Back to Journals » Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management » Volume 12
Clinical utility of nivolumab in the treatment of advanced melanoma
Authors Asmar R, Yang J, Carvajal RD
Received 12 October 2015
Accepted for publication 21 December 2015
Published 26 February 2016 Volume 2016:12 Pages 313—325
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S78039
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Garry Walsh
Ramsey Asmar,1 Jessica Yang,1 Richard D Carvajal1,2
1Department of Medicine, College of Physicians and Surgeons, 2Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA
Abstract: Melanomas are highly immunogenic tumors that evade the immune system by exploiting innate checkpoint pathways, rendering effector T-cells anergic. The immunotherapeutic approach of checkpoint inhibition can restore and invigorate endogenous antitumor T-cell responses and has become an important treatment option for patients with advanced melanoma. The CTLA-4 inhibitor ipilimumab and the PD-1 inhibitors nivolumab and pembrolizumab have been shown to induce durable responses and improve overall survival in metastatic, refractory melanoma. Optimization and validation of pretreatment biomarkers to predict response to these agents is a crucial area of ongoing research. Combination immunotherapy has recently demonstrated superior response rates compared to monotherapy; further investigation is needed to refine combinatorial strategies.
Keywords: nivolumab, immune checkpoint inhibitors, PD-1, melanoma
Introduction
Immunotherapy has recently emerged as the cornerstone of treatment for advanced melanoma, whereby it has significantly improved both quality and length of life for patients with this historically refractory disease (Figure 1).1–7 A refined understanding of T-cell regulatory pathways has led to the development of a novel class of agents known as immune checkpoint inhibitors. These antibodies have the potential to induce durable disease responses in a subset of patients who previously had limited meaningful treatment options. The prototype checkpoint inhibitor ipilimumab, a monoclonal antibody directed against CTLA-4, is distinguished as the first-ever therapy to demonstrate improved overall survival (OS) in metastatic melanoma, earning US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for this population in 2011.8 Two additional inhibitors, nivolumab and pembrolizumab, both targeting the programmed death (PD)-1 pathway, were subsequently approved for the same indication in late 2014.9 Indeed, the remarkable efficacy of these agents in advanced melanoma has set the stage for immunotherapy to become the next great pillar of cancer care, as the paradigm of checkpoint inhibition is now expanding to other tumor types. Despite these successes, immunotherapy responders still represent a minority of patients. Attempts are being made to improve the activity of checkpoint monotherapy with novel combinatorial strategies and to better identify potential responders with biomarker optimization. Here, we provide a brief overview of the current treatment landscape in advanced melanoma, followed by an in-depth review of the PD-1 inhibitor nivolumab and its clinical utility in the metastatic setting.
  | Figure 1 One-year overall survival for patients with advanced-stage melanoma. |
Historical perspective
Historically, advanced melanoma has been associated with a dismal prognosis and limited treatment options. Systemic chemotherapy has been the mainstay of treatment for many years, with surgery and radiation playing more limited roles (primarily for palliation of symptomatic metastases). Unfortunately, the disease is relatively refractory to cytotoxic therapy, with response rates as low as 10%–15%, the majority of which are nondurable.10 The alkylating agent dacarbazine, approved by the FDA for metastatic melanoma in 1975, remained the standard of care through 2011 despite the absence of a survival benefit.1 As our knowledge of melanoma pathogenesis improved, treatment options began to expand (Figure 1). Oncogenic mutations driving disease progression were discovered, notably BRAF V600 mutations (first identified in 2002), which are present in 40%–50% of cases.11,12 The development of novel small molecule inhibitors that selectively target mutant BRAF, eg, vemurafenib and dabrafenib, resulted in significant objective responses and markedly improved survival compared with chemotherapy in BRAF V600E-positive melanoma patients.13,14 Targeted approaches have also been elucidated for other genetically defined melanoma subsets, such as those harboring KIT mutations.15,16 Unfortunately, the majority of patients treated with BRAF inhibitors demonstrate disease progression within 1–2 years due to a wide range of resistance mechanisms. Acquired resistance most frequently develops through reactivation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, yielding a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 6–8 months.17,18 Furthermore, anti-BRAF monotherapy leads to secondary skin cancers in some cases due to paradoxical MAPK pathway activation in BRAF wild-type cells.19 These observations led to the development of trametinib, a selective inhibitor of the downstream signaling kinase MAPK kinase (MEK).20 In an effort to mitigate the development of resistance to BRAF monotherapy, attention then shifted to combined BRAF/MEK inhibition. In a Phase III clinical trial that compared dabrafenib plus trametinib to vemurafenib alone, combination therapy resulted in superior objective response rate (ORR, 64% vs 51%), median PFS (11.4 vs 7.3 months; P<0.001), and OS (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.59; P=0.005), as well as producing dramatically fewer squamous cell skin cancers (1% vs 19%).4 These data established combined BRAF/MEK inhibition as standard first-line therapy for BRAF V600-mutant melanoma. However, effective options remain limited for patients with wild-type BRAF tumors, as well as for those who progress on targeted therapy.
Rationale for immunotherapy
Immunotherapeutic approaches for advanced melanoma have been developed in parallel with the genetically targeted agents described herein. It has long been understood that the human immune system is capable of recognizing malignant cells as foreign due to an accumulation of genetic and epigenetic changes during tumorigenesis and cancer growth. In fact, malignant melanoma is considered one of the most immunogenic tumors, exhibiting a strikingly high somatic mutation burden on account of chronic mutagen exposure (ie, ultraviolet light).21 This characteristic mutational signature results in high prevalence of neoantigens – novel, tumor-specific protein sequences. In theory, endogenous T-cell tolerance to neoantigens should not develop because these peptides do not exist in the normal human genome. Indeed, the presence of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in primary melanomas and metastatic lesions suggests that a natural immune response exists, though this finding does not appear to correlate with a clinically significant antitumor effect.22,23 This important observation suggests that the tumor is capable of evading immunosurveillance via mechanisms of adaptive immune resistance. To this end, immunoevasion has been described as one of the “hallmarks of cancer”.24
Early attempts to modulate the immune system against melanoma were varied and relatively ineffective. These approaches included cancer vaccines, administration of cytokines, and immune cell-based therapies. While such strategies yielded detectable immune responses in some patients, this was merely a surrogate end point; clinical tumor regression was exceedingly low, presumably due to dominant immunosuppressive pathways mediated by the cancer itself. In 1998, the FDA approved interleukin-2 (IL-2) as an immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma based on benefit seen in a small subset of patients. High-dose IL-2 is a potent T-cell growth factor that induces objective responses in ~15%–20% of patients, with 6%–8% of patients experiencing durable complete remissions.2,25 However, high-dose IL-2 has significant toxicity and can be safely administered only in large centers and to patients with excellent performance status (PS). Intensive supportive care is often needed for transient capillary leak syndrome, resulting in hypotension, oliguric renal insufficiency, and in some cases respiratory failure. Randomized comparisons of IL-2 with other treatments have not been possible for this reason, and thus its impact on OS is not well established. Nonetheless, IL-2 remains an appropriate treatment option in carefully selected, high-PS patients with intact organ function.
