Back to Journals » Clinical Ophthalmology » Volume 15
Comparison of Safety and Efficacy Between Ab Interno and Ab Externo Approaches to XEN Gel Stent Placement
Authors Tan NE , Tracer N, Terraciano A, Parikh HA, Panarelli JF, Radcliffe NM
Received 29 November 2020
Accepted for publication 8 January 2021
Published 26 January 2021 Volume 2021:15 Pages 299—305
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S292007
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Nicholas E Tan,1 Nathaniel Tracer,2 Anthony Terraciano,3 Hardik A Parikh,2 Joseph F Panarelli,2 Nathan M Radcliffe4,5
1College of Medicine, State University of New York Downstate Health Sciences University, Brooklyn, NY, USA; 2Department of Ophthalmology, NYU Langone Health, New York, NY, USA; 3College of Arts and Sciences, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, USA; 4Department of Ophthalmology, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, NY, USA; 5New York Eye Surgery Center, Bronx, NY, USA
Correspondence: Nathan M Radcliffe
New York Eye Surgery Center, 1101 Pelham Parkway North, Bronx, NY, USA
Tel +1 718 519 1000
Email [email protected]
Purpose: To compare the safety and efficacy of two different techniques for implantation of the XEN Gel Stent, a minimally invasive surgical device for the treatment of refractory glaucoma.
Methods: A retrospective chart review of eyes that received ab interno or ab externo XEN Gel Stent placement from February 2017 to October 2019 was conducted. A single surgeon (NMR) performed all operations. Eyes that received the XEN implant concomitant with a glaucoma drainage device insertion or that were lost to 6-month follow-up were excluded. Intraocular pressure (IOP) change, change in glaucoma medications, frequency of slit lamp revision procedures, and frequency of secondary glaucoma surgeries were the primary outcomes compared between groups.
Results: Fifty eyes that underwent ab interno placement and 30 eyes that underwent ab externo placement were studied. The ab interno cohort demonstrated a mean IOP reduction of 8.4 ± 1.7 mmHg (28.6% decrease) by 12 months, compared to a mean reduction of 12.8 ± 3.0 mmHg (40.1% decrease) in the ab externo group (p = 0.208). Mean reduction in medication use was 1.81 ± 0.29 medications in the ab interno group and 1.86 ± 0.37 in the ab externo group (p = 0.913). By 12 months, 58% of ab interno eyes had required 5-fluorouracil injection compared to 36.7% of ab externos (p = 0.105). Bleb needling was applied to 42% and 26.7% of the eyes, respectively (p = 0.231). A second glaucoma surgery was necessary for 20% of the ab interno cohort and 10% of the ab externo cohort (p = 0.351).
Conclusion: There were no differences in outcomes between ab interno and ab externo placement of the XEN Gel Stent. Both approaches are safe and effective for lowering IOP.
Keywords: MIGS, glaucoma surgery, bleb, subconjunctival stent, surgical technique
Introduction
By 2040, there will be an estimated 111.8 million people worldwide with glaucoma.1 At present, the primary method of treatment is to reduce intraocular pressure (IOP) in order to prevent loss of retinal nerve fibers and subsequent damage to the visual field. One option to control IOP is minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS). MIGS devices are growing in popularity due to their general ease of use, short surgical recovery times, and relatively reasonable safety profiles.2 Though MIGS mechanisms vary, some approaches include trabecular meshwork reshaping, trabecular meshwork stenting, and subconjunctival stenting. The device of interest to this study, the XEN Gel Stent (Allergan, an Abbvie company, Irvine, CA, USA), is an example of a subconjunctival stent. The XEN is a 6 mm long hydrophilic tube with an internal diameter of 45 µm that creates a permanent channel through the sclera, allowing for controlled passage of aqueous humor from the anterior chamber to the subconjunctival space. By adding a new outflow route, the XEN Gel Stent decreases the accumulation of aqueous humor and lowers IOP.3
The XEN Gel Stent FDA pivotal trial describes an ab interno placement via a clear corneal incision3 and several other studies use this same ab interno approach, but without conjunctival dissection.3–6 However, as surgeons gain experience with the gel stent they are finding other implantation techniques that may be beneficial for the surgeon and the patient, depending on the individual circumstances. Two papers were recently published that detail different techniques using both ab interno and ab externo approaches, with and without conjunctival dissection.7,8 The authors of this paper sought to compare the outcomes of the most commonly reported closed conjunctiva, ab interno placement technique, with an open conjunctiva, ab externo approach that has been adopted by the operating surgeon (NMR). This retrospective chart review compares the outcomes using these two different techniques.
