Back to Journals » Cancer Management and Research » Volume 10
Bioinformatic analysis of four miRNAs relevant to metastasis-regulated processes in endometrial carcinoma
Received 19 March 2018
Accepted for publication 21 May 2018
Published 1 August 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 2337—2346
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S168594
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Lingping Zhu,1,2 Zhiqun Shu,3 Xiaoming Sun2,3
1Department of General Practice, Shenzhen Longhua District Central Hospital, Shenzhen, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of General Practice, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China; 3Pudong Institute for Health Development, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China
Background: The purpose of this study was to investigate the expression of different miRNAs in nonmetastatic and metastatic endometrial cancer Existing evidence indicates that there are many factors affecting the metastasis of endometrial cancer, and miRNAs play an unique role in many processes of endometiral cancer.
Materials and methods: miRNA sequences were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas Project database, and Bioinformatics technique was used to deal with those data.
Results: We elucidated the relation between differentially expressed miRNAs and clinical information for a total of 260 tumor tissues and 22 tumor tissues that had metastasized. We used the threshold of P <0.05| log 2 FC | >1.2 to identify potential miRNAs. Four differentially expressed miRNAs were identified in nonmetastatic and metastatic endometrial cancers. Further differential analysis of metastatic tissue revealed that miR-1247 is associated with metastasis of endometrial cancer to the lung, and miR-3200 is associated with the clinical stage of endometrial cancer. A functional enrichment analysis showed that the four miRNAs may be involved in multiple pathways of cancer, including the Wnt, NOTCH, and TGF-β signaling pathways and signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells. Protein–protein interaction analysis showed that PAK6, SNAP25, MAN1A1, MYB, ZBTB4, UST, ALDH1A3, and NRP2 are hub genes of relevant miRNAs in endometrial cancers.
Conclusion: The current study indicates that these four miRNAs may be related to molecular markers of metastasis of endometrial cancer.
Keywords: endometrial cancer, bioinformatics, miR-1247, protein analysis
Introduction
Endometrial cancer is one of the three major gynecological malignancies, and its incidence has increased over time. Currently, it ranks second among gynecological cancers in developing countries after cervical cancer.1 The prognosis of endometrial cancer depends on the stage of the disease and the type of histology. Occurrence of metastasis is the most important factor influencing the stage of cancer. According to one study, the 5-year relative survival rate of stage IVb endometrial cancer is less than 20%.2 At present, the most common metastatic sites of endometrial cancer are lymph nodes and the cervix. Factors related to lymph node metastasis of endometrial cancer include histological types, depth of myometrial infiltration, and tumor size. At present, there are a few studies focusing on the metastasis of endometrial cancer to other organs. The tumor marker used to determine the dissemination of endometrial cancer is CA125, but its sensitivity to lymph node metastasis is 78% and its specificity is 81%.3 A better marker for the prediction of metastasis of endometrial cancer to other organs is not yet available. Therefore, understanding the molecular mechanism of metastasis of endometrial cancer to other organs, identifying novel biomarkers for early detection of intrauterine membrane cancer, and finding potential drug targets are required.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of regulatory, noncoding RNA molecules, 19–25 nucleotides in length. They are involved in the regulation of posttranscriptional expression of target mRNAs.4 Current research shows that miRNAs are abnormally expressed in various types of malignant tumors, and their chief mechanism of action involves regulation of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Recent studies indicate that miRNAs, such as miR-130b, are involved in the migration and invasion of endometrial cancers. Abnormally expressed miR-130b can induce the expression of E-cadherin and promote epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and tumor cell metastasis.5 Studies have also shown that the miR-200 family is involved in EMT and plays an important role in tumor invasion and metastasis.6 Previous studies have shown that a complex miRNA regulatory network, rather than an individual miRNA, is involved in the regulation of metastasis of endometrial cancer. There are many metastasis-related miRNAs that remain unidentified to date. Identification of miRNAs participating in cancer, elucidation of their respective functions, and access to high-throughput data for miRNA regulatory networks need to be amalgamated for better results in the future.