The large breakthrough that brought immunotherapy back to center stage came on the heels of a major paradigm shift in the late 2000s. Previous strategies had involved stimulating the immune system to recognize specific antigens on tumor cells, thereby generating an antitumor T-cell response. With advances in our understanding of tumor microenvironments and T-cell regulation, a new approach to block inhibitory pathways responsible for downregulating T-cell responses emerged. These so-called “checkpoint” pathways are hardwired into the human immune system for maintenance of self-tolerance. Such regulation of immune response duration and amplitude is necessary to minimize tissue damage during inflammatory and infectious processes. We now recognize that tumor cells are capable of exploiting this checkpoint system as a means of escaping immune detection, part of a process known as cancer immunoediting.
Immune responses and checkpoint pathways
T-cells are activated when the T-cell receptor (TCR) recognizes tumor antigens bound to major histocompatibility complex proteins on antigen-presenting cells (APCs). This interaction leads to differentiation of T-cells into antitumor effectors that are capable of destroying cancer cells expressing the cognate antigen. An additional costimulatory signal is also necessary for T-cell activation, which is provided by the interaction between CD28 (on the T-cell) and B7 proteins (CD80 or CD86 on APCs). Once activated, T-cells upregulate inhibitory (checkpoint) molecules, which attenuate and eventually terminate the T-cell response. Two major inhibitory pathways (CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1) have been well defined and provide targets for checkpoint blockade. CTLA-4 inhibition is only briefly described here; the remainder of the review focuses on the PD-1 inhibitor nivolumab.
CTLA-4 pathway
CTLA-4 delivers a negative modulatory signal during the activation stage of the immune response, generally in the lymph node. It is expressed exclusively on T-cells and is homologous to CD28 but has a much higher affinity for the B7 ligands. After T-cell activation, CTLA-4’s membrane density increases until it eventually outcompetes CD28, abrogating the T-cell response. It also provides a direct inhibitory signal to CD8+ T-cells and enhances the immunosuppressive function of regulatory T-cells (Tregs), in which it is expressed constitutively. CTLA-4 blockade results in enhanced T-cell proliferation, diversification of the TCR repertoire in circulation, and ultimately stimulation of an endogenous antitumor T-cell response.
Ipilimumab is a monoclonal antibody that blocks the CTLA-4 receptor. It was approved for advanced melanoma in 2011 based on two randomized Phase III clinical trials, both of which demonstrated OS improvement in the ipilimumab arm. The first study randomized 676 pretreated patients to one of three arms: ipilimumab + gp100 peptide vaccine, ipilimumab alone, or gp100 alone. Median OS was 10.0 and 10.1 months in the ipilimumab-containing arms vs only 6.4 months in the gp100-only arm (HR: 0.68, P<0.003).3 Objective responses were also significantly higher for those who received ipilimumab. In the second Phase III trial, 502 patients with treatment-naïve advanced melanoma were randomized to ipilimumab + dacarbazine chemotherapy or dacarbazine alone. OS with the combination was 11.2 vs 9.1 months in the control arm, and survival at 3 years was 20.8% vs 12.2% (HR for death: 0.72, P<0.001).26 Due to a high incidence of adverse events in the combination arm (and an unclear benefit with dacarbazine), further development of this combination was not pursued. However, ipilimumab alone is an appropriate first-line option for patients with metastatic melanoma (with or without BRAF mutations). Long-term follow-up data from these early ipilimumab trials are now maturing, with 5-year survival rates of ~20%.
PD-1 pathway
PD-1 is another checkpoint molecule that plays a critical role in T-cell regulation. Unlike CTLA-4, the PD-1 pathway inhibits T-cell activity in peripheral tissues at the time of an inflammatory response. This suppresses harmful autoimmunity and reduces collateral tissue damage under normal circumstances, but this also inhibits effective immune activation within the tumor microenvironment.27,28
PD-1 is a 55 kDa type 1 transmembrane protein encoded by the PDCD1 gene. The protein is a member of the CD28 family of T-cell co-receptors and is composed of an extracellular immunoglobulin (Ig) domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular domain that contains phosphorylation sites. PD-1 is broadly expressed on hematopoietic cells, including CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells, Tregs, natural killer cells, B-cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells (DCs); its expression is upregulated by antigen receptor or cytokine signaling.27 PD-1 has two known ligands: PD-L1 (B7-H1, CD274) and PD-L2 (B7-DC, CD273). Although PD-L2 binds to PD-1 with a threefold higher affinity, PD-L1 has broader expression and has been studied more extensively as both a target and a potential biomarker for response to anti-PD-1 therapy. PD-L1 is expressed on a wide range of solid tumors, including 25%–50% of melanomas (when using a 5% threshold for PD-L1 positivity).29–34
PD-1 engagement with its ligands leads to tyrosine phosphorylation, recruitment of phosphatases, and subsequent dephosphorylation of adjacent signaling molecules. This results in downstream inhibition of the Ras and PI3K/Akt pathways, which in turn reduces T-cell proliferation and survival.35,36 PD-1 signaling inhibits expression of the cell survival factor Bcl-xL and transcription factors associated with effector T-cell function.37,38 The PD-1 pathway has a well-documented role in controlling downstream T-cell effector responses in the periphery to minimize immune-mediated tissue damage during an inflammatory response, and it may additionally regulate T-cell priming and early fate decisions of CD8+ T-cells. During states of chronic antigen exposure (as seen with chronic viral infection and malignancies), persistent high-level PD-1 expression can eventually induce a state of exhaustion among cognate antigen-specific T-cells – a phenomenon known as T-cell anergy – ultimately shifting the immune balance from activation to tolerance. Anergy appears to be at least partially reversible via PD-1 blockade.39 PD-1 may also weaken the interaction between T-cells and APCs. In vitro blockade of PD-L1 results in greater duration of stable contact between T-cells and DCs.40
There are currently two FDA-approved PD-1 inhibitors for advanced melanoma: nivolumab and pembrolizumab. This review focuses primarily on nivolumab. Of note, both agents are approved for use after progression on ipilimumab (and for BRAF-mutated melanoma, after progression on a BRAF inhibitor). However, considering the demonstrated activity of anti-PD-1 antibodies in the frontline setting, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines include the use of anti-PD-1 antibodies as a treatment option for patients with newly diagnosed disease.
