting, active targeting or through the use of stimuli-responsive systems. Active targeting involves the use of ligands that have an increased affinity towards the tumor site via binding to enzymes, receptors or transporters present at that site.8 Folic acid is a ligand that is generally used to target rapidly dividing cells including various types of tumors.9 There are several targeting moieties that have been reported to accumulate in the liver including antibodies, polysaccharides, peptides, aptamers and vitamins. Examples for such ligands are galactose, lactobionic acid (LA), glycyrrhetinic acid (GA), hyaluronic acid, and biotin.10 Accordingly, these ligands were used by several studies for selective targeting of hepatocarcinoma.
The mechanism of active targeting involves the binding of the ligands attached to the NPs to receptors on the cell surface. These receptors may be mutant forms exclusively expressed by cancer cells or they may be overexpressed by the target cells. LA acts by binding to asialoglycoprotein (ASGP) receptors which are overexpressed on the surface of HCC cells.11 GA is another ligand used for selective targeting of this type of cancer cells, and its targeting is based on the ability of GA to bind to surface proteins overexpressed on HCC, however the exact mechanism and receptors involved are still not clear.12,13
A more recent approach for active targeting involves the use of multiple ligands for increased efficiency and selectivity of the targeting system. For example, chitosan (CS) conjugated to LA and GA has been reported as an efficient vector for targeting of liver tumors. The study investigated the liver accumulation of these CS derivative-based NPs without the loading of any active agent. The study showed improved cellular uptake of the dual-ligand NPs compared to CS or single-ligand CS. Additionally, the developed system was more selective towards cancer cells rather than normal cells.14 Another study reported developing a dual-ligand system using mannan and transferrin for gene delivery. The study proved that the developed system was 25% more efficient than a single ligand-based system regarding intracellular uptake in HepG2 and Kupffer cells.15
Some carrier systems and targeting moieties may provide an additional beneficial effect if they have therapeutic or protective effect at the target organ. For example, GA was reported to have a beneficial hepatoprotective effect against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury. A proposed mechanism for such effect is the inhibition of the cytochrome P450 2E1 which is the major enzyme involved in the bioactivation of carbon tetrachloride toxicity.16 Additionally, another study reported that GA has an anticancer effect through the activation of pro-apoptotic pathways by inducing mitochondrial permeability transition.17 CS, a natural polymer which is obtained from chitin through a simple deacetylation process, has been reported to have beneficial anticancer activity. Depolymerized CS products have shown the ability to inhibit angiogenesis and to induce apoptosis through DNA fragmentation.18,19 Moreover, the polymer could be extracted from several sources. Accordingly, it is available at low cost compared to other polymers as poly(ethylene glycol) or poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid). Besides, the polymer has attractive biodegradable and biocompatible properties. It can also easily be modified by grafting on its abundant amino and hydroxyl groups.20,21
In this study, we proposed a new method for the development of a dual-ligand targeted delivery system based on electrostatic interaction for the selective delivery of DOX to HCC cells. We hypothesized that such system, which can be prepared through simple process, would provide efficient drug loading, sustained release profile and enhanced uptake into the tumor cells (Figure 1)
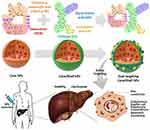 |
Figure 1 Design of dual-ligands core/shell NPs for active targeting of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. |
Experimental Section
Materials
Chitosan (CS) (MW 100,000–300,000), 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid (GA) and lactobionic acid (LA) were purchased from Acros Organics (New Jersey, USA). Acrylic acid, monochloroacetic acid, N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC.HCl), N-Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) and ammonium persulfate (APS) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Darmstadt, Germany). All other solvents and reagents were of analytical grade and were used without further purification.
Cell Lines
Hepatocellular carcinoma cells, Hep-G2 (ATCC® HB-8065™) were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC; Virginia, USA).
Preparation of Carboxymethyl Chitosan (CMCS) and Its Graft Copolymer
The preparation of CMCS and its graft copolymer, CMCS-g-polyacrylate (CMCS-g-PA) was done following the procedures reported by El-Sherbiny.22 Briefly, 2 g of CS was allowed to swell for 2 hrs at room temperature in 50 mL of isopropanol. Afterwards, 80 mL of 60% NaOH solution was added to the suspension followed by refluxing at 85°C for 2 hrs. This was followed by the gradual addition of 100 mL 60% monochloroacetic acid over a period of 10 min. The mixture was then allowed to react for 4 hrs at 65°C with stirring. Finally, the reaction was neutralized using 4M HCl. Insoluble residues were removed by filtration before precipitating the final product using methanol and washing with a mixture of equal volumes of methanol and H2O. Successful synthesis of CMCS was confirmed by Attenuated Total Reflection-Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) analysis (NICOLET, iS10, ThermoScientific).
Graft copolymerization of sodium acrylate onto CMCS (CMCS-g-PA) was done by reacting 0.1 g of CMCS with predetermined amount of the acrylic acid monomer. Before addition, the monomer was neutralized using 4M NaOH and diluted by deionized water to a final concentration of 8.5 mM. The solution was then stirred for 30 min with slow flow of nitrogen gas. Afterwards, the solution was heated to 70°C before adding the aqueous solution of the initiator (APS) dropwise with stirring till reaching a final concentration of 8 mM for the initiator. The reaction was then allowed to occur for 2 hrs before its termination via rapid cooling and allowing air into the flask. The graft copolymer was then separated through precipitation upon pouring into acetone followed by filtration. The obtained CMCS-g-PA copolymer was purified by refluxing in methanol for 20 hrs using a soxhlet extraction apparatus. The grafting was confirmed using FTIR analysis, and the grafting percentage was estimated gravimetrically using the following equation:
(1)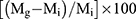
where Mg is the weight of the resulting graft copolymer while Mi is the weight of the initial polymer.22
Development of DOX-Loaded Nanoparticles (Core)
DOX-loaded NPs (core) were prepared through electrostatic interactions between the positively charged DOX and negatively charged CMCS-g-PA aqueous solutions. Factorial 22 experimental design was used to optimize the material criteria contributing to the final formula. Desirability was evaluated based on three equally weighted criteria: minimizing particle size, and maximizing both surface charge and entrapment efficiency. The effects of the two variables and their interactions were evaluated using statistical analysis of variance test (P<0.05) using Design Expert® 10.0.3.1 software (Stat-Ease, Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA).