Although metastasis-associated miRNAs have been found in many endometrial cancers, there were inconsistencies among other studies. These may have been due to small sample sizes, differences in histological subtypes, differences in detection platforms, and various data-processing methods. The Cancer Genome Atlas Project (TCGA) is a research program of the National Cancer Institute and uses the consistency genome platform to analyze at least 20 different tumor types and provides researchers with raw and processed data.7 TCGA has provided a large number of high-throughput sequencing data related to miRNA, methylation, and long ncRNA for patients with endometrial cancer. The purpose of this study was to identify differential miRNA expression in endometrial cancer tissues that either did or did not metastasize, by analyzing high-throughput miRNA data downloaded from TCGA database. In addition, we evaluated differentially expressed and lung cancer-associated miRNAs and predicted their possible target gene functions and signaling pathways, which may lay the foundation for further research in the field of endometrial cancer.
Materials and methods
Data-processing procedure
Original RNA sequences and clinical information were downloaded from TCGA database (https://cancergenome.nih.gov/). Data inclusion criteria were as follows: 1) the sample contains clinical information and miRNA sequence data and 2) metastasis details and other clinical essential information are available. Finally, 282 samples were obtained (including 22 metastatic samples). We used the R language package (Limma package) to process the miRNA sequencing data (1046 miRNAs and reads per million were used in our analyses). The fold change in expression of miRNAs (FCS) log 2 | F c | >1.2 and (adjusted) P <0.05 were considered to denote a significant difference between metastatic and nonmetastatic endometrial cancer tissues.
Correlation analysis of differentially expressed miRNAs and the patients’ metastasis information
Differentially expressed miRNAs were normalized by log2 transformation Spectral, and then, Student’s t-test was conducted to find possible miRNA-related factors (data with P <0.05 were considered significant).
Prediction of target genes of predictive miRNA markers
TargetScan (http://www.targetscan.org/vert_71/), miRDB (http://www.mirdb.org/), PicTar (http://www.pictar.org/cgi-bin/PicTar_vertebrate.cgi), and miRanda (http://34.236.212.39/microrna/home.do) online analysis tools were used to predict the biological targets of miRNAs. Overlapping genes were identified via a Venn diagram to further improve the bioinformatic analysis and the reliability of the predicted target genes. The DAVID database (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/summary.jsp) was employed to determine the Gene Ontology (GO) annotations and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways of overlapping sets of genes. DAVID is an online bioinformatics resource that is aimed to provide researchers with a comprehensive set of functional annotation tools for understanding the biological mechanisms involved in the functioning of a large number of genes or proteins.8 The target genes were then analyzed with GO and enriched by the KEGG Research. A P-value <0.05 and a gene count ≥3 were used as cutoff criteria.
Protein–protein interaction (PPI) analysis
We used STRING (http://string-db.org/), a Web-based tool to analyze the PPI network of selected genes. The STRING database integrates text mining, experimental/biochemical evidence, co-expression data in PubMed, and database correlation to provide an interactive analysis platform in which proteins can be assessed for connections, associations, and interactions.9 All the genes selected from the pathway enrichment analysis were downloaded. Finally, we used the Cytoscape software to screen the selected genes for hub genes (using in+out for more than 4 connections).
Comparison of genes
The expression comparison of genes was conducted by means of GEPIA (http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/), which is an open access website for gene comparison.
Statistical analysis
The data were expressed as mean ± standard error. An independent sample t-test was carried out to analyze the expression of miRNAs in endometrial cancers that either had or had not metastasized. The t-test was performed to assess relations between miRNA expression and clinical characteristics. P-values <0.05 indicated statistical significance. The statistical analyses were performed in the IBM SPSS Statistics software program version 22.0.
