Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 14
Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Improves Spinal Cord Function After Injury in Rats by Activating Autophagy
Authors Gu J, Jin ZS, Wang CM, Yan XF, Mao YQ, Chen S
Received 6 November 2019
Accepted for publication 18 March 2020
Published 29 April 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1621—1631
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S237502
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Yan Zhu
Jun Gu, Zheng Shuai Jin, Chun Ming Wang, Xue Fei Yan, Yuan Qing Mao, Sheng Chen
The Affiliated Jiangsu Shengze Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Suzhou 215228, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Sheng Chen Tel +8618013798189
Email [email protected]
Background: Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a global medical problem. The smallest membrane-bound nanovesicles, known as exosomes, have a role in complex intercellular communication systems and can be used directly as therapeutic agents by acting as important paracrine factors. Nevertheless, the use of exosomes derived from BMSCs (BMSC-Exos) to treat SCI has been less, and the specific mechanism has not yet been reported.
Methods: BMSC-Exos were characterized by TEM, NTA and Western blot. The effects of BMSC-Exos treatment were compared by SCI in vivo model and a series of in vitro experiments.
Results: BMSC-Exos were found to enhance the expression of autophagy-related proteins LC3IIB and Beclin-1 and enabled autophagosomes formation. After BMSC-Exos treatment, there was marked decline in the level of expression of proapoptotic protein cleaved caspase-3, while that of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 was upregulated.
Conclusion: BMSC-Exos can attenuate neuronal apoptosis by promoting autophagy and promote the potential efficacy of functional behavior recovery in SCI rats. In summary, these findings expand the theoretical knowledge and forms a realistic route for the future treatment of SCI by BMSC-Exos.
Keywords: bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, exosomes, spinal cord injury, apoptosis, autophagy
Introduction
Spinal cord injury (SCI) can be divided into two stages: primary mechanical and secondary injury. Secondary injuries, such as axonal destruction, edema, excitotoxicity and inflammation, can lead to neuronal apoptosis that is key in the neurological damage after physiological and functional defects in SCI.1
The transplantation of stem cells is one of the effective methods for treating various nerve injuries. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) can divided several types of cells because they are multifunctional and self-renewing.2 Studies have shown that BMSCs provide a microenvironment that facilitates cell survival by secreting neurotrophic factors, neuroprotective cytokines, and anti-inflammatory molecules as well as by reducing the production of stress-related proteins, reactive oxygen species, and proinflammatory cytokines.3 One study demonstrated that BMSC transplantation is effective in the treatment of acute brain injury.4 There are indications that BMSCs have the potential to treat ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.5 However, there remains a challenge of transplanting stem cells directly into target tissues. For instance, the survival rate of transplanted stem cells in ischemia have been found to be low.6 The limitations of direct stem cell transplantation clinically for the treatment of SCI are further due to some risks such as immune rejection, cell differentiation and tumor formation.
Recently, reports have indicated that transplanted stem cells have an important therapeutic function under paracrine mechanism, and also exosomes have been shown to be key in this process.7 As the smallest endocytic-derived membrane-bound nanovesicles, exosomes take part in the complex intercellular communication systems.8 When under normal or pathological conditions, exosomes are released from different types of cells and by carrying an activity signal they create an effect on the normal functions of the recipient cells. Besides lipids and cellular proteins, exosomes also hosts the cell messenger RNA (mRNA) and microRNA (miRNA).8 BMSC-derived exosomes (BMSC-Exos) have been used in animal models of various diseases including reduction of myocardial ischemia, promotion of skin healing, promotion damaged kidney repair and spinal nerves, and inhibition of liver vitaminization.9–11 Studies have also shown that BMSC-Exos have a repairing effect on SCI, but the specific mechanism is unclear.