Synthesis of Dual Ligands-CS Conjugate (DL-CS)
Two liver targeting ligands (GA and LA) were selected in the present study to be conjugated to the developed nanocarrier system. Synthesis of the dual ligands-CS was done using the procedures reported by Chen et al.14 Briefly, 1 g of CS was dissolved in 80 mL of 1% (v/v) acetic acid solution. On the other hand, 0.5 g of the ligand (GA) was dissolved in 50 mL of DMF with 1 g of EDC.HCl and 0.33 g NHS. The activated GA solution was then added to the CS with stirring at room temperature for 72 hrs. The reaction was terminated, and the resulting CS-GA conjugate was collected by addition to acetone followed by filtration. The obtained product (0.85 g) was then dissolved in 32 mL of TEMED/HCl buffer adjusted at pH 4.7. The second ligand, LA (0.95 g) was in turn dissolved in 8 mL of the same buffer and activated by EDC.HCl (0.6 g) and NHS (0.37 g). The two solutions were then mixed and allowed to react at room temperature for 3 days. The pure dual ligands-CS conjugate (DL-CS) was obtained by extensive dialysis for 72 hrs followed by freeze-drying. The preparation of the conjugate was confirmed by FTIR and 1H-NMR analysis (ECA 500II, JEOL, Japan).
Development of DOX-Loaded Dual Ligands-Decorated Core/Shell Nanoparticles
The preparation of DOX-loaded dual ligands-decorated NPs (DL-NPs, F4) was carried out through a modified method to that reported earlier.7 Briefly, 5 mg of DOX.HCl dissolved into 5 mL of double distilled H2O were neutralized using few drops of NaHCO3. The free drug base was then added dropwise to the pre-determined amount of CMCS-g-PA determined according to the experimental design followed by sonication for 1 min. Afterwards, the DOX/CMCS-g-PA complex nanosuspension was added dropwise to the amount of DL-CS specified by the experimental design with homogenization at 10,000 rpm. The prepared formula was homogenized for an additional 5 mins. For comparison, NPs were prepared following similar procedure but with the outer layer not conjugated to any ligands (F1), conjugated to GA only (F2) or LA only (F3) as presented in Table 1. Blank formulation was also prepared with the two ligands (GA and LA) present but without DOX loaded in its core (F5).
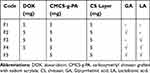 |
Table 1 Composition of Different Formulations |
Evaluation of the prepared core/shell NPs was done using FTIR analysis, dynamic light scattering (DLS; Zetasizer nano ZS, Malvern instruments, UK) and differential Scanning calorimetry (Q20, TA instruments, USA) as well as assessment of particle size and surface morphology using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM; JEOL-JEM- 2100, Japan)
The DOX entrapment efficiency was determined using indirect UV-spectrometric analysis. DOX-DL NPs (F4) were separated by centrifugation at 14,000 rpm for 30 min. Then, free DOX in the supernatant was evaluated by measuring UV-Vis absorbance at λ = 480 nm (Evolution 600, ThermoScientific, USA).
The release profile was also determined using UV-spectrometric analysis. Briefly, a pre-determined weight of the formula equivalent to 1.25 mg DOX was placed in the inner compartment of a two-compartment system. The outer compartment contained 2 mL of PBS buffer at pH 7.4 and the two compartments were separated by a semipermeable cellulose membrane (cutoff 12,000 Mw). At various time intervals, the UV-Vis absorbance at λ = 480 nm of the external compartment was measured with replacing it with 2 mL fresh buffer after each measurement to maintain the sink conditions. Cumulative release profile and model fitting kinetics were estimated according to equations reported by Ali et al.23
In-vitro Cellular Uptake Using Fluorescence Microscopy
To determine the subcellular localization and uptake of DOX-loaded NPs, cultured cells (Hep-G2) were grown overnight on sterile coverslips. Cells were treated with GA mono-ligated NPs and dual-ligated NPs for 4 and 24 hrs. Cells were washed twice with PBS, fixed in cold in ice-cold - methanol/acetone (1:1) for 5 min and air-dried for 15 min. Coverslips were mounted onto slides using mounting containing DAPI (Ultracruz mounting media, Santa Cruz cat. no. Sc-24941, USA). Images were taken using fluorescent microscope where the exposure time was slightly adjusted to improve image acquisition (Olympus BX-53, Olympus Life Science MA, USA), and the images were processed using Image J software.
In-vitro Cellular Uptake Using Flow Cytometry
Hepatocellular carcinoma Hep-G2 cells were maintained as monolayer cultures in high-glucose DMEM (Biowest, cat no. L0103) and RPMI 1640 (Biowest, cat no.L0498) growth media, respectively, supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 in air at 37°C. In addition to control cells, other cells were treated with DOX-loaded NPs (4µM); prototype non-ligated NPs (F1), GA mono-ligated NPs (F2), LA mono-ligated NPs (F3) or dual ligated (GA and LA) NPs (F4) for 4 and 24 hrs. Fluorescence intensities were recorded for 10,000 events using a flow cytometer (Attune acoustic focusing flow cytometer, Thermofischer, USA). The data were analyzed using attune software reporting the median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of individual peaks.
In-vivo Study: Induction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
All in-vivo experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee of Misr University of Science and Technology in accordance with ARRIVE (Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments), and all the guidelines of the institutional animal ethical committee of Misr University of Science and Technology have been followed throughout the study and in the manuscript.