Results
Identification of differentially expressed miRNAs in metastatic endometrial cancers
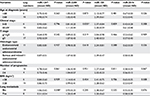
A total of 256 samples lacked follow-up information, and 282 samples were included in this study: 260 endometrial cancer tissues that had not metastasized and 22 cancer tissues (with different follow-up time) that had metastasized. Detailed clinical features included age, metastases, stage, T stage, histological types, and number of pregnancies (Table 1). Based on truncation criteria (P <0.05 and |log 2 FC| >2.0), four differentially expressed miRNAs were identified from 1046 miRNAs (miR-1247 miR-3200, miR-150, and miR-301b) (Table 2).
  | Table 2 Clinical characteristics of metastasis endometrial cancer patients Note: *P<0.05. Abbreviation: BMI, Body Mass Index. |
Four miRNAs identified in metastatic endometrial cancer samples
In order to identify miRNAs that may be associated with clinical and pathological information of patients with metastatic endometrial cancer, we used t-test to assess the correlation between miRNA expression and patient clinical information. The results showed that miR-1247 negatively correlated with the lung metastasis of endometrial cancer (P = 0.048) (Table 1, Figure 1), whereas miR-3200 might be associated with the clinical stage of endometrial cancer (P = 0.035) (Table 1). Meanwhile, we evaluated correlations between miR-150, miR-301b, and clinical information, and there was no significant difference in type, histological stage, number of pregnancies, BMI, and lung metastasis (P >0.05).
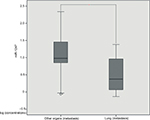  | Figure 1 The miR-1247 expression between other organ metastasis tissues and lung metastasis tissues. Note: *Mean P-value<0.05. |
Target gene prediction and functional analysis
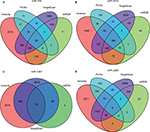
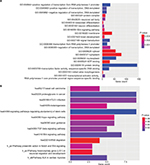
The target genes for the four miRNAs (miR-1247, miR-3200, miR-150, and miR-301b) were predicted using TargetScan, miRDB, PicTar, and miRanda. A total of 12 coinciding genes related to miR-1247, 8 coinciding genes related to miR-3200, 29 coinciding genes related to miR-150, and 169 coinciding genes related to miR-301b were identified (Figure 2). Then, enrichment analysis was performed to understand the biological function of the common target genes. The KEGG pathway is significantly enriched in the Wnt, Notch, and TGF-β signaling pathways and in signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells and proteoglycans in cancer (Figure 3). In addition, the GO biological process terminology mainly enriches protein binding, DNA-binding regulation, RNA regulation, and cell structure, as well as signal transduction pathways (Figure 3).
Searching for the potential hub genes of the four miRNAs
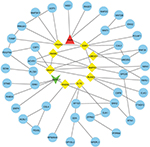
We used the GEPIA website to find possible hub genes (miR-150, miR-3200, and miR-1247) and Cytoscape software to find potential hub genes of miR-301b (Figure 4). Finally, we determined that the hub genes may include PAK6, SNAP25, MAN1A1, MYB, ZBTB4, UST, ALDH1A3, and NRP2 (Figure 5).
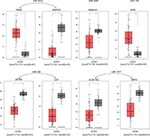  | Figure 5 Expression differences between endometrial cancer and adjacent tissues. Note: *Mean logFC >1.5, P-value <0.05. Abbreviations: FC, fold change; UCEC, Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma. |
Discussion
Although there are few cases of formation of this metastatic lesion in the early stage of endometrial cancer, there are still some patients whose cancer metastasizes and threatens their longevity. The site of metastasis determines the scope of the treatment and surgical resection, which is stressful and physically painful for patients. At present, the indicators used to screen for endometrial cancer metastasis mainly include CA125 and imaging parameters, but the specificity and sensitivity of CA125 are not very high (especially in cases of metastasis outside lymph nodes). Besides, imaging examinations are expensive and inconvenient for real-time monitoring. The use of histopathological diagnosis to estimate the possibility of metastasis will greatly help to determine the prognosis of patients and to find targeted drugs for treating metastasis. Therefore, it is necessary to unravel the underlying molecular mechanisms of the metastasis of endometrial cancer and to identify its novel molecular biomarkers. We often use tumor tissues and normal tissues to identify differentially expressed miRNAs, but this approach may miss some of such miRNAs. In this study, we used a comparison between metastatic and nonmetastatic tumor tissues, and finally four differentially expressed miRNAs were identified. These four miRNAs (miR-1247, miR-3200, miR-150, and miR-301b) were found and confirmed to be associated with metastases in patients with endometrial cancer. We also selected genes that may be targets of these miRNAs and used bioinformatic methods to predict the enrichment pathways and biological functions of the target genes. Furthermore, we predicted their possible hub genes.
