Back to Journals » Journal of Inflammation Research » Volume 7
Vitamin D and inflammatory diseases
Received 11 March 2014
Accepted for publication 8 April 2014
Published 29 May 2014 Volume 2014:7 Pages 69—87
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S63898
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Kai Yin, Devendra K Agrawal
Center for Clinical and Translational Science, Creighton University School of Medicine, Omaha, NE, USA
Abstract: Beyond its critical function in calcium homeostasis, vitamin D has recently been found to play an important role in the modulation of the immune/inflammation system via regulating the production of inflammatory cytokines and inhibiting the proliferation of proinflammatory cells, both of which are crucial for the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. Several studies have associated lower vitamin D status with increased risk and unfavorable outcome of acute infections. Vitamin D supplementation bolsters clinical responses to acute infection. Moreover, chronic inflammatory diseases, such as atherosclerosis-related cardiovascular disease, asthma, inflammatory bowel disease, chronic kidney disease, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and others, tend to have lower vitamin D status, which may play a pleiotropic role in the pathogenesis of the diseases. In this article, we review recent epidemiological and interventional studies of vitamin D in various inflammatory diseases. The potential mechanisms of vitamin D in regulating immune/inflammatory responses in inflammatory diseases are also discussed.
Keywords: asthma, atherosclerosis, chronic kidney disease, inflammatory bowel disease
Introduction
Vitamin D insufficiency or deficiency has increased in the general population and become an important public health issue.1 Vitamin D is mainly known for its favorable effects in calcium and bone metabolism. However, increasing numbers of studies have established that vitamin D insufficiency contributes to a number of diseases, suggesting a range of physiological functions of vitamin D.2–4 Several clinical studies have confirmed that vitamin D plays a crucial role in modulating innate immune responses toward various pathogens.5 Moreover, recent studies indicate that vitamin D can regulate the adaptive immune response in various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.6,7 These results suggest the beneficial effects of vitamin D supplementation in decreasing the risk and adverse outcomes of inflammatory diseases, although the precise effect remains to be elucidated in large clinical trials.
The two major physiologically relevant forms of vitamin D are vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). In humans, vitamin D3 seems to be more effective than vitamin D2 in maintaining the circulatory level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (25[OH]D3), a stable marker of vitamin D status.8,9 The main sources of vitamin D3 are endogenous production from 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin by ultraviolet B energy and dietary intake from foods, including egg yolk, beef liver, and milk products.8,9 Vitamin D3 is metabolized to 25(OH)D3 in the liver by vitamin D 25-hydroxylase and then further hydroxylated by the key enzyme 25-hydroxyl vitamin D3-1α-hydroxylase (CYP27B1) to the biologically active form: calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol [1,25{OH}2D3]).10 1,25(OH)2D3 binds and activates the vitamin D receptor (VDR), a member of the superfamily of nuclear receptors and functions as a ligand-activated transcription factor.11 It is now well recognized that CYP27B1 and VDR are expressed in cells involved in the immune/inflammation system in the human body,12 which provides the biological basis for the role of vitamin D in inflammatory diseases.
Most clinical studies support the view that serum 25(OH)D3 levels of less than 20 ng/mL (50 nmol/L) indicate vitamin D deficiency. Serum 25(OH)D3 levels below 30 ng/mL indicate insufficiency, while levels between 30 and 60 ng/mL (75 and 150 nmol/L) represent normal values.1,13 Epidemiological studies suggest an inverse association between circulating levels of 25(OH)D3 and inflammatory markers, including CRP and interleukin (IL)-6.14 Supplemental vitamin D and calcium have been found to decrease the biomarkers of inflammation.15,16 However, a role for supplementation of vitamin D in modifying inflammatory disease has not been well defined, and it is unclear at present whether vitamin D status is causally related to the pathogenesis of the disease or is merely a marker of health.17 This review summarizes and critically evaluates the data from preclinical, epidemiological, and interventional studies in order to elucidate the role and mechanisms of vitamin D in inflammatory diseases.
Vitamin D signaling and immune/inflammation system
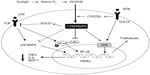
VDR expression has been documented in macrophages, a crucial cell type in the innate immune response.18 In macrophages, activation of the toll-like receptor (TLR1/2) heterodimer by Mycobacterium tuberculosis results in the upregulation of VDR and CYP27B1, leading to induction of the antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin and the killing of intracellular M. tuberculosis.19 In this process, IL-15 links TLR2/1-induced macrophage differentiation to the vitamin D-dependent antimicrobial pathway.20 The increase of CYP27B1 results in the accumulation of 1,25(OH)2D3, which further activates VDR, leading to the target gene transcription via vitamin D response elements located in the regulatory regions of 1,25(OH)2D3 target genes.21 Chen et al22 found that 1,25(OH)2D3 can regulate TLR signaling via stimulating SOCS1 by downregulating miR-155 in macrophages, which provide a novel negative feedback regulatory mechanism for vitamin D to control innate immunity. In a recent study, both forms of vitamin D – 1,25(OH)2D3 and 25(OH)D3 – dose-dependently inhibited lipopolysaccharide-induced p38 phosphorylation, IL-6, and TNFα production by human monocytes via histone H4 in an acetylation-dependent manner.23 Moreover, 1,25(OH)2D3 or its analogs have been shown to initiate the differentiation of myeloid progenitors into macrophages,24 and to reduce MCP-1 and IL-6 expression via inhibiting the activation of NF-κB in macrophages.25 In addition, Vitamin D has been thought to be a natural endoplasmic reticulum stress reliever,26 and can selectively suppress key effector functions of interferon (IFN)-γ-activated macrophages.27 Interestingly, in the presence of 1,25(OH)2D3, VDR has also been found to repress gene transcription via displacing the deoxyribonucleic acid-bound nuclear factor of activated T-cells, thus repressing inflammatory cytokine expression28 (Figure 1).
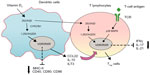
Dendritic cells (DCs) are the most potent antigen-presenting cells. A number of studies have shown that 1,25(OH)2D3 inhibits the differentiation, maturation, and immunostimulatory capacity of human DCs, characterized as the tolerogenic properties, in a VDR-dependent manner.29,30 Molecular mechanisms underlying the modulation of tolerogenic properties of DCs by 1,25(OH)2D3 include decreasing surface expression of major histocompatibility complex II and costimulatory molecules (CD40, CD80, CD86), upregulating inhibitory immunoglobulin-like transcript 3 molecules, and enhancing secretion of chemokine (C–C motif) ligand 22 and IL-1029,31 (Figure 2). The enhancement of DC tolerogenicity by 1,25(OH)2D3 results in the induction of T-regulatory cells, a critical event for suppressing the inflammatory response of T-effector cells.31 1,25(OH)2D3 also acts directly with VDR on the T lymphocyte to inhibit its proliferation.32 Although native T-cells did not express VDR, VDR expression was induced by T-cell antigen-receptor signaling via the alternative p38 MAPK pathway, which is crucial for T-cell antigen-receptor responsiveness in naïve T-cells.33 Recent work has revealed that 1,25(OH)2D3 inhibited production of proinflammatory cytokines, including IFNγ, IL-17, and IL-21 in CD4+CD25− T lymphocytes, and promoted development of T-regulatory cells expressing cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 and FOXP334 (Figure 2). T-cell cytokines also control vitamin D metabolism in macrophages. For example, IFNγ, a T-helper (Th)-1 cytokine, upregulates the macrophage CYP27B1, leading to enhanced bioconversion of 25(OH)D3 to its active metabolite – 1,25(OH)2D3. In contrast, the Th2 cytokine IL-4 induces catabolism of 25(OH)D3 to the inactive metabolite 24,25(OH)2D3,35 suggesting a potential mechanism by which vitamin D metabolism links the cell-mediated immune responses to the innate immune responses, although the exact role of vitamin D in this process remains unclear.