PD-1 inhibition with nivolumab
Nivolumab (formerly ONO-4538, Ono Pharmaceutical, Osaka, Japan; or MDX-1106, BMS-936558, Bristol Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ, USA) is a fully human monoclonal IgG4 antibody that binds PD-1 with high affinity and prevents its interaction with PD-L1 and PD-L2. Nivolumab was developed by immunizing mice transgenic for human Ig loci with recombinant PD-1/human IgG1 Fc fusion protein and Chinese hamster ovary cells expressing human PD-1. Spleen cells from immunized mice were subsequently fused with SP2/0 myeloma cells and screened for hybridomas producing monoclonal antibodies reactive to the PD-1/human IgG1 fusion protein. An engineered mutation (S228P) in the hinge region prevents exchange of IgG4 molecules.41 It binds specifically to PD-1 and not to other members of the lg superfamily, eg, CD28, CTLA-4, ICOS, and BTLA.42 In vitro assays demonstrate that nivolumab potently enhances antigen-specific T-cell responses and cytokine production (interferon-gamma [IFN-γ], IL-2), without detectable antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) – an important feature, as intact ADCC may deplete activated T-cells and thereby diminish antitumor activity.41 Of note, nivolumab does not appear to generate nonspecific T-cell activation in the absence of antigenic stimulus. In mouse models, PD-1 blockade with a monoclonal antibody has been shown to inhibit hematogenous cancer spread.43
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Nivolumab is administered intravenously over 60 minutes, with serum concentrations peaking in 1–4 hours. Its approximate serum half-life ranges from 12 days (at 0.3 mg/kg, 1 mg/kg, or 3 mg/kg doses) to 20 days (at 10 mg/kg dose).42,44 Steady-state concentrations are reached by 12 weeks when administered at 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks.45 Nivolumab has linear pharmacokinetics, with dose-proportional increases in peak concentration and area under the curve. However, Brahmer et al42 noted a discrepancy between the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the drug in a number of patients. PD-1 receptor occupancy appeared to be dose dependent, with mean peak occupancy of 85% observed at 4–24 hours and mean plateau occupancy of 72% observed at ≥57 days, following a single infusion. These data are consistent with the known high affinity of nivolumab for PD-1 – undetectable serum levels (<1.2 μg/mL) are sufficient to occupy >70% of PD-1 receptors.42 A population pharmacokinetic analysis using data from 909 patients showed that the clearance of nivolumab increased with increasing body weight. Age, sex, race, PD-L1 expression, tumor type, tumor size, renal impairment, and mild hepatic impairment did not significantly affect drug clearance.45
Clinical trials with nivolumab
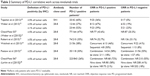
Nivolumab was the first PD-1 inhibitor to be evaluated in the clinic. In early Phase I trials, it induced durable responses in patients with a variety of advanced malignancies including melanoma.42,44 In December 2014, the FDA granted accelerated approval to nivolumab for use in patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma refractory to ipilimumab (and refractory to BRAF inhibition, if BRAF-mutated). In March 2015, nivolumab was also approved for use in metastatic squamous non-small-cell lung cancer with progression on or after platinum-based chemotherapy. Studies investigating nivolumab in advanced melanoma are summarized in Table 1.
Nivolumab monotherapy
The first Phase I trial of nivolumab was conducted in 296 patients with advanced melanoma, non-small-cell lung cancer, prostate cancer, renal cell carcinoma, and colorectal cancer.44 Of the 94 patients with melanoma included in the efficacy analysis, 26 (28%) had objective responses at doses ranging from 0.1 mg/kg to 10.0 mg/kg. The highest response rate (41%) was seen at the 3 mg/kg dose. Responses were durable; 13 out of 18 patients who received treatment for >1 year had a response that lasted 1 year or more. Long-term follow-up of 107 patients with advanced melanoma from this trial showed a similar ORR of 31% (33/107), with median response duration of 2 years as estimated by the Kaplan–Meier method.5 One- and 2-year survival rates were 62% and 43%, respectively, with a median OS of 16.8 months. One- and 2-year PFS rates were 36% and 27%, respectively, with a median PFS of 3.7 months. Interestingly, 12 out of 17 patients (71%) who had discontinued therapy for reasons other than disease progression demonstrated persistent responses for at least 16 weeks (16–56+ weeks).
Another Phase I trial tested nivolumab with or without a multipeptide vaccine (against melanoma antigens gp100, NY-ESO-1, and MART-1) in 90 patients with ipilimumab-refractory or ipilimumab-naïve melanomas.32 The ORR was 25% across all cohorts, with no difference between refractory and naïve patients (26% vs 24%, respectively). Although addition of the vaccine increased posttreatment levels of MART-1-specific CD8+ T-cells in responders, it did not improve clinical efficacy.
Two Phase III studies31,33 have recently demonstrated improved outcomes with nivolumab compared to standard chemotherapy in both previously treated and untreated patients. In CheckMate 037, 405 patients with metastatic melanoma who progressed on ipilimumab (and a BRAF inhibitor if BRAF-mutated) were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to receive nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks or investigator’s choice of chemotherapy (abbreviated as ICC: dacarbazine or carboplatin/paclitaxel).31 Of note, 31 (23%) patients in the ICC group and four (1%) in the nivolumab group did not receive study treatment, largely due to withdrawal of consent. After a median follow-up of 8.4 months, objective responses were seen in 31.7% (38/120) of patients in the nivolumab arm and in 10.6% (5/47) of patients in the ICC arm. Predefined subgroup analyses showed improved responses with nivolumab regardless of BRAF status, prior ipilimumab benefit, or PD-L1 status. Grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events also occurred less frequently with nivolumab than with ICC (9% vs 31%). However, there was no significant difference in 6-month PFS, possibly due to imbalanced adverse patient characteristics (favoring the ICC group), short follow-up time, or false-positive disease progression with an immune-related response.
