Back to Journals » Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment » Volume 11
Case-control association study of ABCB1 gene and major depressive disorder in a local Chinese Han population
Authors Xie W, Zhang L, Wu R, Yu Y, Zhao J, Li L
Received 23 April 2015
Accepted for publication 29 June 2015
Published 4 August 2015 Volume 2015:11 Pages 1967—1971
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S87175
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
Wei-Wei Xie,1,2,* Lin Zhang,1,* Ren-Rong Wu,1 Yan Yu,3 Jing-Ping Zhao,1 Le-Hua Li1
1Mental Health Institute of the Second Xiangya Hospital, National Technology Institute of Psychiatry, Key Laboratory of Psychiatry and Mental Health of Hunan Province, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, 2Department of Psychiatry, Ningbo Kangning Hospital, Ningbo, 3People’s Hospital of Hunan Province, Changsha, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Background: Human P-glycoprotein encoded by the ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 1 (ABCB1) gene is expressed in the blood–brain barrier. ABCB1 protects the brain from many drugs and toxins such as glucocorticoids through the efflux pump. Recent evidence suggests that a specific allele of the ABCB1 gene confers susceptibility to major depressive disorder (MDD) in the Japanese population. The aim of this study was to explore the association of ABCB1 gene polymorphisms with MDD in a local Chinese Han population.
Methods: Two hundred and ninety-two MDD patients and 208 unrelated individuals were matched by age and sex and examined using a case-control design. Six single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the ABCB1 gene, including rs1045642, rs2032583, rs2032582, rs2235040, rs1128503, and rs2235015, were genotyped by ligase detection reaction and multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Linkage disequilibrium and haplotype analysis were investigated in the two study groups.
Results: Significant protection for MDD individuals carrying the TG haplotype of rs1045642–rs2032582 was observed (odds ratio 0.470, 95% confidence interval 0.251–0.897, P=0.01).The rs2032582 (G2677T) and rs1128503 (C1236T) SNPs of ABCB1 showed nominal associations with MDD; the other four SNPs of the ABCB1 gene were not associated with MDD.
Conclusion: Chinese individuals carrying the TG haplotype of rs1045642–rs2032582 had a nearly 53% lower risk of developing MDD. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report to analyze the effect of ABCB1 polymorphism on the risk of MDD in a Chinese population.
Keywords: major depressive disorder,ABCB1 gene, single nucleotide polymorphism, pharmacogenetics
Introduction
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a significant contributor to the global burden of disease and affects people in all communities worldwide.1 According to a disability-adjusted life years survey from the World Health Organization and the World Bank, unipolar depression was ranked fourth in 2012, and is expected to rank second in 2020 and first in 2030.2
The majority of depressed patients have abnormal hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis function, and it is believed that dysregulation of the HPA axis can induce depression. Glucocorticoids are end products and stress response factors in the HPA axis. Stressors can activate the HPA axis and increase glucocorticoid levels in the blood.3 High blood glucocorticoid levels are believed to be toxic to neurons in the brain and to cause depression.4
Human ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 1 (ABCB1), also known as multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1), P-glycoprotein 1, and cluster of differentiation 243 (CD243), is an important cell membrane protein. As one of the ATP-binding cassette transporters, it pumps foreign substances out of cells. This protein is expressed by endothelial cells at the blood–brain barrier, predominantly gathering on the luminal side of brain capillaries and functioning as an ATP-driven efflux pump. ABCB1 has an unusually broad ability to recognize foreign substances and expels hundreds of molecules from the brain, including many types of drugs and glucocorticoids.5
The ABCB1 gene contains single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the encoding regions. Variants such as C3435T (rs1045642), G2677T/A (rs2032582), and rs2032583 have been the most commonly studied by previous researchers. Most studies indicate that ABCB1 haplotypes, the SNPs rs1045642, rs2032582, and rs2032583 affect the response to treatment with antidepressants.5–10
Recently, a study in Japanese MDD patients reported that the A-41G, T-129C, C1236T, and G2677A/T haplotypes were significantly less common and that the C3435T allele was more common when compared with controls.4 The results suggested that a specific allele of the ABCB1 gene confers susceptibility to MDD in the Japanese population.