Vitamin D and inflammatory diseases
Acute infections
Epidemiology studies have indicated seasonal variations in influenza and pneumococcal community-acquired pneumonia, suggesting an association between vitamin D insufficiency due to less sun exposure and acute respiratory infection (ARI).36 A number of clinical studies have suggested an inverse association between 25(OH)D3 levels and ARI (Table 1).37–42 Ginde et al41 performed a secondary analysis of the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, and found a strong negative association between serum 25(OH)D3 levels (<30 ng/mL) and risk of upper respiratory tract infection, which seemed to be stronger in individuals with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In a large retrospective study, vitamin D status was found to have a linear association with seasonal infections and lung function, in which each 10 nmol/L increase in 25(OH)D3 was associated with a 7% lower risk of infection and an 8 mL increase in forced expiratory volume in 1 second.39 Several prospective cohort studies in adults and children further demonstrated that serum vitamin D concentration was associated with acute respiratory tract infection (ARTI): 25(OH)D3 levels <38 ng/mL were associated with increased risk of ARTI.37,40,42 Recently, Mohamed et al38 found that low cord blood 25(OH)D3 levels are associated with increased risk of ARTI in the first 2 years of life, suggesting a necessary early intervention for vitamin D starting from newborns.
Evidence from double-blinded randomized clinical trials (RCTs) for vitamin D interventional studies is warranted to confirm the clinically relevant effect of vitamin D in RTIs. Camargo et al43 investigated whether vitamin D supplementation in children with vitamin D deficiency would lower the risk of ARI. Compared with controls, children receiving vitamin D (300 IU/daily) have been reported to have significantly fewer ARIs during the study period. In another placebo-controlled double-blinded study comprising 164 voluntary young Finnish men (18–28 years of age), the proportion of men remaining healthy throughout the 6-month study period was greater in the intervention group (vitamin D3, 400 IU/daily) than in the placebo group.44 More RCTs with larger populations, however, are warranted to investigate the role of vitamin D supplementation on respiratory health and ARI.
Studies with VDR-knockout mice have been critical in demonstrating the relationship between vitamin D and acute infections.45–49 Compared with VDR+/+ mice, VDR−/− mice exhibited significantly higher Chlamydia trachomatis loading and reduced clearance of chlamydial infection than wild-type VDR+/+ mice, suggesting a vitamin D–VDR pathway involved in respiratory mucosal defense against infections.46 VDR-knockout mice developed an unaltered Th1 response to infection due to impaired upregulation of arginase 1 expression under Leishmania infection.45 Although 1,25(OH)2D3 inhibits the proliferation and differentiation of both T and B lymphocytes, the central mechanism underlying microbial eradication of vitamin D seems to be the inhibition of activation of TLRs in the host cell, which induces the formation of potent antimicrobial peptides.19,50 The additional anti-infection mechanism of vitamin D may be related to the ability to modulate inflammatory factor levels in ARI patients. 25(OH)D3 levels below 21 ng/mL have an inverse relationship with CRP concentration in asymptomatic ambulatory patients.51 However, these associations were not found in symptomatic patients.52 In a randomized controlled trial of vitamin D supplements (1,400 IU/week) in infants, there were no differences in plasma levels of CRP or inflammatory cytokines between the treatment group and the control group.53 The exact effects and mechanisms of vitamin D in infectious diseases therefore require further study.
The functioning of VDR is affected by gene polymorphisms, in which a start codon polymorphism (rs2228570) and three polymorphisms in the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of the VDR gene (rs1544410, rs7975232, and rs731236) are the most commonly studied polymorphisms in the VDR gene.54 There are reports that VDR polymorphism is linked to increased susceptibility to infection. Alagarasu et al have found that the frequency of the C/C genotype of rs7975232 was significantly lower in dengue virus infection patients (DEN) compared to health controls.54 Aslan et al examined VDR gene polymorphisms in urinary tract infections, and found that the ff genotype in rs2228570 was significantly increased in UTI children with urinary tract infection.55 Rathored et al have also found that the patients with ff genotypes in rs2228570 were at high risk of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis with smear-positive disease.56 In a multicenter clinical trial, Levin et al recently investigated the relationship of common variation within genes encoding the vitamin D-binding protein, megalin, cubilin, CYP27B1, CYP24A1, and VDR with low 25(OH)D levels, and found some minor alleles at rs7968585 and rs7968585 within the VDR gene that were related to low 25(OH)D3.57 The results of these studies suggest that VDR gene polymorphisms can be important for the susceptibility of inflammatory diseases, which may be due to the lower 25(OH)D3 status affected by VDR gene polymorphisms.
Atherosclerosis-related cardiovascular disease
It is well known that inflammation plays a key role in the development of atherosclerosis. Inflammatory cells, mainly macrophages and T lymphocytes, produce a wide range of inflammatory cytokines in atherosclerotic lesions, which are critically important in the progression of atherosclerosis-related cardiovascular disease (CVD).58 Numerous studies have verified vitamin D deficiency (25[OH]D3 <20 ng/mL) as one of the new risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD).59,60 Many potential functions of vitamin D – including protection of endothelial function, inhibition of smooth-muscle cell (SMC) proliferation, improvement of lipid profile, and others – have been thought to contribute to the antiatherogenic effect of vitamin D.61–63
Clinical studies have indicated an inverse association between 25(OH)D3 levels and CHD risk (Table 2). Three large retrospective studies demonstrated that 25(OH)D3 levels below 20 ng/mL are associated with increased risk for CHD, including hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity, high serum low-density lipoprotein (LDL), triglyceride (TG), and low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels.17,64,65 Several cross-sectional prospective studies further strengthened this evidence, which demonstrated a significant increase for all-cause mortality when serum 25(OH)D3 levels were less than 30 ng/mL.66–70 In a population-based cohort study, Lim et al71 reported that a low 25(OH)D3 concentration had a higher risk of significant coronary artery stenosis. The odds ratios were 2.08 for 25(OH)D3 concentration of 15–29.9 ng/mL versus at least 30 ng/mL and 3.12 for 25(OH)D3 concentration below 15 ng/mL versus at least 30 ng/mL.
Although observational studies suggest that vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency is related to a higher risk for CVD, data from recent RCTs designed to assess the impact of vitamin D supplementation on cardiovascular outcomes are conflicting (Table 3). Some RCT results have shown that a higher intake of vitamin D is associated with a lower risk of CVD, especially in men, due to the improvement of vascular endothelial function and decrease in inflammation.72–74 However, most evidence at present shows that vitamin supplementation has no effect on vascular disease mortality or all-cause mortality.73–78 Since large well-controlled double-blinded RCTs aiming primarily for cardiovascular end points are still absent, whether or not vitamin D supplementation can significantly improve cardiovascular outcomes is largely unknown. At this time, larger RCTs, which can be used to evaluate the application of vitamin D in cardiology, have yet to be implemented.
  | Table 3 Summary of interventional studies evaluating the effect of vitamin D supplements on cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk |
The regulation of the immune/inflammatory response is one of the most verified mechanisms of the antiatherogenic effect of vitamin D. First, vitamin D exerts protective effects against endothelial dysfunction, an inflammatory process that precedes atherosclerosis, via multiple mechanisms, including stimulating nitric oxide production and inhibiting oxidative stress.59,79 Vitamin D has been found to inhibit contractions, which were endothelium-dependent through inhibiting cyclooxygenase-1 expression and reactive oxygen species production.59,79 In addition, calcitriol significantly repressed the expression of cyclooxygenase 2 and promoted prostaglandin catabolism, both of which reduce the level of prostaglandins and suppress proinflammatory cytokine expression in endotheliocytes.80 Second, 1,25(OH)2D3 may alter macrophage function and gene expression, which is crucial in the formation of foam cells and vascular inflammation response that promote the process of atherosclerosis.26 In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, 1,25(OH)2D3 can inhibit foam-cell formation, and suppresses macrophage cholesterol uptake via reducing peroxisome proliferated-activated receptor-γ-dependent CD36 expression.81 In addition, vitamin D induces an antiatherogenic monocyte/macrophage phenotype via regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress.26 Previous studies by our group have found vitamin D deficiency causes increased proinflammatory cytokine expression in epicardial adipose tissue, which is coupled with increased inflammatory cellular infiltrate, suggesting the anti-inflammation effect of vitamin D in epicardial adipose tissue is a novel mechanism for atheroprotection.82 Third, 1,25(OH)2D3 inhibits the proliferation of vascular SMCs (VSMCs),83 and exerts protective effects against VSMC morphological changes, which further inhibit the secretion of inflammatory molecules.84
In a hypercholesterolemic swine model, our group has found that vitamin D deficiency significantly increases the expression of TNFα in neointimal lesions after balloon angioplasty and that calcitriol has antiproliferative properties in TNFα-stimulated human VSMCs.85 Besides the direct anti-atherogenic effect, vitamin D has a variety of indirect effects on the systemic pathophysiological conditions that promote atherosclerosis, such as improving insulin resistance and hypertension.59 However, Ponda et al17,77 recently reported repletion of 25(OH)D3 levels in the short term does not correct or even ameliorate dyslipidemia, suggesting that the definitive role of vitamin D in CVD remains to be elucidated.