The second Phase III study was CheckMate 066, in which nivolumab was evaluated in patients with previously untreated stage III or IV melanoma without a BRAF mutation.33 Patients (N=418) were randomized 1:1 to nivolumab (3 mg/kg every 2 weeks) or dacarbazine (1,000 mg/m2 body surface area every 3 weeks). Objective responses were seen in 40.0% of patients (84/210) in the nivolumab group, compared to only 13.9% (29/208) in the dacarbazine group. Median PFS and OS at 1 year were significantly longer with nivolumab (5.1 months, 72.9%) compared to dacarbazine (2.2 months, 42.1%). The survival advantage with nivolumab was seen across all prespecified subgroups and occurred independent of PD-L1 status. Consistent with CheckMate 037, grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events occurred less frequently with nivolumab than with dacarbazine (11.7% vs 17.6%).
Combination therapy
With the success of single-agent nivolumab, combinatorial strategies are now being clinically developed in an effort to improve response rates. The preclinical rationale for combination therapy is strong. CTLA-4 and PD-1 are nonredundant pathways that regulate adaptive immunity at different phases of T-cell activation. Dual checkpoint inhibitors are therefore likely to have complementary mechanisms of action, and synergistic activity has been demonstrated in preclinical models.46 There is also evidence that targeted therapy can modulate the immune response to cancer, allowing for rationally designed multimodality combinations with checkpoint inhibitors. Preliminary data from clinical trials indicate that combination therapy may offer superior efficacy, but at the expense of greater toxicity, compared to either CTLA-4 or PD-1 blockade alone.
In a Phase I study, 86 patients with advanced melanoma were treated with either concurrent or sequential treatment with nivolumab and ipilimumab.34 With the concurrent regimen, successive cohorts received escalating doses of nivolumab and ipilimumab administered together every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by nivolumab alone every 3 weeks for four doses. Forty percent of patients treated with concurrent therapy had objective responses. Among those who received the maximum tolerated dose (nivolumab at 1 mg/kg and ipilimumab at 3 mg/kg), the response rate was 53%. Responses were rapid and deep – 16 of 21 responders had a tumor reduction of ≥80% by 12 weeks. Overall clinical activity (defined as conventional, unconfirmed, and immune-related responses, as well as stable disease for at least 24 weeks) was seen in 65% of patients. Although a formal comparison was not made, these initial results suggested greater efficacy with combination therapy. Treatment-related adverse events were similar to those seen with monotherapy and were generally reversible, but occurred in significantly more patients, with grade 3 or 4 events reported in 53% of patients (compared to 14% with nivolumab alone).
In a subsequent Phase II study, 179 patients with previously untreated, unresectable stage III or IV melanoma were randomly assigned (2:1) to combination therapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab or with ipilimumab alone.47 Randomization was stratified according to BRAF mutation status. In the combination group, nivolumab was administered at a dose of 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks; ipilimumab at a 3 mg/kg dose was given 30 minutes after each nivolumab infusion. After four doses of combination therapy, patients were maintained on nivolumab alone. The same dose of ipilimumab was used in the monotherapy group. Among patients with BRAF wild-type tumors, the ORR was 61% (44/72) in the combination group versus 11% (4/37) in the monotherapy group, with complete responses seen in 16 patients (22%) on combination therapy and no patients on monotherapy. Median PFS was not reached with the combination and was 4.4 months with monotherapy. Among those with BRAF V600 mutation-positive tumors, combination therapy offered a similar improvement in ORR and survival compared to ipilimumab alone. As in the previous case, grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events occurred more frequently with combination therapy than with monotherapy (54% vs 24%).
Most recently, interim results from CheckMate 067 were presented at the 2015 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. This large, randomized Phase III study directly compared the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab to nivolumab-only and ipilimumab-only monotherapy.48 Patients (N=945) with previously untreated, unresectable stage III or IV melanoma were randomized 1:1:1 to receive nivolumab alone (3 mg/kg every 2 weeks), nivolumab (1 mg/kg every 3 weeks) plus ipilimumab (3 mg/kg every 3 weeks) for four doses followed by nivolumab alone, or ipilimumab alone (3 mg/kg every 3 weeks). Randomization was stratified according to tumor PD-L1 status, BRAF mutation status, and disease stage. The ORRs were 43.7% (138/316) in the nivolumab group, 57.6% (181/314) in the combination therapy group, and 19.0% (60/315) in the ipilimumab group, with a higher percentage of patients achieving complete response in the combination group (11.5%) than in the nivolumab (8.9%) or the ipilimumab (2.2%) groups. Significantly longer PFS was observed in the nivolumab (6.9 months) and combination (11.5 months) arms than in the ipilimumab arm (2.9 months). Subgroup analyses also showed consistently longer PFS with nivolumab or combined therapy than with ipilimumab. The incidence of grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events was higher in the combination group (55.0%) than with nivolumab (16.3%) or ipilimumab (27.3%) alone, with 83.4% of patients in the combination group requiring immunomodulatory agents (compared to 47.0% and 55.9% of patients in the nivolumab and ipilimumab groups, respectively).
A formal statistical comparison was not made between the nivolumab and nivolumab/ipilimumab groups, but combined therapy resulted in a numerically longer PFS. The ORR with combination therapy (57.6%) was also higher than that seen with nivolumab alone both in this study and in other Phase III trials (~40%).31,33 Future studies and follow-up data will demonstrate whether this increased efficacy translates into improved OS. As discussed in the following section, the PFS benefit with combination therapy versus nivolumab alone may be more pronounced in patients with PD-L1-negative disease, suggesting that PD-L1 expression may be useful as a biomarker to identify patients who are most likely to benefit from dual checkpoint blockade. As of October 2015, the FDA granted accelerated approval for the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab in patients with treatment-naïve, BRAF-wild type, advanced melanoma.
Other combination strategies
The success of combined CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockade has prompted a number of other trials studying the combination of nivolumab with various immune-based therapies. Ongoing clinical trials in patients with advanced melanoma include nivolumab plus RTA 408 (inhibitor of myeloid-derived suppressor cells) (NCT02259231), varlilumab (anti-CD27 antibody) (NCT02335918), INCB24360 (IDO1 inhibitor) (NCT02327078), lirilumab (anti-KIR) (NCT0171479), BMS-986016 (anti-LAG-3) (NCT01968109), and BMS-982470 (IL-21) (NCT01629758).