Methods
IRB exemption for this retrospective digital chart review was obtained from Sterling IRB (Atlanta, GA). All data collection was performed confidentially, following the minimum necessary standard, in such a manner that the subjects’ identities could not be ascertained directly or indirectly. Patient consent to retrospectively review medical records was not required by the IRB because all data were anonymized, and the investigators did not contact or re-identify the subjects for any purposes pertaining to this study. Conduct of the study was performed in accordance with the standards of the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments.
Consecutive patients who underwent XEN Gel Stent implantation by a single surgeon (NMR) from February 2017 to October 2019 were included for analysis. All patients had a diagnosis of open-angle glaucoma and had uncontrolled IOP, progressing glaucoma, and/or an intolerance to topical hypotensive drops. Exclusion criteria included eyes that received a glaucoma drainage device concomitant with XEN Gel Stent insertion and eyes that were lost to follow-up before 6 months. For the first 11 months, the surgeon used an ab interno approach described in other papers.3–6 Following topical anesthesia and proper field dressing, a 1.8 mm corneal incision was made in the inferotemporal quadrant along with a 1 mm superotemporal stabilizing incision. The anterior chamber was then filled with a highly cohesive viscoelastic. A preloaded injector needle was inserted through the inferotemporal incision and across the anterior chamber and implanted in the superonasal quadrant. Viscoelastic was then removed from the anterior chamber. At the completion of the gel stent placement, 40 micrograms of mitomycin-C (MMC) was injected beneath the superior conjunctiva at least 6 mm from the limbus.
The subsequent surgeries were performed using an open conjunctiva, ab externo technique, similar to one described by Panarelli et al.7 The ab externo technique in this study employed a 3 mm wide fornix-based conjunctival peritomy and did not require viscoelastic injection or a corneal incision. Following dissection and cautery of the scleral vessels, sponges soaked in 0.4 mg/mL of MMC were applied to the sclera underneath the peritomy for 2 minutes, followed by copious irrigation. The gel stent was then placed through the sclera and into the anterior chamber using the gel stent injector system. Finally, the conjunctiva was closed at the limbus with two 10-0 nylon wing sutures.
The following information was obtained at the preoperative visit: age, sex, race, left or right eye, concomitant surgery with cataract extraction, Snellen best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), intraocular pressure (IOP), visual field mean deviation (VFMD), number of glaucoma medications, corneal hysteresis (CH), and central corneal thickness (CCT). CH was measured using the Reichert Ocular Response Analyzer and CCT values were sourced from pachymetry. VFMD was obtained using the 24-2 algorithm of the Humphrey Visual Field Test. IOP was measured using Goldmann applanation tonometry. Glaucoma medications were counted as the number of individual hypotensive molecules or oral acetazolamide. For instance, if an eye was prescribed acetazolamide tablets and dorzolamide-timolol drops, three medications would be counted for that eye.
Number of glaucoma medications and IOP values were obtained postoperatively at 1 day, 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year. Final Snellen BCVA for each eye was noted and compared to baseline. Furthermore, 5-fluorouracil (5FU) injections, transconjunctival needle bleb revisions, and secondary glaucoma surgeries were logged when they occurred. In this retrospective study, there were no rigid criteria for 5FU or bleb revision at the slit lamp. However, the treating physician gave 5FU injections for the purpose of inhibiting fibrosis and performed bleb revisions when IOP was trending upwards in the presence of a shrinking or fibrosing bleb.
Events of numerical hypotony and choroidal effusion were also documented. Numerical hypotony was defined as two consecutive measurements of IOP < 6 mmHg during any time in the follow-up period.
All statistical analysis was performed using Microsoft Excel 2016 and StataSE 16 software. For eyes that required additional glaucoma surgery during the follow-up period, IOP and medication values were censored at timepoints after the subsequent surgery to limit confounding. Two-sided unpaired Student’s t-tests were used to compare mean IOP and glaucoma medication values. Multivariable regression analysis was performed to examine the effect of baseline values on mean IOP change in the overall sample. Lastly, hypotony, choroidal effusions, and BCVA loss of two Snellen lines or more from baseline between groups were each evaluated using Fisher’s exact test. Standard deviations were calculated for the baseline averages in Table 1, while standard errors were calculated for mean IOP and glaucoma medication changes. A p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
 |
Table 1 Baseline Characteristics of XEN Gel Stent Eyes |
Results
Fifty eyes in the ab interno cohort and 30 eyes in the ab externo cohort were included in this study and had follow-up data to 6 months. Of those 80 eyes, 45 eyes in the ab interno group (90%) and 24 eyes in the ab externo group (80%) had data to 12 months. Baseline characteristics are reported in Table 1.