Autophagy poses as a highly guarded catabolic phenomena where degradation of cytoplasmic components occurs and it is also results in a variety of illnesses including traumatic brain injury or SCI. Autophagy displays a type of “self-feeding” phenomenon in cells, which mainly eradicates the aged proteins or damaged organelles through the lysosome pathway.12 As an important intracellular degradation system, autophagy recycles and reuses the damaged organelles and macromolecules.12 It has an important role in the survival of cells and also as cell differentiation, growth, survival and homeostasis. Reports indicate that autophagy is crucial for the regulation of cell death during SCI before apoptosis.13 Autophagy is involved in the expression of the autophagy proteins Beclin-1 and light chain 3-II (LC3-II) and is importantly involved in neurodegenerative diseases for cytoprotection.14 However, it is still uncertain if the activation of autophagy after SCI can be promoted by BMSC-Exos.
Herein, according to our knowledge, is the first time that BMSC-Exos has been shown to attenuate neuronal apoptosis by promoting autophagy in the early stage and can promote the potential therapeutic effect of functional behavior recovery in SCI rats.
Materials and Methods
Preparation and Identification of Exosomes
First, BMSCs, purchased from the company (Cyagen, China), were fused to 70–80%, washed with PBS twice and then incubated in stem cell medium without any serum for 48 h (Gibco, USA). The collected medium was centrifuged at 300 g for 10 min and the supernatant obtained via filtration using a 0.22-μm filter that eliminates cell debris. The supernatant was then centrifuged at 4000 g at 4 °C using Amicon Ultra-15 centrifugal filter. To obtain 200 μL solution, the ultrafiltered PBS was washed twice and ultrafiltered. For further exosome purification, a 30% sucrose/D2O pad in an Ultra-ClearTM tube was used and an optima L-100 XP Ultracentrifuge was used to centrifuge the medium at 100,000 g for 60 min at 4 °C. Exosomes that underwent partial purification were obtained using an 18G needle, then they were diluted with PBS, and centrifuged through the filter unit at 4000 g at 4 °C to achieve 200 μL in the final volume. For further experiments, the recovered exosomes were stored at −80 °C. Nanovisual tracking analysis (NTA) was used to determine the size distribution and of concentration exosomes. Morphological identification of exosomes was performed by TEM. The Western blot analysis was employed to analyze the exosome’s surface marker proteins, including CD9, CD63, and TSG101.
Exosomal Uptake
For exosome fluorescent labeling, DiI solution (Eugene, USA) was introduced into PBS and incubated was conducted in accordance to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Ultracentrifugation at 4 °C removed the excess DiI dye. Dil-labeled exosomes (Dil-Exos) were washed with PBS triplicately and late resuspended. They were incubated with neuronal cells for 24 h. PBS was used to wash the cells and then they were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and the absorption of Dil-Exos by the cells was observed by laser confocal microscopy.
Primary Neuron Culture
Twenty-four hour-old sprague-Dawley newborn rats were subjected to 75% ethanol immersion, where the skin and cartilage of the back portion were cut open to separate the spinal cord. The separated spinal cord was rinsed in pre-cooled DMEM/F-12 medium, sliced, and then placed in a tube for centrifugation. Using 0.25% trypsin and 0.05% DNase, the neurons were dissociated in an incubator through digestion at 37 °C for 20 min. Then, on adding the horse serum the reaction halted, then centrifuging of the cells at 4 °C and 300 g for 5 min was performed, and resuspension was done in 10% horse serum solution of DMEM/F12, streptomycin (100 mg/mL), penicillin (100 IU/mL), and glutamine (0.5 mM). Seeding of the cells was done in poly-D-lysine-coated plates after counting, and incubated for 4 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. After the cells exhibited adherence, the seed plate fluid was replaced with a serum-free 96% Neurobasal medium consisting of B27 (2%, w/v), glutamine (0.5 mM), penicillin (100 IU/mL), and streptomycin (100 mg/mL). Every 2 days, half of the medium was replaced and the growth of the cells was monitored using an inverted microscope. Cell culturing was performed for 7 days and used for subsequent experiments.