Asthma
Asthma is a disorder characterized by varying and recurring symptoms of airflow obstruction and bronchial hyperresponsiveness in the setting of inflammation.86 Epidemiologic studies suggest an association between vitamin D deficiency and asthma (Table 4).87–92 Some prospective studies and case-control studies have shown the majority of asthmatic children to be vitamin D-deficient.91,93 Vitamin D deficiency has been found to increase the risk of severe asthma exacerbation, defined as the need for emergency room evaluation or hospitalization.94 A prospective study of adults and children found that low serum 25(OH)D3 levels were associated with increased requirement of steroids in the pediatric asthma group.90 Higher maternal circulating 25(OH)D3 concentrations in pregnancy were independently associated with lower risk of asthma at 5 years old in offspring.92 However, another study showed that high 25(OH)D3 levels in pregnant women could pose an increased risk of asthma in offspring,95 indicating a reasonable level of vitamin D in pregnant women is crucial for maintaining normal bronchial responsiveness in offspring.
  | Table 4 Summary of major clinical studies evaluating the relationship between vitamin D status and asthma risk |
The mechanisms of vitamin D deficiency in asthma pathophysiology are not fully understood. Many researchers have focused on the potential effect of vitamin D in inflammatory response that inhibits the progress of asthma.86 Vitamin D has been found to increase the production of IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine, while decreasing the expression of proinflammatory cytokines in airway SMCs.96,97 In a mouse model, Gorman et al98 recently examined asthma-like responses 24 hours after airway challenge with the experimental allergen ovalbumin in adult offspring born to vitamin D3-replete and vitamin D3-deficient mothers. They found the ability of airway-draining lymph-node cells to proliferate and secrete cytokines in response to ovalbumin ex vivo was significantly enhanced by vitamin D deficiency.98 In a mouse model of allergic airway inflammation, our group has previously found vitamin D deficiency causes an increase in the expression of TNFα, which decreases the expression of VDR and prohibitin, a vitamin D target gene.95 Vitamin D supplementation reduces the levels of TNFα, thereby increasing the expression of VDR and prohibitin, which could be responsible for reducing allergic airway inflammation.99
Inflammatory bowel diseases
Vitamin D deficiency is common in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs), including ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD)100–105 (Table 5). Several retrospective and cross-sectional studies have reported a high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in patients with IBD, which was associated with disease activity and quality of life.101–105 Recently, a prospective cohort study of 72,719 women enrolled in the Nurses’ Health Study examined the relationship between vitamin D status and risk of CD and UC.100 In this study, researchers used Cox proportional hazard modeling to examine the hazard ratio (HR) for incident CD or UC after adjusting for potential confounders. Compared with women with a predicted 25(OH)D3 level less than 20 ng/mL, the multivariate-adjusted HR was 0.38 (95% confidence interval 0.15–0.97) for CD and 0.57 (95% confidence interval 0.19–1.70) for UC for women with a predicted 25(OH)D3 level greater than 30 ng/mL, suggesting higher predicted plasma levels of 25(OH)D3 significantly reduce the risk for incident CD.100
  | Table 5 Summary of major clinical studies evaluating the role of vitamin D status and vitamin D supplementation in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) |
Vitamin D supplementation has shown potential therapeutic benefit for IBD in some small, randomized, double-blind studies (Table 5). Jørgensen et al106 reported that oral supplementation with vitamin D3 (1,200 IU/day for 12 months) significantly reduced the risk of IBD relapse from 29% to 13%. Yang et al107 investigated the effect of high-dose vitamin D3 on serum vitamin D levels and CD activity index. They found supplementation of vitamin D3 (5,000 IU/day for 24 weeks) effectively raised serum 25(OH)D3 and reduced CD activity index scores. Pappa et al108 reported oral doses of 2,000 IU vitamin D3 daily or 50,000 IU vitamin D2 weekly seem to be superior to 2,000 IU vitamin D2 daily in raising serum 25(OH)D3 concentration, and was tolerated among children and adolescents with IBD. Another study has shown that 1,25(OH)2D3 (active form of vitamin D) has a more prominent short-term beneficial effect than 25(OH)D3 (plain vitamin-D) on CD activity.109 Although most studies have now shown vitamin D3 treatment might be effective in IBD, larger, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials needed to elucidate this correlation are lacking.
In VDR-knockout mice models, vitamin D deficiency increases susceptibility to dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis.110 Histological examination revealed the disruption in the epithelial junctions in dextran sodium sulfate-treated VDR–/– mice. 1,25(OH)2D3 preserved the integrity of the tight junctions in Caco-2 cell monolayers.110 Ryz et al111 found that 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment increases host susceptibility to Citrobacter rodentium, an extracellular microbe that causes acute colitis, by suppressing mucosal Th17 immune responses. Taken together, these observations suggest that vitamin D plays a critical role in mucosal barrier homeostasis by preserving the integrity of junctions via regulating the host immune/inflammatory response, leading to decreased susceptibility to mucosal damage and decreased risk of IBD.
Chronic kidney disease
Normal renal function is crucial for vitamin D metabolism.1 Vitamin D deficiency is highly prevalent among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD; 20%–85%).112,113 Studies have demonstrated a strong association between vitamin D deficiency and increased all-cause and CKD mortality in the general population (Table 6).113–118 Chronic low-grade inflammation is a hallmark of CKD, and has been disclosed as one important factor contributing to the progression of CKD and high cardiovascular mortality.10 A prospective cohort study of 444 patients with eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (follow-up time 9.4 years) showed that most patients died from cardiovascular causes.116 Cox proportional hazard modeling has shown multivariate-adjusted HRs (with 95% confidence intervals) in severely vitamin D-deficient (25[OH]D3 <10 ng/mL) compared to vitamin D-sufficient patients (25[OH]D3 ≥30 ng/mL) were 3.79 (1.71–8.43) for all-cause and 5.61 (1.89–16.6) for cardiovascular mortality, suggesting low 25(OH)D3 levels are a crucial factor linking CKD to CVD.116 Another cross-sectional study strengthened this evidence, demonstrating that higher vascular stiffness and endothelial dysfunction were associated with low levels of 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 in CKD patients.119 Vitamin D intake for more than 12 months can significantly reduce the probability of cardiovascular events.117 Low 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 levels are independently associated with albuminuria, a major risk factor for the progression of renal disease linked to all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality.114 Treatment with active vitamin D preparations also has a beneficial effect in decreasing albuminuria.120 Besides regulating inflammation and proteinuria, vitamin D has been found to improve aerobic capacity and increase the level of fetuin-A, an important protective factor for cardiovascular morbidity in pediatric CKD patients.115,121
  | Table 6 Summary of major clinical studies evaluating the relationship between vitamin D status and chronic kidney disease (CKD) risk |
Several randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies have examined the role of vitamin D as a therapeutic agent for CKD (Table 7).120,122–127 High-dose cholecalciferol supplementation (50,000 IU/week for 12 weeks) was safe and sufficient to maintain serum 25(OH)D3 concentrations (≥30 ng/mL) and simultaneously decreased serum MCP-1 concentrations in early CKD.122–124 In moderate CKD patients, both cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) and ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) are effective in increasing 25(OH)D3 and decreasing parathyroid hormone and inflammatory cytokine levels.125,127 In nonhemodialysis patients, supplementation of cholecalciferol with 40,000 IU/week for 8 weeks significantly increased the level of 1,25(OH)2D3 and decreased serum parathyroid hormone and inflammatory cytokine levels.126 However, this effect was not observed in end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients.126 As patients with CKD progress to ESRD, renal CYP27B1 activity decreases, resulting in the impaired formation of 1,25(OH)2D3 in many of these patients.128 Previous attempts to counteract these changes in mineral metabolism with nutritional vitamin D therapy have been unsuccessful.129 For this reason, most therapeutic approaches to treat vitamin D deficiency in ESRD patients favor the use of calcitriol or its associated analogs instead of the use of nutritional vitamin D forms.128,130 Interestingly, in an uncontrolled trial of seven ESRD patients, Stubbs et al128 reported significant and favorable effects after 8 weeks of cholecalciferol supplementation on circulating monocytes and concentration of inflammatory cytokines, which may be have been due to extrarenal production of calcitriol in the setting of minimal renal CYP27B1 activity in ESRD patients.
  | Table 7 Summary of interventional studies evaluating the effect of vitamin D supplements on chronic kidney disease (CKD) risk |
Experimental studies have demonstrated that vitamin D can control inflammation and oxidative stress that prevent CKD progress.131,132 Using a mouse model of obstructed nephropathy, Tan et al132 reported that the synthetic vitamin D analog paricalcitol reduced the infiltration of inflammatory T-cells and macrophages in the obstructed kidney, which was accompanied by a decreased expression of RANTES and TNFα. In a human proximal tubular cell line (HKC-8), paricalcitol inhibited RANTES messenger ribonucleic acid and protein expression and abolished the ability of tubular cells to recruit lymphocytes and monocytes after TNFα stimulation.132 In a study using a uremic rat model, paricalcitol significantly decreased cardiac oxidative stress. When combining with the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor enalapril, paricalcitol further prevented inflammation and oxidative injury in uremic rats.131 These studies provide experimental evidence supporting the role of inflammation in providing a pathological link between vitamin D and CKD.