In the present study, we studied six SNPs in the ABCB1 gene and examined whether ABCB1 is associated with MDD, using 292 Chinese MDD patients and 208 unrelated control individuals from a local Chinese Han population. Haplotype-based association analyses were also performed to investigate the role of specific genotype combinations.
Materials and methods
Subjects
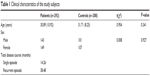
Two hundred and ninety-two patients with single or recurrent depression and 208 healthy controls were included in the study. All individuals were of Chinese Han ethnicity but not biologically related. Patients were recruited from the Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University between May 2006 and November 2012. All patients had more than 9 years of education, ranged in age between 18 and 65 years, and had a diagnosis of MDD as defined in Axis I of the DSM-IV-TR (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, Text Revision) and by a 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale score ≥18. Patients were excluded if they met DSM-IV-TR Axis I criteria for any other mental disorder, have other serious illness, or sequelae of serious illness. Patients were also excluded if they had serious suicide attempts and behavior. Each MDD patient underwent a medical assessment by at least two psychiatrists according to the DSM-IV-TR. Of the 292 MDD patients, 71.6% belonged to the single-episode category and 28.4% to the recurrent-episode category. The 208 controls (101 males, 107 females) were healthy volunteers recruited from the same geographical area and were matched with the patient group for sex, age, and level of education; they were interviewed using the Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview by a research psychiatrist to rule out any Axis I psychiatric disorders, and individuals with a current or past history of psychiatric treatment were excluded. The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee at the Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University and written informed consent was obtained from each patient before enrollment. The clinical characteristics of the two groups are shown in Table 1.
  | Table 1 Clinical characteristics of the study subjects |
Genotyping
Six SNPs of the ABCB1 gene were investigated in this study. They were SNP1 (rs1045642) in exon 27, SNP2 (rs2032583) in intron 22, SNP3 (rs2032582) in exon 22, SNP4 (rs2235040) in intron boundary exon 21, SNP5 (rs1128503) in exon 13, and SNP6 (rs2235015) in intron 5 of the ABCB1 gene. All the genotyping experiments were carried out by Shanghai BioWing Applied Biotechnology Company (http://www.biowing.com.cn) using ligase detection reaction (LDR). The target DNA sequences were amplified using a multiplex polymerase chain reaction method. The LDR was performed using 30 cycles of 95°C for 2 minutes, 94°C for 15 seconds, and 50°C for 25 seconds. The fluorescent products of LDR were differentiated using a 3730 ABI sequencer.
Haplotype and statistical analysis
Distributions of genotype and allele frequencies were compared between the patients and controls using the χ2 test for independence. The observed genotype frequencies were compared with the predicted frequencies to investigate the concordance with Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium. Pair-wise linkage disequilibrium, and haplotype analysis were conducted online using http://analysis.bio-x.cn/myAnalysis.php, a robust and user-friendly software platform that has a series of highly efficient analytical tools for use in association studies. Logistic regression analysis was used to estimate the risk of MDD associated with each genotype; odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were obtained. A P-value less than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Logistic regression analyses were performed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences version 17.0 for Windows software (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA). Adjustment for multiple comparisons was performed by Bonferroni correction.