Double-Labeled Adenovirus mRFP-GFP-LC3 Transfection
For 4 days, the obtained neuronal cells were seeded in confocal culture dishes and then transfected with mRFP-GFP-LC3 lentivirus (Han Heng Bio, China). The cells were then allocated to two groups: control group and BMSC-Exos group (100µg/mL); they were then fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, washed with PBS, and observed by fluorescence confocal. Red spots represent autolysosomes and yellow spots represent autophagosomes.
TEM
Trypsin (Thermo Fisher Scientific) digested the adherent neurons and then centrifuged after cell treatment. After, the supernatant was disposed, 2% glutaraldehyde precooling solution was introduced into the cell pellet at 4 °C for 2 h. Staining of the cell pellet with 2% uranyl acetate solution commenced for 2 h and dehydration in 50%, 70%, 90%, and 100% acetone, followed successively. The ultrastructure of the cells was investigated by electron microscope.
Animals and Grouping
220–260 g thirty adult healthy male SD rats were used in this study. A specific pathogen-free (SPF) animal center laboratory was prepared for rearing rats in a constant environment of 23 ± 0.5 °C with alternate 12-h light and dark cycles. The rats were randomly assigned to Sham group, SCI group, and BMSC-Exos group randomly (n=10/group). The SCI and BMSC-Exos groups were injected with 200 μL saline solution (PBS) and BMSC-Exos (1 μg μL−1 concentration of total protein in PBS), respectively, by intravenous tail administration 1 h after SCI.
Establishment of Rat Model of SCI
Briefly, deep anesthesia for 3 mL/kg body weight a dose of 10% chloral hydrate was induced in male rats intraperitoneal injection. Then, cutting of the skin and muscles of the back ensued, exposing the spine, and the T10 lamina was then removed. After the complete exposure of the dorsal spinal cord surface, the rat was dropped from a height of 12.5 mm using a 10 g rod (2.5 mm in diameter). After successful modeling, the muscles and skin were quickly sutured. To avoid urinary retention, the rat’s bladder was manually and gently evacuated thrice in a day until up to when the restoration of the reflex control of urination was complete. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Suzhou university. All procedures were conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the National Institutes of Health Laboratory Animal Care and Use Guidelines.
Behavioral Assessment
The Basso-Beattie-Bresnahan (BBB) score and footprint test aided the assessment of the motor function, according to previous reports. The scores were determined before surgery and after the 1st, 3rd, 7th, 14th, 21st, and 28th day after surgery. The BBB score ranges from 0 to 21. A total score of 0 represents severe neurological dysfunction and 21is attributed to normal performance. 28 days after surgery, the gait and motor coordination were assessed. Different colored dyes were used to coat the front and rear paws of the rat. The rat which surrounded by a cage, was made to move in a straight direction on a piece of an absorbent paper. Then, the digitized footprint patterns helped to asses the coordination.
Western Blot Analysis
BCA method was utilized to estimate the concentration of total protein extracted. Electrophoresis on the sample by sodium dodecyl sulfate gel was performed, and the separated protein was transferred to a PVDF membrane. The 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) was used to block the membrane at room temperature for 1 h. Primary antibodies included CD9 (1:2000), CD63 (1:1000), TSG101 (1:1000), Calnaxin (1:1000), LC3B (1:1000), Beclin-1 (1:1000; Abcam), P62 (1:1000), Cleaved caspase-3 (1:1000), Bcl-2 (1:1000), and GAPDH (1:5000). It was then incubated with anti-rabbit IgG and anti-mouse IgG (1:2000) for 120 min and then visualized using enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) reagent. The bands were reacted, and the Image J software determined the protein expression levels by densitometry.
