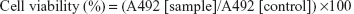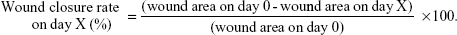Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 9 » Issue 1
Cationic star-shaped polymer as an siRNA carrier for reducing MMP-9 expression in skin fibroblast cells and promoting wound healing in diabetic rats
Authors Li N, Luo H, Yang C, Deng J, Ren M, Xie X, Lin D, Yan L, Zhang L
Received 17 April 2014
Accepted for publication 2 June 2014
Published 15 July 2014 Volume 2014:9(1) Pages 3377—3387
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S66368
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Na Li,1,* Heng-Cong Luo,1,* Chuan Yang,1 Jun-Jie Deng,2 Meng Ren,1 Xiao-Ying Xie,1 Diao-Zhu Lin,1 Li Yan,1 Li-Ming Zhang2
1Department of Endocrinology, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, People’s Republic of China; 2DSAPM Lab and PCFM Lab, Institute of Polymer Science, Department of Polymer and Materials Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Background: Excessive expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) is deleterious to the cutaneous wound-healing process in the context of diabetes. The aim of the present study was to explore whether a cationic star-shaped polymer consisting of ß-cyclodextrin (ß-CD) core and poly(amidoamine) dendron arms (ß-CD-[D3]7) could be used as the gene carrier of small interfering RNA (siRNA) to reduce MMP-9 expression for enhanced diabetic wound healing.
Methods: The cytotoxicity of ß-CD-(D3)7 was investigated by 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay (MMT) method in the rat CRL1213 skin fibroblast cell line. The transfection efficiency of ß-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-small interfering RNA (siRNA) complexes was determined by confocal microscopy and flow cytometry. Quantitative real time (RT) polymerase chain reaction was performed to measure the gene expression of MMP-9 after the transfection by ß-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes. The ß-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes were injected on the wounds of streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Wound closure was measured on days 4 and 7 post-wounding.
Results: ß-CD-(D3)7 exhibited low cytotoxicity in fibroblast cells, and easily formed the complexes with MMP-9-siRNA. The ß-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes were readily taken up by fibroblast cells, resulting in the downregulation of MMP-9 gene expression (P<0.01). Animal experiments revealed that the treatment by ß-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes enhanced wound closure in diabetic rats on day 7 post-wounding (P<0.05).
Conclusion: ß-CD-(D3)7 may be used as an efficient carrier for the delivery of MMP-9-siRNA to reduce MMP-9 expression in skin fibroblast cells and promote wound healing in diabetic rats.
Keywords: gene carrier, small interfering RNAs, matrix metalloproteinase-9, diabetic foot ulceration
Introduction
Diabetic foot ulceration, a common complication of diabetes, has emerged as a significant burden to the health care industry.1 Clinical observations have indicated that treatment options for diabetic ulcers are insufficient in many cases, and disease progression can ultimately lead to limb amputation. Therefore, a detailed understanding of the pathobiology of diabetic refractory ulcers is necessary. A number of pathophysiologic changes are considered to be responsible for impaired wound healing of diabetic patients. Many researchers have indicated that a retarded remodeling process is caused by abnormally elevated levels of a matrix metalloproteinase (MMP), a superfamily of proteases that can degrade various kinds of extracellular matrix.2–4 In nondiabetic wounds, MMPs are important for remodeling defective tissues by increasing the migration of fibroblasts and endothelial cells of the connective tissues. Their expression levels are tightly controlled to remove denatured fibrillar collagen and assist proper development of granulation tissues during the wound-healing process. Their activities are increased in the early healing phase and then decreased as the healing process completes. Abnormal expression of MMPs, especially MMP-9, in chronic diabetic wounds, has been previously studied.5,6 Our previous comparative study analyzed the dynamic changes of MMP-9 expression in skin wounds of diabetic and nondiabetic rats, and showed that high expression and activity of MMP-9 contributed to delayed healing at the late stage of wound healing (after the seventh day) much more than at the early stage (before the third day).7 In 2009, Liu et al8 reported that a high MMP-9 expression level in diabetic wound exudates was predictive of poor wound healing. A subsequent study in a murine model of wound healing further supported the concept that MMP-9 delayed the wound-healing process.9 Consequently, the breakdown rates of matrix proteins such as collagen and elastin override the remodeling rates of the defected tissues because of the higher activities of MMP-9. Many growth factors, including epidermal growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor, showed limited effectiveness toward highly active MMP-9 and other hydrolytic enzymes.10–12 Therefore, the direct inhibition of MMP-9 through RNA interference (RNAi) may represent a feasible strategy by which to improve chronic wound healing.
