Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 16
Advances in Subcutaneous Delivery Systems of Biomacromolecular Agents for Diabetes Treatment
Authors Li C , Wan L, Luo J, Jiang M, Wang K
Received 24 September 2020
Accepted for publication 9 January 2021
Published 17 February 2021 Volume 2021:16 Pages 1261—1280
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S283416
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
Chen Li1 12 2,* Long Wan1 12 2,* Jie Luo1 12 2, Mingyan Jiang1 12 2, Keke Wang1 12 2
1Department of Pharmacy, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, 110001, Liaoning, People’s Republic of China; 2School of Pharmacy, China Medical University, Shenyang, 110122, Liaoning, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Correspondence: Keke Wang
Department of Pharmacy, The First Hospital of China Medical University, 155 Nanjing North Street, Shenyang, 110001, Liaoning, People’s Republic of China
Tel +86-24-83282662
Email [email protected]
Abstract: Diabetes mellitus is a major threat to human health. Both its incidence and prevalence have been rising steadily over the past few decades. Biomacromolecular agents such as insulin and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists are commonly used hypoglycemic drugs that play important roles in the treatment of diabetes. However, their traditional frequent administration may cause numerous side effects, such as pain, infection or local tissue necrosis. To address these issues, many novel subcutaneous delivery systems have been developed in recent years. In this review, we survey recent developments in subcutaneous delivery systems of biomacromolecular hypoglycemic drugs, including sustained-release delivery systems and stimuli-responsive delivery systems, and summarize the advantages and limitations of these systems. Future opportunities and challenges are discussed as well.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus, subcutaneous injection, insulin, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists, sustained-release, stimuli-responsive
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disorder symptom caused by the low secretion of insulin by β-cells or the inefficient combination of insulin with β-cell surface receptors, leading to high blood glucose levels and even some serious or fatal associated complications, such as macrovascular and microvascular diseases.1 In 2018, there were 451 million people with diabetes worldwide, and that number is estimated to increase to 693 million in 2045.2 Therefore, diabetes is a serious threat to the world population health with limited treatment options. At present, various kinds of antidiabetic agents, such as metformin, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors (AGIs), insulin-secretagogue, thiazolidinediones (TZDs) and insulin, are used to treat hyperglycemia.3 The mentioned drugs are taken orally, except for insulin and GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1Ras), which are administered subcutaneously. To date, insulin administration is still the major therapy for the treatment of diabetes, but GLP-1Ras is gaining increasing attention.
Insulin and GLP-1 receptor agonists are biomacromolecular drugs that are administered by subcutaneous injection for their structural and stability-related reasons.4 The human insulin hormone is a 51 amino acid protein (5.8 kDa, Figure 1A), that forms “A” (21 amino acids) and “B” (30 amino acids) chains connected by a disulfide bond.5 Based on the development of insulin, short-acting insulins, such as regular (R) insulin, aspart, lispro, and glulisine, and long-acting insulins, such as neutral protamine hagedorn (NPH) insulin, glargine, detemir and degludec, are administered one to four times daily to treat diabetes.6 GLP-1 receptor agonists are synthetic peptides with structural resistance to DPP-4 proteolysis or improved recombinant human GLP-1.7 The most widely used drugs in the clinic are exenatide and liraglutide, which are composed of 39 amino acids (4.19 kDa, Figure 1B) and 29 amino acids (3.75 kDa, Figure 1C), respectively.8,9 In addition to these two drugs, some novel GLP-1 receptor agonists have been developed and used,10 such as another short-acting drug lixisenatide,11,12 and other long-acting drugs, such as albiglutide,13,14 dulaglutide,15,16 and semaglutide.17 In addition, long-acting GLP-1Ras requires weekly subcutaneous administration, while both short-acting GLP-1Ras and insulin require one or multiple daily subcutaneous administration, which can cause psychological stress leading to poor patient compliance. Thus, many researchers have focused on finding alternative routes of administration or reducing the frequency of injections to lessen the inconvenience and drawbacks of frequent injections.18 Some noninvasive administration routes are being investigated, including pulmonary, oral, nasal, transdermal and buccal delivery.19 Initially, a dry powder inhaler was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicine Agency (EMA) for pulmonary insulin delivery, but this was withdrawn and its development was discontinued in 2007 because of the inconvenience of the device and its unstable bioavailability due to different respiratory factors.20 Oral delivery is known as the most patient-friendly route, but it is highly challenging to ensure that peptide/protein drugs are stable in the gastrointestinal tract and to obtain a high bioavailability.21 Due to many difficulties, the oral delivery of peptide/protein drugs has been being studied for many years with no major breakthrough and only a few products have been investigated in phase II trials, including long-acting insulin analog tablets, enteric-coated insulin capsules,22 and insulin gel capsules.23 Moreover, nasal and transdermal routes are difficult to use in the clinic due to the disadvantages of their small surface area, long-term damage to nasal passages,24 low permeability and allergic reactions to skin.25 On account of the pharmaceutical limitations and bioavailability problems, those noninvasive delivery routes require high drug loadings to achieve the expected blood glucose control, which is difficult to realize in the clinic. Therefore, subcutaneous delivery with high bioavailability is still the main delivery route of biomacromolecular drugs for treating diabetes, and it still requires further pharmaceutical developments to reduce the frequency of administration and eliminate the injection discomfort.