A total of 25 female wistar rats were randomly assigned to 5 groups. Induction of HCC was achieved using modified procedures to those reported in previous studies.24 The first group (G1) was non-tumor group and served as the negative control for the study. The other four groups (G2-G5) received intra-peritoneal injection of 40 mg/kg N-nitrosodiethylamine. The tumor-inducing effect was augmented by giving a dose of 2 mL/kg chloroform 2 weeks after the N-nitrosodiethylamine dose. Tumor formation was detected by measuring α-fetoprotein in blood samples taken after 18 weeks of induction.
Liver samples were then evaluated by pathological examination to confirm the formation of tumors and to determine the cancer stage following the WHO guidelines.25 According to the guidelines, liver tumors are classified into 4 grades of decreasing degree differentiation. Grade (I) tumors are well-differentiated tumors with cancer lesions consisting of increased nuclear/cytoplasmic (N/C) ratio with minimal atypia arranged in a thin trabecular pattern. Frequent pseudoglandular or acinar structures and frequent fatty changes are observed. Grade (II) tumors are moderately differentiated with cancer cells arranged in the form trabeculae consisting of three or more cells in thickness. Cells are characterized by round nuclei with distinct nucleoli and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm. Pseudoglandular pattern is also frequently observed, and pseudo-glands frequently include bile or a proteinaceous fluid. Grade (III) tumors are poorly differentiated tumors that lack distinct sinusoid-like blood spaces. Large tumor nests are observed with only slit-like blood vessels. Neoplastic cells have increased N/C ratio and frequent pleomorphism, including bizarre giant cells. The highest grade (grade IV) tumors are solid tumors that are completely undifferentiated. Cells have spindle or round shape, containing little cytoplasm with high N/C ratio.
In-vivo Study: Targeting of DL-NPs
Rats of the negative control group (G1) and the positive control group (G2) were kept untreated to indicate the healthy state and the tumor state, respectively. G3 was treated with a blank unloaded carrier system (F5) to show the effect of the carrier itself while G4 was treated with the loaded NPs equivalent to 5 mg/Kg DOX once weekly for 4 weeks. The last group G5 was treated with free 5 mg/Kg DOX once weekly for 4 weeks.
In-vivo Study: Serological Tests
After 4 weeks, the animals were sacrificed by cervical dislocations and liver weights of all animals were recorded, and the various organs were collected for further assessment. Serum was collected from each group. Treatment efficiency was monitored by measuring α-fetoprotein (AFP) using ELISA kit (Anogen, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada) and liver function biomarkers: ALT and AST using colorimetric kit (ProDia international, Germany).26 Serum ALP was estimated using kit (Biolabo SA, France),27 as well as the kidney function: albumin, serum creatinine and urea were assessed using commercial colorimetric kits (Spectrum, Egypt).
In-vivo Study: Histology
For histopathological examination, liver, kidney and heart tissue specimens were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin. The fixed specimens were then trimmed, washed and dehydrated in ascending grades of alcohol, cleared in xylene, embedded in paraffin, sectioned at 4–6 μm thickness and stained by hematoxylin and eosin.28
Renal lesions were assessed by light microscopic examination in blinded fashion using a scale of 0 to 5, according to the severity of tubular cell necrosis, apoptosis, degeneration, regeneration, tubular dilatation and protein casts, glomerular vacuolization, glomerular mesangial cell proliferation, and interstitial lymphocytic infiltration in the S1/S2 segments or S3 segments: 0 = normal histology; 1 = tubular epithelial cell degeneration, without significant necrosis or apoptosis; 2–5 = <25%, <50%, <75% and ≥75% of the tubules showing tubular epithelial cell necrosis and apoptosis accompanied with other concomitant alterations, respectively.
Statistical Analysis
Data for experiments are expressed as means ± standard error from three replicate experiments unless otherwise indicated. Significant differences were examined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post-hoc tests or ranks (Kruskal–Wallis) based on the normality and equal variance tests (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001) using the software GraphPad Prism Software version 6.
Results and Discussion
Synthesis of CMCS-g-PA
Figure 2A shows the synthetic scheme for CMCS-g-PA copolymer. CS was first converted into a water-soluble form (CMCS) via carboxymethylation using monochloroacetic acid that can undergo nucleophilic attack reaction based on the presence of the good leaving Cl group.
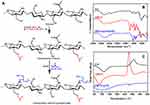 |
Figure 2 Synthesis and characterization of carboxymethyl chitosan-g-poly acrylic acid (CMCS-g-PAA) sodium salt: (A) an illustration of the synthesis steps, (B) FTIR, and (C) DSC. |
Graft copolymerization of the acrylic monomer on the synthesized CMCS was achieved using free radical polymerization. The reaction was initiated using the APS that acts as a thermal initiator. The use of basic conditions for the reactions aims at converting of acrylic acid monomer into its salt to increase the negative charge onto the resulting graft copolymer (CMCS-g-PA).