Since its first report in 1998, RNAi has rapidly become a powerful strategy both in basic research and in the development of efficient therapeutics.13,14 RNAi is a process by which RNA molecules, with sequences complementary to a gene’s coding sequence, induce the degradation of corresponding messenger RNAs (mRNAs), thus blocking the translation of the mRNA into protein.15,16 RNAi is initiated by exposing cells to a long double-stranded RNA via transfection or endogenous expression. dsRNAs are processed into smaller fragments (typically 21–23 nucleotides) of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs),17 which form a complex with the RNA-induced silencing complexes.18 The introduction of siRNA into mammalian cells leads to the downregulation of target genes without triggering interferon responses.17 Gene therapy using siRNA has shown great potential for diseases caused by abnormal gene expression or mutation.19–21
One difficulty that gene therapy strategies encounter is the need for an efficient, easy, and minimally toxic mode of siRNA delivery to cells.22–24 Cationic star-shaped polymers based on cyclodextrins (CDs) have recently attracted considerable attention as nonviral gene carriers due to their dense molecular architecture with moderate flexibility.25 It is known26 that CDs have low immunogenicity and toxicity and can enhance the absorption and resistance to nucleases through binding and interacting with oligonucleotides. In this context, Xu et al27 designed the cationic star-shaped polymers consisting of a β-CD core and poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) or its block copolymer arms, and Srinivasachari et al28 reported on a series of multivalent polycationic “click clusters” based on a β-CD core and oligoethyleneamine arms.
In this study, a cationic star-shaped polymer consisting of a β-CD core and poly(amidoamine) dendron arms, namely β-CD-(D3)7, was explored for the first time as a carrier of MMP-9-siRNA to suppress MMP-9 expression in rat fibroblast cells via RNAi. In particular, animal experiments were performed to demonstrate the efficacy of β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes in decreasing MMP-9 expression and promoting wound healing in diabetic skin tissues.
Materials and methods
Materials
β-CD-(D3)7 was synthesized in our lab by the click conjugation of per-6-azido-β-CD with propargyl focal point poly(amidoamine) dendron (D3, third generation), as reported in our previous publication.29 Lipofectamine® 2000 was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). MMP-9-siRNA was purchased from Shanghai GenePharma Co., Ltd., Shanghai, People’s Republic of China. Sprague Dawley rats weighing 250–300 g were obtained from the Experimental Animal Center of Sun Yat-sen University (Guangzhou, People’s Republic of China). All care and handling of the animals was performed in accordance with the requirements of the Experimental Animal Center of Sun Yat-sen University. All other reagents were of analytical or high-performance liquid chromatography grade.
Preparation and characterization of β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes
The β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes were prepared at various charge ratios by mixing equal volumes of β-CD-(D3)7 with MMP-9-siRNA in phosphate-buffered saline. The charge ratio (amino group to phosphate group [N/P]) was calculated as a ratio of the number of primary amines in the polymer to the number of anionic phosphate groups in the MMP-9-siRNA. The samples were then vortexed and incubated at 37°C for 15 minutes to ensure formation of the complex. For the resultant β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes, their particle sizes in aqueous system were measured at 25°C using a ZetaPALS zeta potential analyzer (Brookhaven Instruments Corporation, Holtsville, NY, USA). Their morphology was observed using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (JEM2010; JEOL, Tokyo, Japan). Briefly, one drop of β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complex suspension was placed on a copper grid and incubated for 60 seconds. The sample was negatively stained with 2% (w/v) uranyl acetate solution for 60 seconds. Excess liquid was removed by blotting with filter paper.