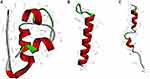 |
Figure 1 Computer-generated images of insulin (A), exenatide (B) and liraglutide (C). |
In recent decades, a number of drug delivery systems have been developed to overcome the limitations and drawbacks of subcutaneous administration. Various carriers, such as hydrogels, liposomes, microparticles and nanoparticles, can realize long-acting or stimuli-responsive release behaviors of insulin or GLP-1 drugs to achieve a desirable quality of life in diabetic patients. In this review, we will focus on the different sustained release systems and stimuli-responsive systems for the subcutaneous delivery of antidiabetic agents and biomacromolecular drugs, including polymeric materials, lipid-based carriers, inorganic nanoparticles, glucose-responsive insulin systems, ultrasound-triggered systems, and pH- or temperature-triggered systems (Figure 2). Moreover, the advantages and limitations associated with these carriers, as well as future opportunities and challenges will be discussed.
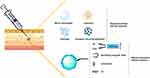 |
Figure 2 Schematic illustration of various subcutaneous delivery systems used for antidiabetic biomacromolecular drugs. |
Subcutaneous Sustained-Release Delivery Systems
Under normal physiological conditions, basal insulin secretion is steady and continuous. Long-acting insulins with a single daily predormital injection, such as protamine hagedorn insulin, insulin glargine and insulin detemir, have been extensively used to attain sufficient basal glycemic control,26,27 as have long-acting GLP-1Ras. However, injections with longer durations need to be developed to make them more convenient and avoid the risk of hypoglycemia. Due to their high molecular weight, short half-life and vulnerability to enzymatic degradation, it is very difficult for these peptide/protein drugs to obtain longer durations.28 Numerous novel systems have been investigated for insulin and GLP-1Ras delivery to improve their stability and duration, including polymeric micronanocarriers, in-situ hydrogels, liposomes, and inorganic micro/nanoparticles.
Polymer-Based Micro/Nanocarriers
Colloidal micro/nanoparticle systems with large surface areas significantly enhance epithelial permeability and improve the bioavailability of protein and peptide drugs.29 Various biodegradable polymers approved by the FDA are commercially available for drug delivery in micro/nanoparticle formulations.21 By modifying the polymer structure, these polymeric carriers, such as Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA), Poly (lactic acid) (PLA) or Chitosan (CS), can realize structural stability and sustained release of the protein and peptide drugs.
