Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 14
Apoptosis and oxidative stress as relevant mechanisms of antitumor activity and genotoxicity of ZnO-NPs alone and in combination with N-acetyl cysteine in tumor-bearing mice
Authors El-Shorbagy HM , Eissa SM, Sabet S , El-Ghor AA
Received 10 February 2019
Accepted for publication 9 April 2019
Published 27 May 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 3911—3928
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S204757
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
Haidan M El-Shorbagy, Shaymaa M Eissa, Salwa Sabet, Akmal A El-Ghor
Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt
Background: Several in vitro studies have revealed that zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) were able to target cancerous cells selectively with minimal damage to healthy cells.
Purpose: In the current study, we aimed to evaluate the antitumor activity of ZnO-NPs in Ehrlich solid carcinoma (ESC) bearing mice by measuring their effect on the expression levels of P53, Bax and Bcl2 genes as indicators of apoptotic induction in tumor tissues. Also, we assessed the potential ameliorative or potentiation effect of 100 mg/kg N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) in combination with ZnO-NPs.
Materials and methods: ESC bearing mice were gavaged with three different doses of ZnO-NPs (50, 300 and 500 mg/kg body weight) alone or in combination with NAC for seven consecutive days. In addition to measuring the tumor size, pathological changes, zinc content, oxidative stress biomarkers and DNA damage in ESC, normal muscle, liver and kidney tissues were assessed.
Results: Data revealed a significant reduction in tumor size with a significant increase in p53 and Bax and decrease in Bcl2 expression levels in the tissues of ZnO-NPs treated ESC bearing mice. Moreover, a significant elevation of MDA accompanied with a significant reduction of CAT and GST. Also, a marked increase in all comet assay parameters was detected in ZnO-NPs treated groups. On the other hand, the combined treatment with ZnO-NPs and NAC significantly reduced reactive oxygen species production and DNA damage in liver and kidney tissues in all ZnO-NPs treated groups.
Conclusion: ZnO-NPs exhibited a promising anticancer efficacy in ESC, this could serve as a foundation for developing new cancer therapeutics. Meanwhile, the combined treatment with ZnO-NPs and NAC could act as a protective method for the healthy normal tissue against ZnO-NPs toxicity, without affecting its antitumor activity.
Keywords: ZnO-NPs, antitumor, Ehrlich solid carcinoma, N-acetyl cysteine, oxidative stress, DNA damage
Introduction
Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs), among the most common metal oxides NPs, have received considerable attention due to their low production cost, ability to form diverse structures and various biological purposes such as bio-imaging probes, beauty agents, drug delivery and immune-modulatory agent.1–3 In addition, ZnO-NPs are being used in the food industry as additives and in packaging due to their antifungal and antibacterial properties4,5
Despite the promising antitumor activity of ZnO-NPs in vitro, very limited studies have been performed on the animal model system. The advantage of using ZnO-NPs in cancer treatment is attributed to their cytotoxicity against cancer cells with a minimal damage to healthy cells.6 ZnO-NPs of different particle sizes ranging from 5 to 175 nm proved their cytotoxicity in Murine and cancer cells such as tumor U87, HepG-2, MCF-7, Colo320 and HeLa8.7–10 The exposure of MCF7 and A549 cells to ZnO-NPs (16–19 nm) to various concentrations ranged from (2.5–1,000 μg/mL) for 72 hrs, significantly reduced the cell viability in a concentration-dependent manner.11 Cancer is characterized by an imbalance between cell division and cell death.12 Therefore, apoptosis is a key process in cancer treatment and is controlled by a large number of genes such as the tumor suppressor gene P53, pro-apoptotic gene Bax and anti-apoptotic gene Bcl2. P53 is considered as the master guardian of the cell and is able to stimulate cell cycle checkpoints, while the Bax/Bcl2 protein ratio determines the life or death of cells.13–16 In addition, P53 is capable of upregulating the expression of Bax and downregulating the expression of Bcl2.17 Consequently, evaluation of the expression of some apoptotic-related genes after administration of different ZnO-NPs doses will be an indicative marker of the antitumor activity of ZnO-NPs in ESC bearing mice.
Concurrently, it is of great importance to study the potential toxicity and safety of ZnO-NPs in order to evaluate its hazardous effect on the normal healthy tissues. ZnO bulk materials, at sizes larger than 100 nm, are considered to be relatively biocompatible and generally recognized as safe substances by the FDA. A previous in vivo toxicity study has shown that ZnO-NPs did not induce micronuclei formation in bone marrow or DNA damage in lung cells of rats after exposure to different doses (15, 30 and 50 mg/kg) of triethozycaprylylsilane-coated ZnO.18 Another study on mice has revealed that 50 nm ZnO-NPs did not induce micronuclei formation at concentrations up to 5 g/kg body weight (BW).19 However, acute oral exposure to high doses of ZnO-NPs (1–5 g/kg BW) has been reported to damage the liver, spleen and pancreas tissues in mice.20 Moreover, repeated dermal exposure to ZnO-NPs for 28 days has caused a dose-dependent toxicity on the skin of Sprague–Dawley rats.21 These controversial data urge the need to find methods that reduce the toxicity of ZnO-NPs to benefit from their antitumor activity and other wide applications.
N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) is the glutathione (GSH) precursor which causes an elevation of GSH levels that support the antioxidant and nitric oxide systems during infection, inflammation, stress and exposure to toxins.22–24 NAC has decreased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in rat astrocytes and has reversed the elevated proportion of apoptotic cells in U87 human glial cells induced by ZnO-NPs.25–27 These findings suggest that cells’ pretreatment with NAC could reverse the toxic effect of ZnO-NPs that is mediated via ROS production.28 In addition, NAC manifests a promising effect in cancer prevention as they possess anti-carcinogenic properties.29–31 In vitro NAC has been reported to inhibit the growth and invasive behavior of human cancer cells, such as colorectal,32 bladder,33,34 prostate,35 tongue36 and lung carcinoma cell.37 Moreover, NAC at a high dose (1g/kg IV) can act as a chemo-protectant against cisplatin nephrotoxicity in rats.38
Therefore, in the present study, we assessed the potential antitumor activity, toxicity of ZnO-NPs and the underlying molecular mechanisms after oral administration of different doses (50, 300 and 500 mg/kg) in murine Ehrlich solid carcinoma (ESC) bearing mice. In addition, we investigated the ameliorative or the potentiation effects of NAC against ZnO-NPs genotoxicity in the healthy and cancerous cells within the tumor-bearing mice.