Liver inflammatory disease
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) refers to the presence of hepatic steatosis without significant alcohol use or other known liver disease, and is characterized by chronic portal inflammation.133 Recent studies emphasize the role of insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and proinflammatory cytokines in the development and progression of NAFLD.134,135 Vitamin D serum levels negatively correlate with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Supplementation of vitamin D has been found to reduce insulin resistance in obese children.134 Recently, lower vitamin D levels were found to be independently associated with increased severity of steatosis, necroinflammation, and fibrosis in NAFLD.136,137 Furthermore, serum vitamin D levels that could predict the severity of NAFLD independently of other metabolic characteristics and relate vitamin D to NAFLD are largely unknown. Considering that inflammation is followed by steatosis in most NAFLD patients,138 vitamin D may be involved in NAFLD through its ability to modulate the immune/inflammation system. Recently, Roth et al139 fed young (25-day-old) Sprague Dawley rats with a low-fat diet alone, with vitamin D depletion, or with a Westernized diet, and found that vitamin D-depleted animals fed a Westernized diet exhibited significantly greater hepatic steatosis and inflammation compared to low-fat diet groups, which may be related to the upregulation of TLR2, TLR4, TLR9, and endotoxin receptor CD14 in the liver, suggesting vitamin D depletion exacerbates NAFLD, possibly by way of endotoxin exposure in a Westernized diet rat model. Low vitamin D serum levels have also been found to correlate with the severity of inflammation and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B and C viruses, where cellular immunity played crucial roles in the progress of diseases.140,141 In hepatitis B, VDR polymorphisms have been associated with infection susceptibility and clinical course in different populations.142 Taken together, these data indicate a potential link between vitamin D and viral hepatitis.
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system, which affects more than 2 million individuals worldwide. Growing evidence suggest that vitamin D deficiency might be one of the most important environmental factors for the prevalence, relapse rate, and progression of MS143–146 (Table 8). In a large prospective case-control study of 7 million US military personnel, high circulating levels of 25(OH)D3 were found to be associated with a lower risk of MS, in which every 50 nmol/L increase in serum 25(OH)D3 led to a 41% decrease in MS risk.145 Another prospective study of 35,794 mothers of participants in the Nurses’ Health Study II has shown that the relative risk of MS was lower among women born to mothers with high milk or vitamin D intake during pregnancy.147 In addition, serum 25(OH)D3 concentrations in patients with MS were also found to be related to the relapse of the disease. Mowry et al found that each 10 ng/mL increase in 25(OH)D3 level was associated with a 15% lower risk of a new T2 lesion and a 32% lower risk of a gadolinium-enhancing lesion. Each 10 ng/mL increase in vitamin D level was associated with lower subsequent disability, suggesting higher vitamin D levels were associated with lower relapse risk.143
  | Table 8 Summary of the major clinical studies evaluating the relationship between vitamin D status and multiple sclerosis (MS) risk |
Although a link between vitamin D supplementation and decreased risk of MS has been widely assumed, present vitamin D-repletion therapies have not yet shown a significant effect on the progress of MS (Table 8). In a retrospective cohort study of 116,671 female registered nurses, intake of vitamin D (≥400 IU/day) from multivitamins was not been found to statistically reduce the risk of MS.145 Moreover, no published RCTs of vitamin D repletion so far – low dose or high dose – have shown any benefit on relative risk of MS relapse.148–150 However, in a high-dose vitamin D3-supplementation RCT (20,000 IU/day for 12 weeks) in MS patients, vitamin D was found to increase proportion of IL-10+ CD4+ T-cells and decrease the ratio between IFNγ+ and IL-4+ CD4+ T-cells.151 Moreover, in a myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-induced animal model of MS, vitamin D significantly attenuated central nervous system inflammation and demyelination, accompanied by a lower amount of IFNγ-producing myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-specific T-cells via a developmental stage-dependent manner.152
These results suggest the exact effect of vitamin D repletion on the risk of MS remains to be clarified, since large, high-quality, randomized trials are still lacking.
Other inflammation/ immune-related disorders
Inflammation has also been found to play an important role in other chronic diseases, including hypertension, diabetes, chronic lower-back pain (CLBP), and congestive heart failure (HF). Several reviews have thoroughly discussed the relationship between vitamin D and hypertension or diabetes.153,154 There is clear evidence to support an association between low plasma levels of 25(OH)D3 and hypertension and type 2 diabetes.153,154 Furthermore, clinical trials aimed at testing the effect of vitamin D supplementation on hypertension and type 2 diabetes documented a dose-dependent blood pressure-lowering and insulin sensitivity-increasing effect of vitamin D in patients.155–157 However, in a recent randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, high-dose oral vitamin D3 (100,000 IU) for 6 months seemed not to reduce blood pressure or left ventricular mass in patients with resistant hypertension.158 Because the 6-month period used in this study may have been too short a period to detect meaningful effects of vitamin D on left ventricular mass and function, longer trials and detailed studies are needed to better investigate the definite role of vitamin D supplementation in various forms of hypertension.
Nonspecific lower-back pain is one of the most common reasons for CLBP that burdens health care systems with high cost. Human population studies have shown that plasma levels of vitamin D are inversely associated with risk for CLBP.159 However, results from a double-blind RCT of 53 patients aged 18–40 years with nonspecific CLBP showed no significant effect of vitamin D supplementation (50,000 IU) in decreasing the pain visual analog scale score of the patients.160 Vitamin D deficiency is associated with loss of muscle strength and poor outcomes in patients with HF. In a double-blind RCT in 31 patients (25[OH]D3 levels ≤37.5 ng/mL), vitamin D3 repletion (50,000 IU) decreased aldosterone in patients with HF and low serum vitamin D, suggesting that vitamin D may be an important adjunct to standard HF therapy.161
Apart from inflammatory disorders, vitamin D deficiency has been found to be associated with immune-related disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.162,163 Randomized placebo-controlled trials have shown that vitamin D supplementation seems to ameliorate inflammatory and hemostatic markers and show a tendency toward subsequent clinical improvement in these diseases.146,163,164 In a healthy population, vitamin D levels were significantly higher in antinuclear antibody-negative individuals than antinuclear antibody-positive individuals.165 Along with this finding is the additional observation that vitamin D deficiency is associated with certain immune abnormalities in such autoimmune disorders as systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis.163,166 Recently, a retrospective cross-sectional study showed the risk of auto- and cellular immune abnormalities is increased in women with recurrent pregnancy losses and vitamin D deficiency.167
Conclusion
The remarkable expression of the CYP27B1 and VDR genes by macrophages, DCs, and T lymphocytes suggests that the immune/inflammation system could be a target for the effect of vitamin D. Emerging evidence from clinical studies has indicated that vitamin D deficiency is associated with several inflammatory diseases; however, the question remains whether or not vitamin D deficiency contributes to the etiology of inflammatory disease or if vitamin D deficiency is simply a manifestation of these diseases. In acute infection and autoimmune disorders, preliminary evidence suggests an important role of vitamin D supplementation in decreasing the risk of disease. The pathophysiological process in many chronic inflammatory diseases, including atherosclerosis, is complex and confounded by various metabolic factors. Whether vitamin D supplementation is beneficial in the prognosis of these diseases requires further evaluation in larger prospective trials with a focus on major outcome events. In addition, dose-response randomized trials are necessary to identify threshold effects and possible adverse effects in vitamin D therapy. Future studies should aim to characterize optimal ranges of vitamin D status following vitamin D therapy, and should focus on determining the exact relationship between vitamin D dose and outcomes during the progression of diseases.
