Back to Journals » Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment » Volume 14
Aripiprazole combination for reversal of paliperidone-induced increase in prolactin level
Authors Zhi P, Wang Y, Quan W, Su Y, Zhang H
Received 3 March 2018
Accepted for publication 1 June 2018
Published 27 August 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 2175—2179
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S167129
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
Pu Zhi,1,* Yanqiong Wang,1,* Wei Quan,1,2 Yanli Su,1 Hui Zhang1
1Department of Psychiatry, Xi’an Mental Health Center, Institute of Mental Health, Xi’an Medical University, Xi’an, China; 2Department of Natural Medicine, Institute of Materia Medica, School of Pharmacy, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi’an, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract: Hyperprolactinemia is a common side effect of antipsychotic drugs. Although changes of antipsychotic drugs or reduction of their doses can solve this problem, a modification of the treatment regimen can lead to instability in patients. Herein, we followed up a patient with elevated prolactin caused by paliperidone and found that the prolactin level was decreased after the administration of a combination with a low-dose aripiprazole. In addition, we summarized and analyzed the findings from the case and the literature review conducted.
Keywords: aripiprazole, schizophrenia, prolactin
Introduction
Hyperprolactinemia is a recognized adverse reaction to the use of antipsychotic drugs.1 The administration of second-generation antipsychotics, such as amisulpride, risperidone, and paliperidone, can significantly increase the level of serum prolactin.2 However, a sustained elevation of prolactin may lead to irregular menstruation and disturbance of endocrine hormone levels, and thus causes amenorrhea, infertility, galactorrhea, dizziness, visual disorders, etc.3 In this report, we present a case of a female patient with hyperprolactinemia caused by the use of paliperidone, and in whom its combination with aripiprazole significantly reduced the level of prolactin. Under the premise of stabilizing the patient’s condition and continuing medication, this therapeutic method exerted a good clinical effect.
Case presentation
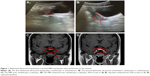
The patient was a 12-year-old girl (student) with total disease duration of 3 years. The onset started from around November 2014, and was manifested as fussiness, unwillingness to go to school (as she had not wanted to hear someone talking about her or to be unjustly hurt), unwillingness to see others, and insomnia. The specific diagnosis and medication were unclear, and she did not adhere to the treatment. In January 2016, she experienced recurrent symptoms: she imagined someone was talking about her, trying to hurt her, and was unwilling to communicate with people. She had uncoordinated emotional reactions and exhibited weight loss, poor appetite, and no menstruation after menarche. According to ICD-10 diagnostic criteria, she was diagnosed with schizophrenia and admitted to our hospital. Admission routine examinations showed no obvious abnormalities. Due to the absence of menstruation, she underwent abdominal ultrasound to rule out uterine organic disease. The result showed normal physiological structure of the uterus (Figure 1A, the uterus with dimensions of 43 × 28 × 18 mm, regular shape, uniform distribution of internal echoes, centralized endometrial line, and endometrial thickness of approximately 8 mm). The thyrotropin level was 4.76 uIU/mL (reference values: 0.4–4.5 uIU/mL), and the serum prolactin level was 18.79 ng/mL (Table 1, reference values: 3.12–23.03 ng/mL). Based on these test results, we considered that the absence of menstruation was associated with unstable ovarian function and regulative mechanisms as well as disorders of various hormone endocrine levels.4 The patient was closely observed and given olanzapine 20 mg/day, and discharged with improved psychiatric symptoms after 1 month of treatment.
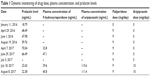  | Table 1 Dynamic monitoring of drug dose, plasma concentration, and prolactin levels |
Subsequently, the patient adhered to the outpatient treatment prescribed. However, she experienced excessive sleepiness during the daytime and was thus unable to go to school normally, due to the administration of olanzapine. Her regimen was changed to paliperidone (9 mg/day) after clinical evaluation, and improvement in her psychiatric symptoms was obtained upon adherence to this regimen. In April 2016, her prolactin level was 48.49 ng/mL, which then increased to 70.04 ng/mL in April 2017 (Table 1). Dynamic monitoring revealed that her prolactin level continued to rise. Taking into account the patient’s age and the effects of the therapy on menstruation and reproduction, we performed examinations to exclude the potential effect of pituitary organic disease on prolactin levels. Cerebral MRI revealed topical protuberance on the right side of the pituitary gland, and the pituitary enhancement scan showed a uniform pituitary T2 signal, with full right margin and no obvious abnormal enhancement (Figure 1C and D). Therefore, the influence of the pituitary gland on the prolactin level was ruled out, and the elevated prolactin level was considered to be caused by paliperidone administration.