PLGA-Based Carriers
PLGA is a copolymer composed of lactic acid and glycolic acid in different ratios. Due to its biodegradability and biocompatibility, PLGA has been approved by the FDA and the EMA for various drug delivery systems in humans.30 PLGA micro/nanoparticles have many advantages that make them suitable for the delivery of macromolecules, including protecting drugs from degradation, sustained release behavior, simple methods of production, easy modification and targeting capabilities.31 Initially, Barichello and coworkers applied the precipitation-solvent evaporation method to prepare PLGA nanoparticles loaded with lipophilic, hydrophilic drugs and insulin (an amphiphilic drug). Because insulin is insoluble in organic solvents, its encapsulation efficiency was 6.8–12.1%, which was much lower than that of lipophilic drugs.32 Then, the author loaded PLGA-insulin nanoparticles (INPs) into Pluronic F-127 (PF-127) gels to obtain a controlled release behavior. After subcutaneous administration in rats, the mean residence time (MRT) of INP-loaded 30% PF-127 was delayed from 1.3±0.3 h to 3.8±0.5 h and the AUC was 1.5 times higher than that of INP.33 The high serum insulin level lasted for 12 hours. However, the studied system did not meet the expected sustained release behavior. Shenoy et al improved an emulsion-solvent evaporation method to form PLGA-insulin microspheres (37 to 52 μm) to increase the insulin entrapment efficiency to 60.24±2.23% and maintain steady blood glucose levels after administration in diabetic rats within 60 days.34 However, it is difficult to control the initial burst release and ensure protein stability during degradation in unmodified macromolecules and PLGA carriers.35,36
Some methods can be used to avoid these issues. First, stabilizers can be added into the system for complexation or modification of the drugs. In Yin and coworkers’ research, PLGA microspheres (MS) loaded with GLP-1 were obtained by S/O/O solvent extraction and zinc carbonate was utilized to make GLP-1 more stable.37 The initial burst release was significantly reduced from 37.2% to 7.5% and a 4-week period of controlled release in vitro was achieved by zinc complexation. After administration in diabetic mice, GLP-1 MS showed a sustained long-term pharmacological efficacy, decreasing the blood glucose level for a period of 28 days. According to previous studies, polyethylene glycol (PEG)-conjugated peptides exhibited improved pharmacological stability compared with native peptides.38,39
Lim et al prepared PEGylated Exendin-4 (Ex4) PLGA microspheres with improved circulatory stability and decreased immunogenic response compared to that of native Ex4. Compared to Ex4 microspheres with a burst release of 43.8%, PEG-Ex4 microspheres exhibited a much smaller burst release of 10.8% on day 1 in vitro and a sustained release profile for 14 days following near zero-order kinetics in vivo.40
Second, the preparation approach can be improved to reduce the burst release and increase the entrapment efficiency of the peptides. A nonaqueous processing medium was used in the emulsion solvent extraction method for the preparation of PLGA microspheres to ensure a low burst release and a high entrapment efficiency.41 Xuan et al used silicon oil as the external phase in the w/o/o method to prepare exenatide-PLGA microspheres. Compared with the w/o/w method, the encapsulation efficiency of microspheres prepared with the w/o/o method increased from 65.3% to 98.0%. The microspheres ensured the stability of exenatide in release buffer for up to 28 days and exhibited a sustained release behavior. After subcutaneous administration in mice, the t1/2 of PLGA microspheres was 120.650±44.184 h, which was about approximately 120-fold higher than the t1/2 of the exenatide aqueous solution injection.42 Kim et al invented a monoaxial ultrasonic atomizer method to prepare insulin-loaded microcapsules with a mean particle size of 50 μm (Figure 3). Following the administration of these microcapsules in type 1 diabetes rats, plasma insulin concentration was maintained stable for 30 days and the blood glucose levels were controlled at 100–200 mg/dL in a period of 55 days.43
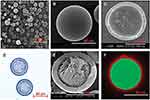 |
Figure 3 SEM pictures of microcapsules by monoaxial ultrasonic atomizer method. (A) Picture of freeze-dried microcapsules, (B) picture of one microcapsule, (C) the cross-sectioned picture. (D) Light microimage of microcapsules loading insulin, (E) picture of a cross-sectioned microcapsule loading insulin, and (F) confocal laser microimage of FITC microcapsules loading insulin with nile red PLGA. Reprinted with permission from Kim BS, Oh JM, Hyun H et al Insulin-loaded microcapsules for in vivo delivery. Mol Pharm. 2009;6(2):353–365. Copyright © 2009 American Chemical Society.43 |
Third, structural modifications of the micro/nanocarriers can protect proteins from degrading in an acidic microenvironment, which can avoid the denaturation and bioactivity decline of loaded proteins. Jiang et al developed a composite microsphere consisting of a poly (acryloyl hydroxyethyl starch) (AcHES) hydrogel containing insulin encapsulated in PLGA microparticles. This composite matrix system effectively protected the protein. SDS-PAGE and MALDI-TOF MS analysis showed the stability of insulin, and the in vitro release profile showed only a small burst release effect. After subcutaneous injection, the system provided sustained release performance with glucose suppression in diabetic rats for 8~10 days.44 According to the previous report, PEGylation is an effective modification of protein-based drug systems that can increase their stability and reduce the drug toxicity effectively.45 Thus, Saravanan et al attached poly PEG to insulin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles (ISPPLG NPs) prepared by the w/o/w emulsion solvent evaporation method.46 A high encapsulation efficiency of 66% was achieved by the ISPPLG4 NPs, which showed a cumulative release of insulin for up to 6 h. The NPs exhibited a pronounced hypoglycemic effect with reduced triacylglycerol, lipid peroxidation and cholesterol levels, restoring the damage to the tissues of diabetic rats. Recently, cholic acid (CA)-initiated PLGA and water-soluble polyethyleneimine cross-linked polyethylene glycol (PEI-PEG) (CA-PLGA-b-(PEI-PEG)) self-assembled micelles were prepared, which trapped insulin via electrostatic interactions. Then, the microspheres (MIC-MS) were manufactured by the double emulsion method (Figure 4). Internal acidification of the PLGA MS during degradation was avoided by incorporating PEI to ensure the stability of insulin.47 The MIC-MS exhibited a sustained release phase with nearly zero-order release kinetics with a 3.6% daily insulin release lasting for 10 days and a decrease in the initial burst release from 38.39% to 19.97% during the first 12 h.48 MIC-MS is a novel system with great potential for the long-acting delivery of insulin or other proteins.