Material and methods
Chemicals
ZnO-NPs (<100 nm, purity >99%, Cat. No. 544906), N-Acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), and all other chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, Missouri, USA). Kits for all biochemical parameters were purchased from Bio-diagnostic Company (Giza, Egypt). Other molecular kits are listed elsewhere.
Nanoparticles preparation, characterization and biodistribution
ZnO-NPs of different doses (50, 300 and 500 mg/kg) were dispersed in deionized water and resuspended by ultrasonic vibration (130 W, 20 kHz) for 20 mins for all experimental work. ZnO-NPs suspensions were vortexed for 1 min before each administration.
The morphology and size of ZnO-NPs were determined by transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM, Tecnai G20, FEI, Netherland). The surface zeta potential measurements were also performed with the Malvern, UK Zetasizer Nano ZS. For TEM, a drop of ZnO-NPs solution (8 µg/mL in Milli-Q) was deposited on carbon-coated copper grids. The fills on the TEM grids were allowed to dry prior to measurement.39
Biodistribution of ZnO-NPs was quantified by the determination of zinc levels in the normal muscle, ESC muscle, liver and kidney using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) (Thermo Scientific iCAP 7000).19
Animals
Adult (6 weeks old) C 57BL/6 mice weighing 25–30 g were obtained from the animal house of the National Research Center (NRC, Giza) and acclimatized for 1 week prior to the experiments in an environment of controlled temperature (22–25°C), humidity and 12-hr light/dark cycle. Mice were housed in polypropylene cages (5 animals/cage) and permitted for free standard laboratory diet ad libitum. All the experimental procedures were carried out in accordance with the international guidelines for care and use of laboratory animals. The animal experimental protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (CU-IACUC) at Faculty of Science, Cairo University (CU/I/F/38/18).
Tumor induction and experimental design
Murine Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma (ESC) bearing mouse was obtained from National Cancer Institute, Cairo University (Giza, Egypt). Mice were intramuscularly implanted with 0.2 mL of Ehrlich tumor cell suspension (containing about 2×106 viable cells) in the thigh of the left hind leg. Once solid tumor appeared on day 10; mice were randomly divided into 8 groups (5 animal/group) and were orally gavaged for seven consecutive days as follows: ESC group received deionized water alone, ESC+NAC group received 100 mg/kg BW of NAC, ESC+50ZnO-NPs, ESC+300ZnO-NPs and ESC+500ZnO-NPs groups received doses of ZnO-NPs of 50, 300 and 500 mg/kg BW, respectively. These doses are in consistence with OECD TG 420 guidelines for investigating the oral toxicity of any new substance and according to Tice and Shelby40 toxicity research.40 ESC+50ZnO-NPs+NAC, ESC+300ZnO-NPs+NAC and ESC+500ZnO-NPs+NAC groups received 100 mg/kg BW of NAC followed by ZnO-NPs doses of 50, 300 and 500 mg/kg BW, respectively, in addition to a negative control group that was not induced with tumor and received distilled water only.
Tumor size was measured every four days using Vernier caliper, the following formula was used to estimate the tumor volume: Tumor volume (mm3) = Length (mm) × (width (mm))2/2.41 The individual relative tumor volume (RTV) was measured by Vx/V1, where Vx is the volume in mm3 at a given time and V1 at the start of treatment. Tumor growth inhibition (% TGI) was calculated using the equation 100−(T/C×100), where T is the mean RTV of the treated tumor and C is the mean RTV in the control group at the same point time.
Sample collection
On the 8th day, animals were anesthetized using sodium thiopental (0.5%) and were sacrificed by cervical dislocation. The livers, kidneys, right thigh muscles and solid tumor in the left thigh of mice were immediately dissected out and tissues were cut into four parts. One part was homogenized in ice-cold saline (0.9% w/v) using a homogenizer to obtain 20% homogenate. The homogenate was centrifuged at 3,000 rpm for 15 mins at 4ºC, and the resultant supernatant was used for biochemical analysis. The other parts were preserved either in 10% formalin and embedded in paraffin wax blocks for histopathological and immunohistochemical analysis, or in RNA later and stored directly at −80ºC for gene expression analysis, or minced in Hanks buffer then stored directly at −20ºC for comet analysis.
Histopathological examination
For pathological studies, fresh portions of liver, kidney, muscle and ESC from each experimental group were immediately fixed in 10% buffered formalin. They were then embedded in paraffin, sectioned by microtome into 5 µm thickness and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. The stained sections were evaluated by a histopathologist unaware of the treatments using light microscopy (U-IIIMulti-point Sensor System; Nikon, Tokyo, Japan).
Assessment of oxidative stress biomarkers
The previously prepared homogenates from kidney, liver, muscle and ESC muscle were used to measure malondialdehyde (MDA),42 glutathione-S-transferase (GST)43 and catalase (CAT)44 using Bio-diagnostic assay kits according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Comet assay
The comet assay was performed as previously described.45 The degree of DNA damage was assessed according to various endpoints. Tail length was used to estimate the extent of DNA damage distant from the nucleus, while % DNA in tail represents the intensity of all tail pixels divided by the total intensity of all pixels in the comet and tail moment=tail length×% DNA in tail/100.