Graft copolymerization was achieved with a percentage of 2390% as determined using gravimetric analysis. In addition to the significant increase in weight after the extensive washing of residual initiator, non-reacting acrylate monomer and the formed PA homopolymer, the grafting was confirmed using FTIR analysis (Figure 2B). The absorbance spectrum of CS showed a broad peak around 3354 cm−1 which can be attributed to the N-H and O-H stretching vibrations. The peak around 2870 cm−1 can be due to the Sp3 hydrogens. The spectrum also showed an additional peak at 1592 cm−1 which can be attributed to the amide C=O stretching. The peaks at 1592, 1417 and 1377 cm−1 can be assigned to the carbonyl stretching in the amide I, II and III regions. The spectrum of CMCS was characterized by the presence of the carboxylic carbonyl symmetric and asymmetric stretching peaks at 1413 and 1732 cm−1, respectively. It can also be observed that the peak for the C-O was shifted from 1150 cm−1 to 1134 cm−1 with increasing intensity which shows that the substitution mostly occurred at the hydroxyl group. Grafting of polyacrylate onto the polymer could be confirmed by the presence of the peak at 1322 cm−1 with a decrease in the intensity of the peak at the 1100 cm−1 which is a characteristic peak for polysaccharides.22
The thermal characteristics of the synthesized CS derivatives (CMCS and CMCS-g-PA) were also evaluated using DSC measurements. Samples were heated under constant rate of 10°C/min under nitrogen flow using power compensation mode. As shown in Figure 2C, the CS thermogram demonstrated an endothermic peak at 112.54°C, which can be attributed to the loss of water molecules bound to the free OH and NH2 groups. The thermogram also has an exothermic peak at 307.46°C which is mainly due to the thermal decomposition. In the case of CMCS, it was observed that the dehydration endothermic peak was shifted to 84.46°C and the decomposition peak was also shifted to a similar extent to appear at 277.6°C. The graft copolymer (CMCS-g-PA) thermogram showed a peak at 101.77°C which is assigned also to the loss of water molecules. Additionally, a drift in the heat flow was observed at 276.87°C which corresponds to the amorphous part of the CS caused by grafting with the bulky PA chains. It can also be noted that the decomposition peak disappeared which indicates the consumption of the amino groups during the grafting process.
Synthesis of Dual Ligands-CS Conjugate (DL-CS)
Synthesis of the dual ligands-CS conjugate (DL-CS) was done following the method reported by Chen et al as shown in Figure 3A.14 Conjugation of both GA and LA onto CS was achieved by click reaction using EDC.HCl and NHS for activation of the reactants. GA was first activated through the formation of O-acylisourea ester, however such intermediate is highly unstable and rapidly reverts to the inactivated form. Accordingly, NHS was added to such reaction to stabilize the activated intermediate through the formation of a relatively more stable NHS-ester. Such intermediate greatly favors the formation of the final amines with CS and thus improves the overall efficiency of the reaction. The same mechanism with similar reaction was used for the grafting of the second targeting ligand, LA. The ratio between different reactants; LA, GA and EDC.HCl and chitosan was selected following the reported study and successful grafting was confirmed using 1H-NMR and FTIR.
 |
Figure 3 Synthesis of dual ligand-Chitosan (DL-CS): (A) Chemical illustration for the synthesis of DL-CS, (B–D) NMR spectra of CS, CS-LA, and CS-GA, respectively, (E) FTIR, and (F) DSC measurements. |
1H-NMR was used to confirm the conjugation of CS with the targeting moieties (GA and LA) as shown in Figure 3B–D. The CS spectrum showed a characteristic peak at around δ3.5 which can be attributed to the protons on C-2 of the glucosamine ring. The protons of the amino groups appeared at δ2.9 while the protons attached to C3, C4, C5 and C6 appeared as a large peak at around δ4.6. Conjugation of the LA was confirmed by the appearance of the peak at around δ3.95 which refers to the protons of the open pyranose ring linked to the CS backbone. Conjugation of the other ligand, GA can be confirmed by the appearance of the peak at δ1.8 which is attributed to the tertiary proton of C9 of the GA molecules.14,29
FTIR spectrometry was used also to confirm the synthesis of DL-CS with the spectrum shown in Figure 3E. Unmodified CS demonstrated characteristic peaks at around 1592 and 1417 cm−1 which correspond to the amide I and amide II regions, respectively, in addition to the amide III peak noted at around 1377 cm−1. Conjugation of GA was indicated by the shifting of the amide I and amide II bands to 1645 cm−1 and 1557 cm−1 with increased sharpness and intensity of the amide I peak. Conjugation of LA was in turn confirmed by the appearance of a new peak at 1740 cm−1 which can be attributed to the carbonyl groups of the ester bonds. Moreover, the intensity of the amide I peak further increased.14
The thermal properties of the synthesized DL-CS were evaluated using DSC (Figure 3F). As apparent from the figure, the GA thermogram showed a sharp endothermic peak at 305°C which corresponds to its melting point. On the other hand, LA depicted small endothermic peaks at around 69.5°C, 240°C and 267°C. The compound also showed an exothermic peak at around 296°C. The thermogram of CS-GA conjugate demonstrated a weak endothermic peak at around 110°C which corresponds to the loss of water molecules. The decreased intensity of the peak may indicate a reduction in the amount of water bound to the polymer, CS upon the GA conjugation onto its amino groups. The exothermic peak of the unmodified CS was shifted after conjugation to 236°C. The dual ligand-CS conjugate (DL-CS) in turn did not depict any clear dehydration peak which can be attributed to the decreased polarity of the polymer by the two conjugation steps. It also depicted two-step exothermic peak at around 272°C which can be attributed to the degradation of CS as well as conjugated LA.
