Back to Journals » Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare » Volume 13
Bladder Dysfunction in Iranian Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
Authors Azadvari M , Emami Razavi SZ , Shahrooei M, Naser Moghadasi A, Azimi A, Farhadi-Shabestari HR
Received 3 January 2020
Accepted for publication 6 March 2020
Published 2 April 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 345—349
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JMDH.S244697
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Mohaddeseh Azadvari,1,2 Seyede Zahra Emami Razavi,2 Masumeh Shahrooei,3 Abdorreza Naser Moghadasi,3 Amirreza Azimi,3 Hamid Reza Farhadi-Shabestari3
1Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Department, Sina Hospital, Multiple Sclerosis Research Center, Neuroscience Institute, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran; 2Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Department, Imam Khomeini Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran; 3Multiple Sclerosis Research Center, Neuroscience Institute, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Correspondence: Seyede Zahra Emami Razavi Imam Khomeini Hospital, Keshavarz AVE, Tehran 1419733141, Iran
Tel +98 21 6119 2291
Fax +98 21 66581604
Email [email protected]
Background: Bladder dysfunction is one of the most disabling problems in multiple sclerosis patients, associated with lower quality-of-life and social isolation. There have been few studies regarding bladder dysfunction in Iranian patients with multiple sclerosis. Therefore, this study was designed to assess bladder dysfunction in Iranian patients with multiple sclerosis.
Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted in the MS Clinic of Sina Hospital (affiliated to Tehran University of Medical Sciences) between January 2019 and January 2020. Patients were asked to fill the valid and reliable Persian version of the 8-item Actionable Bladder Symptom Screening Tool (ABSST) questionnaire. Demographic data and accompanying symptoms such as fatigue, depression, anxiety, bowel dysfunction, urinary problems and walking status were recorded.
Results: Two hundred and twenty-eight cases were enrolled. One hundred and eighty-three were female (80.3%) and 45 (19.7%) were male (F/M ratio=4). The mean ABSST score was 6.8± 5.7. Based on the cut-off value of eight, 83 (28.8%) had actionable bladder symptoms (36.4%). The mean age and duration of the disease were significantly higher in the group with ABSST≥ 8. The number of patients with urinary retention, dribbling, and incontinence was significantly higher in the second group, while the number of individuals who could walk without help was significantly higher in the first group (ABSST< 8). Logistic regression analysis by considering an ABSST score of less or more than 8 as dependent and age, sex, duration of the disease, marital status, education level, and BMI as independent variables showed that age, education level, and duration of the disease are independent predictors.
Conclusion: According to these results, nearly one-third of Iranian patients with MS suffer from an overactive bladder, which should be considered by physicians.
Keywords: multiple sclerosis, bladder dysfunction, Iran
Introduction
An autoimmune disease of the central nervous system, multiple sclerosis (MS) is characterized by demyelination and life-long disability.1,2 The disease affects all aspects of a patient’s life and impairs quality-of-life.3 Different factors such as psychological problems, poor sleep, pain perception, bladder/bowel dysfunction, and sexual dysfunction can negatively impact the quality-of-life in these patients.1,4–7
Bladder dysfunction is one of the most disabling aspects of MS, and affects 50–80% of all cases. This symptom can influence the social activity of these patients and impair quality-of-life.7 Bladder dysfunction is related to inferior physical functioning with longer disease duration.8 It should be considered that bladder dysfunction is a socially disturbing complication of MS,9 as it could disrupt routine activities and affairs.10 Previous urodynamic studies in MS cases have demonstrated detrusor hyperreflexia or hyporeflexia and detrusor sphincter dyssynergia in such patients.11–13
Although the number of MS patients has increased dramatically in Iran, no research has been carried out to evaluate bladder dysfunction. Therefore, we designed this study to assess bladder dysfunction in Iranian patients with multiple sclerosis.
Methods
This cross-sectional study was conducted in the MS clinic of Sina Hospital (affiliated to Tehran University of Medical Sciences) between January 2019 and January 2020.