RNA extraction, cDNA synthesis and real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR)
To assess the expression of Bax, Bcl2 and P53 genes, total cellular RNA was extracted from examined muscles of control and treated animals using GeneJET™ RNA purification kit (Thermo Scientific, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol and stored at −80ºC. One microgram RNA was reversed transcribed using RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The primers were designed using NCBI Primer blast and synthesized by Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA) (Table 1).
 | Table 1 Primers sequence’ used in quantitative real-time PCR assays |
qPCR was carried out in a 25 µL reaction volume using SYBR green master mix (Maxima SYBR Green/ROX qPCR Master Mix (2x) kit) and was performed in StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystem, Foster City, CA, USA) according to the kit’s manual instructions. PCR program was adjusted as follows: an initial heat activation step at 95ºC for 15 mins followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95ºC for 15 s, annealing and elongation at 60ºC for 1 min and samples were analyzed in triplicates for each gene. Expression of the studied genes was normalized to the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) as an internal control gene. Relative gene expression was calculated by the 2−ΔΔCt formula.
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemical examinations of P53 and caspase-3 were performed using streptavidin-biotin method by Histostain-plus kit (Zymed, USA). Paraffin sections of normal and ESC muscle 5 mm thick were dewaxed in xylene and rehydrated through graded alcohols, and then antigens were retrieved by heating in Tris–EDTA buffer. Non-specific binding was blocked by 10% non-immune serum, and then tissues were incubated for 2 hrs in primary antibody diluted 1:50 with TBS. For negative control; tissues were incubated with TBS without primary antibody. The endogenous peroxidase activity of tissues was blocked with 3% hydrogen peroxide for 10 mins (BioGenex, San Ramon, CA, USA). For visualization; tissues were incubated with 100 mL horseradish peroxidase (HRP) labeled rabbit or mouse secondary antibody and then DAB chromogen was added. For counterstaining, sections were stained with hematoxylin, then dehydrated and mounted. Sections were examined using light microscope (Zeiss) to evaluate P53 and caspase-3 immuno-staining.
Statistical analysis
Results were analyzed using Statistical Package of the Social Sciences (SPSS 23). Multi-way analysis of variance (MANOVA) was chosen to study the effect of the protection (with and without NAC), different ZnO-NPs doses (0, 50, 300 and 500 mg/kg BW), tissue type (liver, kidney, muscle and muscle with ESC), experimental time (1, 4, 8 days) and their interactions on all the studied parameters. One-way ANOVA was conducted to study the effect of protection, ZnO-NPs doses on the expression level of P53, Bax and Bcl2 in ESC muscle. Bonferroni’s test was conducted to compare between the studied groups. Regression analysis and correlation coefficient analysis were applied to study the relationships between the studied variables. Data were expressed as a mean±standard error of mean (SEM).
Results
ZnO-NPs characterization
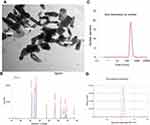
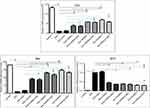
ZnO-NPs measured with transmission electron microscope (TEM) showed an average particle size=40 nm, majority of the particles comprised rod and polygonal shapes (rod NPs average width and length were 34 nm and 90 nm, respectively) with smooth surface (Figure 1A). The crystal structure of the ZnO-NPs was characterized by XRD with Cu Kα radiation (λ=0.15418 nm). X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of the ZnO-NPs indicated that the samples comprised crystalline wurtzite structure and no characteristic impurity peaks were identified, suggesting a high quality of the ZnO-NPs (Figure 1B). Zeta potential of ZnO-NPs was +19.6 mV and zeta deviation=3.42 mV (Figure 1D). The hydrodynamic diameter of 100% ZnO-NPs was 242 d.nm and with pdl value 0.34 as determined by the dynamic light scattering (DLS) (Figure 1C).
ZnO-NPs biodistribution
ZnO nanoparticles biodistribution was estimated by ICP MS in normal and treated groups. Measurements per gram of dry weight of triplet samples are presented as mean±SEM (Table 2). Zn level (µg/g) in different studied tissues significantly (P<0.05) increased in a dose-dependent manner compared to the untreated ESC group. ESC given dose 500 mg/kg ZnO-NPs alone have the highest Zn level (22.86±1.19) compared with the other examined tissues in different treated groups. No significant difference (P>0.05) was observed between groups treated with ZnO-NPs alone and those treated with NAC and ZnO-NPs.
 | Table 2 Levels of Zn (µg/g) in muscle, liver and kidney of mice treated with different doses of ZnO-NPs (50, 300 and 500 mg/kg) with or without NAC pretreatment |
ZnO-NPs reduced the solid tumor size
The antitumor activity was estimated every four days using Vernier caliper. The average tumor volume was 329±24.4 mm3 after 10 days of inoculation. After oral administration of ZnO-NPs, the rate of tumor growth was inhibited by 31.5% and 46% at dose 300 and 500 mg/kg ZnO-NPs, respectively. The tumor volume (TV in mm3) and relative tumor volume (RTV) significantly (P<0.05) reduced in all ZnO-NPs treated groups compared to untreated ESC group, and no significant (P>0.05) difference was observed in TV and RTV between groups treated with ZnO-NPs alone and those treated with NAC and ZnO-NPs (Figure 2).
Histopathological examination
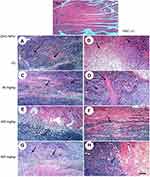
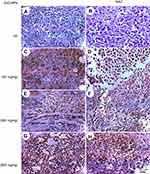
Microscopic examination of skeletal muscles stained with H&E showed no histopathological alteration in normal muscle bundles, while ESC of untreated control showed necrosis of muscles and masses of chromatophilic tumor cells between the necrotic muscles and intact anaplastic area. ZnO-NPs treated groups showed masses of necrotic tumor cells surrounded by granulation tissue. The incidence of tumor necrosis increased with ZnO-NPs treatment (Figure 3).
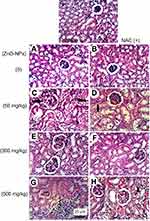
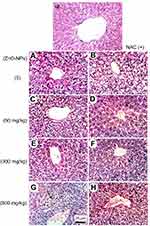
Regarding kidney tissues in normal untreated control and in ESC bearing mice groups untreated or treated with NAC, they showed normal histological structure of renal parenchyma and no histopathological alteration, while in ZnO-NPs treated groups, there were many vacuolations of renal tubular epithelium and protein cast in Bowman’s space and mononuclear inflammatory cells infiltration. On the other hand, groups of ZnO-NPs pre-treated with NAC showed no histopathological changes at dose 300 mg/kg, while at dose 500 mg/kg, vacuolation of renal epithelia and renal cast in the lumen of renal tubules could be detected (Figure 4).