For patients with BRAF V600 mutations, combining checkpoint inhibitors with BRAF and/or MEK inhibitors may also improve response rates, as preclinical work demonstrates that these targeted agents have potential immunomodulatory effects. BRAF-mutated melanoma cells treated with either a MEK inhibitor or BRAF-targeted RNA interference displayed decreased production of immunosuppressive cytokines (eg, IL-10, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α, vascular endothelial growth factor), implying that the MAPK pathway plays an important role in cancer immune evasion.49 BRAF inhibitors may further enhance cancer-directed immune responses by increasing melanoma antigen expression and tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T-cells. Attempts to combine CTLA-4 inhibitors with targeted agents have raised significant toxicity concerns, however. A study investigating ipilimumab plus vemurafenib in BRAF-mutated advanced melanoma patients was terminated early due to grade 3 hepatotoxicity in six out of ten patients.50 In another Phase I study, the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib, with or without the MEK inhibitor trametinib, was investigated in combination with ipilimumab for V600E/K mutation-positive unresectable or metastatic melanoma. Here, the triplet therapy cohort was closed due to grade 3–4 colitis complicated by perforation in two patients.51
Increased PD-L1 expression has also been observed with BRAF inhibition, suggesting that combined PD-1/BRAF blockade may be synergistic.52 Trials evaluating the combination of nivolumab and dabrafenib and/or trametinib will be open to enrollment in the near future (NCT0222478, NCT02357732).
Sequencing of therapy
As the armamentarium of treatment options for advanced melanoma continues to expand, the issue of optimal sequencing of therapy has become increasingly relevant, particularly for patients with BRAF-mutated disease. Broadly speaking, BRAF/MEK inhibitors offer relatively high response rates, with rapid onset of action (ie, days to weeks), but disease relapse is common. In contrast, responses may take longer to manifest with checkpoint inhibitors (ie, weeks to months), with lower overall response rates compared to targeted therapy, but with the potential for long-lasting remissions. With these characteristics in mind, patients with high tumor burden, significant symptoms, or impending organ dysfunction are typically treated with a BRAF inhibitor first, considering the higher likelihood of achieving a rapid response. For patients who are asymptomatic or have limited disease burden, checkpoint inhibition may be administered first. However, this approach is based primarily on retrospective data,53 and prospective studies are needed to better define optimal sequencing of therapy. To this end, a randomized Phase III trial is being conducted comparing different sequences in patients with stage III–IV BRAF V600 melanoma (NCT02224781).
Tumor response kinetics
Responses to nivolumab and other checkpoint inhibitors are heterogeneous in terms of both pattern and kinetics. Collective experience in melanoma suggests that the traditionally used Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) or modified World Health Organization criteria have significant limitations and are insufficient to characterize the activity of immunotherapy. By standard RECIST criteria, radiographic increase in tumor size or the appearance of new lesions indicates disease progression, which is conventionally equatable with drug failure. With nivolumab, however, unique response patterns are sometimes not captured by RECIST. Some patients appear to have initial radiographic progression, which is then followed by a durable response; others may display a mixed radiographic response, but with an overall improvement in total tumor burden. These distinctive response patterns are still associated with favorable survival, indicating that nivolumab can offer a meaningful therapeutic effect even if conventional definitions of progressive disease have been met. Delayed immune activity and/or peritumoral lymphocyte infiltration may be responsible for this so-called “pseudoprogression”. These important observations led to the development of novel immune-related response criteria, so that immunotherapeutic agents are not prematurely discontinued in psuedoprogressors.54 Immune-related progression-free survival has thus been adopted as a key end point with nivolumab therapy.
Predictive biomarkers
Checkpoint inhibitors are effective for only a fraction of melanomas; therefore, the development of biomarkers to predict efficacy and select appropriate patients is a crucial area of ongoing research. This has proven to be challenging, as the immune response to malignancy is strikingly dynamic and under complex regulation. As of now, no pretreatment biomarker has been validated for standard-of-care use. Early correlative work pointed to a number of potential markers for ipilimumab efficacy, including increased peripheral blood absolute lymphocyte count, upregulated T-cell activation markers, inflammatory gene signatures in the tumor microenvironment, and circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells.55–59 More recently, the relationship between a tumor’s mutational landscape and the benefit from CTLA-4 blockade was assessed.60 Whole-exome sequencing was performed on tumor tissue and matched blood samples from melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab or tremelimumab. Nonsynonymous somatic mutations and their candidate neoantigens were characterized; neoantigen peptides were then tested for their ability to activate CD8+ T-cells. The investigators noted that higher mutational load correlated with the “degree” of clinical benefit, but by itself, this was not sufficient to predict benefit. Furthermore, a specific neoantigenic signature was identified and subsequently validated in melanomas with a strong response to CTLA-4 blockade.
Because PD-L1 is found within the tumor microenvironment, its expression would seem to be a rational biomarker. However, numerous factors make PD-L1 assessment challenging; intratumoral heterogeneity, dynamic/inducible expression levels, and differing methodologies for immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining (ie, multiple antibody clones, no standard cutoff for positivity) are just a few examples that highlight the complexity of PD-L1 validation. While some studies have correlated PD-L1 expression with poor prognosis and more invasive disease, several others do not demonstrate a clear association, or in some cases, even show an association with improved survival.61–64 Furthermore, it remains unknown whether PD-L1 expression in tumor cell versus infiltrating immune cell is more relevant. Upregulation of tumor cell PD-L1, which is probably induced by T-cell release of IFN-γ, has been well described as a mechanism of adaptive immune resistance in both animal models and humans.64,65 However, a number of recent studies have noted that PD-L1 expression on infiltrating immune cells, but not on tumor cells, is predictive of clinical outcomes after PD-1 inhibition in melanoma and other solid tumors.66,67
In the original Phase I study of nivolumab for advanced melanoma, 42 pretreatment tumor samples were tested for PD-L1 expression by IHC with the 5H1 antibody clone. Five percent expression was used as the cutoff for PD-L1 positivity. Of 17 patients with PD-L1-negative tumors, none had an objective response, whereas nine of 25 (36%) with PD-L1-positive disease responded.44 Despite this initial finding, subsequent trials have clearly demonstrated that PD-L1-negative melanomas may also exhibit a response, although at lower rates. For example, in CheckMate 037 (nivolumab vs ICC), positive tumor PD-L1 status (28-8 antibody clone, ≥5%) was associated with a higher ORR (43.6%); however the PD-L1-negative response rate was still as high as 20.3%, suggesting that nivolumab may provide clinical benefit irrespective of pretreatment PD-L1 analysis.31 Similar data were reported in the Phase III study of nivolumab vs dacarbazine.33 To this end, the clinical utility of PD-L1 expression in melanoma remains unclear and PD-L1 staining should not be used as a marker to select patients for treatment with PD-1 inhibitors. Of note, in the aforementioned CheckMate 067, patients with PD-L1-negative tumors had longer PFS with combination therapy than with nivolumab alone (11.2 vs 5.3 months).48 This lends support to the strategy of adding ipilimumab to anti-PD1 therapy in the PD-L1-negative setting, despite the potential risk for increased toxicity. Correlative work evaluating PD-L1 with nivolumab in advanced melanoma is summarized in Table 2.