The identification and characterization of the molecular mechanisms responsible for recognizing and responding to vitamin D in the immune/inflammation system has widened our view of the essential components of a healthy immune response. Nonetheless, many key questions remain to be addressed. These include the cell type-specific roles of VDR in the progression of inflammatory diseases and the mechanisms of cross talk between VDR and other nuclear receptors, such as the retinoid X receptor and liver X receptor, which stimulate the intracellular pathway to exert the anti-inflammation effect. In addition, a single measurement of serum vitamin D status or the current standard value is unlikely to be valid in all situations. The development of research to refine existing biomarkers or establish new indicators that takes many factors into account and to identify useful functional biomarkers of vitamin D status in specific tissues will offer key insights into the development of targeted therapies for individuals with functional vitamin D insufficiency or deficiency in inflammatory diseases, though the research methodology for these potential biomarkers remains to be elucidated.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by research grants HL112597, HL116042, and HL120659 from the US National Institutes of Health to DKA. The content of this review is solely the responsibility of the authors, and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:266–281. | |
Langlois M, Duprez D, Delanghe J, De Buyzere M, Clement DL. Serum vitamin C concentration is low in peripheral arterial disease and is associated with inflammation and severity of atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2001;103:1863–1868. | |
Pittas AG, Harris SS, Stark PC, Dawson-Hughes B. The effects of calcium and vitamin D supplementation on blood glucose and markers of inflammation in nondiabetic adults. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:980–986. | |
Wu S, Sun J. Vitamin D, vitamin D receptor, and macroautophagy in inflammation and infection. Discov Med. 2011;11:325–335. | |
White JH. Vitamin D signaling, infectious diseases, and regulation of innate immunity. Infect Immun. 2008;76:3837–3843. | |
Tiosano D, Wildbaum G, Gepstein V, et al. The role of vitamin D receptor in innate and adaptive immunity: a study in hereditary vitamin D-resistant rickets patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:1685–1693. | |
Olliver M, Spelmink L, Hiew J, Meyer-Hoffert U, Henriques-Normark B, Bergman P. Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D on innate and adaptive immune responses to Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 2013;208:1474–1481. | |
Logan VF, Gray AR, Peddie MC, Harper MJ, Houghton LA. Long-term vitamin D3 supplementation is more effective than vitamin D2 in maintaining serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D status over the winter months. Br J Nutr. 2013;109:1082–1088. | |
Armas LA, Hollis BW, Heaney RP. Vitamin D2 is much less effective than vitamin D3 in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:5387–5391. | |
Querfeld U. Vitamin D and inflammation. Pediatr Nephrol. 2013;28:605–610. | |
Nagy L, Szanto A, Szatmari I, Szeles L. Nuclear hormone receptors enable macrophages and dendritic cells to sense their lipid environment and shape their immune response. Physiol Rev. 2012;92:739–789. | |
Brennan A, Katz DR, Nunn JD, et al. Dendritic cells from human tissues express receptors for the immunoregulatory vitamin D3 metabolite, dihydroxycholecalciferol. Immunology. 1987;61:457–461. | |
Rosen CJ. Clinical practice. Vitamin D insufficiency. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:248–254. | |
Liu LC, Voors AA, van Veldhuisen DJ, et al. Vitamin D status and outcomes in heart failure patients. Eur J Heart Fail. 2011;13:619–625. | |
Björkhem-Bergman L, Nylén H, Norlin AC, et al. Serum levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and the CYP3A biomarker 4β-hydroxycholesterol in a high-dose vitamin D supplementation study. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013;41:704–708. | |
Hopkins MH, Owen J, Ahearn T, et al. Effects of supplemental vitamin D and calcium on biomarkers of inflammation in colorectal adenoma patients: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2011;4:1645–1654. | |
Ponda MP, Huang X, Odeh MA, Breslow JL, Kaufman HW. Vitamin D may not improve lipid levels: a serial clinical laboratory data study. Circulation. 2012;126:270–277. | |
Kreutz M, Andreesen R, Krause SW, Szabo A, Ritz E, Reichel H. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 production and vitamin D3 receptor expression are developmentally regulated during differentiation of human monocytes into macrophages. Blood. 1993;82:1300–1307. | |
Liu PT, Stenger S, Li H, et al. Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response. Science. 2006;311:1770–1773. | |
Krutzik SR, Hewison M, Liu PT, et al. IL-15 links TLR2/1-induced macrophage differentiation to the vitamin D-dependent antimicrobial pathway. J Immunol. 2008;181:7115–7120. | |
Korf H, Wenes M, Stijlemans B, et al. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 curtails the inflammatory and T cell stimulatory capacity of macrophages through an IL-10-dependent mechanism. Immunobiology. 2012;217:1292–1300. | |
Chen Y, Liu W, Sun T, et al. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D promotes negative feedback regulation of TLR signaling via targeting microRNA-155-SOCS1 in macrophages. J Immunol. 2013;190:3687–3695. | |
Zhang Y, Leung DY, Richers BN, et al. Vitamin D inhibits monocyte/macrophage proinflammatory cytokine production by targeting MAPK phosphatase-1. J Immunol. 2012;188:2127–2135. | |
Ohta M, Okabe T, Ozawa K, Urabe A, Takaku F. 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol) stimulates proliferation of human circulating monocytes in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1985;185:9–13. | |
Sanchez-Niño MD, Bozic M, Córdoba-Lanús E, et al. Beyond proteinuria: VDR activation reduces renal inflammation in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012;302: F647–F657. | |
Riek AE, Oh J, Sprague JE, et al. Vitamin D suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes an antiatherogenic monocyte/macrophage phenotype in type 2 diabetic patients. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:38482–38494. | |
Helming L, Bose J, Ehrchen J, et al. 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a potent suppressor of interferon γ-mediated macrophage activation. Blood. 2005;106:4351–4358. | |
White JH. Vitamin D metabolism and signaling in the immune system. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2012;13:21–29. | |
Griffin MD, Lutz W, Phan VA, Bachman LA, McKean DJ, Kumar R. Dendritic cell modulation by 1alpha, 25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its analogs: a vitamin D receptor-dependent pathway that promotes a persistent state of immaturity in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:6800–6805. | |
Piemonti L, Monti P, Sironi M, et al. Vitamin D3 affects differentiation, maturation, and function of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2000;164:4443–4451. | |
Takeda M, Yamashita T, Sasaki N, et al. Oral administration of an active form of vitamin D3 (calcitriol) decreases atherosclerosis in mice by inducing regulatory T cells and immature dendritic cells with tolerogenic functions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30:2495–2503. | |
Mayne CG, Spanier JA, Relland LM, Williams CB, Hayes CE. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 acts directly on the T lymphocyte vitamin D receptor to inhibit experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol. 2011;41:822–832. | |
von Essen MR, Kongsbak M, Schjerling P, Olgaard K, Odum N, Geisler C. Vitamin D controls T cell antigen receptor signaling and activation of human T cells. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:344–349. | |
Jeffery LE, Burke F, Mura M, et al. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and IL-2 combine to inhibit T cell production of inflammatory cytokines and promote development of regulatory T cells expressing CTLA-4 and FoxP3. J Immunol. 2009;183:5458–5467. | |
Edfeldt K, Liu PT, Chun R, et al. T-cell cytokines differentially control human monocyte antimicrobial responses by regulating vitamin D metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:22593–22598. | |
White AN, Ng V, Spain CV, Johnson CC, Kinlin LM, Fisman DN. Let the sun shine in: effects of ultraviolet radiation on invasive pneumococcal disease risk in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. BMC Infect Dis. 2009;9:196. | |
Science M, Maguire JL, Russell ML, Smieja M, Walter SD, Loeb M. Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and risk of upper respiratory tract infection in children and adolescents. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:392–397. | |
Mohamed WA, Al-Shehri MA. Cord blood 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and the risk of acute lower respiratory tract infection in early childhood. J Trop Pediatr. 2013;59:29–35. | |
Berry DJ, Hesketh K, Power C, Hypponen E. Vitamin D status has a linear association with seasonal infections and lung function in British adults. Br J Nutr. 2011;106:1433–1440. | |