Cell culture
Rat CRL1213 dermal fibroblast cells (number 4032860) were purchased from American Type Culture Collection ([ATCC] Manassas, VA, USA). Fibroblast cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium ([DMEM] Thermo Fisher Scientific) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum ([FBS] Thermo Fisher Scientific) at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2.
Cell viability assay
Fibroblast cells were seeded at a density of 0.9×104/well in 96-well plates. Then, 200 μL of DMEM was added per well, and the cells were incubated for 24 hours. Subsequently, the cells were treated with different concentrations of β-CD-(D3)7. After 24, 48, or 72 hours, the cells were incubated in the dark with a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) solution for 4 hours at 37°C. After the supernatants were aspirated, dimethyl sulfoxide was added to each well, and the plates were agitated to dissolve the formazan crystal product. The absorbance at 492 nm was then measured using a microplate reader (Wellscan MK3, Labsystems Ltd. OY, Vantaa, Finland). The cell viability was calculated according to the following formula (with “A” showing absorbance):
| (1) |
The experiment was repeated three times.
Agarose gel electrophoresis
The ability of β-CD-(D3)7 to complex MMP-9-siRNA was examined via gel electrophoresis (AlphaImager HP, ProteinSimple, Santa Clara, CA, USA). For this purpose, β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes with N/P ratios of 40:1, 30:1, 20:1, or 10:1 were formed. Negative control complexes were also generated (by incubating MMP-9-siRNA in the absence of β-CD-[D3]7). After incubation for 15 minutes at room temperature, MMP-9-siRNA complexation was studied via agarose gel retardation assays. The samples were electrophoresed in a 4% agarose gel at 80 V for 20 minutes. MMP-9-siRNA was visualized using an ultraviolet transilluminator (AlphaImager HP, ProteinSimple, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
In vitro transfection experiment
Fibroblast cells were seeded in 24-well plates (Corning Incorporated, Corning, NY, USA) at an initial density of 1×105 cells per well in 0.5 mL medium. After culturing for 12 hours, the cell culture medium was replaced with serum-free medium (opti-MEM; Thermo Fisher Scientific). β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes were formed at different mass ratios (40:1, 30:1, 20:1, 10:1, and 4:1). At all ratios, carboxyfluorescein-labeled siRNA was used at a fixed final concentration of 40 nmol/L. The cells were incubated with the complexes in serum-free culture medium for 4 hours at 37°C. Then, the medium was replaced with fresh medium containing 10% serum, and the cells were incubated for 24 hours. The transfection efficiency of the β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes was determined via confocal microscopy (LSM 510 META; Carl Zeiss Meditec AG, Jena, Germany) and flow cytometry (FACSCalibur™; BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA). The percentages of dead cells after transfection were also evaluated via flow cytometry. The transfection efficiency of the commercially available transfection reagent Lipofectamine 2000 was also evaluated. The experiment was repeated three times.
Establishment of an MMP-9 overexpressing cell model
Fibroblast cells were seeded in six-well plates at an initial density of 3×105 cells per well. After 24 hours, the cell culture medium was replaced with medium supplemented with 0.5% FBS for cell synchronization. After 24 hours, the culture medium was replaced with fresh culture medium containing 25 mmol/L glucose; 1 μg/mL lipopolysaccharide was also added for 18 hours to stimulate MMP-9 expression. Cells cultured in medium containing 25 mmol/L glucose alone were used as control. Quantitative real time (RT) polymerase chain reaction was performed to determine the level of MMP-9 gene expression.
Inhibition effect on MMP-9 expression
After the establishment of a model with high MMP-9 expression, β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes with a mass ratio of 20:1 (selected based on the transfection efficiency experiment) or Lipofectamine 2000/MMP-9-siRNA complexes were added. The final concentration of siRNA was 40 nmol/L and concentration of Lipofectamine 2000 was 0.2%. The sequences of MMP-9 siRNA were 5′-GGGCUUAGAUCAUUCUUCATT-3 and 3′-UGAAGAAUGAUUAAGCCCAG-5. After incubation for 4 hours, the medium was replaced with culture medium containing 25 mmol/L glucose and 10% FBS. Quantitative RT polymerase chain reaction was performed to determine the level of MMP-9 gene expression after 24 hours.