Organizational Preparation
A potent dose of chloral hydrate was used to anesthetize the rats and the cutting of the chest and abdomen skin commenced. To fully expose the chest cavity, the xiphoid was raised exposing the thoracic cavity along the ribs. Then, clamping of the sternum with hemostatic forceps forced it backwards to allow fixing of an empty needle into the heart. At the right atrial appendage, a small gap was cut to infuse ice-cold saline through the heart. Until the viscera of the rat turned whitish, the process was halted and to indicate that the blood was replaced by saline, a colorless liquid was made to overflowed from the right atrial appendage. To make the limbs and trunk of the rat stiff, sustained perfusion with 4% paraformaldehyde was conducted. While maintaining the integrity of the tissue, the spine was removed, exposing the lamina and the spinal cord was carefully separated. The portion of the spinal cord between 1 cm from the head and the tail was taken. Fixing and dehydration of the tissue was performed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 24 h and 30% sucrose solution for 48 h respectively. Dehydration was considered to be thorough when the tissue sank at the bottom of the container. The tissue was then embedded in an OTC embedding agent, and the frozen slice was sliced along the longitudinal axis of the spinal cord. The slice thickness was 18 µm, and it was placed on a polylysine-treated anti-offset slide. For subsequent use, all slides were stored at −80 °C.
Immunofluorescence Staining of Immune Cells and Tissues
Primary antibodies used in this study included MAP2 (1:200), LC3B (1:400), NeuN (1:800), and P62 (1:50), and the secondary antibody was a Cy3- or FITC-conjugated secondary antibody (1:200). First, cells or spinal cord sections were disrupted in Triton X-100 PBS solution (0.3%, w/v) for 20 min and then blocked with native goat serum PBS solution (10%, v/v). Incubation of the with primary antibody was conducted overnight at 4 °C, washed triplicately in PBS, and treated with secondary antibody for 2 h. To obtain a fluorescent image, the nuclei were then stained with DAPI. All images for different exposure times and conditions were taken at the same time.
TUNEL Staining
After the sections were fixed, ruptured, and blocked, they were incubated at 37 °C for 1 h with the colorimetric TUNEL reaction mixture (Promega), stained with DAPI, and analyses conducted under a fluorescence microscope. Then calculation of the number of TUNEL-positive cells in each group was conducted.
Statistical Analysis
SPSS 17.0 statistical software performed the statistical analysis, and the mean ± standard deviation was utilized as a way to express the results. One-way analysis of variance analyzed the differences between groups followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. Differences with P ≤ 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant.
Results
Identification and Uptake of BMSC-Exos
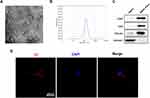
Exosomes were obtained from the BMSC culture supernatants through ultrafiltration-centrifugation combined with ultracentrifugation. After isolation and purification, the BMSC nanoparticles were characterized by TEM, NTA, and Western blot. TEM image suggests that the BMSC nanoparticles have the typical exosomal structures (Figure 1A). NTA suggests that the particle size distribution of these nanoparticles is between 30 and 150 nm (Figure 1B), which is similar to that in other reports. Furthermore, positive specific exosomal surface markers CD9, CD63, and TSG101 can be found in BMSC-Exos through Western blot (Figure 1C), which corroborates the presence of exosomes. The above analyses suggest the successful isolation and identification of the exosomes extracted from BMSCs.
To further investigate whether neuronal cells can absorb BMSC-Exos, in vitro incubation of Dil-Exos with neuronal cells was performed, and fluorescence microscopy was utilized to observe this uptake. After 24 h of incubation, Dil-Exos were found to be taken up by neuronal cells and transferred to the cytoplasm (Figure 1D). All together, these findings indicate that neuronal cells can take up BMSC-Exos. In vivo experiments demonstrated that Dil-Exos can reach the site of spinal cord injury and be absorbed by nerve cells after injection (Supplementary Figure 1). In summary, these data show that BMSC-Exos can be transmitted to the SCI area and be absorbed by nerve cells.
Identification of Primary Cultured Neurons in vitro
MAP2 is specific for neurons and promotes assembly and stability of microtubule networks; therefore, it is considered as a hallmark of mature neurons. Cells isolated from neonatal rats exhibit neuronal morphology consisting of cell bodies, dendrites, and axons, and express MAP2. Culturing of primary neurons was performed until the 7th day; neuronal nuclei were identified by NeuN, and neuronal axons were identified by MAP2 expression (Supplementary Figure 2).