Sabetta JR, DePetrillo P, Cipriani RJ, Smardin J, Burns LA, Landry ML. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and the incidence of acute viral respiratory tract infections in healthy adults. PLoS One. 2010;5:e11088. | |
Ginde AA, Mansbach JM, Camargo CA Jr. Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and upper respiratory tract infection in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169:384–390. | |
Laaksi I, Ruohola JP, Tuohimaa P, et al. An association of serum vitamin D concentrations <40 nmol/L with acute respiratory tract infection in young Finnish men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:714–717. | |
Camargo CA Jr, Ganmaa D, Frazier AL, et al. Randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation and risk of acute respiratory infection in Mongolia. Pediatrics. 2012;130:e561–e567. | |
Laaksi I, Ruohola JP, Mattila V, Auvinen A, Ylikomi T, Pihlajamäki H. Vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of acute respiratory tract infection: a randomized, double-blinded trial among young Finnish men. J Infect Dis. 2010;202:809–814. | |
Ehrchen J, Helming L, Varga G, et al. Vitamin D receptor signaling contributes to susceptibility to infection with Leishmania major. FASEB J. 2007;21:3208–3218. | |
He Q, Ananaba GA, Patrickson J, et al. Chlamydial infection in vitamin D receptor knockout mice is more intense and prolonged than in wild-type mice. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;135:7–14. | |
Schauber J, Dorschner RA, Coda AB, et al. Injury enhances TLR2 function and antimicrobial peptide expression through a vitamin D- dependent mechanism. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:803–811. | |
Whitcomb JP, Deagostino M, Ballentine M, et al. The role of vitamin D and vitamin D receptor in immunity to Leishmania major infection. J Parasitol Res. 2012;2012:134645. | |
Yang HF, Zhang ZH, Chang ZQ, Tang KL, Lin DZ, Xu JZ. Vitamin D deficiency affects the immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in mice. Clin Exp Med. 2013;13:265–270. | |
Anandaiah A, Sinha S, Bole M, et al. Vitamin D rescues impaired Mycobacterium tuberculosis-mediated tumor necrosis factor release in macrophages of HIV-seropositive individuals through an enhanced Toll-like receptor signaling pathway in vitro. Infect Immun. 2013;81:2–10. | |
Amer M, Qayyum R. Relation between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and C-reactive protein in asymptomatic adults (from the continuous National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001 to 2006). Am J Cardiol. 2012;109:226–230. | |
Lucidarme O, Messai E, Mazzoni T, Arcade M, du Cheyron D. Incidence and risk factors of vitamin D deficiency in critically ill patients: results from a prospective observational study. Intensive Care Med. 2010;36:1609–1611. | |
Trilok-Kumar G, Arora H, Rajput M, et al. Effect of vitamin D supplementation of low birth weight term Indian infants from birth on cytokine production at 6 months. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2012;66:746–750. | |
Alagarasu K, Honap T, Mulay AP, Bachal RV, Shah PS, Cecilia D. Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms with clinical outcomes of dengue virus infection. Hum Immunol. 2012;73:1194–1199. | |
Aslan S, Akil I, Aslan G, Onay H, Ozyurt BC, Ozkinay F. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism in children with urinary tract infection. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012;27:417–421. | |
Rathored J, Sharma SK, Singh B, et al. Risk and outcome of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and serum 25(OH)D. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2012;16:1522–1528. | |
Levin GP, Robinson-Cohen C, de Boer IH, et al. Genetic variants and associations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations with major clinical outcomes. JAMA. 2012;308:1898–1905. | |
Yin K, Deng X, Mo ZC, et al. Tristetraprolin-dependent post-transcriptional regulation of inflammatory cytokine mRNA expression by apolipoprotein A-I: role of ATP-binding membrane cassette transporter A1 and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:13834–13845. | |
Kassi E, Adamopoulos C, Basdra EK, Papavassiliou AG. Role of vitamin D in atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2013;128:2517–2531. | |
Stojanovic OI, Lazovic M, Vuceljic M. Association between atherosclerosis and osteoporosis, the role of vitamin D. Arch Med Sci. 2011;7:179–188. | |
Merke J, Milde P, Lewicka S, et al. Identification and regulation of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor activity and biosynthesis of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Studies in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells and human dermal capillaries. J Clin Invest. 1989;83:1903–1915. | |
Rebsamen MC, Sun J, Norman AW, Liao JK. 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 induces vascular smooth muscle cell migration via activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Circ Res. 2002;91:17–24. | |
Wang H, Xia N, Yang Y, Peng DQ. Influence of vitamin D supplementation on plasma lipid profiles: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Lipids Health Dis. 2012;11:42. | |
Park S, Lee BK. Vitamin D deficiency is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease in Koreans aged ≥50 years: results from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Nutr Res Pract. 2012;6:162–168. | |
Martins D, Wolf M, Pan D, et al. Prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors and the serum levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in the United States: data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:1159–1165. | |
Zhao G, Ford ES, Li C, Croft JB. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality among US adults with hypertension: the NHANES linked mortality study. J Hypertens. 2012;30:284–289. | |
Wasson LT, Shimbo D, Rubin MR, Shaffer JA, Schwartz JE, Davidson KW. Is vitamin D deficiency a risk factor for ischemic heart disease in patients with established cardiovascular disease? 10-Year follow-up of the Nova Scotia Health Survey. Int J Cardiol. 2011;148:387–389. | |
Semba RD, Houston DK, Bandinelli S, et al. Relationship of 25-hydroxyvitamin D with all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in older community-dwelling adults. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2010;64:203–209. | |
Wang TJ, Pencina MJ, Booth SL, et al. Vitamin D deficiency and risk of cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2008;117:503–511. | |
Dobnig H, Pilz S, Scharnagl H, et al. Independent association of low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168:1340–1349. | |
Lim S, Shin H, Kim MJ, et al. Vitamin D inadequacy is associated with significant coronary artery stenosis in a community-based elderly cohort: the Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:169–178. | |
Harris RA, Pedersen-White J, Guo DH, et al. Vitamin D3 supplementation for 16 weeks improves flow-mediated dilation in overweight African-American adults. Am J Hypertens. 2011;24:557–562. | |
Zittermann A, Frisch S, Berthold HK, et al. Vitamin D supplementation enhances the beneficial effects of weight loss on cardiovascular disease risk markers. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;89:1321–1327. | |
Sun Q, Shi L, Rimm EB, et al. Vitamin D intake and risk of cardiovascular disease in US men and women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;94:534–542. | |
Cauley JA, Chlebowski RT, Wactawski-Wende J, et al. Calcium plus vitamin D supplementation and health outcomes five years after active intervention ended: the Women’s Health Initiative. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2013;22:915–929. | |
Gepner AD, Ramamurthy R, Krueger DC, Korcarz CE, Binkley N, Stein JH. A prospective randomized controlled trial of the effects of vitamin D supplementation on cardiovascular disease risk. PLoS One. 2012;7:e36617. | |
Ponda MP, Dowd K, Finkielstein D, Holt PR, Breslow JL. The short-term effects of vitamin D repletion on cholesterol: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32:2510–2515. | |
Yiu YF, Yiu KH, Siu CW, et al. Randomized controlled trial of vitamin D supplement on endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis. 2013;227:140–146. | |
Wong MS, Delansorne R, Man RY, Svenningsen P, Vanhoutte PM. Chronic treatment with vitamin D lowers arterial blood pressure and reduces endothelium-dependent contractions in the aorta of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010;299: H1226–H1234. | |
Krishnan AV, Feldman D. Molecular pathways mediating the anti-inflammatory effects of calcitriol: implications for prostate cancer chemoprevention and treatment. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010;17:R19–R38. | |
Oh J, Weng S, Felton SK, et al. 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D inhibits foam cell formation and suppresses macrophage cholesterol uptake in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2009;120:687–698. | |
Gupta GK, Agrawal T, DelCore MG, Mohiuddin SM, Agrawal DK. Vitamin D deficiency induces cardiac hypertrophy and inflammation in epicardial adipose tissue in hypercholesterolemic swine. Exp Mol Pathol. 2012;93:82–90. | |