Microscopic examination of liver stained with H&E in normal untreated control showed normal histological structure of the central vein and surrounding hepatocytes. ZnO-NPs treated group illustrated vacuolar degeneration of hepatocytes and massive mononuclear inflammatory cells infiltration in the portal triad at 300 and 500 mg/kg, respectively. On the other hand, groups of ZnO-NPs pre-treated with NAC showed no histopathological lesions at dose 50 mg/kg, while at dose 300 and 500 mg/kg showed degeneration of hepatocytes and congestion of hepatoportal blood vessel (Figure 5).
ZnO-NPs induced oxidative stress and DNA damage
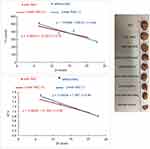
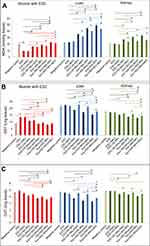
MDA is the most representative product of lipid peroxidation, and its concentration can indicate the rate and intensity of lipid peroxidation within the body. The current study revealed a significant elevation in MDA level (nmol/gm) and marked reduction in GST and CAT activity (P<0.05) in ZnO-NPs treated groups compared to untreated ESC group in all examined tissues. pretreatment with NAC showed no significant difference (P>0.05) in all oxidative parameters in ESC, while a significant decrease (P<0.05) in the MDA level and a significant increase (P<0.05) in the activity of both CAT and GST were recorded in the liver and kidney of all treated groups, and that indicated the protective effect of NAC against ZnO-NPs oxidative stress without affecting ZnO-NPs antitumor activity (Figure 6).
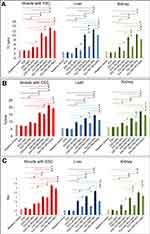
All examined tissues in ZnO-NPs treated groups showed statistically significant increase (P<0.05) of all DNA damage parameters (tail length, % DNA in tail and tail moment) in a dose-dependent manner compared to the untreated ESC group, and 500 mg/kg represent the highest effective (P<0.05) dose compared to the other doses. Pretreatment with NAC in ESC revealed no significant difference, while it showed a significant reduction (P<0.05) in all DNA damage parameters compared to ZnO-NPs alone in liver and kidney (Figures 7 and 8).
ZnO-NPs altered the expression levels of some apoptotic genes in ESC
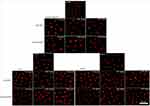
Results showed that ZnO-NPs significantly altered the expression levels of mRNA of P53, Bax and Bcl2 genes in ESC. The mRNA expression level of tumor suppressor gene P53 and pro-apoptotic gene Bax was significantly upregulated (P<0.05), while the expression of anti-apoptotic gene Bcl2 was significantly downregulated (P<0.05) in ZnO-NPs treated groups as compared with the untreated ESC group. In addition, the fold change of P53 and Bax genes was significantly higher (P<0.05) in the normal muscle compared to untreated ESC group. No significant difference was found between ZnO-NPs groups and ZnO-NPs groups pre-treated with NAC (Figure 9).
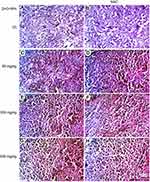
Moreover, the expression of P53 and caspase-3 proteins was assessed in the muscle of all treated groups by immunohistochemistry and showed an elevation in the expression of P53 and caspase-3 proteins, where ESC of mice treated with 500 mg/kg of ZnO-NPs showed the highest expression level of P53 and caspase-3 proteins (Figures 10 and 11).
Discussion
ZnO nanoparticles manifested a promising cytotoxic effect against several cancer cell types; like PC-3, HCT116, A549 and MDA-MB-231.46 Despite the amazing anticancer activity of ZnO-NPs in different cancer cell types, there are very limited studies performed in vivo . The current study was designed to evaluate the antitumor activity of ZnO-NPs in ESC bearing mice after oral administration of ZnO-NPs different doses (50, 300 and 500 mg/kg) and to investigate their potential toxicity in normal tissues, such as liver and kidney as being the target sites of ZnO-NPs.19 In addition, we investigated the ameliorative or the potentiation effect of NAC against ZnO-NPs genotoxicity in healthy and cancerous cells in ESC bearing mice.
In our study, ZnO-NPs were found to be biodistributed in the different tissues under investigation in a dose-dependent manner, Zn level was higher in ESC than in liver and kidney and this could be attributed to the electrostatic characteristics of ZnO nanoparticles, where ZnO-NPs have neutral hydroxyl groups attached to their surface that play a critical role in their surface charge. At physiological pH conditions, the isoelectric point of ZnO-NPs equals 9–10;47,48 therefore, ZnO-NPs will have a strong positive surface charge under these conditions. Cancer cells have a high concentration of anionic phospholipids on their outer membrane.49,50 Consequently, ZnO-NPs could be driven by the electrostatic attraction towards the cancer environment promoting cellular uptake causing higher level of Zn in the tumor tissue compared to the other healthy tissues.
Previous studies revealed that ZnO-NPs exert some antitumor activity, where induction of ROS and depletion in antioxidant system is considered as one of the mechanistic pathways of ZnO-NPs to persuade cancer cell death,51,52 as the increase of ROS level leads to decrease in the level of antioxidative enzymes in the cells and eventually results in an oxidative damage to the cells and tissues.53 Our data indicated that ZnO-NPs treatment increased the level of MAD, the most representative product of lipid peroxidation, and caused depletion in the antioxidant enzymes such as GST and CAT in all examined tissues (ESC, liver and kidney) compared to untreated ESC group. This is in harmony with the previous studies which indicated that ZnO-NPs were able to increase 8-oxodG level and ROS production in Caco-2 cells and embryonic kidney cells.54,55
It was reported that oxidative stress occurs due to disturbance in the balance between ROS production and depletion in the antioxidant defense mechanism.56 ROS, such as H2O2, •OH and •O2‾, may spontaneously react with nucleophilic centers in the cell, and thereby covalently bind to nucleic acid, RNA and proteins and result in a single strand break, a double strand break and DNA adduct formation and therefore can induce DNA damage.57 ZnO-NPs have been reported to induce ROS generation, oxidative DNA damage and upregulate apoptosis in HepG2 cells, cervical carcinoma cells, colon adenorectal carcinoma cells and nasal mucosa cells.58–62 Moreover, Caco-2 cells exposed to ZnO-NPs were not able to repair the oxidative DNA damage that was efficiently repaired after TiO2-NPs treatment, which indicated that the high oxidant environment caused by ZnO-NPs can induce DNA damage and affect the repair pathways.55 In accordance, we reported a significant increase in the DNA damage parameters in all examined tissues especially in ESC and the inability of NAC to reverse the action in the solid carcinoma. This DNA damage could be one of the most significant reasons of cancer cell death and tumor growth inhibition in ZnO-NPs treated groups.