There were no statistically significant differences between cohorts for any of the recorded preoperative values. The ab externo cohort included a higher percentage of Hispanic/Latino eyes and African American eyes compared to the ab interno cohort, which had a relatively higher percentage of White and Asian eyes. The ab externo cohort also had a higher percentage of females (70%) compared to the ab interno cohort (48%). XEN Gel Stent surgery was combined with cataract extraction in eight cases (10%) of the total sample. Mean preoperative IOP (23.52 vs 26.53), current glaucoma medications (3.70 vs 4.07), VFMD (−16.08 vs −16.87), and CCT (527.15 vs 532.00) were each slightly lower in the ab interno cohort versus the ab externo cohort.
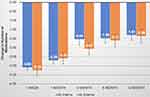
After censoring for secondary glaucoma surgery, 36 ab interno eyes and 21 ab interno eyes were eligible for 12-month data analysis (Table 2). By 12 months, the mean IOP change was −8.4 ± 1.7 mmHg (−28.6%) in the ab interno group and −12.8 ± 3.0 mmHg (−40.1%) in the ab externo group, respectively (Figure 1; p = 0.208). Glaucoma medication use decreased by 1.81 ± 0.29 (−45.3%) and by 1.86 ± 0.37 (−50.8%), respectively (Figure 2; p = 0.913). Differences in both IOP changes and glaucoma medication changes throughout the follow-up period were not statistically significant (Figures 1 and 2). Furthermore, differences in mean IOP measurements at each visit were not significant (Table 2).
 |
Table 2 Mean IOP in XEN Gel Stent Eyes During Follow-Up |
Multivariable regression analysis revealed that a higher baseline IOP was significantly associated (p < 0.001) with greater mean IOP reduction by 12 months. Age, baseline number of medications, CCT, and CH were the other remaining variables included in the combined regression, and none were found to be significantly associated with 12-month IOP reduction.
Postoperative bleb needling and 5FU injections were performed with greater frequency in the ab interno group compared to the ab externo cohort, but the differences did not reach statistical significance (Table 3). A higher rate of reoperation for glaucoma was observed in the ab interno group (20%) compared to the ab externo group (10%) (Table 4). The 13 total additional glaucoma surgeries consisted of Ahmed Glaucoma Valves, Baerveldt Glaucoma Implants, trabeculectomy, transscleral cyclophotocoagulation, and a second XEN Gel Stent in the same eye.
 |
Table 3 5FU and Bleb Needling During Follow-Up of XEN Gel Stent Eyes |
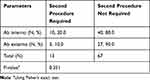 |
Table 4 Second Glaucoma Procedure During Follow-Up of XEN Gel Stent Eyes |
Complications included numerical hypotony, choroidal effusion, and loss of BCVA (Table 5). Both groups had similar rates of numerical hypotony, with a 3.8% incidence of this finding overall. Two eyes in the ab interno group developed choroidal effusions, both of which resolved with medical management. There were no cases of hypotony maculopathy, shallow anterior chamber, or implant extrusion/erosion. Eight eyes in the overall sample experienced vision reduction of two Snellen lines or more by the end of follow-up, with identical rates between groups. Cataract formation accounted for two cases in the ab interno group and a single case in the ab externo group. Glaucomatous progression was the most likely reason for vision loss in the remaining five eyes. Notably, of those five eyes, one in the ab interno group had a baseline VFMD of −28.01 and two in the ab externo group had baseline VFMDs of −31.91 and −32.80. These deficits are close to double the average for their respective surgery groups at baseline. The two remaining eyes that lost vision were in the ab interno group and did not have significant VFMD deficits. These two eyes had poorly controlled IOP by the end of follow-up, with readings of 25 mmHg and 31 mmHg. None of the differences in adverse events between the ab interno and ab externo groups met significance.