Results
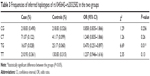
The distributions of genotypes and alleles for the examined ABCB1 gene SNPs in patients and controls are shown in Table 2. Multivariate logistic analysis was used to adjust for potential risk factors, including sex and age, of the six SNPs in the ABCB1 gene. No significant difference was observed in the allelic distributions of the rs1045642, rs2032583, rs2235040, and rs2235015 SNPs between patients and controls. The rs2032582 and rs1128503 SNPs, both of which are located in the ABCB1 gene coding region (exon 22 and exon 13, respectively) were associated with MDD. For the rs2032582 and rs1128503 polymorphisms, the minor T allele was significantly increased in patients when compared with controls (OR 1.325, 95% CI 1.028–1.707 and adjusted OR 1.338, 95% CI 1.037–1.726 for rs2032582; OR 1.317, 95% CI 1.016–1.707, adjusted OR 1.322, 95% CI 1.02–1.715 for rs1128503), but the statistical significance of this difference disappeared after Bonferroni correction (P>0.05). Using haplotype analysis, rs1045642 and rs2032582 were in strong linkage disequilibrium (D’=0.8, r2=0.47). Although haplotype analysis did not reveal any significant association with MDD, the TG haplotype of rs1045642–rs2032582 was associated with a lower risk of developing the disorder (OR 0.470, 95% CI 0.251–0.8897, P=0.01; Table 3). The association remained statistically significant after Bonferroni correction (P=0.04).
Discussion
The results of a genetic study of the association of six SNPs of the ABCB1 gene with MDD in a local Chinese Han population demonstrated significant protection against MDD in individuals carrying the TG haplotype of rs1045642–rs2032582. Chinese individuals carrying the TG haplotype of rs1045642–rs2032582 had a nearly 53% decreased risk of developing MDD. The rs1045642 and rs2032582 cover a region about 21,973 kb between exon 27 and exon 22. Among the six SNPs studied, no association between risk of MDD and the presence of a specific allele or genotype was observed. To our knowledge, this is the first report on the genetic association of ABCB1 gene polymorphism with MDD in a case-control design in Chinese Han people in Mainland China.
To date, over 100 polymorphisms that occur at a frequency of greater than 5% have been identified in the ABCB1 gene in Caucasians. It is known that rs2032582 (G2677T/A), a missense mutation in exon 21 that results in an amino acid change from Ala 893 to Ser or Thr, is associated with altered P-glycoprotein 1 expression, while rs1128503, a synonymous variant within exon 12 of the gene, occurring at position 1236 (C>T) and amino acid position 412 (Gly), may be in linkage disequilibrium with other functional variants.11,12 However, the functional effect of many common polymorphisms in the ABCB1 gene remains unknown.6
The association of ABCB1 (MDR1) gene with the risk of mood disorders was inconsistent in previous studies. Qian et al were the first to report that mood disorder was associated with possible alteration of P-glycoprotein 1 activity corresponding to ABCB1 gene polymorphism.13 Sixty-two patients with mood disorder and 160 controls were investigated in a Japanese study, and the results showed that the frequencies of MDR1 2677 G/A, the A/A genotype, and the A allele in mood disorders were significantly higher than in controls. Another Japanese study that included 631 MDD patients and 1,100 controls4 suggested that rs1045642 (C3435T) T allele or TT genotype carriers are susceptible to development of MDD. With respect to the other four SNPs (rs2188524, rs3213619, rs1128503, rs2032582), there was no significant difference in genotype or allele distribution. Ozbey et al reported that the rs1045642 C allele or CC genotype, but not the T allele, was associated with susceptibility to MDD in a Turkish population.14 Santos et al compared the distribution of allele and genotype frequencies for ABCB1 C1236T, G2677TA, and C3435T in 80 MDD patients and 160 controls. The results did not reveal any statistically significant association between the ABCB1 gene and MDD, but a significant protection against MDD in males carrying the T allele of the three polymorphisms was observed.15 Similarly, Crisafulli et al did not find any susceptible polymorphisms within the ABCB1 gene; however, as these authors mentioned, their limited sample size (145 MDD patients) may be one reason.16 The impact of ethnic variation on genetic distribution may explain the above inconsistency, and further studies with larger samples in different ethnic groups are needed.