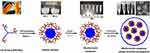 |
Figure 4 Synthetic processes and structure diagrams of MIC-MS. Reprinted by permission from Springer Nature. Wang J, Li S, Chen T et al Nanoscale cationic micelles of amphiphilic copolymers based on star-shaped PLGA and PEI cross-linked PEG for protein delivery application. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(8):93. Copyright 2019.48 |
PLA-Based Carriers
PLA is a well-known biodegradable and biocompatible polyester. Due to its amphiphilicity, it is widely used in protein delivery systems for oral administration.49,50 However, in the subcutaneous route, only a few PLA microspheres were used for the delivery of hypoglycemic macromolecule drugs. Yeh et al developed a w/o/w solvent evaporation method with electrolytes in the continuous phase to prepare insulin-loaded PLA microparticles. Among the studied electrolytes, NaCl resulted in a high loading efficiency (49% to 38% without electrolytes) and a high amount of insulin (%) on the microparticle surface, on the outer layer and inside the core with values of 8, 37 and 43%, respectively, which were 24, 14 and 7% without electrolytes. Due to the addition of electrolytes, more insulin was found distributed inside the core, which led to the sustained release accompanying the degradation of PLA microspheres.51 However, the method of preparation including the absorption of protein onto the polymer surface, the moisture effect and the generation of an acidic pH environment within the microspheres, resulted in the instability of the proteins in PLA polymers.52,53 In the conventional preparation process of the w/o/w emulsion, insulin acted as surfactant and preferably adsorbed at the water/oil interfaces, which caused insulin unfolding, inactivation, and irreversible aggregation.52,54 Therefore, many researchers have aimed to improve the preparation methods to ensure the stability of insulin in PLA microparticles. Sheshala et al constructed insulin-loaded PLA-PEG microspheres with a controlled level of plasma insulin over a 1-week time period upon a single subcutaneous administration in diabetic rats. The released percentage of insulin increased with the ratio of PLA-PEG ranging from 8:2 to 3:7 because of the large pores that are formed when PEG transfers from the internal aqueous phase to the external aqueous phase. However, the release percentage surprisingly decreased for PLA-PEG ratios of 2:8 to 1.5:8.5 because of the lower amount of PEG incorporated in the microspheres. Therefore, the addition of an appropriate amount of PEG is beneficial for obtaining excellent release behavior and ensuring the structural stability of insulin.55
Chitosan Derivative-Based Carriers
CS is a natural cationic polysaccharide, approved for application in wound dressings by the FDA and listed in the pharmacopoeias of many countries.56 The increasing utilization of chitosan and its derivatives in oral or mucosal drug delivery is based on their superior mucoadhesive properties and penetration-enhancing effects. Quaternized chitosan, one of the CS derivatives, can reverse its positive charge in neutral conditions, which leads to an increase in residence time and bioavailability.57 On the basis of this principle, Zhang et al explored a cholic acid and N-(2-hydroxy)-propyl-3-trimethylammonium chloride modified chitosan (HTCC-CA), used as a liver-targeted insulin delivery in neutral environment. A liver targeted delivery vehicle of insulin, consisting of CA modified HTCC, was developed by Zhang et al In neutral environment, HTCC retains a cationic charge that can enhance its adhesion to negatively charged insulin through electrostatic attraction and increase the uptake by the liver. CA can further enhance the hepatic uptake through increased binding with insulin via hydrophobic interactions. In vitro, the insulin release profile was prolonged and the cellular uptake of insulin was increased to 466%. And the bioavailability of this system in diabetic rats was up to 475%. Compared to free insulin, the time period of the blood glucose level lower than 70% (PT-70%) of these nanoparticles was significantly prolonged as well.58 Later, the same research group modified fatty acids to replace CA and increase the surface hydrophobicity of the nanoparticles and the stability of insulin loaded inside the nanoparticles. The higher the surface hydrophobicity of the nanoparticles was, the better was the antidiabetic efficacy. Compared to free insulin group, the relative pharmacological availabilities of nanoparticles modified by lauric acid and oleic acid were 233% and 311%, respectively, following subcutaneous administration in diabetic mice.59 Thus, the modification of positively charged HTCC and the introduction of hydrophobic groups onto nanoparticle surfaces can effectively realize the liver-targeted delivery of insulin.