Diabetic models
Sprague Dawley rats weighing 250–300 g were used for these experiments. Diabetes was induced via a single intraperitoneal injection of freshly dissolved streptozocin (50 mg/kg of body weight; Sigma-Aldrich Co., St Louis, MO, USA) in 0.1 mol/L citrate buffer (pH 4.5). Three days after streptozocin injection, the serum glucose levels of the rats were examined. Rats displaying random blood glucose levels >16.7 mmol/L were considered diabetic and were selected for further experimentation.
Full-thickness skin wound preparation
Six weeks after modeling, rats were anesthetized using ethyl ether. Their dorsal hair was shaved using an electric clipper, and the surgical areas were disinfected with an alcohol/iodine solution. A sterile template 1.8 cm in diameter was placed on each side of the mid-back, and a full-thickness wound to the deep fascia corresponding to the size of the template was generated by excising the skin. The wounding day was considered as day 0.
Animal grouping and interventions
Twenty diabetic rats were randomly separated into four groups (n=5): 1) the diabetic group, consisting of untreated wounded diabetic rats; 2) the MMP-9-siRNA control group, consisting of wounded diabetic rats treated with MMP-9- siRNA solution; 3) the β-CD-(D3)7 group, consisting of wounded diabetic rats treated with β-CD-(D3)7 solution; and 4) the β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA group, consisting of wounded diabetic rats treated with β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complex solution. Each wound (1.8×1.8 cm) was made on the back of each rat by removing the whole skin, including the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue, with surgical scissors.
Measurement of wound closure
The wounds on each rat were digitally photographed on days 0, 2, 4, 6, and 7. The wound size was calculated on days 4 and 7 using ImageJ software (v 1.36b; National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA). The percentage of wound closure was calculated according to the following formula:
Statistical analyses
The results were expressed as the means ± standard deviation, and the statistical software program SPSS (v 16.0; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used to perform the calculations. Student’s t-test (two-tailed) was used for statistical analyses, and analysis of variance was used for data subjected to multiple comparisons, followed by Bonferroni post hoc analysis comparisons between two groups. A P-value <0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Results and discussion
Cytotoxicity of β-CD-(D3)7
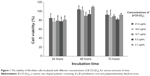
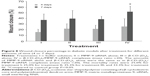
To investigate the cytotoxicity of β-CD-(D3)7, cell viability was determined by the MTT method. Figure 1 shows the viability of fibroblast cells incubated with different concentrations (21.3 μg/mL, 16.0 μg/mL, 10.7 μg/mL, 5.3 μg/mL, or 2.1 μg/mL) of β-CD-(D3)7 for various amounts of time (24 hours, 48 hours, or 72 hours). As can be seen in Figure 1, no significant difference in cell viability was observed between groups of fibroblast cells treated with different concentrations of β-CD-(D3)7, regardless of incubation time. Compared to a commercially available poly(amidoamine) dendrimer (poly(amidoamine), G=4), which has been reported in the literature as a standard nonviral gene carrier with a maximum safe dosage of only 10 μg/mL,30–32 β-CD-(D3)7 displayed much lower cytotoxicity. Moreover, the cell viability did not show mainly dose-dependent decrease nor mainly time-dependent increase. This could be attributed to the introduction of β-CD core with good biocompatibility,33 which would be an advantage were β-CD-(D3)7 used as a carrier for the delivery of MMP-9-siRNA.