Regarding our negative findings, we conducted power calculations using PASS 11 software to assess the power of our study, and determined that the power of the six SNPs in our study varied from 8.1% to 58.4%. Our samples may have been too small and lacked the statistical power to detect differences likely to be associated with single SNPs. Another limitation was that the A allele for rs2032582 was not detected in our study, and has a frequency of about 15% in the Chinese population.17 Larger and more homogenous samples will be included in our future research to improve the statistical power.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National R&D Special Fund for Health Profession (grant 201002003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant 81270019), and National Science and Technology Major Projects for Major New Drugs Innovation and Development (2012ZX09303014-001).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Marcus M, Yasamy MT, van Ommeren M, et al. Depression: a global public health concern. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Department of Mental Health and Substance Abuse; 2012. Available from: http://www.who.int/mental_health/management/depression/who_paper_depression_wfmh_2012.pdf. Accessed July 14, 2015. | ||
Möller HJ, Bitter I, Bobes J, et al. Position statement of the European Psychiatric Association (EPA) on the value of antidepressants in the treatment of unipolar depression. Eur Psychiatry. 2012;27(2):114–128. | ||
Kunugi H, Hori H, Adachi N, Numakawa T. Interface between hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in depression. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2010;64(5):447–459. | ||
Fujii T, Ota M, Hori H, et al. Association between the functional polymorphism (C3435T) of the gene encoding P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and major depressive disorder in the Japanese population. J Psychiatr Res. 2012;46(4):555–559. | ||
de Klerk OL, Nolte IM, Bet PM, et al. ABCB1 gene variants influence tolerance to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in a large sample of Dutch cases with major depressive disorder. Pharmacogenomics J. 2013;13(4):349–353. | ||
Rosenhagen MC, Uhr M. The clinical impact of ABCB1 polymorphisms on the treatment of psychiatric diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(26):2843–2851. | ||
Lin KM, Chiu YF, Tsai IJ, et al. ABCB1 gene polymorphisms are associated with the severity of major depressive disorder and its response to escitalopram treatment. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2011;21(4):163–170. | ||
Menu P, Gressier F, Verstuyft C, Hardy P, Becquemont L, Corruble E. Antidepressants and ABCB1 gene C3435T functional polymorphism: a naturalistic study. Neuropsychobiology. 2010;62(3):193–197. | ||
Sarginson JE, Lazzeroni LC, Ryan HS, Ershoff BD, Schatzberg AF, Murphy GM Jr. ABCB1 (MDR1) polymorphisms and antidepressant response in geriatric depression. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2010;20(8):467–475. | ||
Singh AB, Bousman CA, Ng CH, Byron K, Berk M. ABCB1 polymorphism predicts escitalopram dose needed for remission in major depression. Transl Psychiatry. 2012;2:e198. | ||
Bly MJ, Bishop JR, Thomas KL, Ellingrod VL. P-glycoprotein (PGP) polymorphisms and sexual dysfunction in female patients with depression and SSRI-associated sexual side effects. J Sex Marital Ther. 2013;39(3):280–288. | ||
Li YH, Wang YH, Li Y, Yang L. MDR1 gene polymorphisms and clinical relevance. Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2006;33(2):93–104. | ||
Qian W, Homma M, Itagaki F, et al. MDR1 gene polymorphism in Japanese patients with schizophrenia and mood disorders including depression. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006;29(12):2446–2450. | ||
Ozbey G, Yucel B, Taycan SE, et al. ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to major depression, but not with a clinical response to citalopram in a Turkish population. Pharmacol Rep. 2014; 66(2):235–238. | ||
Santos M, Carvalho S, Lima L, et al. Common genetic polymorphisms in the ABCB1 gene are associated with risk of major depressive disorder in male Portuguese individuals. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2014;18(1):12–19. | ||
Crisafulli C, Chiesa A, Han C, et al. Case-control association study of 36 single-nucleotide polymorphisms within 10 candidate genes for major depression and bipolar disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2013;209(1):121–123. | ||
Qiu HR, Dong HJ, Pan SY, Miao K. The single nucleotide polymorphism and haplotype analysis of MDR1 in Jiangsu Han population of China. Biomed Pharmacother. 2012;66(6):459–463. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.