Other Polymer-Based Carriers
Poly (hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyhexanoate (PHBHHx) is one of the members of the microbial polyhydroxyalkanoate biopolyester family and is used as a biodegradable nanocarrier for the specific and sustained release of hydrophobic drugs.60 Nevertheless, hydrophilic insulin cannot be readily encapsulated into PHBHHx nanoparticles because of the strong lipophilic nature of PHBHHx. Peng and his team prepared an insulin phospholipid complex (INS-PLC) to enhance the lipophilicity of insulin and loaded insulin into biodegradable PHBHHx nanoparticles (INS-PLC-NPs)61 and PHBHHx 3D scaffolds (INS-PLC-SCAs),62 respectively. In those two systems, insulin showed sustained release in vitro. Twenty percent of insulin was released within 31 days from INS-PLC-NPs and 6% of insulin was released within 120 days from INS-PLC-SCAs. After subcutaneous implantation in streptozotocin (STZ) -induced diabetic rats, the hypoglycemic effect was significantly prolonged compared to that of the administration of insulin solution. The therapeutic effect lasted for more than 80 h in case of the INS-PLC-NPs and for more than 130 h in case of the INS-PLC-SCAs; in addition, the pharmacological bioavailability was enhanced 3.5-fold and 4-fold, respectively. Therefore, PHBHHx carriers are promising candidates for a long-term insulin release formulation. To further prolong the hypoglycemic effect of insulin and significantly reduce the injection frequency, the same researchers combined INS-PLC-NPs and chitosan-based thermosensitive hydrogels to formulate INS-PLC-NP-loaded CS/GP hydrogels (NP-CS/GP). The hypoglycemic effect of NP-CS/GP following subcutaneous injection in diabetic rats lasted for more than 5 days, longer than INS-PLC-NP and INS-CS/GP. Therefore, the introduction of CS/GP hydrogels has great potential for ultralong-acting insulin injections.63
Another biodegradable, biocompatible polymeric carrier is microspheres of p(CPP:SA). After the water-soluble degradation products formed, the anhydride bonds of this CPP:SA copolymer would be hydrolyzed. Insulin microspheres were fabricated by the w/o/w double emulsion solvent evaporation technique.64 The molar ratio of the CPP:SA copolymer could affect the insulin encapsulation efficiency (EE) and in vitro release profile. When the zinc oxide was added and the content of CPP was increased, the burst release of insulin was reduced and the in vitro release was prolonged over a month. After administration to diabetic rats, the serum insulin and the glucose levels were both prolonged for up to 35 days, which was consistent with the in vitro results. To evaluate the stability of insulin in the CPP:SA microspheres during these long time periods, SDS-PAGE, CD spectroscopy, TOP MS and SE-HPLC were used. The results indicated that the released insulin was conformationally and chemically stable and bioactive during the sustained release phase.65
In situ Gelling Systems
As in situ hydrogels are sensitive to the environment and responsive to specific molecules, they can be used as drug delivery systems to protect drugs from adverse environments and control drug release.66 In situ gelling systems are biodegradable solutions with high biocompatibility. Because in situ gelling systems are safe and effective, they can be considered an alternative method to traditional subcutaneous injection of insulin.
Temperature-Sensitive Hydrogels
Temperature-sensitive hydrogels are aqueous polymer solutions at room temperature and transform to a sol-gel form at physiological temperature.