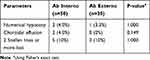 |
Table 5 Adverse Events During Follow-Up of XEN Gel Stent Eyes |
Discussion
Ab externo XEN Gel Stent placement is becoming increasingly popular among ophthalmic surgeons. However, to the authors’ knowledge, there have been few clinical studies comparing the safety and efficacy of ab interno and ab externo techniques. This retrospective analysis demonstrates that an ab externo, open conjunctiva gel stent placement is similar in safety and efficacy to an ab interno, closed conjunctiva technique. Reduction in IOP and glaucoma medications were similar in magnitude between groups, or trended towards superiority in the ab externo cohort. Multivariable regression revealed that for the overall sample, a higher baseline IOP was predictive of greater IOP reduction following XEN Gel Stent implantation, as has been found in some other glaucoma device studies.9,10 In contrast, a recent prospective trial of a trabecular microbypass stent combined with cataract surgery revealed that preoperative IOPs above 26 mmHg were associated with less IOP reduction.11 The authors proposed that collapsed collector channels secondary to high IOP contributed to the decreased effectiveness. Since the XEN Gel Stent creates a new outflow tract separate from the trabecular meshwork, collector channel collapse may not have had the same effects in the current study. It may even be possible that collector channel collapse encouraged more flow through the subconjunctival stent, explaining why IOP control was greater for XEN eyes with high preoperative pressures. The non-significant 4.4 mmHg advantage in 12-month IOP reduction for eyes in the ab externo group was possibly a byproduct of that cohort having a higher mean baseline IOP.
Safety profiles were also similar and favorable for both techniques. Vision loss of two lines or more occurred in 10% of the full sample. This is reasonable given that most of the eyes with vision loss either developed a visually significant cataract or had advanced glaucomatous progression prior to surgical intervention. Overall, the ab externo and ab interno implants were well tolerated.
The difference in the incidence of bleb revisions and secondary surgeries was comparable and non-significant but trended towards superiority in the ab externo cohort. Our results are similar to those reported by Gallardo et al,12 who found no significant differences between eyes that underwent ab interno placement and eyes that underwent ab externo placement of the XEN Gel Stent. In contrast, Purgert et al13 did note a statistically significant difference (p = 0.002) between techniques in terms of needling, with ab externo placement resulting in less need for needling. For the current study, it is possible that a larger sample size may have provided the power to elucidate a statistically relevant difference in postoperative needling or antimetabolite usage. More uniform criteria on when to perform bleb revisions may also have yielded different results. Some surgeons believe that the ab externo approach allows for better immediate visualization of the implant and greater perioperative control of stent placement, possibly leading to more optimal bleb morphology. While we could not verify such a claim in this study, our results do not definitively preclude the possibility of the ab externo approach having a clinically relevant bleb advantage.
Another interesting finding regarding the overall sample was that baseline corneal hysteresis was not associated with the degree of IOP control conferred by XEN Gel Stent placement. This contrasts with the effects of corneal hysteresis on the magnitude of IOP reduction seen in other studies with prostaglandin drops or selective laser trabeculoplasty.14,15 Lower baseline corneal hysteresis is significantly associated with greater IOP reduction with both of these treatment modalities. This discrepancy may suggest that corneal hysteresis does not have an effect on bleb morphology.
The advantages of this study include the racial diversity of the patient population, the comprehensive baseline parameters obtained, and the clinical pertinence of our endpoints for both ophthalmologists and their patients. The principal disadvantages of the study include the retrospective nature and limited sample size. Eighty percent of the ab externo group and 90% of the ab interno group had follow-up data to 12 months. Had the remaining eyes been available for 12-month follow-up data, it is possible that the additional numbers would have allowed the differences between groups to reach statistical significance.
Another disadvantage of this study is that it does not account for the differences in technique proficiency with time. It is possible, for instance, that differences between ab interno and ab externo safety profiles would change if the operating surgeon had a similar depth of experience with the ab externo approach as he had with the ab interno approach prior to this dataset being compiled. Furthermore, perioperative MMC delivery method varied between groups. Ab internos received MMC injection, while ab externos received MMC sponge. A recent prospective study comparing these two MMC delivery techniques in trabeculectomies revealed no significant differences in IOP control, surgical success, medication reduction, bleb morphology, or complications.16 Trabeculectomy is similar to the XEN Gel Stent in that both create subconjunctival blebs. Based on current knowledge, it is unclear if MMC delivery method (needle or sponge) would significantly impact IOP control in the XEN Gel Stent. It is an important feature of this current study that the method of MMC application was not identical between groups, but further research is warranted to determine if the method truly modifies XEN outcomes.
Conclusion
Overall, there were no differences in outcomes between the ab interno and ab externo groups. No statistically significant differences were found in terms of IOP control, medication reduction, slit lamp procedures, secondary glaucoma surgeries, or adverse events. The results of this chart review support the use of either ab externo or ab interno insertion of the XEN Gel Stent from the standpoints of safety and glaucoma management. Of course, physician comfort and individual surgical circumstances may dictate which technique is used in practice. There is a need for further, prospective studies that utilize multiple surgeons and a greater sample size to more definitively compare the safety and efficacy of the two approaches.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Adrianne S Resek for her assistance with reviewing and editing the manuscript.