In the presence of DNA damage or cellular stress, P53 triggers cell-cycle arrest to provide time for the damage to be repaired or for self-mediated apoptosis.15 This is in consistence with the present data that showed upregulation in the expression level of both tumor suppressor gene P53 and pro-apoptotic gene Bax and downregulation in the expression level of anti-apoptotic gene Bcl2 in ESC of ZnO-NPs treated mice. Similarly, a previous in vitro study asserted an increase in the expression level of P53 and Bax genes after treatment with ZnO-NPs.63 Upregulation of both P53 and Bax genes and downregulation of Bcl2 gene after ZnO-NPs treatment indicated the induction of apoptosis in ESC that could be the pathway of tumor cells destruction. These data were in accordance with some recent studies that proved the anticancer activity of ZnO-NPs against A549, MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cell line64,65 and loss of cell viability, cytotoxicity and apoptotic induction in different types of breast cancer cells like MDA-MB-231and MCF-7 cells.66
Taken together, ZnO-NPs treatment led to overproduction of ROS, depletion in the antioxidant system, DNA damage and induction of apoptosis. All these events led to tumor cell death and tumor volume reduction, indicated by the significant reduction in the tumor volume of ESC in left thigh of the mice that appeared at doses 300 and 500 mg/kg of ZnO-NPs, with tumor growth inhibition 31.5% and 46% in both doses, respectively. Moreover, the histopathological examination of tumor tissue agreed with the previously illustrated data, where ZnO-NPs treatment led to masses of necrotic tumor cells surrounded by granulation tissue.
In addition, pretreatment with NAC had no significant effect, neither on the tumor volume reduction nor on the antitumor efficacy of ZnO-NPs. Similarly, a previous study illustrated that NAC had no effect on the antitumor activity of ifosfamide.67,68 This might be due to the disruption of the ROS scavenging system in the tumor tissue as indicated by the significant reduction of antioxidant enzymes levels, so the elevation of ROS cannot be compensated through the action of NAC alone. In addition, our study indicated that ZnO-NPs could induce apoptosis via Bax, Bcl2 and P53 signaling pathway, which may act as another alternative way for killing tumor cell that does not depend on the ROS production.69
On the other hand, the toxicity of ZnO-NPs in the liver and kidney could be detected clearly through the histopathological examination that revealed vacuolation of renal tubular epithelium and inflammatory cells infiltration and vacuolar degeneration of hepatocytes. In the same context, a previous study revealed that two weeks inhalation to occupational relevant level of ZnO-NPs led to renal inflammation through lymphocytic infiltration.70 Also, the study conducted by Esmaeillou et al71 has illustrated the swelling of the proximal tubular epithelial cells, hydropic degeneration and necrosis of tubular epithelial cells in mice exposed to ZnO-NPs through oral gavage.71
However, these histopathological lesions in different tissues other than solid carcinoma were eliminated and reduced in ZnO-NPs groups pretreated with NAC. This might be due to the antioxidant properties of NAC that increased GSH levels to support the antioxidant system during inflammation, stress and exposure to toxins.22–24 In addition, previous studies illustrated that NAC was capable to prevent nephrotoxicity induced by ifosfamide without affecting the antitumor efficacy of ifosfamide,68 through decreasing lipid peroxides and increasing glutathione-S-transferase and repairing morphological damage in renal tubules and glomeruli of rat.72 Moreover, pretreatment with (100 mg/kg) of NAC repaired the oxidative DNA damage induced by (500 mg/kg) of ZnO-NPs in mice, which may be contributed to the effective role of NAC in reducing the ROS production as previously indicated in rat astrocytes25–27,73
Although NAC had no significant effect on the antitumor activity of ZnO-NPs in ESC in our study, another study illustrated an anticancer activity of NAC, where it inhibited the DNA synthesis in human astrocytoma cells.74 In addition, NAC was able to inhibit abnormal cell cycle progression in human lymphoma cells and induce cell cycle arrest in murine papilloma cells.75,76 Despite several evidence establishing anti-apoptotic effects of NAC that protects normal cells against cytotoxic stimuli, there are reports arguing for a pro-apoptotic effect of NAC. Liu et al76 and Havre et al77 reported that NAC selectively was capable of inducing apoptosis via p53 mediated pathway in several oncogenically transformed fibroblasts, but not in normal cells.76,77 This is disagreeing with our data as NAC exerted no significant effect on P53 gene expression in ESC. Moreover, a recent study demonstrated that NAC can act as a chemo-protectant without decreasing the antitumor efficacy of cisplatin in pediatric tumor models.38 These controversial data regarding NAC raise an urging need to investigate its mechanism of action in vivo.
Conclusion
Several studies demonstrated antitumor activity of ZnO-NPs in numerous cell lines but lacked in vivo evaluation. Our study revealed that ZnO-NPs possess a strong inhibition effect against cancerous tissue in mice by inducing severe oxidative stress, DNA damage and induction of apoptosis via P53-mediated pathway. Moreover, pretreatment with NAC provided a chemo-protection for the healthy normal tissues (liver and kidney) without decreasing the antitumor efficacy of ZnO-NPs in ESC bearing mice. Therefore, new cancer therapeutic strategies including ZnO-NPs combined with NAC could be developed.