Some studies have shown that the total recurrence rate of endometrial cancer is 13%, whereas the probability of recurrence of cancer among low-risk patients is 3% or less; the possibility of recurrence in less than 3 years is 68%–100%. Most methods of diagnosis include imaging. The proportion of cases diagnosed by physical examination and by means of CA125 is only 15%;10 thus, the existing methods for diagnosing metastases of endometrial cancer are not ideal. Several studies showing an association of miRNAs with the metastasis of endometrial cancer uncovered several miRNAs. miR-200b, which can suppress the expression of TMP2, was found to be related to the metastasis of endometrial cancer, suggesting that miRNAs may be deeply involved in such metastases.11 MMP-13 is an important component of the matrix metalloprotein family and is closely related to tumor invasion and metastasis.12 Some studies have shown that the expression of MMP-13 is higher in endometrial cancer tissues and may be closely related to the degree of tissue infiltration and lymphatic metastasis.13 Meanwhile, MMP-13 is a target gene of miR-125b; thus, it can be assumed that miR-125b participates in the inhibition of endometrial cancer invasion by affecting MMP-13. Although there are no studies on the direct effects of miR-1247 on endometrial cancer, research has shown that miR-1247 can serve as an inhibitor of pancreatic cancer through downregulation of RCC2 by increasing the degree of methylation of CpG islands.14 These studies indicate that downregulation of miR-1247 might be associated with the metastasis of endometrial cancer and that miR-1247 is an inhibitor of endometrial cancer. Although no studies have shown the association of miR-3200 with the metastasis of endometrial cancer, there are research articles showing that miR-320d correlates with EMT of endometrial cancer, and related studies have revealed that miR-320d can inhibit EMT-related protein expression with the PBX3 gene as a mediator, thereby suppressing the EMT function of endometrial cancer in JEC cells.15 Additionally, research suggests that upregulation of miR-150 is associated with endometriosis, and the other 13 miRNAs that are associated with endometriosis include miR-145, miR-143, miR-99a, miR-99b, miR-126, miR-100, miR-125b, miR-125a, miR-223, miR-194, miR-365, miR-29c, and miR-1 as well as 8 downregulated miRNAs (miR-200a, miR-141, miR-200b, miR-142-3p, miR-424, miR-34c, miR-20a, and miR-196b).16 It can be concluded that miR-150 may participate in the metastasis of endometrial tissue. miR-301b has been demonstrated to be involved in bladder cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and EMT. Upregulation of miR-301b controls the downregulation of EGR1 and promotes proliferation of bladder cancer cells. Perhaps miR-150 may also have similar regulatory effects on endometrial cancer.17
This study also revealed that the lung metastasis of endometrial cancer is related to miR-1247, which may be related to the lung affinity of miR-1247. Studies have shown that silencing of miR-1247 by DNA methylation can promote the invasion and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer, and STMN1 was found to be a direct target gene of miR-1247, whereas upregulation of miR-1247 can inhibit the metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer.18 Furthermore, miR-1247-3P is known to be activated by fibroblasts leading to lung metastasis of hepatoma cells.19 These findings suggest that miR-1247 may have lung affinity, and the elevated miR-1247 levels in pathological specimens may increase the detection rate of lung metastases. We have found that miR-1247 may be related to target genes such as NRP2, KLH17, SEMA6D, MYCBP2, MPP3, CARD14, TMEM184B, NHLH1, PFKFB3, MRPS23, SFRP5, and ALDH1A3. Target gene prediction can provide directions for further research on their roles and respective mechanisms of action in cancer.