Inclusion criteria included an age between 18–55 years, definite MS diagnosis, and no relapse for at least 1 month. Exclusion criteria comprised cognitive impairment, systemic diseases such as diabetes, brain trauma, previous surgery of genitourinary system, and urinary tract infection during the last week.
Following the Declaration of Helsinki, written informed consent was obtained from all cases. This study was approved by the ethics committee of Tehran medical university with the code number IR.TUMS.MEDICINE.REC.1397.041.
Patients were asked to fill the valid and reliable Persian version of the 8-item Actionable Bladder Symptom Screening Tool (ABSST) questionnaire.14 The ABSST questionnaire includes eight questions with answers ranging from zero (no symptoms or impact) to three (extreme symptoms or impact). Total score is the sum score of all questions (minimum=0, maximum=24). The cut-off value of eight is considered to indicate actionable bladder. Question number nine is a yes/no question, asking if the patient needs help for his/her bladder symptoms and is not included in the final score.
The Persian version has excellent internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha=0.91) with an intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) of 0.86. The CVR (content validity ratios) and CVI (content validity indexes) of all questions are between 0.66 and 1.14
Data regarding age, sex, age at the first symptom onset, education level, marital status, family history of MS, symptoms such as fatigue, depression, anxiety, bowel dysfunction, urinary frequency during the day and/or night, urinary urgency, incontinence during the day and night, dysuria, dribbling, urinary retention, and whether help was needed for walking were recorded.
We used SPSS software version 22 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL) to perform data analysis. Data are presented as Mean±SD for continuous variables or frequencies for categoricalones. An independent sample t-test was used for comparison between quantitative variables. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
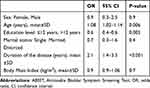
Two hundred and twenty-eight cases were enrolled, out of which 183 were female (80.3%) and 45 (19.7%) male (F/M ratio=4). Basic characteristics of patients are summarized in Table 1.
 |
Table 1 Basic Characteristics of Enrolled Cases |
The most common reported symptom was fatigue followed by anxiety. Among urinary symptoms, day-time frequency and urgency were the most common symptoms (Table 2).
 |
Table 2 Symptoms of Enrolled Patients |
The mean ABSST score was 6.8±5.7. Based on a cut-off value of eight, 83 (28.8%) had actionable bladder symptoms (36.4%). The mean age and duration of the disease were significantly higher in the group with ABSST≥8. There was no significant difference regarding sex in two groups (p=0.57). The number of patients with urinary retention, dribbling, and incontinency was significantly higher in the second group, while the number of individuals who could walk without help was significantly higher in the first (ABSST<8) (Table 3). According to question number nine, 72 (31.5%) needed help for voiding.
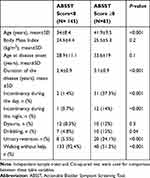 |
Table 3 Comparison of Different Factors Between Two Groups According to Actionable Bladder Symptom Screening Tool (ABSST) Score |
Logistic regression analysis by considering ABSST scores less or more than 8 as dependent and age, sex, duration of the disease, marital status, education level, and BMI as independent variables demonstrated age, education level, and duration of the disease as independent predictors (Table 4).
Discussion
Results of the current study showed that 28% of MS patients suffering from neurogenic bladder are of older age or have longer duration of disease. We also found a higher prevalence of neurogenic bladder symptoms in patients who needed help for walking.
Nakipoglu et al15 assessed 52 MS patients in Turkey and reported a higher duration of disease and age in cases with urinary symptoms, and urgency as the most frequent urinary symptom. In accordance with this evidence, our results were also indicative of frequency, incontinence, and urgency as the most common urinary symptoms.
In a previous study conducted in Turkey, Akkoç et al16 found the most prevalent symptoms in MS patients with overactive bladder to be urinary urgency, followed by frequency and incontinence. In their study, the mean ABSST score was 4.37±3.78, while it was 6.8±5.7 in our study. They also found a positive correlation between walking problems and overactive bladder.
In a cohort study conducted by Zecca et al,18 nearly one-third of patients reported urinary incontinency, while Hennessey et al17 reported urinary dysfunction in 44% of enrolled patients. Mahajan et al19 evaluated 9,702 MS patients and reported moderate-to-severe urinary symptoms in 65%.