Carthy EP, Yamashita W, Hsu A, Ooi BS. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and rat vascular smooth muscle cell growth. Hypertension. 1989;13:954–959. | |
Tukaj S, Trzonkowski P, Tukaj C. Regulatory effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on vascular smooth muscle cells. Acta Biochim Pol. 2012;59:395–400. | |
Gupta GK, Agrawal T, Del Core MG, Hunter WJ 3rd, Agrawal DK. Decreased expression of vitamin D receptors in neointimal lesions following coronary artery angioplasty in atherosclerotic swine. PLoS One. 2012;7:e42789. | |
Finklea JD, Grossmann RE, Tangpricha V. Vitamin D and chronic lung disease: a review of molecular mechanisms and clinical studies. Adv Nutr. 2011;2:244–253. | |
Camargo CA Jr, Rifas-Shiman SL, Litonjua AA, et al. Maternal intake of vitamin D during pregnancy and risk of recurrent wheeze in children at 3 y of age. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;85:788–795. | |
Erkkola M, Kaila M, Nwaru BI, et al. Maternal vitamin D intake during pregnancy is inversely associated with asthma and allergic rhinitis in 5-year-old children. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009;39:875–882. | |
Freishtat RJ, Iqbal SF, Pillai DK, et al. High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among inner-city African American youth with asthma in Washington, DC. J Pediatr. 2010;156:948–952. | |
Goleva E, Searing DA, Jackson LP, Richers BN, Leung DY. Steroid requirements and immune associations with vitamin D are stronger in children than adults with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129:1243–1251. | |
Korn S, Hübner M, Jung M, Blettner M, Buhl R. Severe and uncontrolled adult asthma is associated with vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency. Respir Res. 2013;14:25. | |
Morales E, Romieu I, Guerra S, et al. Maternal vitamin D status in pregnancy and risk of lower respiratory tract infections, wheezing, and asthma in offspring. Epidemiology. 2012;23:64–71. | |
Bener A, Ehlayel MS, Tulic MK, Hamid Q. Vitamin D deficiency as a strong predictor of asthma in children. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012;157:168–175. | |
Brehm JM, Schuemann B, Fuhlbrigge AL, et al. Serum vitamin D levels and severe asthma exacerbations in the Childhood Asthma Management Program study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126:52–58. e5. | |
Gale CR, Robinson SM, Harvey NC, et al. Maternal vitamin D status during pregnancy and child outcomes. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2008;62:68–77. | |
Song Y, Qi H, Wu C. Effect of 1,25-(OH)2D3 (a vitamin D analogue) on passively sensitized human airway smooth muscle cells. Respirology. 2007;12:486–494. | |
Xystrakis E, Kusumakar S, Boswell S, et al. Reversing the defective induction of IL-10-secreting regulatory T cells in glucocorticoid-resistant asthma patients. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:146–155. | |
Gorman S, Tan DH, Lambert MJ, Scott NM, Judge MA, Hart PH. Vitamin D(3) deficiency enhances allergen-induced lymphocyte responses in a mouse model of allergic airway disease. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2012;23:83–87. | |
Agrawal T, Gupta GK, Agrawal DK. Vitamin D deficiency decreases the expression of VDR and prohibitin in the lungs of mice with allergic airway inflammation. Exp Mol Pathol. 2012;93:74–81. | |
Ananthakrishnan AN, Khalili H, Higuchi LM, et al. Higher predicted vitamin D status is associated with reduced risk of Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:482–489. | |
Levin AD, Wadhera V, Leach ST, et al. Vitamin D deficiency in children with inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56:830–836. | |
Ulitsky A, Ananthakrishnan AN, Naik A, et al. Vitamin D deficiency in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: association with disease activity and quality of life. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2011;35:308–316. | |
Pappa HM, Gordon CM, Saslowsky TM, et al. Vitamin D status in children and young adults with inflammatory bowel disease. Pediatrics. 2006;118:1950–1961. | |
Sentongo TA, Semaeo EJ, Stettler N, Piccoli DA, Stallings VA, Zemel BS. Vitamin D status in children, adolescents, and young adults with Crohn disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;76:1077–1081. | |
Jahnsen J, Falch JA, Mowinckel P, Aadland E. Vitamin D status, parathyroid hormone and bone mineral density in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2002;37:192–199. | |
Jørgensen SP, Agnholt J, Glerup H, et al. Clinical trial: vitamin D3 treatment in Crohn’s disease – a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;32:377–383. | |
Yang L, Weaver V, Smith JP, Bingaman S, Hartman TJ, Cantorna MT. Therapeutic effect of vitamin D supplementation in a pilot study of Crohn’s patients. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2013;4:e33. | |
Pappa HM, Mitchell PD, Jiang H, et al. Treatment of vitamin D insufficiency in children and adolescents with inflammatory bowel disease: a randomized clinical trial comparing three regimens. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:2134–2142. | |
Miheller P, Muzes G, Hritz I, et al. Comparison of the effects of 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D and 25 hydroxyvitamin D on bone pathology and disease activity in Crohn’s disease patients. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009;15:1656–1662. | |
Kong J, Zhang Z, Musch MW, et al. Novel role of the vitamin D receptor in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal mucosal barrier. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008;294:G208–G216. | |
Ryz NR, Patterson SJ, Zhang Y, et al. Active vitamin D (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3) increases host susceptibility to Citrobacter rodentium by suppressing mucosal Th17 responses. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;303:G1299–G1311. | |
Ali FN, Arguelles LM, Langman CB, Price HE. Vitamin D deficiency in children with chronic kidney disease: uncovering an epidemic. Pediatrics. 2009;123:791–796. | |
Satirapoj B, Limwannata P, Chaiprasert A, Supasyndh O, Choovichian P. Vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency with stages of chronic kidney disease in an Asian population. BMC Nephrol. 2013;14:206. | |
Isakova T, Gutiérrez OM, Patel NM, Andress DL, Wolf M, Levin A. Vitamin D deficiency, inflammation, and albuminuria in chronic kidney disease: complex interactions. J Ren Nutr. 2011;21:295–302. | |
Petchey WG, Howden EJ, Johnson DW, Hawley CM, Marwick T, Isbel NM. Cardiorespiratory fitness is independently associated with 25-hydroxyvitamin D in chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;6:512–518. | |
Pilz S, Tomaschitz A, Friedl C, et al. Vitamin D status and mortality in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26:3603–3609. | |
Santoro D, Gitto L, Ferraro A, Satta E, Savica V, Bellinghieri G. Vitamin D status and mortality risk in patients with chronic kidney disease. Ren Fail. 2011;33:184–191. | |
Seeherunvong W, Abitbol CL, Chandar J, Zilleruelo G, Freundlich M. Vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency in children with early chronic kidney disease. J Pediatr. 2009;154:906–911. e1. | |
London GM, Guérin AP, Verbeke FH, et al. Mineral metabolism and arterial functions in end-stage renal disease: potential role of 25-hydroxyvitamin D deficiency. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:613–620. | |
Molina P, Górriz JL, Molina MD, et al. The effect of cholecalciferol for lowering albuminuria in chronic kidney disease: a prospective controlled study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014;29:97–109. | |
Schaible J, Wigger M, Staude H, et al. Serum fetuin-A and vitamin D in children with mild-to-severe chronic kidney disease: a cross-sectional study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27:1107–1113. | |
Alvarez JA, Law J, Coakley KE, et al. High-dose cholecalciferol reduces parathyroid hormone in patients with early chronic kidney disease: a pilot, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;96:672–679. | |
Alvarez JA, Zughaier SM, Law J, et al. Effects of high-dose cholecalciferol on serum markers of inflammation and immunity in patients with early chronic kidney disease. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2013;67:264–269. | |
Chandra P, Binongo JN, Ziegler TR, et al. Cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) therapy and vitamin D insufficiency in patients with chronic kidney disease: a randomized controlled pilot study. Endocr Pract. 2008;14:10–17. | |
Kooienga L, Fried L, Scragg R, Kendrick J, Smits G, Chonchol M. The effect of combined calcium and vitamin D3 supplementation on serum intact parathyroid hormone in moderate CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:408–416. | |
Marckmann P, Agerskov H, Thineshkumar S, et al. Randomized controlled trial of cholecalciferol supplementation in chronic kidney disease patients with hypovitaminosis D. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27:3523–3531. | |
Shroff R, Wan M, Gullett A, et al. Ergocalciferol supplementation in children with CKD delays the onset of secondary hyperparathyroidism: a randomized trial. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;7:216–223. | |