Dhawan et al prepared ten formulations that mixed a fixed concentration of insulin with different polymer solutions containing varied concentrations of PLGA and varied ratios of benzyl alcohol (BA) and benzyl benzoate (BB).67 From in vivo studies in mice, they concluded that the formulation containing PLGA and a combination of hydrophilic and hydrophobic solvents could reduce the burst effect and prolong the release.
For example, PLGA–PEG–PLGA triblock copolymer, a long-acting thermoreversible drug delivery system, is one of the research hotspots. Choi et al used this triblock copolymer as an injectable implant system, loading insulin with a concentration of 6 mg/mL for sustained insulin release. The released insulin level was steady and approached a constant within 2 weeks, and the blood glucose levels in Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) rats were maintained in the euglycemic range during insulin release.68 However, a high burst release is often observed in the release profile of insulin-loaded formulations. Thus, a delivery system containing PLA-PEG-PLA triblock copolymers and zinc-insulin was developed.69 The results showed that insulin with 40% (w/w) PLA-PEG-PLA (molecular weight 1584–1500–1584 Da) could be released continuously at a controlled rate over a 3-month time period and the release profile could be changed by altering the composition and concentration of the polymer or by adding metal ions. Recently, a novel delivery system was developed by incorporating oleic acid-grafted-chitosan oligosaccharide‑zinc-insulin complexes into PLA-PEG-PLA.70 In vivo studies showed that, after a single administration, the basal insulin level could be maintained stably at 21 mU/L over 91 days and the blood glucose could be controlled to 120 mg/dL over 63 days in STZ-induced diabetic rats, which is almost satisfiable to the physiological basal insulin requirement. In addition, it did not cause inflammation, tissue damage, collagen deposition or other adverse reactions and was therefore suitable for use as a long-acting delivery system.
These triblock copolymers can load not only insulin, but also other antidiabetic peptides. Initially, an optimized thermogel formulation, containing 2 mg/mL exenatide by mixing three additives (1.25 wt % zinc acetate, 5 wt % PEG200, and 5 wt % sucrose) in a 1:1 hydrogel mixture.71 It was illustrated that the additives used above could reduce the burst release significantly and increase the complete release of exenatide in the later period. Results showed that both the in vitro and in vivo release could be sustained for more than 7 days in this formulation. Moreover, the effects between two methods of administration had been compared, free EXE given twice a day or the hydrogel formulation of EXE given on day 0 and day 10, and results demonstrated that the concentration of insulin is much higher, while the concentration of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) was lower in hydrogel system.72 Therefore, this formulation of exenatide was much more beneficial on the promotion of the secretion of insulin, the sustained glycemic control and the patient compliance.
Later, two thermogelling triblock copolymers, poly (ε-caprolactone-co-glycolic acid)-poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (ε-caprolactone-co-glycolic acid) (PCGA-PEG-PCGA) and PLGA-PEG-PLGA, were synthesized to load liraglutide.73 Liraglutide is a fatty acid-modified antidiabetic polypeptide with higher hydrophobicity than insulin and exenatide. In vitro release profiles indicated that within 9 days, 56% of the loaded liraglutide was released from the PCGA-PEG-PCGA formulation. In contrast, over 85% of the loaded liraglutide was sustained for release from the PLGA-PEG-PLGA formulation. The in vivo tests showed that the hypoglycemic effect was prolonged for one week, which was consistent with the in vitro release profile. Thus, the PCGA-PEG-PCGA thermogel is a beneficial long-acting system for liraglutide release.
Recently, Zhuang et al synthesized PCGA-PEG-PCGA, PLGA-PEG-PLGA and a 1:1 mixed hydrogel of the two components to load lixisenatide.74 Lixisenatide was released quickly from the PCGA-PEG-PCGA formulation in vitro and the accumulated release was 84.3 ± 2.3% during the first 5 days. In contrast, only 58.2 ± 0.4% of the lixisenatide was released from the PLGA-PEG-PLGA formulation in a 10-day time period. Lixisenatide was released continually from the 1:1 mixed hydrogel over a 10-day period, and the accumulated release reached 93.1 ± 2.8%. The in vivo study showed that after a single subcutaneous injection, the plasma lixisenatide level was maintained for 9 days. Therefore, the mixed hydrogel formulation is beneficial for the long-term delivery of lixisenatide.