To maintain the patient’s stable condition, she was given a combination of aripiprazole rather than discontinuing the regimen or replacing or reducing the dose of paliperidone.5,6 Starting from July 5, the patient was given a combined dose of aripiprazole (5 mg/day) and paliperidone (9 mg/day), and her prolactin level lowered to 23.42 ng/mL after 15 days of therapy (Table 1). The examination of her abdominal ultrasound scan revealed the following data: uterine dimensions of 51 × 37 × 22 mm, regular shape, uniform distribution of the echoes, centralized endometrial line, and endometrial thickness of about 8 mm (Figure 1B). Her prolactin level decreased significantly after the combined use of 5 mg aripiprazole and 9 mg paliperidone, but did not fall within the reference range. Hence, the dose of aripiprazole was increased to 10 mg/day, and 1 month later the prolactin level reduced to 22.38 ng/mL, which was within the reference range (Table 1). In addition, the patient’s condition was stable during the period of the combined use of aripiprazole and paliperidone, and no adverse reactions related to the use of aripiprazole or paliperidone were observed.
Discussion
An elevated serum prolactin level during treatment may cause amenorrhea, galactorrhea, anovulation, infertility, and so on, which are some of the common adverse reactions in the use of antipsychotic drugs. Prolactin is a polypeptide hormone which is synthesized and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland.7 Its secretion is mainly affected by the tuberoinfundibular and tuberohypophysial pathways8 and is regulated by many neurotransmitters, of which dopamine and serotonin are the most important. Dopamine can inhibit the release of prolactin, and 5-HT, as a prolactin-stimulating factor, can increase the secretion of prolactin, which is a mechanism utilized in the regulation of prolactin levels in the body. Since paliperidone is a receptor blocker of central 5-HT and dopamine D2, in addition to improving psychotic symptoms and stabilizing mood, it also blocks dopamine D2 receptors on the tuberoinfundibular pathway to induce disinhibition and release of prolactin, which results in the mechanism of elevation of prolactin in a certain proportion of the population.9
Currently, there are several strategies to promote the elevation of prolactin, such as lowering the dose of antipsychotics, replacing them with other antipsychotics, or adding dopaminergic agonists. However, all these strategies may cause a risk of instability in patients.10 It has previously been reported that aripiprazole, a dopamine receptor partial agonist, can effectively improve the hyperprolactinemia caused by risperidone and its active metabolite 9-hydroxyrisperidone (paliperidone).11–14 Adjunctive aripiprazole is a potential treatment option for hyperprolactinemia in youth who have achieved clinical stability on monotherapy.15 Thus, in the case in the present study, we used aripiprazole to validate and evaluate the specific therapeutic effect of aripiprazole and provide the basis for clinical treatment.
The serum prolactin level was decreased after the patient was given 5 mg of aripiprazole for 2 weeks, but was not reduced to within the range of the reference values. Nevertheless, it was diminished and fell within the reference value range by increasing the dose of aripiprazole to 10 mg. We found that aripiprazole effectively reduced the increased level of prolactin caused by paliperidone. The underlying mechanism may be through the upregulation of dopamine insufficiency by aripiprazole, which is an effective, high-affinity D2 receptor partial agonist. Aripiprazole also downregulates dopamine hyperfunction and is thus a dopamine transmitter stabilizer.16 In addition, this drug can also inhibit anterior pituitary secretion of prolactin while inhibiting Dopamine (DA) activity on pathways with DA hyperfunction in the midbrain margin.17 As pointed out previously, as a dopamine neurotransmitter stabilizer, it can be targeted to regulate the prolactin level.
The combined medication in the case described herein was expected to improve the adverse reactions of paliperidone while not affecting its therapeutic effect. The patient had stable mental health status and did not experience fluctuations or other adverse reactions after receiving the combination of paliperidone and aripiprazole. Dynamic monitoring showed that the serum prolactin level was decreased significantly. Therefore, the combination did not influence the effect of paliperidone but reduced the paliperidone-induced elevation of prolactin.18,19 Although both drugs are metabolized by 2D6 and 3A4 enzymes, only a limited proportion of paliperidone (≤40%) is metabolized by these enzymes, and paliperidone dose not inhibit nor induce 2D6 and 3A4 enzymes.20 Thus, the plasma concentration of other drugs is not influenced by the administration of paliperidone. In the present study, the patient’s plasma concentration of paliperidone fluctuated after the combined administration but was still within the target range of 20–60 ng/mL.