Formation of β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes
The ability of β-CD-(D3)7 to condense MMP-9-siRNA into particulate structures was confirmed by agarose gel electrophoresis, particle size measurements, and TEM observation. Figure 2A shows the electrophoretic mobility of MMP-9-siRNA in the complexes between β-CD-(D3)7 and MMP-9-siRNA at various ratios of amino group (in β-CD-(D3)7) to phosphate group (in MMP-9-siRNA), defined as N/P ratio. As can be seen in Figure 2A, the migration of MMP-9-siRNA in agarose gel was completely retarded when the N/P ratio was equal to or higher than 4. Therefore, β-CD-(D3)7 could combine MMP-9-siRNA and condense complexes into nanoparticles due to the relatively higher density of primary amino group.
| (2) |
Figure 2B shows the particle size of β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes at various N/P ratios. It was found that β-CD-(D3)7 could efficiently compact MMP-9-siRNA into small nanoparticles. Moreover, the mean particle size decreased from 268 nm to 110 nm with the increase of N/P ratio from 6 to 60. Figure 2C gives a representative TEM image and particle size distribution for the β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes at the N/P ratio of 30. It was found that these complexes had a spherical morphology and a narrow particle size distribution.
Transfection efficiency of β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes
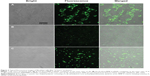
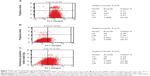
The transfection efficiency of β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes was investigated in fibroblast cells by confocal microscopy and flow cytometry. For a comparative study, Lipofectamine 2000/MMP-9-siRNA complexes were investigated for the same purpose. Figure 3 gives typical fluorescence images of transfected fibroblast cells. In the case of β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes with a low mass ratio of 4, only weak fluorescence signals were observed. At the mass ratio of 20, however, the cells transfected by β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes showed remarkable fluorescence signals, which were stronger than those of the cells transfected by Lipofectamine 2000/MMP-9-siRNA complexes. Further analyses were carried out by flow cytometry, as shown in Figure 4. The percentages of the cells in quadrants upper right and lower right represent the transfection efficiency, and the percentages of the cells in quadrants 2 and 3 represent the percentage of dead cells after transfection. The transfection efficiency and cell death percentages were determined, respectively, to be 28.93% and 1.32% for the cells treated by β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes with the mass ratio of 4; 98.78% and 5.57% for the cells treated by β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes with the mass ratio of 20; and 64.89% and 1.21% for the cells treated by Lipofectamine 2000/MMP-9-siRNA complexes with the mass ratio of 20. Similarly, β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes with other mass ratios (10, 30, and 40) were also investigated with respect to their transfection efficiency and cell death percentage, as depicted in Figure 5. These results confirmed high transfection efficiency of β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes in fibroblast cells.
Inhibition of MMP-9 by β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes
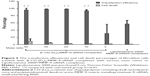
To determine whether β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes induced the downregulation of MMP-9 expression, the treatment by β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes with the mass ratio of 20 was compared to the treatment by Lipofectamine 2000/MMP-9-siRNA complexes. Figure 6 shows the effects of these treatments on MMP-9 mRNA downregulation in rat dermal fibroblast cells. After incubation in the media containing 25 mmol/L glucose and lipopolysaccharide (1 μg/mL) for 18 hours, MMP-9 expression in fibroblast cells was increased by 73% (P<0.01) when compared to the untreated group. When compared to the MMP-9 overexpression group, MMP-9 expression was decreased by 68% for the cells transfected by β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes, and by 80% for the cells transfected by Lipofectamine 2000/MMP-9-siRNA complexes. Therefore, β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes could effectively inhibit MMP-9 expression in fibroblast cells after the transfection, similar to Lipofectamine 2000/MMP-9-siRNA complexes. In addition, the protein expression level of MMP-9 in diabetic animals was found to decrease from 30.35±5.97 to 1.78±0.61 when treated with β-CD-(D3)7/MM9-siRNA complexes.