Preparation of DOX-Loaded Dual Ligands-Decorated Core/Shell NPs
The DOX-loaded dual ligands-decorated core/shell NPs were prepared through polyelectrolyte complexation according to one of our previously published studies.7 In that study, we used electrostatic interactions to develop carrier systems to deliver DOX to the brain. The effect of various process parameters including sonication time, pH as well as homogenization time and speed on the properties of the developed nanoparticles was investigated. The optimized process parameters were used in this study for the development of the nanoparticles after performing preliminary experiments that confirmed that these conditions still apply to the new formulations using the chitosan derivatives. Accordingly, the preparation focused on the ratio between the various components of the nanoparticles using the previously obtained optimized process conditions.7
Initially, the free base of DOX was obtained by neutralization with the least amount of aqueous NaHCO3 solution. This is essential to provide the chance for DOX to interact with the graft copolymer (CMCS-g-PA) instead of being blocked by the Cl− ions. Addition of the DOX to the acidic CMCS-g-PA solution results in the protonation of DOX converting it again to the positively charged form which can then interact with the negatively charged carboxylic groups of the graft copolymer. The presence of huge number of acrylates in the pendant chains of the copolymer (CMCS-g-PA) resulted in the presence of excess of the negatively charged carboxylic groups which were then used to interact with the positively charged amino groups of the DL-CS polymer coating.7
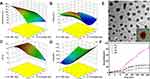
The ratio between DOX, CMCS-g-PA and DL-CS was optimized using factorial 22 experimental design as shown in Figure 4A–D. Size, charge and entrapment efficiency were set as the target criteria. The optimization process aimed at decreasing the particle size, increasing the surface positive charge and maximizing the drug entrapment efficiency. Results of the optimization experiments showed little effect on the charge of the particles which remained negative or neutral in most of the tested ratios. This can be attributed to the very high negative charge of the CMCS-g-PA attributed to the high grafting percentage (2390%) and the relatively low molecular weight of the grafted acrylate monomer. All the prepared formulations provided acceptable entrapment efficiency in the range of 80–100%. Accordingly, size was the most critical criteria for the optimization process. Smaller size of NPs below 500 nm was desired to allow efficient delivery of the particles towards the tumor site benefiting from the enhanced permeability and retention effect.30 It was also desired to avoid dropping the particle size below 150 nm since particles larger than this size were reported to inherently accumulate in the liver which would provide an additive targeting effect.31 Results showed that the optimum ratio of the NPs constituents was to use equal mass ratio of the DOX, CMC-g-PA and DL-CS. This ratio provided particle size around 274 nm as determined by DLS measurements. This size was also similar to the size obtained by HRTEM imaging (Figure 4E). The NPs seemed to have irregular boarders with electronically dense core. This may confirm the expected structure with the presence of the electron-rich DOX and CMCS-g-PA in the core of the NPs. The irregular boarders of the NPs may be explained by the fact that DL-CS is conjugated to two bulky molecules (Figure 3A) of very different structures which prevent the stacking of the polymer chains into a homogenous dense surface.
In-vitro Drug Release Profile
The prepared formulations were able to significantly sustain the release of the loaded DOX for more than 10 days (Figure 4F). The prolonged release pattern of the relatively hydrophilic drug can be attributed to the ionic interaction between the drug and its counter ion, CS-g-PA copolymer. It was also found that the presence of the two ligands in F4 increased the DOX release rate to around 85% in 10 days compared to around 20% release in the same period by the non-ligated and mono-ligated NPs (F1-F3). This effect may be attributed to two factors decreasing the integrity and increasing the breakdown of the NPs. The first factor is the conjugation of the ligands to the amino groups of CS which decreases the availability of positive charges thus decreasing the interaction between CMCS-g-PA and the DL-CS. The other factor is the steric effect of the ligands which prevents the tight stacking of the outer layer. Moreover, the integrity of the outer layer may also be affected by the difference in the hydrophobic and hydrophilic nature of the two ligands. GA is mainly hydrophobic with its five fused saturated rings and few polar groups, while LA, on the other hand, is hydrophilic with 8 hydroxyl groups and much smaller core structure. The difference in the nature of these ligands would make the packing of the outer layer more loosely and allowing faster release of the loaded drug. On the other hand, grafting of LA seems to increase the packing of the outer layer with its hydrophilic nature as well as the ability to form multiple hydrogen bonds that may have resulted in the slow release of the loaded drugs.
The release profiles of all formulations were fitted to several kinetic models like zero order, first order, Higuchi and Korsmeyer–Peppas. It was found that the suitable model for all formulations was Korsmeyer–Peppas model (r2 ranged from 0.97 to 0.99) where n (diffusional exponent value) was 0.492 and 0.388 for F1 and F2, respectively, which represents fickian diffusion model and was 0.586 and 0.616 for F3 and F4, respectively, which represents anomalous transport model. These findings confirm the effect of surface decoration on the drug diffusion mechanism from NPs matrix.32
In-vitro Cellular Uptake
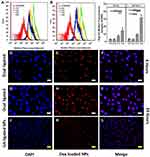
The cellular uptake of the NPs decorated with the two ligands either separately or together was evaluated using flow cytometry. The NPs were tested on HepG2 cells (Figure 5). Flow cytometry analysis of Hep-G2 control cells and cells treated with formula F1-F4 showed a significant increase in the MFI as indicated by overlaid cytometric histograms after 4 hrs and 24 hrs (Figure 5A and B). Following 4 hrs treatment with DOX-loaded NPs, all pairwise comparison showed that F4 significantly increased cellular uptake of DOX, relative to F1 (P<0.001), F2 (P<0.001) and F3 (P<0.01) (Figure 5C). After 24 hrs, there was further increase in the cellular uptake of DOX for the dual-ligand formula (F4) as indicated by the increase in the MFI to more than double its value after 4 hrs (Figure 5C). Compared with other formula, F4 was significantly higher (P<0.0001) than the other three tested formulations, F1 – F3. The LA-conjugated NPs (F3) also showed an increase in the MFI but to much less extent. The MFI for F3 was significantly higher (P<0.05) than F1 and F2. Such findings prove the ability of the dual ligands to enhance the uptake of DOX into the cells. It also indicates that LA has a certain degree of ability to enhance cellular uptake. Although the GA-ligated NPs did not show significant enhancement in cellular uptake, presence of GA ligand with the LA moieties resulted in a significant enhancement in cellular uptake. Such results indicate that GA provides a synergistic effect with LA by conditioning the cells for enhanced uptake of the LA decorated NPs. On the other hand, LA is a disaccharide that can bind to asialoglycoprotein receptors which are in turn overexpressed on Hep-G2 cells.33 Fluorescence images of cellular uptake and localization of F3 and F4 on Hep-G2 cancer cells are shown in Figure 5D–L. The reflected red fluorescence indicates the efficient cellular uptake and internalization of the DOX-loaded NPs. The nuclear localization of the developed NPs is evident in the merged images of cells stained with DOX and DAPI. As shown in images, the nuclear localization of F4 was enhanced relative to the F3 NPs. These results were in accordance with the flow cytometry results.