To gain insights into the molecular functions of the four miRNAs, we predicted their target genes and analyzed the related pathways and GO annotations. Aberrant signaling pathways are crucial for the metastasis of endometrial cancer. We found that the four miRNAs can regulate several key signaling pathways, including Wnt, Notch, and TGF-β cascades and signaling pathways regulating the pluripotency of stem cells. Recent studies indicate that the Wnt pathway is involved in the proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of endometrial cancer,20,21 and novel Wnt pathway-related regulatory mechanisms have also been discovered.22 Some studies have shown that SHARP1 can inhibit the metastasis of endometrial cancer through the Notch channel, by inhibiting EMT.23 Similarly, research has shown that endometrial cancer metastasis is associated with EMT, and EMT is regulated by the TGF-β cascade.24 The abovementioned predicted partial channels may be related to the pathways involved in the regulation of endometrial cancer metastasis, which require further studies.
We used PPI network and Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis to find hub genes of relevant miRNAs. PAK6, SNAP25, MAN1A1, MYB, ZBTB4, UST, ALDH1A3, and NRP2 were found to be core genes. Some investigators have reported that PAK6 is overexpressed in prostate cancer, and PAK6 may participate in the regulation of mobility and in stress responses.25 SNAP25 has been proved to take part in the autolysosomal dynamics and the progression of some epithelial cancers.26 MYB has been proved to be linked to the development of aggressive endometrial carcinoma;27 meanwhile, c-Myb is related to the malignancy and prognosis of endometrial carcinoma.28 All these evidence suggest that MYB may be an important factor of the metastasis process. Most of the hub genes appearing in the predictions have been reported to be possibly related to endometrial cancer. There are reports that have not yet been confirmed and require verification in the future.
This study identified metastasis-associated miRNAs and predicted their relevant target genes, hub genes, possible functions, and pathways, but these data have not yet been validated experimentally. Besides, cases of metastasized tumors in endometrial cancer are relatively few in the follow-up information, and metastasized tissues are difficult to obtain; therefore, a greater number of samples is required for future studies. Meanwhile, we did not use pair analyses in our process considering the relatively small sample size, which may bring some confounding factors into our results.
Conclusion
We identified four miRNA markers as potential metastasis predictors for patients with endometrial cancer, and we found putative core genes and pathways involved in endometrial cancer. Nonetheless, further studies are necessary to validate our findings. Moreover, functional studies are needed to explore the molecular mechanisms of action of these miRNAs in the metastasis of endometrial cancer.
Data sharing statement
All related data could be downloaded from previous website.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;56(2):106. | ||
NIH [webpage on the Internet]. SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Endometrial Cancer. Available from: http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/corp.html. Accessed January 13, 2014. | ||
Hsieh CH, ChangChien CC, Lin H, et al. Can a preoperative CA 125 level be a criterion for full pelvic lymphadenectomy in surgical staging of endometrial cancer? Gynecol Oncol. 2002;86(1):28–33. | ||
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–297. | ||
Li BL, Lu W, Lu C, et al. CpG island hypermethylation-associated silencing of microRNAs promotes human endometrial cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2013;13(1):44. | ||
Snowdon J, Zhang X, Childs T, Tron VA, Feilotter H. The microRNA-200 family is upregulated in endometrial carcinoma. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e22828. | ||
Chandran UR, Medvedeva OP, Barmada MM, et al. TCGA expedition: a data acquisition and management system for TCGA data. PLoS One. 2016;11(10):e0165395. | ||