Disclosure
Nathan M Radcliffe reports personal fees from Allergan during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Alimera, Aerie, Eyenovia, Equinox, Eyepoint, Glaukos, Ivantis, New World Medical, Bausch & Lomb, Beaver Visitec, Carl Zeiss Meditec, Alcon, Sight Sciences, Spyglass, Iridex, Lumenis, Novartis, Thea, Reichert, Shire, and Ocular Therapeutix, outside the submitted work. Joseph F Panarelli reports personal fees from Aerie, CorneaGen, Glaukos, Santen, New World Medical, and Allergan, outside the submitted work. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Tham YC, Li X, Wong TY, et al. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2014;121(11):2081–2090. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.05.013
2. Lavia C, Dallorto L, Maule M, Ceccarelli M, Fea AM. Minimally-invasive glaucoma surgeries (MIGS) for open angle glaucoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2017;12(8):e0183142. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0183142
3. XEN® Gel Stent. Directions for use. Allergan; 2017. Available from: https://allergan-web-cdn-prod.azureedge.net/actavis/actavis/media/allergan-pdf-documents/labeling/xen/dfu_xen_glaucoma_treatment_system_us_feb2017.pdf.
4. Schlenker MB, Gulamhusein H, Conrad-Hengerer I, et al. Efficacy, safety, and risk factors for failure of standalone ab interno gelatin microstent implantation versus standalone trabeculectomy. Ophthalmology. 2017;124:1579–1588. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2017.05.004
5. Lenzhofer M, Kersten-Gomez I, Sheybani A, et al. Four-year results of a minimally invasive transscleral glaucoma get stent implantation in a prospective multi-centre study. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2018;47(5):581–587. doi:10.1111/ceo.13463
6. Mansouri K, Guidotti J, Rao HL, et al. Prospective evaluation of standalone XEN gel implant and combined phacoemulsification-XEN gel implant surgery: 1-year results. J Glaucoma. 2018;27(2):140–147. doi:10.1097/IJG.0000000000000858
7. Panarelli JF, Yan DB, Francis B, Craven ER. XEN gel stent open conjunctiva technique: a practical approach paper. Adv Ther. 2020;37:2538–2549. doi:10.1007/s12325-020-01278-1
8. Vera V, Gagne S, Myers JS, Ahmed IIK. Surgical approaches for implanting XEN gel stent without conjunctival dissection. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020;14:2361–2371. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S265695
9. Neiweem A, Bussel II, Schuman JS, et al. Glaucoma surgery calculator: limited additive effect of phacoemulsification on intraocular pressure in ab interno trabeculectomy. PLoS One. 2016;11(4):e0153585. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0153585
10. Singh IP Prospective, randomized, multicenter clinical investigation of the Glaukos iStent inject.
11. Konopińska J, Kozera M, Kraśnicki P, Mariak Z, Rękas M. The effectiveness of first-generation iStent microbypass implantation depends on initial intraocular pressure: 24-month follow-up-prospective clinical trial. J Ophthalmol. 2020;2020:8164703. doi:10.1155/2020/8164703
12. Gallardo M, Porter M, Vincent L, Garza A, Kheirkhah A Outcomes following implantation of an anterior segment drainage device (Xen45 Gel stent) via an ab-interno or ab-externo approach in patients with uncontrolled open angle glaucoma.
13. Purgert RJ, Lin MM, Mehran N, Zakaria S, Lee D, Myers JS Outcomes of ab interno versus ab externo XEN gel stent implantation.
14. Agarwal DR, Ehrlich JR, Shimmyo M, Radcliffe NM. The relationship between corneal hysteresis and the magnitude of intraocular pressure reduction with topical prostaglandin therapy. Br J Ophthalmol. 2012;96(2):254–257. doi:10.1136/bjo.2010.196899
15. Hirneiß C, Sekura K, Brandlhuber U, Kampik A, Kernt M. Corneal biomechanics predict the outcome of selective laser trabeculoplasty in medically uncontrolled glaucoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013;251(10):2383–2388. doi:10.1007/s00417-013-2416-2
16. Do JL, Xu BY, Wong B, et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing subconjunctival injection to direct scleral application of Mitomycin C in trabeculectomy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2020;220:45–52. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2020.07.002
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.