In-vivo Assessment of Liver Tumor Active Targeting and Anticancer Activity
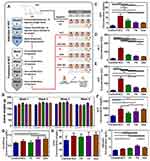
Liver tumors were induced in the wistar rats using N-nitrosodiethylamine. Tumor induction took around 18 weeks based on weekly measurement of alpha feto protein (AFP) in blood. Tumor formation was also confirmed after histopathological examination of the liver tissues in one of the rats (Figure 6A). N-nitrosodiethylamine is bioactivated in the liver by metabolism to yield O6-ethyl deoxyguanosine and O4 and O6-ethyl deoxythymidine. These products are able to form DNA adducts, eventually resulting in carcinogenesis.34 N-nitrosodiethyl has been used to induce tumors in a large number of animal species for in-vivo testing including zebra fish, mouse, rat, dog and rabbit.35 Generally, the weight of animals was also recorded. The results of such measurements are summarized in Figure 6B.
Serum Biomarkers
Serum biomarkers were also used to confirm the formation of the HCC tumor. This can be observed by the significant increase (P < 0.0001) in the AFP in the positive control (HCC induced) compared to the negative control (healthy) rats (Figure 6C). The tumor formation affected the liver functions on the macro level as can be observed by the significant increase in the concentrations of ALT (P <0.0001), AST (P < 0.0001) and ALP (P < 0.001) liver enzymes in the serum of HCC-bearing rats compared to healthy rats (Figure 6D–F). The same biomarkers were also used for monitoring of the treatment efficiency and safety in addition to histopathological examination at the end of treatment. Serum creatinine, urea and albumin were also measured to evaluate the safety of the developed formula on the kidney function (Figure 6G–I) which can be affected as a secondary damage upon use of diethylnitrosamine and CCl4 for tumor induction or as a side effect of DOX. In our study, there was no significant increase in the urea level with tumor induction or treatment. Creatinine, on the other hand, seems to increase as a side effect of the tumor induction process but there was no significant increase related to free DOX or the prepared formulations. Assessment of albumin concentration showed somehow confusing results particularly with the increased concentration as with F4. Possible explanation can be attributed to the interference caused by complexation between GA and albumin that has been reported to increase the UV-Vis absorbance.36
It can be observed that the drug-loaded NPs (F4) were able to improve significantly the levels of various biomarkers by reducing AFP, ALT and AST. Interestingly, it is noted that the blank NPs (F5) which are composed of the CMCS-g-PA and the dual-ligands CS (DL-CS) only without DOX were also able to some extent to treat the tumor and improve the serum biomarkers levels. This can be attributed to the hepatoprotective and anticancer effects of the two attached ligands as well as CS.37
Histopathological Examination
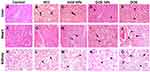
Histopathological examination is a useful tool to directly detect the effect of the developed formulations. The most favored therapy aims at eradicating tumor cells by inducing apoptosis rather than necrosis. Treatment should also allow healing of the pathological lesions and restoring normal tissue architecture. Light microscopic observation of liver in the healthy control group showed normal large polygonal cells with prominent round nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm, and few spaced hepatic sinusoids arranged between the hepatic cords with fine arrangement of Kupffer cells (Figure 7A). Histopathological alterations caused by the oncogenic lesions were observed in liver sections of the HCC group. The histopathological findings indicated that the tumors formed were of grade II according to the WHO guidelines.25 These findings included focal neoplastic polyhedral to round cells with dense, centrally located vesicular nuclei. Hepatocellular carcinomas ranged from well-differentiated to highly anaplastic undifferentiated lesions in addition to vascular degeneration of hepatocytes can be observed as indicated by the arrows. Hepatic cords were dissolved appearing as empty vacuoles aligned by strands of necrotic hepatocytes (Figure 7B). Livers of rats treated with blank carrier system (F5) revealed similar histological picture of the HCC group with massive multifocal necrosis of hepatic lobules indicated by arrows. Mononuclear cell infiltration mainly lymphocytes and macrophages are seen in Figure 7C. Congestion and dilatation of central vein and hepatic sinusoid were also noticed. Histopathological examination of liver samples for F4-treated group showed swelling of hepatocytes with hyperplasia of kuffper cells. Mononuclear cell infiltration, mainly lymphocytes and macrophages, were seen. Apoptosis of hepatocytes and numerous binucleated cells were noticed. Regenerated hepatocytes with the reorganization of hepatic cords are noticed in Figure 7D. Liver of rats treated by free DOX showed swelling of hepatocytes, disorganization of hepatic cords and hyperplasia of kuffper cells areas. Few number of apoptotic bodies were seen in-between the neoplastic cells. Mononuclear cell infiltration mainly lymphocytes and macrophages were seen. Such observations confirm the higher therapeutic efficiency of the developed formula compared to the control drug as indicated by its ability to induce apoptosis rather than necrosis. It also had the advantage of allowing regeneration of the tissues restoring the normal structure of the tissue which was not observed when rats were treated using plain DOX (Figure 7E).
The histological slide from the cardiac muscle of control healthy animals showed branching of the striated muscle that form parallel muscle fibers, centrally placed nuclei and intercalated discs (Figure 7F). Sections from untreated animals with induced HCC, cardiac muscle showed degenerative changes and mild intramuscular edema (Figure 7G). Rats treated with the blank carrier (F5) showed the same histological structure of cardiac muscle of the healthy rats without any significant disruption of cardiac muscle fibers (Figure 7H). The cardiac muscle of animals treated by F4 showed focal degenerative changes in form of swelling of muscle bundles and mild inter-muscular edema as shown in Figure 7I. On the other hand, cardiac muscle of animals treated by commercial DOX showed massive Zenker’s necrosis of cardiac muscle which appeared as deeply eosinophilic areas scattered in-between muscle bundles. Also, inter-muscular edema and hemorrhages were noticed (Figure 7J). DOX-induced cardiomyopathy is the most critical side effect of this anticancer agent. In some cases, DOX may result in fatal myocardial infarction and death. The mechanism for such effect involves the upregulation of toll-like receptor, toll-like receptor-2 and toll-like receptor-4. This consequently result in activation of nuclear factor kB which ultimately results in inflammation and necrosis of cardiac cells.38 Upon accumulation of DOX to around 500 mg/m2, the risk of fatal congestive heart failure increases to around 20%.39 Targeted F4 NPs showed better safety profile compared to the conventional DOX. This is obvious when comparing the more profound Zenker’s necrosis in the rats treated with conventional DOX to the focal necrosis observed in the rats treated with F4.