Wound healing efficiency
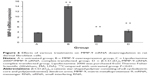
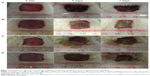
To evaluate the wound healing efficiency, the skin wounds in diabetic models were treated for various amounts of time with buffer solution, MMP-9-siRNA alone, β-CD-(D3)7 alone, and β–CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes (mass ratio =20), respectively, as shown in Figure 7. Figure 8 gives the wound-closure percentages in these cases. As can be seen in Figure 8, the wound-closure percentage in the case of MMP-9-siRNA alone did not show an obvious increase when compared to the percentages in the cases of buffer solution or β-CD-(D3)7 alone. In contrast, the use of β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes resulted in enhanced wound healing, particularly after treatment for 7 days. This may be attributed to the inhibition of β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes to MMP-9 expression in fibroblast cells. In addition, the level of blood glucose in the experimental animals was found to be 30.3±3.79 mmol/L and 24.5±11.6 mmol/L (P>0.05) before and after treatment with β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes, respectively. Further investigations will focus on the mechanism for enhanced wound healing in diabetic rats.
Conclusion
As a new cationic star-shaped polymer, β-CD-(D3)7 has good biocompatibility and strong complexation ability to MMP-9-siRNA. The resultant β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes exhibited high transfection efficiency and reduced MMP-9 expression in skin fibroblast cells. In addition, the use of β-CD-(D3)7/MMP-9-siRNA complexes resulted in enhanced wound healing in diabetic models.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51273216, 21074152, 81270916 and 81170766); Major Projects of People’s Livelihood Science and Technology in Guangzhou (201300000102);the Key Project of Scientific and Technical Innovation for Universities in Guangdong Province (cxzd1102); the Key Project of Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(10251008901000010); the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (S2013010012549); the Guangdong Province Sci-Tech exchange and cooperation grant by Guangdong Science and Technology Department (2010B050700017); and the Key Development Layout and Preferential Development Fields of Science and Technology of Guangdong Province (2009B030801150).The authors would like to thank Ping Zhu, Guo-Juan Lao, Shao-Yun Hao, Dong Ma, Guan-Hai Wang, Pei-Lian Liu, Zong-Cun Chen and Huan Weng for their technical assistance.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Boulton AJ, Vileikyte L, Ragnarson-Tennvall G, Apelqvist J. The global burden of diabetic foot disease. Lancet. 2005;366(9498):1719–1724. | ||
Lobmann R, Ambrosch A, Schultz G, Waldmann K, Schiweck S, Lehnert H. Expression of matrix-metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in the wounds of diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 2002;45(7):1011–1016. | ||
Lobmann R, Schultz G, Lehnert H. Proteases and the diabetic foot syndrome: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(2):461–471. | ||
Wysocki AB, Staiano-Coico L, Grinneill F. Wound fluid from chronic leg ulcers contains elevated levels of metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9. J Invest Dermatol. 1993;101(1):64–68. | ||
Ambrosch A, Halevy D, Fwity B, Brin T, Lobmann R. Effect of daptomycin on local interleukin-6, matrix metalloproteinase-9, and metallopeptidase inhibitor 1 in patients with MRSA-infected diabetic foot. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2013;12(2):100–105. | ||
Dinh T, Tecilazich F, Kafanas A, et al. Mechanisms involved in the development and healing of diabetic foot ulceration. Diabetes. 2012;61(11):2937–2947. | ||
Yang C, Zhu P, Yan L, Chen L, Meng R, Lao G. Dynamic changes in matrix metalloproteinase 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 levels during wound healing in diabetic rats. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2009;99(6):489–496. | ||
Liu Y, Min D, Bolton T, et al. Increased matrix metalloproteinase-9 predicts poor wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(1):117–119. | ||