Abbreviation list
ZnO-NPs, zinc oxide nanoparticles; ESC, ehrlich solid carcinoma; NAC, N-acetyl-L-cysteine; TEM, transmission electron microscope; ICP-MS, inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry; TV, tumor volume; RTV, relative tumor volume; TL, tail length; DLS, dynamic light scattering; XRD, X-ray diffraction;TM, tail moment; BW, body weight.
Ethics approval
The experiments were performed in accordance with the research protocols established by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. All the experimental procedures were done following the international guidelines, Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The animal experimental protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (CU-IACUC) at Faculty of Science, Cairo University (CU/I/F/38/18).
Data availability
Raw data supporting the results reported in the manuscript are available with the authors.
Acknowledgments
The study was conducted at the Genetics Laboratory, Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Authors would like to thank professor Dr Koukap Abd-elazez Ahmed for her great help in sectioning, staining, photographing and examining the histological specimens, and Dr Atef Ali for his assistance in assessing statistics. The study was partially funded by Cairo University to buy some kits and reagents.
Author contributions
Shaymaa M Eissa performed the experiments, analyzed and graphed data, and wrote initial draft of the manuscript. Haidan M El-Shorbagy, Salwa Sabet and Akmal A El-Ghor conceived, designed, planned, and supervised the study; they also analyzed data, interpreted results, wrote, critically revised and edited the manuscript. All authors read the manuscript and approved submission. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Laurenti M, Cauda V. ZnO nanostructures for tissue engineering applications. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017;7:11. doi:10.3390/nano7120458
2. Saptarshi SR, Feltis BN, Wright PF, Lopata AL. Investigating the immunomodulatory nature of zinc oxide nanoparticles at sub-cytotoxic levels in vitro and after intranasal instillation in vivo. J Nanobiotechnology. 2015;13:6. doi:10.1186/s12951-015-0067-7
3. Kalpana V, Devi Rajeswari V. A review on green synthesis, biomedical applications, and toxicity studies of ZnO NPs. Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2018;2018:3569758.
4. Rokbani H, Daigle F, Ajji A. Combined Effect Of Ultrasound Stimulations And Autoclaving On The Enhancement Of Antibacterial Activity Of ZnO and SiO(2)/ZnO Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018;8:3. doi:10.3390/nano8030129
5. Youssef AM, El-Nahrawy AM, Abou Hammad AB. Sol-gel synthesis and characterizations of hybrid chitosan-PEG/calcium silicate nanocomposite modified with ZnO-NPs and (E102) for optical and antibacterial applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;97:561–567. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.059
6. Hassan HFH, Mansour AM, Abo‐Youssef AMH, Elsadek BE, Messiha BAS. Zinc oxide nanoparticles as a novel anticancer approach; in vitro and in vivo evidence. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;44(2):235–243. doi:10.1111/1440-1681.12681
7. Palanikumar L, Ramasamy S, Balachandran C. Antibacterial and cytotoxic response of nano zinc oxide in gram negative bacteria and colo 320 human adenocarcinoma cancer cells. Curr Nanosci. 2013;9(4):469–478. doi:10.2174/1573413711309040009
8. Namvar F, Rahman HS, Mohamad R, et al. Cytotoxic effects of biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles on murine cell lines. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:593014.
9. Wahab R, Siddiqui MA, Saquib Q, et al. ZnO nanoparticles induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in HepG2 and MCF-7 cancer cells and their antibacterial activity. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;117:267–276. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.02.038
10. Wahab R, Kaushik NK, Verma AK, et al. Fabrication and growth mechanism of ZnO nanostructures and their cytotoxic effect on human brain tumor U87, cervical cancer HeLa, and normal HEK cells. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2011;16(3):431–442. doi:10.1007/s00775-010-0740-0
11. Selvakumari D, Deepa R, Mahalakshmi V, Subhashini P, Lakshminarayan N. Anti cancer activity of ZnO nanoparticles on MCF7 (breast cancer cell) and A549 (lung cancer cell). Asian Res Pub Net J Eng Appl Sci. 2015;10:5418–5421.
12. Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–674. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
13. Sherr CJ. Principles of tumor suppression. Cell. 2004;116(2):235–246.
14. Ahamed M, Karns M, Goodson M, et al. DNA damage response to different surface chemistry of silver nanoparticles in mammalian cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008;233(3):404–410. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2008.09.015
15. Farnebo M, Bykov VJ, Wiman KG. The p53 tumor suppressor: a master regulator of diverse cellular processes and therapeutic target in cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;396(1):85–89. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.152
16. Chougule M, Patel AR, Sachdeva P, Jackson T, Singh M. Anticancer activity of Noscapine, an opioid alkaloid in combination with Cisplatin in human non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2011;71(3):271–282. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2010.06.002
17. Deng X, Gao F, Flagg T, Anderson J, May WS. Bcl2’s flexible loop domain regulates p53 binding and survival. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26(12):4421–4434. doi:10.1128/MCB.01647-05
18. Landsiedel R, Ma-Hock L, Van Ravenzwaay B, et al. Gene toxicity studies on titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanomaterials used for UV-protection in cosmetic formulations. Nanotoxicology. 2010;4(4):364–381. doi:10.3109/17435390.2010.506694
19. Li C-H, Shen -C-C, Cheng Y-W, et al. Organ biodistribution, clearance, and genotoxicity of orally administered zinc oxide nanoparticles in mice. Nanotoxicology. 2012;6(7):746–756. doi:10.3109/17435390.2011.620717
20. Wang B, Feng W, Wang M, et al. Acute toxicological impact of nano-and submicro-scaled zinc oxide powder on healthy adult mice. J Nanopart Res. 2008;10(2):263–276. doi:10.1007/s11051-007-9245-3
21. Surekha P, Kishore AS, Srinivas A, et al. Repeated dose dermal toxicity study of nano zinc oxide with Sprague-Dawley rats. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2012;31(1):26–32. doi:10.3109/15569527.2011.595750
22. Millea PJ. N-acetylcysteine: multiple clinical applications. Am Fam Physician. 2009;80:3.
23. Agarwal A, Munoz-Nájar U, Klueh U, Shih S-C, Claffey KP. N-acetyl-cysteine promotes angiostatin production and vascular collapse in an orthotopic model of breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 2004;164(5):1683–1696. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63727-3
24. Albini A, Morini M, D’Agostini F, et al. Inhibition of angiogenesis-driven Kaposi’s sarcoma tumor growth in nude mice by oral N-acetylcysteine. Cancer Res. 2001;61(22):8171–8178.