Stubbs JR, Idiculla A, Slusser J, Menard R, Quarles LD. Cholecalciferol supplementation alters calcitriol-responsive monocyte proteins and decreases inflammatory cytokines in ESRD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21:353–361. | |
Zisman AL, Hristova M, Ho LT, Sprague SM. Impact of ergocalciferol treatment of vitamin D deficiency on serum parathyroid hormone concentrations in chronic kidney disease. Am J Nephrol. 2007;27:36–43. | |
Albalate M, de la Piedra C, Ortiz A, et al. Risk in dosing regimens for 25-OH vitamin D supplementation in chronic haemodialysis patients. Nephron Clin Pract. 2012;121:c112–c119. | |
Husain K, Ferder L, Mizobuchi M, Finch J, Slatopolsky E. Combination therapy with paricalcitol and enalapril ameliorates cardiac oxidative injury in uremic rats. Am J Nephrol. 2009;29:465–472. | |
Tan X, Wen X, Liu Y. Paricalcitol inhibits renal inflammation by promoting vitamin D receptor-mediated sequestration of NF-kappaB signaling. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;19:1741–1752. | |
Brunt EM, Kleiner DE, Wilson LA, et al. Portal chronic inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a histologic marker of advanced NAFLD-clinicopathologic correlations from the nonalcoholic steatohepatitis clinical research network. Hepatology. 2009;49:809–820. | |
Kelishadi R, Saleka S, Saleka M, Hashemipoura M, Movahedian M. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on insulin resistance and cardiometabolic risk factors in children with metabolic syndrome: a triple-masked controlled trial. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2014;90:28–34. | |
Wongwiwatthananukit S, Sansanayudh N, Phetkrajaysang N, Krittiyanunt S. Effects of vitamin D(2) supplementation on insulin sensitivity and metabolic parameters in metabolic syndrome patients. J Endocrinol Invest. 2013;36:558–563. | |
Pirgon O, Cekmez F, Bilgin H, Eren E, Dundar B. Low 25-hydroxyvitamin D level is associated with insulin sensitivity in obese adolescents with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2013;7:e235–e320. | |
Jablonski KL, Jovanovich A, Holmen J, et al. Low 25-hydroxyvitamin D level is independently associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2013;23:792–798. | |
Tilg H, Moschen AR. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology. 2010;52:1836–1846. | |
Roth CL, Elfers CT, Figlewicz DP, et al. Vitamin D deficiency in obese rats exacerbates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and increases hepatic resistin and Toll-like receptor activation. Hepatology. 2012;55:1103–1111. | |
Schaalan MF, Mohamed WA, Amin HH. Vitamin D deficiency: correlation to interleukin-17, interleukin-23 and PIIINP in hepatitis C virus genotype 4. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:3738–3744. | |
Zitt E, Sprenger-Mähr H, Knoll F, Neyer U, Lhotta K. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with poor response to active hepatitis B immunisation in patients with chronic kidney disease. Vaccine. 2012;30:931–935. | |
Zúñiga S, Firrincieli D, Housset C, Chignard N. Vitamin D and the vitamin D receptor in liver pathophysiology. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2011;35:295–302. | |
Mowry EM, Waubant E, McCulloch CE, et al. Vitamin D status predicts new brain magnetic resonance imaging activity in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2012;72:234–240. | |
Martinelli V, Dalla Costa G, Colombo B, et al. Vitamin D levels and risk of multiple sclerosis in patients with clinically isolated syndromes. Mult Scler. 2014;20:147–155. | |
Munger KL, Levin LI, Hollis BW, Howard NS, Ascherio A. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and risk of multiple sclerosis. JAMA. 2006;296:2832–2838. | |
Pierrot-Deseilligny C, Rivaud-Péchoux S, Clerson P, de Paz R, Souberbielle JC. Relationship between 25-OH-D serum level and relapse rate in multiple sclerosis patients before and after vitamin D supplementation. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2012;5:187–198. | |
Mirzaei F, Michels KB, Munger K, et al. Gestational vitamin D and the risk of multiple sclerosis in offspring. Ann Neurol. 2011;70:30–40. | |
Burton JM, Kimball S, Vieth R, et al. A phase I/II dose-escalation trial of vitamin D3 and calcium in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 2010;74:1852–1859. | |
Shaygannejad V, Janghorbani M, Ashtari F, Dehghan H. Effects of adjunct low-dose vitamin D on relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis progression: preliminary findings of a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Mult Scler Int. 2012;2012:452541. | |
Kampman MT, Steffensen LH, Mellgren SI, Jørgensen L. Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on relapses, disease progression, and measures of function in persons with multiple sclerosis: exploratory outcomes from a double-blind randomised controlled trial. Mult Scler. 2012;18:1144–1151. | |
Smolders J, Peelen E, Thewissen M, et al. Safety and T cell modulating effects of high dose vitamin D3 supplementation in multiple sclerosis. PLoS One. 2010;5:e15235. | |
Adzemovic MZ, Zeitelhofer M, Hochmeister S, Gustafsson SA, Jagodic M. Efficacy of vitamin D in treating multiple sclerosis-like neuroinflammation depends on developmental stage. Exp Neurol. 2013;249:39–48. | |
Ozfirat Z, Chowdhury TA. Vitamin D deficiency and type 2 diabetes. Postgrad Med J. 2010;86:18–25; quiz 24. | |
Tamez H, Thadhani RI. Vitamin D and hypertension: an update and review. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012;21:492–499. | |
Sugden JA, Davies JI, Witham MD, Morris AD, Struthers AD. Vitamin D improves endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and low vitamin D levels. Diabet Med. 2008;25:320–325. | |
Forman JP, Scott JB, Ng K, et al. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on blood pressure in blacks. Hypertension. 2013;61:779–785. | |
Asemi Z, Hashemi T, Karamali M, Samimi M, Esmaillzadeh A. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on glucose metabolism, lipid concentrations, inflammation, and oxidative stress in gestational diabetes: a double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;98:1425–1432. | |
Witham MD, Ireland S, Houston JG, et al. Vitamin D therapy to reduce blood pressure and left ventricular hypertrophy in resistant hypertension: randomized, controlled trial. Hypertension. 2014;63:706–712. | |
Lewis PJ. Vitamin D deficiency may have role in chronic low back pain. BMJ. 2005;331:109. | |
Sandoughi M, Zakeri Z, Mirhosainee Z, Mohammadi M, Shahbakhsh S. The effect of vitamin D on nonspecific low back pain. Int J Rheum Dis. Epub October 14, 2013. | |
Boxer RS, Hoit BD, Schmotzer BJ, Stefano GT, Gomes A, Negrea L. The effect of vitamin D on aldosterone and health status in patients with heart failure. J Card Fail. Epub February 4, 2014. | |
Cantorna MT, Mahon BD: Mounting evidence for vitamin D as an environmental factor affecting autoimmune disease prevalence. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2004;229:1136–1142. | |
Abou-Raya A, Abou-Raya S, Helmii M. The effect of vitamin D supplementation on inflammatory and hemostatic markers and disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Rheumatol. 2013;40:265–272. | |
Leventis P, Patel S. Clinical aspects of vitamin D in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47:1617–1621. | |
Ritterhouse LL, Crowe SR, Niewold TB, et al. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increased autoimmune response in healthy individuals and in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1569–1574. | |
Kahl LE, Kamboh MI, Decroo S, Ferrell RE. Alpha-1-antitrypsin (PI) and vitamin-D binding globulin (GC) phenotypes in rheumatoid arthritis: absence of an association. Dis Markers. 1989;7:71–78. | |
Ota K, Dambaeva S, Han AR, Beaman K, Gilman-Sachs A, Kwak-Kim J. Vitamin D deficiency may be a risk factor for recurrent pregnancy losses by increasing cellular immunity and autoimmunity. Hum Reprod. 2014;29:208–219. | |
Stricker H, Tosi Bianda F, Guidicelli-Nicolosi S, Limoni C, Colucci G. Effect of a single, oral, high-dose vitamin D supplementation on endothelial function in patients with peripheral arterial disease: a randomised controlled pilot study. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2012;44:307–312. | |
Brehm JM, Celedón JC, Soto-Quiros ME, et al. Serum vitamin D levels and markers of severity of childhood asthma in Costa Rica. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;179:765–771. | |
Moe SM, Saifullah A, LaClair RE, Usman SA, Yu Z. A randomized trial of cholecalciferol versus doxercalciferol for lowering parathyroid hormone in chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5:299–306. | |
Runia TF, Hop WC, de Rijke YB, Buljevac D, Hintzen RQ. Lower serum vitamin D levels are associated with a higher relapse risk in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 2012;79:261–266. | |
Munger KL, Chitnis T, Frazier AL, Giovannucci E, Spiegelman D, Ascherio A. Dietary intake of vitamin D during adolescence and risk of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol. 2011;258:479–485. |
 © 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.