The presence of pretreatment tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T-cells is another potential marker of response to PD-1 inhibition. A recent study of 46 patients with advanced melanoma receiving pembrolizumab found higher baseline CD8+ cell densities at the tumor-invasive margin in patients who demonstrated a treatment response, compared to those who progressed on therapy.68 Among responders, serial biopsies demonstrated increasing CD8+ cell density at both the invasive front and in the tumor center, a finding that was absent among progressors. These data were used to construct a prediction model that accurately predicted response to pembrolizumab in 13 out of 15 advanced melanoma patients in a subsequent validation set.
Safety and tolerability
Overall, nivolumab is well tolerated. In early Phase I trials, the most common adverse events were low-grade fatigue, musculoskeletal side effects (eg, arthralgia, arthritis, myalgia, joint stiffness, bone pain, weakness), decreased appetite, nausea, diarrhea, rash, and pruritus.42,44 The frequency and severity of adverse events were generally similar across all tested dose levels. The first published Phase III trial comparing nivolumab to dacarbazine in patients with previously untreated BRAF-wild type melanoma reported a similar toxicity profile for nivolumab.33 Other treatment-related adverse events that occurred in at least 3% of patients include pyrexia, pain, cough, flushing, hypotension, dermatitis acneiform, photosensitivity reaction, abdominal pain, dry mouth, hyperuricemia, and hypophosphatemia.5 Reported hematologic disorders include anemia, thrombocytopenia, decrease in CD4+ lymphocyte count (seen in up to 36% of patients in a Phase I trial), lymphopenia, and neutropenia.42 Long-term evaluation of safety, with up to 2 years of monitoring for some patients, yielded findings that were comparable to the results of initial studies. Of 107 patients with melanoma, 22% experienced grade 3–4 adverse events. The most common events of any grade were fatigue, rash, and diarrhea. Toxicities were not cumulative with prolonged drug exposure and occurred primarily during the first 6 months of therapy.5
Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) are of special interest considering nivolumab’s mechanism of action, although severe toxicities are far less common with PD-1 blockade compared with ipilimumab. Almost any organ system can be affected by irAEs. Potential events include pneumonitis, allergic rhinitis, rash, pruritus, vitiligo, alopecia, diarrhea secondary to enteritis or colitis, hepatitis, nephritis, polyarticular arthropathies, endocrinopathies (eg, adrenal insufficiency, diabetes, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, thyroiditis, hypophysitis), and hypersensitivity or infusion-related reactions. In the long-term follow-up conducted by Topalian et al,44 potential irAEs of any grade were seen in 54% of patients with melanoma, the most common being skin disorders (36%), gastrointestinal events (18%), and endocrinopathies (13%). Five percent of patients experienced grade 3–4 events. In general, the majority of immune-related toxicities are reversible with treatment interruption and, in some cases, corticosteroids. Endocrine disorders are managed with supplementation. Pneumonitis is perhaps the most serious potential complication of PD-1 inhibition – early recognition and management are required to minimize morbidity. One trial reported three deaths associated with refractory pneumonitis in two patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and in one patient with colorectal cancer.44
Quality of life
Considering the significant toxicities associated with conventional chemotherapy, targeted therapies and immunotherapy may offer patients improved quality of life (QoL), in addition to greater efficacy. That being said, immunotherapy does have the potential to cause toxicity (as described herein) and can be associated with delayed responses. As such, there has been recent interest in assessing patient experiences and QoL with these different therapies. A study by Shuk et al69 examined patient perspectives on ipilimumab at different time points relative to treatment initiation and response. Participants generally regarded ipilimumab positively and felt that it had significantly fewer side effects compared to prior therapies and had minimal impact on their QoL. However, these results may be biased considering that patients who experienced more severe side effects were excluded from continued participation. In CheckMate 066 (nivolumab vs dacarbazine), the effects of nivolumab on patient QoL were assessed using the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire (EORTC QLQ-C30) and the EuroQol-five-dimension questionnaire (EQ-5D).70 Mean baseline QoL scores were similar in the nivolumab and dacarbazine groups. Over time, the nivolumab group demonstrated no change in EORTC scores, and an improvement in EQ-5D scores. Direct comparison with QoL scores in the dacarbazine group was not feasible due to the high attrition rate in that arm, but considering the higher frequency of grade 3 or 4 adverse events observed with chemotherapy, it is possible that nivolumab improved QoL in addition to PFS. Ongoing QoL assessments will be important as we consider the risks and benefits of combination therapy, which is associated with significantly greater toxicity than is monotherapy. In CheckMate 067 (combination nivolumab/ipilimumab vs monotherapy), patients in the combination group were more liable to discontinue treatment due of adverse effects.48
Conclusion and future directions
With the advent of immune checkpoint inhibition, the treatment landscape for advanced melanoma has changed dramatically – never before has there been this much potential for durable responses and improved survival. As PD-1 inhibitors gain a central role in the management of this deadly disease, many important questions will need to be answered. Further study is necessary to develop and optimize biomarkers in order to define the subset of patients most likely to derive benefit. Genomic/mutational profiling of tumors may play a role in predicting immunotherapeutic response and will be critical in further illuminating the relationship between oncogenic signaling pathways and immune escape. Combination strategies require refinement and Phase III validation, and studies are needed to define the optimal duration of therapy. The risks of long-term exposure to these agents remain largely unknown – a better understanding of potential chronic toxicities is likely to emerge in the coming years. Lastly, checkpoint inhibition for melanoma requires exploration in the adjuvant setting, in which it may be of value in eradicating micrometastatic disease. The era of immunotherapy has only just begun – there is much work yet to do.