BMSC-Exos Induce Autophagy Activation in vitro
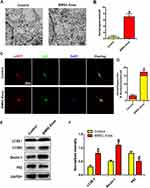
Since autophagy is crucial for the protection against SCI, the impact of BMSC-Exos on the activation of autophagy was examined. To detect autophagy-related indicators, neuronal cells were cultured with or without BMSC-Exos. TEM results suggests that the was an increase in the number of autophagosomes in BMSC-Exos-treated cells compared to that in the Control group (Figure 2A and B). For better understanding of autophagy, neurons were transfected with mRFP-GFP-LC3 virus and the autophagy flux was observed using a laser confocal microscope. For this assay, autophagic lysosomes were labeled with red fluorescence (red spots) and the autophagosomes were labeled with red and green fluorescence (yellow spots). There were more yellow and red spots in the BMSC-Exos group than in the Control group (Figure 2C and D). The autophagy-related proteins were detected by Western blot. The results indicate that BMSC-Exos treatment enhanced the expression of LC3BII and Beclin-1 autophagy-related proteins and decreased the expression of the P62 protein (Figure 2E and F). BMSC-Exos was found to be activated by autophagy in the neuronal cells.
Neuroprotective Effect of BMSC-Exos on SCI
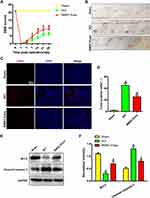
The BBB score evaluated the effect of BMSC-Exos treatment on the motor recovery function after SCI. The findings revealed that the recovery of motor function was gradually improved in the BMSC-Exos and SCI groups after 1 week of treatment. Compared to the SCI group, the BBB score of the BMSC-Exos group continued to increase significantly in 2–4 weeks after SCI (Figure 3A). Gait analysis showed that the coordination of front paw and hind paw movement was significantly decreased after SCI, but compared to the SCI group, the gait recovery of the BMSC-Exos-treated group was markedly accelerated and the movement coordination was improved (Figure 3B).
Subsequently, neuronal apoptosis in the SCI area was detected by TUNEL staining method. The TUNEL experiment confirmed that the proportion of TUNEL-positive neurons in the BMSC-Exos group was lower than that in the SCI group on the third day after SCI (Figure 3C and D). In addition, Western blot analysis showed an increase in apoptosis-related proteins in the spinal cord after SCI. The level of the proapoptotic protein cleaved caspase-3 was significantly decreased compared to the SCI group and that of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 was increased in the BMSC-Exos group (Figure 3E and F). These results indicate that BMSC-Exos treatment has a certain neuroprotective effect on the injured spinal cord and assists in the functional behavior recovery after SCI.
BMSC-Exos Induces Activation of Autophagy After SCI
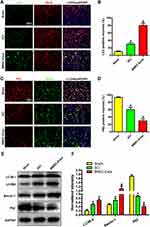
To investigate the activation of autophagy after BMSC-Exos treatment, neurons were subjected to immunohistochemical staining for LC3 and P62, and the number of LC3/NeuN/DAPI and P62/NeuN/DAPI double-positive cells was counted. Compared to the SCI groups, the cells in the BMSC-Exos-treated group showed increased expression of LC3 (Figure 4A and B) and decreased expression of P62 (Figure 4C and D), indicating that BMSC-Exos promoted autophagy after SCI; this finding was corroborated by the in vitro test results. The results of immunofluorescence analysis were confirmed by Western blot analysis. Compared to the SCI group, the LC3BII and Beclin-1 proteins expressions were increased in the BMSC-Exos group on the third day after injury, while the expression of the P62 protein was decreased (Figure 4E and F). These results indicate that BMSC-Exos treatment promotes autophagy of neuronal cells after SCI.