Approximately 80% of MS patients report urinary symptoms after almost six months of disease onset.20 Previous studies demonstrated that bladder symptoms could be the initial symptom in 2–30% of MS patients and the only presentation in 3%.12,21,22
Urinary urgency is experienced by 38–99%, and frequency by 26–82% of MS patients. Voiding phase symptoms are less common, with a prevalence ranging from 6–49%.23,24 Dysuria was found in 9% of our patients, which is lower than previously reported rates (13–36%).12,15,25
The prevalence of OAB ranges from 37–99% based on screening tools and assessment,26 which is defined as urgency, urge incontinence, urinary frequency, and nocturia.27 OAB symptom severity is correlated with disease duration and exacerbation. Our results demonstrated that disease duration was significantly higher in cases with ABSST≥8 and was a significant positive predictor of overactive bladder, which is in agreement with studies conducted by Mahajan et al19 and Akkoç et al.16
The number of MS patients has increased dramatically in Iran in the recent years, necessitating the need for comprehensive evaluation of patients to detect and control comorbidities.28,29 As a complication of MS, OAB may cause anxiety, stress, and social withdrawal in patients, thus lowering quality-of-life.
This study had some limitations. First, it was conducted in a tertiary hospital where some patients may have taken drugs that alter urinary symptoms before referring to our clinic. Second, we did not assess the quality-of-life of these patients. Further multi-centric studies with quality-of-life assessment are recommended.
Conclusion
According to our results, approximately one-third of Iranian patients with MS suffer from overactive bladder, which should be considered by physicians. Management of urinary problems can limit secondary complications such as anxiety, depression, and social isolation.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Ghajarzadeh M, Jalilian R, SAhraian MA, et al. Pain in patients with multiple sclerosis. Maedica. 2018;13(2):125.
2. Jongen PJ, Blok BF, Heesakkers JP, Heerings M, Lemmens WA, Donders R. Validation of a dutch version of the actionable 8-item screening questionnaire for neurogenic bladder overactivity in multiple sclerosis: an observational web-based study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2015;13(1):175. doi:10.1186/s12955-015-0368-4
3. Ghajarzadeh M, Azizi S, Moghadasi AN, et al. Validity and reliability of the persian version of the perception de la scle’rose en plaques et de ses pousse’es questionnaire evaluating multiple sclerosis-related quality of life. Int J Prev Med. 2016;7.
4. Askari F, Ghajarzadeh M, Mohammadifar M, Azimi A, Sahraian MA, Owji M. Anxiety in patients with multiple sclerosis: association with disability, depression, disease type and sex. Acta Med Iran. 2014;889–892.
5. Ghajarzadeh M, Jalilian R, Mohammadifar M, Sahraian MA, Azimi A. Sexual function in women with multiple sclerosis. Acta Med Iran. 2014;315–318.
6. Ghajarzadeh M, Sahraian MA, Fateh R, Daneshmand A. Fatigue, depression and sleep disturbances in Iranian patients with multiple sclerosis. Acta Med Iran. 2012;244–249.
7. Vitkova M, Rosenberger J, Krokavcova M, et al. Health-related quality of life in multiple sclerosis patients with bladder, bowel and sexual dysfunction. Disabil Rehabil. 2014;36(12):987–992. doi:10.3109/09638288.2013.825332
8. Nortvedt M, Riise T, Myhr K, Landtblom A-M, Bakke A, Nyland H. Reduced quality of life among multiple sclerosis patients with sexual disturbance and bladder dysfunction. Multiple Sclerosis J. 2001;7(4):231–235. doi:10.1177/135245850100700404