Kidney of healthy rats showed normal histological structure characterized by circumscribe glomeruli with normal structure of capillary tufts and Bowman’s capsule. The renal tubules of both proximal and distal convoluted tubules showed intact epithelial lining and arrangement scoring (0) as shown in Figure 7K. Kidney tissues of HCC rats displayed mild degenerative changes of tubular epithelial lining and presence of intratubular cellular albuminus material without significant necrosis or apoptosis scoring (1) as indicated in Figure 7L. It can be observed from Figure 7M that renal tissues from rats treated with F5 have the same histological picture of renal parenchyma of HCC animals with marked inter-tubular edema scoring (1). Rats treated by the developed DOX-loaded formula (F4) showed tubular epithelial cells degeneration with few number of necrotic tubular epithelial lining as indicated by the arrows. Some renal tubules showed intraluminal proteinaceous eosinophilic material. Tubular epithelial cell revealed necrosis and apoptosis <25% scoring (2) (Figure 7N). On the other side, kidneys of animals treated by commercial doxorubicin showed massive necrosis of tubular epithelial lining and shrinkage of glomerular tufts and widening of Bowman’s capsule. Tubular epithelial cell showed necrosis and apoptosis <75% scoring (4) as noted from Figure 7O. DOX is known to damage glomerular podocytes resulting in nephropathy and proteinuria.40 The mechanism of toxicity involves altering the normal functioning of the mitochondria through inhibiting the activity of complexes I and IV. This results in a sequence of events that eventually result in glomerulosclerosis. Such findings confirm that the higher safety of the developed targeted formula compared to the conventional DOX. The effect of such toxicity is augmented by the fact that the kidney has low regeneration ability and thus its ability for normal functioning is lost by the time when the glomeruli are damaged. Moreover, damaging the kidneys affects the whole body due to its major role in regulating the composition of blood and other body fluids.41 The results of the histopathological examination showed that our developed targeted formula loaded with DOX was safer than the conventional DOX. This was evident as the necrosis and apoptosis of the tubular epithelial cells were reduced from <75% to <25%.
Conclusion
In this study, we report the design, development and evaluation of a dual ligand-based targeted nanocarrier system for the selective delivery of chemotherapeutics to liver tumors. The developed carrier was tested in-vitro and in-vivo and showed enhanced cellular uptake as well as efficiency and safety profile compared to conventional chemotherapy. The carrier system was prepared through electrostatic interactions providing versatility for using it as a platform for targeted and selective delivery of other similar drugs through simple modifications. Our future studies will investigate the efficiency of this selective system on higher tumor grades. The effect of the charges may also be investigated using negatively charged or neutral polymers as the outer coating of the system decorated with the targeting moieties.
Disclosure
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript; this includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties; and they report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(1):7–30. doi:10.3322/caac.21332
2. Xie Z, Wang J, Liu M, Chen D, Qiu C, Sun K. CC-223 blocks mTORC1/C2 activation and inhibits human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 2017;12(3):e0173252. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0173252
3. Martindale SS. The complete drug reference London. Pharm Press J Med Libr Assoc. 2012;100:75–76. doi:10.3163/1536-5050.100.1.018
4. Chatterjee K, Zhang J, Honbo N, Karliner JS. Doxorubicin cardiomyopathy. Cardiology. 2010;115(2):155–162. doi:10.1159/000265166
5. Barenholz YC. Doxil®—the first FDA-approved nano-drug: lessons learned. J Control Release. 2012;160(2):117–134. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.03.020
6. O’Brien MER, Wigler N, Inbar M, et al. Reduced cardiotoxicity and comparable efficacy in a Phase III trial of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin HCl (CAELYXTM/Doxil®) versus conventional doxorubicin for first-line treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2004;15(3):440–449. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdh097
7. Hefnawy A, Khalil IA, El-Sherbiny IM. Facile development of nanocomplex-in-nanoparticles for enhanced loading and selective delivery of doxorubicin to brain. Nanomedicine. 2017;12(24):2737–2761. doi:10.2217/nnm-2017-0243
8. Mazzucchelli S, Truffi M, Fiandra L, Sorrentino L, Corsi F. Targeted approaches for HER2 breast cancer therapy: news from nanomedicine? World J Pharmacol. 2014;3(4):72–85. doi:10.5497/wjp.v3.i4.72
9. Shen M-Y, Liu T-I, Yu T-W, et al. Hierarchically targetable polysaccharide-coated solid lipid nanoparticles as an oral chemo/thermotherapy delivery system for local treatment of colon cancer. Biomaterials. 2019;197:86–100. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.01.019
10. Yang R, Meng F, Ma S, Huang F, Liu H, Zhong Z. Galactose-decorated cross-linked biodegradable poly (ethylene glycol)-b-poly (ε-caprolactone) block copolymer micelles for enhanced hepatoma-targeting delivery of paclitaxel. Biomacromolecules. 2011;12(8):3047–3055. doi:10.1021/bm2006856
11. Zhang J, Li C, Xue Z-Y, et al. Fabrication of lactobionic-loaded chitosan microcapsules as potential drug carriers targeting the liver. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(4):1665–1673. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2010.11.042
12. Negishi M, Irie A, Nagata N, Ichikawa A. Specific binding of glycyrrhetinic acid to the rat liver membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 1991;1066(1):77–82. doi:10.1016/0005-2736(91)90253-5
13. Zhang C, Wang W, Liu T, et al. Doxorubicin-loaded glycyrrhetinic acid-modified alginate nanoparticles for liver tumor chemotherapy. Biomaterials. 2012;33(7):2187–2196. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.11.045