Jiao X, Sherman BT, Huang da W, et al. DAVID-WS: a stateful web service to facilitate gene/protein list analysis. Bioinformatics. 2012;28(13):1805–1806. | ||
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, et al. STRINGv10: protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:D447–D452. | ||
Fung-Kee-Fung M, Dodge J, Elit L, et al; Cancer Care Ontario Program in Evidence-based Care Gynecology Cancer Disease Site Group. Follow-up after primary therapy for endometrial cancer: a systematic review. Gynecol Oncol. 2006;101(3):520–529. | ||
Dai Y, Xia W, Song T, et al. MicroRNA-200b is overexpressed in endometrial adenocarcinomas and enhances MMP2 activity by downregulating TIMP2 in human endometrial cancer cell line HEC-1A cells. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013;23(1):29–34. | ||
Zhang C, Tang W, Li Y. Matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) is a direct target of osteoblast-specific transcription factor osterix (Osx) in osteoblasts. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50525. | ||
Tüshaus L, Hopert AC, Strunck E, Schubert C, Wünsche W, Vollmer G. Estrogenic and antiestrogenic regulation of MMP-2 and MMP-13 mRNA in RUCA-I endometrial tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2003;198(1):99–106. | ||
Yi JM, Kang EJ, Kwon HM, et al. Epigenetically altered miR-1247 functions as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(16):26600–26612. | ||
Wang J, Gong FQ, He K, Yao SZ, Niu G. MicroRNA-320d inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition function in endometrial carcinoma JEC cells by PBX3. J Sun Yat-sen Univ (Med Sci). 2017;38(5):651–657. | ||
Ohlsson Teague EM, Van der Hoek KH, Van der Hoek MB, et al. MicroRNA-regulated pathways associated with endometriosis. Mol Endocrinol. 2009;23(2):265–275. | ||
Yan L, Wang Y, Liang J, Liu Z, Sun X, Cai K. miR-301b promotes the proliferation, mobility and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of bladder cancer cells by targeting EGR1. Biochem Cell Biol. 2017;95(5):571–577. | ||
Zhang J, Fu J, Pan Y, Zhang X, Shen L. Silencing of miR-1247 by DNA methylation promoted non-small-cell lung cancer cell invasion and migration by effects of STMN1. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:7297–7307. | ||
Fang T, Lv H, Lv G, et al. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-1247-3p induces cancer-associated fibroblast activation to foster lung metastasis of liver cancer. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):191. | ||
van der Zee M, Jia Y, Wang Y, et al. Alterations in Wnt–β-catenin and Pten signalling play distinct roles in endometrial cancer initiation and progression. J Pathol. 2013;230(1):48–58. | ||
Wang T, Wang M, Fang S, Wang Q, Fang R, Chen J. Fibulin-4 is associated with prognosis of endometrial cancer patients and inhibits cancer cell invasion and metastasis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 2017;8(12):18991–19012. | ||
Zhao Y, Yang Y, Trovik J, et al. A novel wnt regulatory axis in endometrioid endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 2014;74(18):5103–5117. | ||
Liao Y, He X, Qiu H, et al. Suppression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by SHARP1 is linked to the NOTCH1 signaling pathway in metastasis of endometrial cancer. BMC Cancer. 2014;14(1):487. | ||
Lei XF, Wang L, Yang J, Sun LZ. TGFbeta signaling supports survival and metastasis of endometrial cancer cells. Cancer Manag Res. 2009;1(1):15–24. | ||
Kaur R, Yuan X, Lu ML, Balk SP. Increased PAK6 expression in prostate cancer and identification of PAK6 associated proteins. Prostate. 2008;68(14):1510–1516. | ||
Mu Y, Yan X, Li D, et al. NUPR1 maintains autolysosomal efflux by activating SNAP25 transcription in cancer cells. Autophagy. 2018;14(4):654–670. | ||
Krakstad C, Tangen IL, Hoivik EA, et al. ATAD2 overexpression links to enrichment of B-MYB-translational signatures and development of aggressive endometrial carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6(29):28440–28452. | ||
Feng YK, Lu L, Zhang YQ, He L, Lin W. [Expression and clinical significances of c-myb and Bax proteins in endometrial carcinoma]. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2014;45(5):797–800. Chinese. |
 © 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.