Disclosure
Dr Richard D Carvajal receives personal fees and grants from AstraZeneca and receives personal fees alone from Novartis, Janssen, Merck, Genentech, Iconic, and Aura Biosciences. The other authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Chapman PB, Einhorn LH, Meyers ML, et al. Phase III multicenter randomized trial of the Dartmouth regimen versus dacarbazine in patients with metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17(9):2745–2751. | ||
Sparano JA, Fisher RI, Sunderland M, et al. Randomized phase III trial of treatment with high-dose interleukin-2 either alone or in combination with interferon alfa-2a in patients with advanced melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 1993;11(10):1969–1977. | ||
Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF, et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(8):711–723. | ||
Robert C, Karaszewska B, Schachter J, et al. Improved overall survival in melanoma with combined dabrafenib and trametinib. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(1):30–39. | ||
Topalian SL, Sznol M, McDermott DF, et al. Survival, durable tumor remission, and long-term safety in patients with advanced melanoma receiving nivolumab. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(10):1020–1030. | ||
Robert C, Ribas A, Wolchok JD, et al. Anti-programmed-death-receptor-1 treatment with pembrolizumab in ipilimumab-refractory advanced melanoma: a randomised dose-comparison cohort of a phase 1 trial. Lancet. 2014;384(9948):1109–1117. | ||
Sznol M, Kluger HM, Callahan MK, et al. Survival, response duration, and activity by BRAF mutation (MT) status of nivolumab (NIVO, anti-PD-1, BMS-936558, ONO-4538) and ipilimumab (IPI) concurrent therapy in advanced melanoma (MEL). J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(15 suppl):LBA9003. | ||
Page DB, Postow MA, Callahan MK, Allison JP, Wolchok JD. Immune modulation in cancer with antibodies. Annu Rev Med. 2014;65:185–202. | ||
Ott PA, Hodi FS, Robert C. CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: new immunotherapeutic modalities with durable clinical benefit in melanoma patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(19):5300–5309. | ||
Lui P, Cashin R, Machado M, Hemels M, Corey-Lisle PK, Einarson TR. Treatments for metastatic melanoma: synthesis of evidence from randomized trials. Cancer Treat Rev. 2007;33(8):665–680. | ||
Curtin JA, Fridlyand J, Kageshita T, et al. Distinct sets of genetic alterations in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(20):2135–2147. | ||
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417(6892):949–954. | ||
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, et al; BRIM-3 Study Group. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(26):2507–2516. | ||
Hauschild A, Grob JJ, Demidov LV, et al. Dabrafenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma: a multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;380(9839):358–365. | ||
Carvajal RD, Antonescu CR, Wolchok JD, et al. KIT as a therapeutic target in metastatic melanoma. JAMA. 2011;305(22):2327–2334. | ||
Hodi FS, Corless CL, Giobbie-Hurder A, et al. Imatinib for melanomas harboring mutationally activated or amplified KIT arising on mucosal, acral, and chronically sun-damaged skin. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(26):3182–3190. | ||
Shi H, Hugo W, Kong X, et al. Acquired resistance and clonal evolution in melanoma during BRAF inhibitor therapy. Cancer Discov. 2014;4(1):80–93. | ||
Van Allen EM, Wagle N, Sucker A, et al; Dermatologic Cooperative Oncology Group of Germany (DeCOG). The genetic landscape of clinical resistance to RAF inhibition in metastatic melanoma. Cancer Discov. 2014;4(1):94–109. | ||
Su F, Viros A, Milagre C, et al. RAS mutations in cutaneous squamous-cell carcinomas in patients treated with BRAF inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(3):207–215. | ||
Falchook GS, Lewis KD, Infante JR, et al. Activity of the oral MEK inhibitor trametinib in patients with advanced melanoma: a phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(8):782–789. | ||
Alexandrov LB, Nik-Zainal S, Wedge DC, et al. Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer. Nature. 2013;500(7463):415–421. | ||
van Oijen M, Bins A, Elias S, et al. On the role of melanoma-specific CD8+ T-cell immunity in disease progression of advanced-stage melanoma patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(14):4754–4760. | ||
Mihm MC Jr, Clemente CG, Cascinelli N. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in lymph node melanoma metastases: a histopathologic prognostic indicator and an expression of local immune response. Lab Invest. 1996;74(1):43–47. | ||
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–674. | ||
Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Topalian SL, et al. Treatment of 283 consecutive patients with metastatic melanoma or renal cell cancer using high-dose bolus interleukin 2. JAMA. 1994;271(12):907–913. | ||
Robert C, Thomas L, Bondarenko I, et al. Ipilimumab plus dacarbazine for previously untreated metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(26):2517–2526. | ||
Francisco LM, Sage PT, Sharpe AH. The PD-1 pathway in tolerance and autoimmunity. Immunol Rev. 2010;236:219–242. | ||
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:677–704. | ||
Zou W, Chen L. Inhibitory B7-family molecules in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(6):467–477. | ||
Rozali EN, Hato SV, Robinson BW, Lake RA, Lesterhuis WJ. Programmed death ligand 2 in cancer-induced immune suppression. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:656340. | ||
Weber JS, D’Angelo SP, Minor D, et al. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma who progressed after anti-CTLA-4 treatment (CheckMate 037): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(4):375–384. | ||
Weber JS, Kudchadkar RR, Yu B, et al. Safety, efficacy, and biomarkers of nivolumab with vaccine in ipilimumab-refractory or -naive melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(34):4311–4318. | ||
Robert C, Long GV, Brady B, et al. Nivolumab in previously untreated melanoma without BRAF mutation. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(4):320–330. | ||
Wolchok JD, Kluger H, Callahan MK, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(2):122–133. | ||
Riley JL. PD-1 signaling in primary T cells. Immunol Rev. 2009;229(1):114–125. | ||
Pedoeem A, Azoulay-Alfaguter I, Strazza M, Silverman GJ, Mor A. Programmed death-1 pathway in cancer and autoimmunity. Clin Immunol. 2014;153(1):145–152. | ||
Chemnitz JM, Parry RV, Nichols KE, June CH, Riley JL. SHP-1 and SHP-2 associate with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif of programmed death 1 upon primary human T cell stimulation, but only receptor ligation prevents T cell activation. J Immunol. 2004;173(2):945–954. | ||