25. Spagnuolo G, D’Antò V, Cosentino C, Schmalz G, Schweikl H, Rengo S. Effect of N-acetyl-L-cysteine on ROS production and cell death caused by HEMA in human primary gingival fibroblasts. Biomaterials. 2006;27(9):1803–1809. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.10.022
26. Fu A-L, Dong Z-H, Sun M-J. Protective effect of N-acetyl-L-cysteine on amyloid β-peptide-induced learning and memory deficits in mice. Brain Res. 2006;1109(1):201–206. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.06.042
27. Fukami G, Hashimoto K, Koike K, Okamura N, Shimizu E, Iyo M. Effect of antioxidant N-acetyl-L-cysteine on behavioral changes and neurotoxicity in rats after administration of methamphetamine. Brain Res. 2004;1016(1):90–95. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2004.04.072
28. Kim JH, Jeong MS, Kim DY, Her S, Wie MB. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce lipoxygenase-mediated apoptosis and necrosis in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem Int. 2015;90:204–214. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2015.09.002
29. Albini A, D’Agostini F, Giunciuglio D, Paglieri I, Balansky R, De Flora S. Inhibition of invasion, gelatinase activity, tumor take and metastasis of malignant cells by N-acetylcysteine. Int J Cancer. 1995;61(1):121–129.
30. Singh R, Shah R, Turner C, Regueira O, Vasylyeva TL. N-acetylcysteine renoprotection in methotrexate induced nephrotoxicity and its effects on B-cell lymphoma. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol. 2015;36(4):243–248. doi:10.4103/0971-5851.171545
31. Kozak YS, PanchuK R, Skorokhyd N, Lehka L, StoIka R. Impact of N-acetylcysteine on antitumor activity of doxorubIcin and landomycin in NK/ly lymphoma-bearing mIce. Ukrainian Biochem J. 2018;90(2):46–54. doi:10.15407/ubj90.02.046
32. Nargi JL, Ratan RR, Griffin D E. p53-independent inhibition of proliferation and p21(WAF1/Cip1)-modulated induction of cell death by the antioxidants N-acetylcysteine and vitamin E. Neoplasia. 1999;1(6):544–556.
33. Kawakami S, Kageyama Y, Fujii Y, Kihara K, Oshima H. Inhibitory effect of N-acetylcysteine on invasion and MMP-9 production of T24 human bladder cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2001;21(1a):213–219.
34. Supabphol A, Muangman V, Chavasiri W, Supabphol R, Gritsanapan W. N-acetylcysteine inhibits proliferation, adhesion, migration and invasion of human bladder cancer cells. J Med Assoc Thai. 2009;92(9):1171–1177.
35. Lee YJ, Lee DM, Lee CH, et al. Suppression of human prostate cancer PC-3 cell growth by N-acetylcysteine involves over-expression of Cyr61. Toxicol In Vitro. 2011;25(1):199–205. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2010.10.020
36. Lee MF, Chan CY, Hung HC, Chou IT, Yee AS, Huang CY. N-acetylcysteine (NAC) inhibits cell growth by mediating the EGFR/Akt/HMG box-containing protein 1 (HBP1) signaling pathway in invasive oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 2013;49(2):129–135. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.08.003
37. Hann SS, Zheng F, Zhao S. Targeting 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 by N-acetyl-cysteine through activation of peroxisome proliferators activated receptor alpha in human lung cancer cells, the role of p53 and p65. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2013;32:43. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-32-43
38. Muldoon LL, Wu YJ, Pagel MA, Neuwelt EA. N-acetylcysteine chemoprotection without decreased cisplatin antitumor efficacy in pediatric tumor models. J Neurooncol. 2015;121(3):433–440. doi:10.1007/s11060-014-1657-1
39. Sharma R. Kinetic measurements from in situ TEM observations. Microsc Res Tech. 2009;72(3):144–152. doi:10.1002/jemt.20667
40. Tice RR, Shelby MD. International workshop on standardisation of genotoxicity test procedures. Report of in vivo subgroup. Mutat Res. 1994;312(3):287–292.
41. Sanceau J, Poupon MF, Delattre O, Sastre-Garau X, Wietzerbin J. Strong inhibition of Ewing tumor xenograft growth by combination of human interferon-alpha or interferon-beta with ifosfamide. Oncogene. 2002;21(50):7700–7709. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205881
42. Mayer AG, Tortugas T. Florida, as a station for research in biology. Science. 1903;17(422):190–192. doi:10.1126/science.17.422.190
43. Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB. Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem. 1974;249(22):7130–7139.
44. Aebi H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:121–126.
45. Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, et al. Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2000;35(3):206–221.