Discussion
SCI is a medical problem worldwide. Secondary injury has a significant effect on SCI and is caused by various factors including apoptosis, oxidative stress, inflammation and autophagy.1,15 This present work is the first demonstration that BMSC-Exos can suppress neuronal apoptosis enhancing autophagy and improving the behavioral function of rats. Briefly, the abundance of autophagy-related protein LC3IIB and Beclin-1 were found to be increased by BMSC-Exos, which also promoted the autophagosomes formation. After BMSC-Exos treatment, there was notable decline in the abundance of cleaved caspase-3 in SCI rats. However, there was an upregulation in the level of Bcl-2.
Given the recent developments in transplantation treatments, BMSCs are beneficial as they possess strong self-renewal and differentiation ability, and also low immunogenicity, thus drawing immense interest.16 Previous reports have shown that BMSCs have a unique neuroprotective effect and can aid in the functional recovery after SCI.17 However, it has also been suggested that only 1% of transplanted BMSCs can be transferred to the desired target tissue, successfully. In addition, after intravenous injection, a large number of transplanted BMSCs are trapped in the liver and lungs.18 Although BMSC therapy is successful in several animal disease models, there are still some underlying problems yet to be solved before the translation of this approach into clinical applications due to the great physiological differences between animals and humans.
Exosomes produced from many cell-types contain surface antigens which vary depending on the source cell.8 The vesicles facilitate cell-to-cell communication based on bioactive lipids, proteins and RNA. Numerous studies indicate that that various types of MSC-Exos play a role in cell protection, angiogenesis, antiapoptosis and inflammation regulation.19 BMSC-Exos have been utilized in numerous fields including immunological diseases, cardiovascular diseases, kidney damage, nervous system diseases and tumors.20,21 In regeneration medicine, exosomes may have an edge over stem cells because they are limited by direct stem cell transplantation.22 The transplantation therapy of stem cell probably functions through a paracrine mechanism. Hence, we postulated that direct transplantation of BMSC-Exos can remove the impediments brought as a result of direct inoculation of stem cell therapy. First, we successfully extracted BMSCs and prepared highly concentrated dispersions of exosomes from the supernatant of stem cells. NTA findings indicated that the exosomes have a diameter of 30–150 nm and these results were confirmed by TEM and exosomal CD63, CD9, and TSG101.
The developmental process of SCI is complex, and apoptosis is a major process of secondary injury of SCI. After neuronal injury, there was an upregulation of the expression of the proapoptotic protein cleaved caspase-3, while there was a downregulation of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2.23,24 To verify the BMSC-Exos protective effect on neurons after SCI, we evaluated the extent of neuronal apoptosis after SCI by TUNEL staining in vivo. As expected, the apoptosis of injured spinal cord cells was found to be effectively prevented by BMSC-Exos according to findings from in vivo TUNEL experiments. Western blot results showed the downregulation of the expression of proapoptotic markers in the injured spinal cord, while that of antiapoptotic markers was upregulated, thus further confirming our results. The BBB score and gait analysis also showed that the gait recovery of the animals after BMSC-Exos treatment was significantly accelerated, and the movement coordination improved, indicating that BMSC-Exos accelerates the motor function restoration after SCI.
Recent studies show that autophagy influences the recovery of motor function following SCI.25,26 It is also involved in numerous neurodegenerative illnesses as well as in ischemic and traumatic brain damage.27 Several studies show that autophagy is essential to the regulation of cell homeostasis as it acts as a quality control process for cellular biomolecules.28 Cells develop adaptive and protective mechanisms to survive due to cellular stress-induced autophagy. After autophagy, LC3IIB and Beclin-1 were upregulated and P62 expression was downregulated.29–31 Numerous reports have suggested that in the models of trauma-based brain injury in rats, a reduction in cell damage can be induced by an increase in autophagy by treating the components of the lesion.32 Notably, that self-protection mechanism induced by autophagy is thought to be induced by traumatic SCI in several experimental model of cell injury.13 Baixauli et al discovered that exosomes with are very important for maintaining RNA homeostasis and intracellular protein due to their special ability to utilize both autophagy-lysosomal pathways for the elimination of intracellular stress conditions.33 However, there is no report indicating if BMSC-Exos can cause autophagy to target cells so as to avert tissue damage. In our work, co-incubation of BMSC-Exos induced autophagy was found when in vitro electron microscopy and mRFP-GFP-LC3 lentiviral transfection tests were conducted. To further understand the mechanism of BMSC-Exos-induced autophagy, in vivo immunofluorescence experiments confirmed that BMSC-Exos can effectively increase the expression of LC3 and downregulate the expression of P62, further confirming our in vitro results. The BMSC-Exos was found to increase the expression of autophagy-related proteins LC3IIB and Beclin-1 and decrease the expression of P62 on the third day after SCI after Western blot test.