Reiss MJ, Han YP, Garcia E, Goldberg M, Yu H, Garner WL. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 delays wound healing in a murine wound model. Surgery. 2010;147(2):295–302. | ||
Chen SM, Ward SI, Olutoye OO, Diegelmann RF, Kelman Cohen I. Ability of chronic wound fluids to degrade peptide growth factors is associated with increased levels of elastase activity and diminished levels of proteinase inhibitors. Wound Repair Regen. 1997;5(1):23–32. | ||
Trengove NJ, Stacey MC, MacAuley S, et al. Analysis of the acute and chronic wound environments: the role of proteases and their inhibitors. Wound Repair Regen. 1999;7(6):442–452. | ||
Lauer G, Sollberg S, Cole M, et al. Expression and proteolysis of vascular endothelial growth factor is increased in chronic wounds. J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115(1):12–18. | ||
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391(6669):806–811. | ||
Hammond SM, Boettcher S, Caudy AA, Kobayashi R, Hannon GJ. Argonaute2, a link between genetic and biochemical analyses of RNAi. Science. 2001;293(5532):1146–1150. | ||
Hannon GJ. RNA interference. Nature. 2002;418(6894):244–251. | ||
Sharp PA. RNAi and double-strand RNA. Genes Dev. 1999;13(2):139–141. | ||
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 2001;411(6836):494–498. | ||
Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001;409(6818):363–366. | ||
Fuchs U, Damm-Welk C, Borkhardt A. Silencing of disease-related genes by small interfering RNAs. Curr Mol Med. 2004;4(5):507–17. | ||
Cheng JC, Moore TB, Sakamoto KM. RNA interference and human disease. Mol Genet Metab. 2003;80(1–2):121–8. | ||
Joo MK, Yhee JY, Kim SH, Kim K. The potential and advances in RNAi therapy: Chemical and structural modifications of siRNA molecules and use of biocompatible nanocarriers. J Control Release. 2014. | ||
Mao CQ, Du JZ, Sun TM, et al. A biodegradable amphiphilic and cationic triblock copolymer for the delivery of siRNA targeting the acid ceramidase gene for cancer therapy. Biomaterials. 2011;32(11):3124–3133. | ||
Hallaj-Nezhadi S, Lotfipour F, Dass CR. Delivery of nanoparticulate drug delivery systems via the intravenous route for cancer gene therapy. Pharmazie. 2010;65(12):855–859. | ||
Wang J, Lu Z, Wientjes MG, Au JL. Delivery of siRNA therapeutics: barriers and carriers. AAPS J. 2010;12(4):492–503. | ||
Georgiou TK, Vamvakaki M, Patrickios CS, Yamasaki EN, Phylactou LA. Nanoscopic cationic methacrylate star homopolymers: synthesis by group transfer polymerization, characterization and evaluation as transfection reagents. Biomacromolecules. 2004;5:2221–2229. | ||
Cryan SA, Holohan A, Donohue R, Darcy R, O’Driscoll CM. Cell transfection with polycationic cyclodextrin vectors. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2004;21:625–633. | ||
Xu FJ, Zhang ZX, Ping Y, Li J, Kang ET, Neoh KG. Star-shaped cationic polymers by atom transfer radical polymerization from beta-cyclodextrin cores for nonviral gene delivery. Biomacromolecules. 2009;10:285–293. | ||
Srinivasachari S, Fichter KM, Reineke TM. Polycationic beta-cyclodextrin “click clusters”: monodisperse and versatile scaffolds for nucleic acid delivery. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:4618–4627. | ||
Deng J, Li N, Mai KJ, Yang C, Yan L, Zhang LM. Star-shaped polymers consisting of a b-cyclodextrin core and poly(amidoamine) dendron arms: binding and release studies with methotrexate and siRNA. J Mater Chem. 2011;21:5273–5281. | ||
Ma K, Hu MX, Qi Y, et al. PAMAM-triamcinolone acetonide conjugate as a nucleus-targeting gene carrier for enhanced transfer activity. Biomaterials. 2009;30:6109–6118. | ||
Patil ML, Zhang M, Betigeri S, Taratula O, He H, Minko T. Surface-modified and internally cationic polyamidoamine dendrimers for efficient siRNA delivery. Bioconjug Chem. 2008;19(7):1396–1403. | ||
Fischer D, Li Y, Ahlemeyer B, Krieglstein J, Kissel T. In vitro cytotoxicity testing of polycations: influence of polymer structure on cell viability and hemolysis. Biomaterials. 2003;24(7):1121–1131. | ||
Uekama K, Hirayama F, Irie T. Cyclodextrin drug carrier systems. Chem Rev. 1998;98(5):2045–2076. |
 © 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.