It is noteworthy that the reasons for the lack of menstruation after menarche were complex and might have been associated with the large secretion of prolactin. Nonetheless, an increase of prolactin levels was observed while no significant variation in the thickness of the endometrium was established. After a year of observation, we conclude that although elevated prolactin levels might affect and introduce changes in the menstrual cycle, they are unlikely to influence the thickness of the endometrium,21,22 which might be associated with the absence of Pit-1 (pituitary-specific transcription factor) expression in the endometrium.23,24 Nevertheless, the long-term influence of prolactin on the thickness of the endometrium remains to be observed.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form, the patient and the parent of the patient have given their written informed consent for their images and other clinical information to be reported in the article. They understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Author contributions
All authors contributed toward data analysis, drafting and revising the paper and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Rosenbloom AL, Arlan LR. Correction: hyperprolactinemia with antipsychotic drugs in children and adolescents. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol. 2013;2013(1):13. | ||
Svestka J, Synek O, Tomanová J, Rodáková I, Cejpková A. Differences in the effect of second-generation antipsychotics on prolactinaemia: six weeks open-label trial in female in-patients. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2007;28(6):881–888. | ||
Bostwick JR, Guthrie SK, Ellingrod VL. Antipsychotic-induced hyperprolactinemia. Pharmacotherapy. 2009;29(1):64–73. | ||
Black WP, Govan AD. Laparoscopy and ovarian biopsy for the assessment of secondary amenorrhea. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972;114(6):739–747. | ||
Qiao Y, Yang F, Li C, et al. Add-on effects of a low-dose aripiprazole in resolving hyperprolactinemia induced by risperidone or paliperidone. Psychiatry Res. 2016;237:83–89. | ||
Li X, Tang Y, Wang C. Adjunctive aripiprazole versus placebo for antipsychotic-induced hyperprolactinemia: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e70179. | ||
Rainka MM, Capote HA, Ross CA, Gengo FM. Attenuation of risperidone-induced hyperprolactinemia with the addition of aripiprazole. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2009;34(5):595–598. | ||
Fitzgerald P, Dinan TG. Prolactin and dopamine: what is the connection? A review article. J Psychopharmacol. 2008;22(2 Suppl):12–19. | ||
Broekhof R, Gosselink MJ, Pijl H, Giltay EJ. The effect of aripiprazole and quinagolide, a dopamine agonist, in a patient with symptomatic pituitary prolactinoma and chronic psychosis. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2012;34(2):209.e1–e3 | ||
de Berardis D, Fornaro M, Serroni N, et al. Treatment of antipsychotic-induced hyperprolactinemia: an update on the role of the dopaminergic receptors D2 partial agonist aripiprazole. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov. 2014;8(1):30–37. | ||
Chen JX, Su YA, Wang SL, et al. Aripiprazole treatment of risperidone-induced hyperprolactinemia. J Clin Psychiatry. 2009;70(7):1058–1059. | ||
Raghuthaman G, Venkateswaran R, Krishnadas R. Adjunctive aripiprazole in risperidone-induced hyperprolactinaemia: double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. BJPsych Open. 2015;1(2):172–177. | ||
Zhao J, Song X, Ai X, et al. Adjunctive aripiprazole treatment for risperidone-induced hyperprolactinemia: an 8-week randomized, open-label, comparative clinical trial. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0139717. | ||
Ranjbar F, Sadeghi-Bazargani H, Niari Khams P, Arfaie A, Salari A, Farahbakhsh M. Adjunctive treatment with aripiprazole for risperidone-induced hyperprolactinemia. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015;11:549–555. | ||
Curran RL, Badran IA, Peppers V, et al. Aripiprazole for the treatment of antipsychotic-induced hyperprolactinemia in an adolescent boy. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2016;26(5):490–491. | ||
Kessler RM. Aripiprazole: what is the role of dopamine D(2) receptor partial agonism? Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(9):1310–1312. | ||
Inoue T, Domae M, Yamada K, Furukawa T. Effects of the novel antipsychotic agent 7-(4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1-piperazinyl]butyloxy)-3,4-dihydro-2(1H)-quinolinone (OPC-14597) on prolactin release from the rat anterior pituitary gland. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;277(1):137–143. | ||
Shin C, Han C, Pae CU, Patkar AA. Precision medicine for psychopharmacology: a general introduction. Expert Rev Neurother. 2016;16(7):831–839. | ||
Zhao JP, Shi SX. Prevention guide to mental illness-Chinese Medical Association. Beijing. Chin Med Electron Audio-Video Publis House. 2015:183–185. | ||
Mauri MC, Volonteri LS, Colasanti A, Fiorentini A, de Gaspari IF, Bareggi SR. Clinical pharmacokinetics of atypical antipsychotics: a critical review of the relationship between plasma concentrations and clinical response. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2007;46(5):359–388. | ||
Xia SY, Zhang YR, Yu H, Meng X, Zhang P, Liu J. Treatment of antipsychotic drug-induced phlegm dampness type amenorrhea by Wuji Powder and a small dose aripiprazole: a clinical study. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med. 2014;34(12):1440–1443. | ||
Dutta UR, Ponnala R, Pidugu VK, Dalal AB. Chromosomal abnormalities in amenorrhea: a retrospective study and review of 637 patients in South India. Arch Iran Med. 2013;16(5):267–270. | ||
Rhodes SJ, Dimattia GE, Rosenfeld MG. Transcriptional mechanisms in anterior pituitary cell differentiation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994;4(5):709–717. | ||
Shemanko CS. Prolactin receptor in breast cancer: marker for metastatic risk. J Mol Endocrinol. 2016;57(4):R153–R165. |
 © 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.