Taken together, this is the first demonstration that BMSC-Exos can attenuate neuronal apoptosis by promoting autophagy in the early stage and promote the potential therapeutic effect of functional behavior recovery in SCI rats. Therefore, these findings expand the knowledge and form a realistic route for the future treatment of SCI by BMSC-Exos.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Suzhou Science and Technology Bureau Science and Technology Livelihood Project 2018 (SS201850), Suzhou Revitalizing the key talent’s subsidy project in science and education 2017 (KJXW2017076) and Wujiang District Science and Education 2017 and 2018 (wwk201709, wwk201820).
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. McDonald JW, Sadowsky C. Spinal-cord injury. Lancet. 2002;359(9304):417–425. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07603-1
2. Esrefoglu M. Role of stem cells in repair of liver injury: experimental and clinical benefit of transferred stem cells on liver failure. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(40):6757–6773. doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i40.6757
3. Li H, Wang C, He T, et al. Mitochondrial transfer from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to motor neurons in spinal cord injury rats via gap junction. Theranostics. 2019;9(7):2017–2035. doi:10.7150/thno.29400
4. Feng Y, Ju Y, Cui J, Wang L. Bone marrow stromal cells promote neuromotor functional recovery, via upregulation of neurotrophic factors and synapse proteins following traumatic brain injury in rats. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(1):654–660. doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.6619
5. Vahidinia Z, Azami Tameh A, Nejati M, et al. The protective effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of ischemic stroke via reducing the C-Jun N-terminal kinase expression. Pathol Res Pract. 2019;215(9):152519. doi:10.1016/j.prp.2019.152519
6. Balsam LB, Wagers AJ, Christensen JL, Kofidis T, Weissman IL, Robbins RC. Haematopoietic stem cells adopt mature haematopoietic fates in ischaemic myocardium. Nature. 2004;428(6983):668–673. doi:10.1038/nature02460
7. Ratajczak MZ, Jadczyk T, Pedziwiatr D, Wojakowski W. New advances in stem cell research: practical implications for regenerative medicine. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2014;124(7–8):417–426. doi:10.20452/pamw.2355
8. Thery C, Witwer KW. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750.
9. Zhao J, Li X, Hu J, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes attenuate myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury through miR-182-regulated macrophage polarization. Cardiovasc Res. 2019;115(7):1205–1216. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvz040
10. Xu R, Zhang F, Chai R, et al. Exosomes derived from pro-inflammatory bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduce inflammation and myocardial injury via mediating macrophage polarization. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(11):7617–7631. doi:10.1111/jcmm.14635
11. Li C, Jiao G, Wu W, et al. Exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit neuronal apoptosis and promote motor function recovery via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Transplant. 2019;28:963689719870999.