9. Chancellor M, Blaivas J. Urological and sexual problems in multiple sclerosis. Clin neurosci. 1994;2(3–4):189–195.
10. Tang DH, Colayco D, Piercy J, Patel V, Globe D, Chancellor MB. Impact of urinary incontinence on health-related quality of life, daily activities, and healthcare resource utilization in patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity. BMC Neurol. 2014;14(1):74. doi:10.1186/1471-2377-14-74
11. Ukkonen M, Elovaara I, Dastidar P, Tammela T. Urodynamic findings in primary progressive multiple sclerosis are associated with increased volumes of plaques and atrophy in the central nervous system. Acta Neurol Scand. 2004;109(2):100–105. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0404.2003.00184.x
12. Goldstein I, Siroky MB, Sax DS, Krane RJ. Neurourologic abnormalities in multiple sclerosis. J Urol. 1982;128(3):541–545. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(17)53037-2
13. Petersen T, Pedersen E. Neurourodynamic evaluation of voiding dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1984;69(6):402–411. doi:10.1111/ane.1984.69.issue-6
14. Azadvari M, Naser Moghadasi A, Azimi A, et al. Persian adaptation of actionable bladder symptom screening tool among patients with multiple sclerosis. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2020;13:79.
15. Nakipoglu G, Kaya A, Orhan G, et al. Urinary dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. J Clin Neurosci. 2009;16(10):1321–1324. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2008.12.012
16. Akkoc Y, Ersoz M, Yuceyar N, et al. Overactive bladder symptoms in patients with multiple sclerosis: frequency, severity, diagnosis and treatment. J Spinal Cord Med. 2016;39(2):229–233. doi:10.1179/2045772315Y.0000000021
17. Hennessey A, Robertson N, Swingler R, Compston D. Urinary, faecal and sexual dysfunction in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol. 1999;246(11):1027–1032. doi:10.1007/s004150050508
18. Zecca C, Riccitelli G, Disanto G, et al. Urinary incontinence in multiple sclerosis: prevalence, severity and impact on patients’ quality of life. Eur J Neurol. 2016;23(7):1228–1234. doi:10.1111/ene.2016.23.issue-7
19. Mahajan ST, Patel PB, Marrie RA. Under treatment of overactive bladder symptoms in patients with multiple sclerosis: an ancillary analysis of the NARCOMS patient registry. J Urol. 2010;183(4):1432–1437. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2009.12.029
20. Phe V, Chartier–Kastler E, Panicker JN. Management of neurogenic bladder in patients with multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Urol. 2016;13(5):275. doi:10.1038/nrurol.2016.53
21. Gallien P, Robineau S, Nicolas B, Le Bot M-P, Brissot R, Verin M. Vesicourethral dysfunction and urodynamic findings in multiple sclerosis: a study of 149 cases. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998;79(3):255–257. doi:10.1016/S0003-9993(98)90003-X
22. Miller A, Lublin F, Coyle PK. Multiple Sclerosis in Clinical Practice. CRC Press; 2003.
23. Kasabian NG, Krause I, Brown WE, Khan Z, Nagler HM. Fate of the upper urinary tract in multiple sclerosis. Neurourol Urodyn. 1995;14(1):81–85.
24. Amarenco G, Kerdraon J, Denys P. Bladder and sphincter disorders in multiple sclerosis clinical, urodynamic and neurophysiological study of 225 cases. Revue neurologique. 1995;151(12):722–730.
25. Wheeler JS
26. De Sèze M, Ruffion A, Denys P, Joseph P-A, Perrouin-Verbe B, group IFN-Ues. The neurogenic bladder in multiple sclerosis: review of the literature and proposal of management guidelines. Multiple Sclerosis J. 2007;13(7):915–928. doi:10.1177/1352458506075651
27. Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the standardisation sub‐committee of the international continence society. Neurourol Urodynamics. 2002;21(2):167–178.
28. Hosseinzadeh A, Baneshi MR, Sedighi B, Kermanchi J, Haghdoost AA. Incidence of multiple sclerosis in Iran: a nationwide, population-based study. Public Health. 2019;175:138–144. doi:10.1016/j.puhe.2019.07.013
29. Mohebi F, Eskandarieh S, Mansournia MA, Mohajer B, Sahraian MA. Multiple sclerosis in Tehran: rising prevalence alongside stabilizing incidence - true increase or enhanced diagnosis? Arch Iran Med. 2019;22(8):429–434.
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.