Nurieva R, Thomas S, Nguyen T, et al. T-cell tolerance or function is determined by combinatorial costimulatory signals. EMBO J. 2006;25(11):2623–2633. | ||
Goldberg MV, Maris CH, Hipkiss EL, et al. Role of PD-1 and its ligand, B7-H1, in early fate decisions of CD8 T cells. Blood. 2007;110(1):186–192. | ||
Fife BT, Pauken KE, Eagar TN, et al. Interactions between PD-1 and PD-L1 promote tolerance by blocking the TCR-induced stop signal. Nat Immunol. 2009;10(11):1185–1192. | ||
Wang C, Thudium KB, Han M, et al. In vitro characterization of the anti-PD-1 antibody nivolumab, BMS-936558, and in vivo toxicology in non-human primates. Cancer Immunol Res. 2014;2(9):846–856. | ||
Brahmer JR, Drake CG, Wollner I, et al. Phase I study of single-agent anti-programmed death-1 (MDX-1106) in refractory solid tumors: safety, clinical activity, pharmacodynamics, and immunologic correlates. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(19):3167–3175. | ||
Iwai Y, Terawaki S, Honjo T. PD-1 blockade inhibits hematogenous spread of poorly immunogenic tumor cells by enhanced recruitment of effector T cells. Int Immunol. 2005;17(2):133–144. | ||
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(26):2443–2454. | ||
Paik PK, Drilon A, Yu H, et al. Response to MET inhibitors in patients with stage IV lung adenocarcinomas harboring MET mutations causing exon 14 skipping. Cancer Discov. 2015;5(8):842–849. | ||
Curran MA, Montalvo W, Yagita H, Allison JP. PD-1 and CTLA-4 combination blockade expands infiltrating T cells and reduces regulatory T and myeloid cells within B16 melanoma tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(9):4275–4280. | ||
Postow MA, Chesney J, Pavlick AC, et al. Nivolumab and ipilimumab versus ipilimumab in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2006–2017. | ||
Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, et al. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(1):23–34. | ||
Sumimoto H, Imabayashi F, Iwata T, Kawakami Y. The BRAF-MAPK signaling pathway is essential for cancer-immune evasion in human melanoma cells. J Exp Med. 2006;203(7):1651–1656. | ||
Ribas A, Hodi FS, Callahan M, Konto C, Wolchok J. Hepatotoxicity with combination of vemurafenib and ipilimumab. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(14):1365–1366. | ||
Puzanov I, Callahan MK, Linette GP, et al. Phase 1 study of the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib (D) with or without the MEK inhibitor trametinib (T) in combination with ipilimumab (Ipi) for V600E/K mutation-positive unresectable or metastatic melanoma (MM). J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(15 suppl):abstr2511. | ||
Frederick DT, Piris A, Cogdill AP, et al. BRAF inhibition is associated with enhanced melanoma antigen expression and a more favorable tumor microenvironment in patients with metastatic melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(5):1225–1231. | ||
Ackerman A, Klein O, McDermott DF, et al. Outcomes of patients with metastatic melanoma treated with immunotherapy prior to or after BRAF inhibitors. Cancer. 2014;120(11):1695–1701. | ||
Wolchok JD, Hoos A, O’Day S, et al. Guidelines for the evaluation of immune therapy activity in solid tumors: immune-related response criteria. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(23):7412–7420. | ||
Ku GY, Yuan J, Page DB, et al. Single-institution experience with ipilimumab in advanced melanoma patients in the compassionate use setting: lymphocyte count after 2 doses correlates with survival. Cancer. 2010;116(7):1767–1775. | ||
Carthon BC, Wolchok JD, Yuan J, et al. Preoperative CTLA-4 blockade: tolerability and immune monitoring in the setting of a presurgical clinical trial. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(10):2861–2871. | ||
Ji RR, Chasalow SD, Wang L, et al. An immune-active tumor microenvironment favors clinical response to ipilimumab. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2012;61(7):1019–1031. | ||
Kitano S, Postow MA, Ziegler CG, et al. Computational algorithm-driven evaluation of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cell frequency for prediction of clinical outcomes. Cancer Immunol Res. 2014;2(8):812–821. | ||
Postow MA, Chasalow SD, Yuan J, et al. Pharmacodynamic effect of ipilimumab on absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) and association with overall survival in patients with advanced melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(15 suppl):abstr9052. | ||
Snyder A, Makarov V, Merghoub T, et al. Genetic basis for clinical response to CTLA-4 blockade in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(23):2189–2199. | ||
Sznol M, Chen L. Antagonist antibodies to PD-1 and B7-H1 (PD-L1) in the treatment of advanced human cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(5):1021–1034. | ||
Karim R, Jordanova ES, Piersma SJ, et al. Tumor-expressed B7-H1 and B7-DC in relation to PD-1+ T-cell infiltration and survival of patients with cervical carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(20):6341–6347. | ||
Konishi J, Yamazaki K, Azuma M, Kinoshita I, Dosaka-Akita H, Nishimura M. B7-H1 expression on non-small cell lung cancer cells and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and their PD-1 expression. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(15):5094–5100. | ||
Taube JM, Anders RA, Young GD, et al. Colocalization of inflammatory response with B7-h1 expression in human melanocytic lesions supports an adaptive resistance mechanism of immune escape. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4(127):127ra137. | ||
Pardoll DM. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(4):252–264. | ||
Herbst RS, Soria JC, Kowanetz M, et al. Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature. 2014;515(7528):563–567. | ||
Powles T, Eder JP, Fine GD, et al. MPDL3280A (anti-PD-L1) treatment leads to clinical activity in metastatic bladder cancer. Nature. 2014;515(7528):558–562. | ||
Tumeh PC, Harview CL, Yearley JH, et al. PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature. 2014;515(7528):568–571. | ||
Shuk E, Roth K, Goodman-Davis N, et al. Effects of response kinetics upon patient perceptions of ipilimumab, Society for Melanoma Research 2013 Congress, 17–20 November, 2013, Philadelphia, PA, USA. Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research. 26(6):1001. | ||
Long G, Atkinson V, Ascierto PA, et al. Effect of nivolumab (NIVO) on quality of life (QoL) in patients (pts) with treatment-naive advanced melanoma (MEL): results of a phase III study (Checkmate 066). J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(suppl):abstr9027. |
 © 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.