46. Krishna PG, Ananthaswamy PP, Yadavalli T, Mutta NB, Sannaiah A, Shivanna Y. ZnO nanopellets have selective anticancer activity. Mater Sci Eng C. 2016;62:919–926. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2016.02.039
47. Degen A, Kosec M. Effect of pH and impurities on the surface charge of zinc oxide in aqueous solution. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2000;20(6):667–673. doi:10.1016/S0955-2219(99)00203-4
48. Rasmussen JW, Martinez E, Louka P, Wingett DG. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for selective destruction of tumor cells and potential for drug delivery applications. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2010;7(9):1063–1077. doi:10.1517/17425247.2010.502560
49. Papo N, Shahar M, Eisenbach L, Shai Y. A novel lytic peptide composed of DL-amino acids selectively kills cancer cells in culture and in mice. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(23):21018–21023. doi:10.1074/jbc.M211204200
50. Peetla C, Vijayaraghavalu S, Labhasetwar V. Biophysics of cell membrane lipids in cancer drug resistance: implications for drug transport and drug delivery with nanoparticles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(13–14):1686–1698. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2013.09.004
51. Moos PJ, Chung K, Woessner D, Honeggar M, Cutler NS, Veranth JM. ZnO particulate matter requires cell contact for toxicity in human colon cancer cells. Chem Res Toxicol. 2010;23(4):733–739. doi:10.1021/tx900203v
52. Bisht G, Rayamajhi S. ZnO nanoparticles: a promising anticancer agent. Nanobiomed. 2016;3(Godište 2016):3–9. doi:10.5772/63437
53. Carmody RJ, Cotter TG. Signalling apoptosis: a radical approach. Redox Rep. 2001;6(2):77–90. doi:10.1179/135100001101536085
54. Guan R, Kang T, Lu F, Zhang Z, Shen H, Liu M. Cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, and genotoxicity in human hepatocyte and embryonic kidney cells exposed to ZnO nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2012;7(1):602. doi:10.1186/1556-276X-7-602
55. Zijno A, De Angelis I, De Berardis B, et al. Different mechanisms are involved in oxidative DNA damage and genotoxicity induction by ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles in human colon carcinoma cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2015;29(7):1503–1512. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2015.06.009
56. Pryor WA. Cancer and free radicals. Basic Life Sci. 1986;39:45–59.
57. Kang DH. Oxidative stress, DNA damage, and breast cancer. AACN Clin Issues. 2002;13(4):540–549.
58. Sharma V, Anderson D, Dhawan A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and genotoxicity in human liver cells (HepG2). J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2011;7(1):98–99.
59. Hackenberg S, Scherzed A, Technau A, et al. Cytotoxic, genotoxic and pro-inflammatory effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles in human nasal mucosa cells in vitro. Toxicol In Vitro. 2011;25(3):657–663. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2011.01.003
60. Sharma V, Anderson D, Dhawan A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and ROS-triggered mitochondria mediated apoptosis in human liver cells (HepG2). Apoptosis. 2012;17(8):852–870. doi:10.1007/s10495-012-0705-6
61. Pandurangan M, Enkhtaivan G, Kim DH. Anticancer studies of synthesized ZnO nanoparticles against human cervical carcinoma cells. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2016;158:206–211. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.03.002
62. Bai Aswathanarayan J, Rai Vittal R, Muddegowda U. Anticancer activity of metal nanoparticles and their peptide conjugates against human colon adenorectal carcinoma cells. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(7):1444–1451. doi:10.1080/21691401.2017.1373655
63. Gao F, Ma N, Zhou H, et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticles-induced epigenetic change and G2/M arrest are associated with apoptosis in human epidermal keratinocytes. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:3859–3874. doi:10.2147/IJN.S107021
64. Boroumand Moghaddam A, Moniri M, Azizi S, et al. Eco-friendly formulated zinc oxide nanoparticles: induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in the MCF-7 cancer cell line. Genes (Basel). 2017;8:10. doi:10.3390/genes8100281
65. Rajeshkumar S, Kumar SV, Ramaiah A, Agarwal H, Lakshmi T, Roopan SM. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles usingMangifera indica leaves and evaluation of their antioxidant and cytotoxic properties in lung cancer (A549) cells. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2018;117:91–95. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2018.06.009
66. Othman BA, Greenwood C, Abuelela AF, et al. Targeted cancer therapy: correlative light-electron microscopy shows RGD-targeted ZnO nanoparticles dissolve in the intracellular environment of triple negative breast cancer cells and cause apoptosis with intratumor heterogeneity (Adv. Healthcare Mater. 11/2016). Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(11):1248. doi:10.1002/adhm.201670053
67. Chen N, Hanly L, Rieder M, Yeger H, Koren G. The effect of N-acetylcysteine on the antitumor activity of ifosfamide. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011;89(5):335–343. doi:10.1139/y11-028
68. Hanly L, Figueredo R, Rieder M, Koropatnick J, Koren G. The effects of N-acetylcysteine on ifosfamide efficacy in a mouse xenograft model. Anticancer Res. 2012;32(9):3791–3798.
69. Vimala K, Sundarraj S, Paulpandi M, Vengatesan S, Kannan S. Green synthesized doxorubicin loaded zinc oxide nanoparticles regulates the Bax and Bcl-2 expression in breast and colon carcinoma. Process Biochem. 2014;49(1):160–172. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2013.10.007
70. Adamcakova-Dodd A, Stebounova LV, Kim JS, et al. Toxicity assessment of zinc oxide nanoparticles using sub-acute and sub-chronic murine inhalation models. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2014;11(1):15. doi:10.1186/1743-8977-11-15
71. Esmaeillou M, Moharamnejad M, Hsankhani R, Tehrani AA, Maadi H. Toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles in healthy adult mice. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2013;35(1):67–71. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2012.11.003
72. Chen N, Aleksa K, Woodland C, Rieder M, Koren G. N-Acetylcysteine prevents ifosfamide-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 2008;153(7):1364–1372. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.15
73. Pati R, Das I, Mehta RK, Sahu R, Sonawane A. Zinc-oxide nanoparticles exhibit genotoxic, clastogenic, cytotoxic and actin depolymerization effects by inducing oxidative stress responses in macrophages and adult mice. Toxicol Sci. 2016;150(2):454–472. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfw010
74. Arora-Kuruganti P, Lucchesi PA, Wurster RD. Proliferation of cultured human astrocytoma cells in response to an oxidant and antioxidant. J Neurooncol. 1999;44(3):213–221.
75. Kurata S-I. Selective activation of p38 MAPK cascade and mitotic arrest caused by low level oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(31):23413–23416. doi:10.1074/jbc.C000308200
76. Liu M, Wikonkal NM, Brash D E. Induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors and G(1) prolongation by the chemopreventive agent N-acetylcysteine. Carcinogenesis. 1999;20(9):1869–1872.
77. Havre PA, O’Reilly S, McCormick JJ, Brash D E. Transformed and tumor-derived human cells exhibit preferential sensitivity to the thiol antioxidants, N-acetyl cysteine and penicillamine. Cancer Res. 2002;62(5):1443–1449.
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.