12. Mizushima N, Komatsu M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 2011;147(4):728–741. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.026
13. Sekiguchi A, Kanno H, Ozawa H, Yamaya S, Itoi E. Rapamycin promotes autophagy and reduces neural tissue damage and locomotor impairment after spinal cord injury in mice. J Neurotrauma. 2012;29(5):946–956. doi:10.1089/neu.2011.1919
14. He M, Ding Y, Chu C, Tang J, Xiao Q, Luo ZG. Autophagy induction stabilizes microtubules and promotes axon regeneration after spinal cord injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(40):11324–11329. doi:10.1073/pnas.1611282113
15. Rong Y, Liu W, Zhou Z, et al. Harpagide inhibits neuronal apoptosis and promotes axonal regeneration after spinal cord injury in rats by activating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Brain Res Bull. 2019;148:91–99. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.03.014
16. Abbasi-Malati Z, Roushandeh AM, Kuwahara Y, Roudkenar MH. Mesenchymal stem cells on horizon: a new arsenal of therapeutic agents. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2018;14(4):484–499. doi:10.1007/s12015-018-9817-x
17. Wu Q, Wang Q, Li Z, et al. Human menstrual blood-derived stem cells promote functional recovery in a rat spinal cord hemisection model. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(9):882. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0847-8
18. Phinney DG, Prockop DJ. Concise review: mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells: the state of transdifferentiation and modes of tissue repair–current views. Stem Cells. 2007;25(11):2896–2902. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2007-0637
19. Xin H, Li Y, Cui Y, Yang JJ, Zhang ZG, Chopp M. Systemic administration of exosomes released from mesenchymal stromal cells promote functional recovery and neurovascular plasticity after stroke in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33(11):1711–1715. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2013.152
20. Wang C, Wang M, Xu T, et al. Engineering bioactive self-healing antibacterial exosomes hydrogel for promoting chronic diabetic wound healing and complete skin regeneration. Theranostics. 2019;9(1):65–76. doi:10.7150/thno.29766
21. Milano G, Biemmi V, Lazzarini E, et al. Intravenous administration of cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosomes protects against doxorubicin/trastuzumab-induced cardiac toxicity. Cardiovasc Res. 2019. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvz108
22. Baglio SR, Pegtel DM, Baldini N. Mesenchymal stem cell secreted vesicles provide novel opportunities in (stem) cell-free therapy. Front Physiol. 2012;3:359. doi:10.3389/fphys.2012.00359
23. Seki T, Hida K, Tada M, Koyanagi I, Iwasaki Y. Role of the bcl-2 gene after contusive spinal cord injury in mice. Neurosurgery. 2003;53(1):
24. Springer JE, Azbill RD, Knapp PE. Activation of the caspase-3 apoptotic cascade in traumatic spinal cord injury. Nat Med. 1999;5(8):943–946. doi:10.1038/11387
25. Rong Y, Liu W, Lv C, et al. Neural stem cell small extracellular vesicle-based delivery of 14-3-3t reduces apoptosis and neuroinflammation following traumatic spinal cord injury by enhancing autophagy by targeting Beclin-1. Aging. 2019;11(18):7723–7745. doi:10.18632/aging.102283
26. Rong Y, Liu W, Wang J, et al. Neural stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles attenuate apoptosis and neuroinflammation after traumatic spinal cord injury by activating autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(5):340. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-1571-8
27. Guo F, Liu X, Cai H, Le W. Autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases: pathogenesis and therapy. Brain Pathol, 2018;28(1):3–13.
28. Singh R, Cuervo AM. Autophagy in the cellular energetic balance. Cell Metab. 2011;13(5):495–504. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2011.04.004
29. Huang R, Liu W. Identifying an essential role of nuclear LC3 for autophagy. Autophagy. 2015;11(5):852–853. doi:10.1080/15548627.2015.1038016
30. Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT, Tang D. The Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2011;18(4):571–580. doi:10.1038/cdd.2010.191
31. Lamark T, Svenning S, Johansen T. Regulation of selective autophagy: the p62/SQSTM1 paradigm. Essays Biochem. 2017;61(6):609–624. doi:10.1042/EBC20170035
32. Galluzzi L, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Blomgren K, Kroemer G. Autophagy in acute brain injury. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016;17(8):467–484. doi:10.1038/nrn.2016.51
33. Baixauli F, Lopez-Otin C, Mittelbrunn M. Exosomes and autophagy: coordinated mechanisms for the maintenance of cellular fitness. Front Immunol. 2014;5:403. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00403
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.