14. Chen H, Li M, Wan T, et al. Design and synthesis of dual-ligand modified chitosan as a liver targeting vector. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012;23(2):431–441. doi:10.1007/s10856-011-4494-1
15. Jing F, Li J, Liu D, Wang C, Sui Z. Dual ligands modified double targeted nano-system for liver targeted gene delivery. Pharm Biol. 2013;51(5):643–649. doi:10.3109/13880209.2012.761245
16. Jeong HG, You HJ, Park SJ, et al. Hepatoprotective effects of 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury: inhibition of cytochrome P450 2E1 expression. Pharmacol Res. 2002;46(3):221–227. doi:10.1016/S1043-6618(02)00121-4
17. Salvi M, Fiore C, Armanini D, Toninello A. Glycyrrhetinic acid-induced permeability transition in rat liver mitochondria. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;66(12):2375–2379. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2003.08.023
18. Prashanth KVH, Tharanathan RN. Depolymerized products of chitosan as potent inhibitors of tumor-induced angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2005;1722(1):22–29. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2004.11.009
19. Wu H, Yao Z, Bai X, Du Y, Lin B. Anti-angiogenic activities of chitooligosaccharides. Carbohydr Polym. 2008;73(1):105–110. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.11.011
20. Li Z, Ramay HR, Hauch KD, Xiao D, Zhang M. Chitosan–alginate hybrid scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2005;26(18):3919–3928. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.09.062
21. Jayakumar R, Prabaharan M, Reis RL, Mano J. Graft copolymerized chitosan—present status and applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2005;62(2):142–158. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.07.017
22. El-Sherbiny IM. Enhanced pH-responsive carrier system based on alginate and chemically modified carboxymethyl chitosan for oral delivery of protein drugs: preparation and in-vitro assessment. Carbohydr Polym. 2010;80(4):1125–1136. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.01.034
23. Ali IH, Khalil IA, El-Sherbiny IM. Single-dose electrospun nanoparticles-in-nanofibers wound dressings with enhanced epithelialization, collagen deposition, and granulation properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(23):14453–14469. doi:10.1021/acsami.6b04369
24. Sadik NAH, EL-Maraghy SA, Ismail MF. Diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in rats: possible chemoprevention by blueberries. Afr J Biochem Res. 2008;2(3):81–87.
25. Tamura S, Kato T, Berho M, et al. Impact of histological grade of hepatocellular carcinoma on the outcome of liver transplantation. Arch Surg. 2001;136(1):25–30. doi:10.1001/archsurg.136.1.25
26. Reitman S, Frankel S. A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957;28(1):56–63. doi:10.1093/ajcp/28.1.56
27. Kind PRN, King EJ. Estimation of plasma phosphatase by determination of hydrolysed phenol with amino-antipyrine. J Clin Pathol. 1954;7(4):322. doi:10.1136/jcp.7.4.322
28. Bancroft JD, Gamble M. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques. Elsevier health sciences; 2008.
29. Geçer A, Yıldız N, Çalımlı A, Turan B. Trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles enhances dissolution of the poorly water soluble drug candesartan-cilexetil. Macromol Res. 2010;18(10):986–991. doi:10.1007/s13233-010-1004-0
30. Torchilin V. Tumor delivery of macromolecular drugs based on the EPR effect. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63(3):131–135. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2010.03.011
31. Longmire M, Choyke PL, Kobayashi H. Clearance properties of nano-sized particles and molecules as imaging agents: considerations and caveats. Nanomedicine. 2008;3:703–717. doi:10.2217/17435889.3.5.703
32. Costa P, Lobo JMS. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2001;13(2):123–133. doi:10.1016/S0928-0987(01)00095-1
33. Lin WJ, Chen TD, Liu CW, Chen JL, Chang FH. Synthesis of lactobionic acid-grafted-pegylated-chitosan with enhanced HepG2 cells transfection. Carbohydr Polym. 2011;83(2):898–904. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.08.072
34. Verna L, Whysner J, Williams GM. N-nitrosodiethylamine mechanistic data and risk assessment: bioactivation, DNA-adduct formation, mutagenicity, and tumor initiation. Pharmacol Ther. 1996;71(1–2):57–81. doi:10.1016/0163-7258(96)00062-9
35. Bogovski P, Bogovski S. Special report animal species in which n‐nitroso compounds induce cancer. Int j Cancer. 1981;27(4):471–474. doi:10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0215
36. Zhou N, Liang Y-Z, Wang P. 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid interaction with bovine serum albumin. J Photochem Photobiol a Chem. 2007;185(2–3):271–276. doi:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2006.06.019
37. Wan X, Luo M, Li X, He P. Hepatoprotective and anti-hepatocarcinogenic effects of glycyrrhizin and matrine. Chem Biol Interact. 2009;181(1):15–19. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2009.04.013
38. Tacar O, Sriamornsak P, Dass CR. Doxorubicin: an update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and novel drug delivery systems. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2013;65(2):157–170. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.2012.01567.x
39. Sakata Y, Dong J-W, Vallejo JG, et al. Toll-like receptor 2 modulates left ventricular function following ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;292(1):H503–H509. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00642.2006
40. Okuda S, Oh Y, Tsuruda H, Onoyama K, Fujimi S, Fujishima M. Adriamycin-induced nephropathy as a model of chronic progressive glomerular disease. Kidney Int. 1986;29(2):502–510. doi:10.1038/ki.1986.28
41. Carvalho C, Santos RX, Cardoso S, et al. Doxorubicin: the good, the bad and the ugly effect. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(25):3267–3285. doi:10.2174/092986709788803312
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.