Poly (ethylene oxide)–poly (propylene oxide)–poly (ethylene oxide) (PEO–PPO–PEO), also named Pluronic, is a nonionic amphiphilic triblock copolymer that made by a propylene glycol initiator and the sequential addition of propylene and ethylene oxides.75 PF-127 is a typical thermosensitive reversible material that can convert from a gel to a solid at physiological temperature. The PF-127 gel can be used as a controlled delivery system for insulin.33 Nasir et al studied different formulations consisting of PF-127 alone or PF-127 with methylcellulose in different proportions and the in vitro and in vivo results indicated that the optimal formulation containing 15% w/v PF-127 and 3% w/v methylcellulose prolonged the insulin release and maintained basal plasma insulin levels for 10 days.76
Subsequently, PF-127 gel was used to prepare a formulation with high loaded insulin concentration (up to 80 mg/mL, equal to 2200 IU/mL), and in vivo studies demonstrated that the blood glucose levels in diabetic rats could promptly be controlled to normal and the action could be remained for approximately 17 days, which was well correlated with the in vitro results.77 Therefore, PF-127 gel can be used as a long-acting insulin delivery system.
Some articles suggested that PF-127 could also be used to load different forms of insulin or other antidiabetic peptides. Chen and coworkers dispersed insulin-loaded liposomes into a PF-127 gel.78 The results suggested that this system permitted the sustained release of insulin for up to 7 days with a higher bioavailability than single liposomes or PF-127 gels containing insulin. And another delivery system, multilayered NPs/PF-127 mixtures loaded with exenatide, was improved. Compared with free exenatide or exenatide-loaded multilayered NPs, this mixed formulation not only prolonged the release, but also significantly enhanced the hypoglycemic effect of exenatide.79
Chitosan can also be used in thermosensitive long-acting systems. Ghasemi et al studied the application of a chitosan/β-glycerol phosphate (CS/β-Gp) hydrogel containing 8% (w/v) β-Gp and 0.01 mg/mL insulin as a sustained delivery system and found that the hypoglycemic effect lasted 5 days in diabetic mice following a single subcutaneous injection.80 Another system, decanoic acid-modified glycol chitosan (DA-GC) hydrogels loaded with palmitic acid-modified exendin-4 (Ex4-C16), was showed that this formulation prolonged the release of Ex4-C16 for over 10 days.81
There are many other materials applicable as long-acting thermosensitive hydrogels. Higashi and coworkers illustrated that PEGylated insulin loaded in polypseudorotaxanes (PPRXs) with cyclodextrins (CyDs) maintained the hypoglycemic effect and considerably increased the area under the plasma glucose level-time curve (AUCG).82,83 The in vitro release rate of PEGylated insulin in the γ-CyD PPPX was higher than that in α-CyD PPPX. Later, the CyDs PPPX hydrogel system delivering non-PEGylated insulin was investigated, and the results were consistent with Higashi et al.84 Therefore, γ-CyD PPPX is a potential sustained release system for PEGylated or non-PEGylated insulin.
Poly (ethylene glycol)-block-poly (alanine-co-phenyl alanine) (PEG-PAF) is another applicable material. A PEG-PAF hydrogel formulation containing 13.8 mg insulin/kg was injected in rats and showed a decreased blood sugar levels for over 18 days.85
Tetra-PEG hydrogel microspheres with a self-cleaving β-eliminative covalent linker can be used as a novel long-acting delivery system for exenatide release. Schneider and coworkers investigated the pharmacokinetic properties of this system, which showed that exenatide was released slowly and had a half-life of approximately 7 days.86 However, the results indicated that exenatide would degrade in the subcutaneous depot. The authors found that [Gln 28] exenatide, which possesses similar pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties than exenatide, remained stable for a longer time period.87,88 They also demonstrated that the half-life of [Gln 28] exenatide in the tetra-PEG hydrogel delivery system was approximately one month, and that the hypoglycemic effect could be maintained for a month after a single subcutaneous injection in cats. Therefore, this [Gln 28] exenatide formulation has the potential to treat diabetes.
pH- and Temperature-Sensitive Hydrogels
As the poly (β-amino ester) (PAE) copolymer is sensitive to pH and the poly (ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL-PEG-PCL) copolymer is sensitive to temperature, PAE-PCL-PEG-PCL-PAE is dual-sensitive hydrogel (Figure 5A). Huynh and coworkers verified that this pentablock copolymer transferred from a sol to a gel in response to both temperature and pH. The in vivo test in SD rats showed that after subcutaneous injection at pH 7.0 and 10°C, insulin was released continuously from the complex hydrogel (5 mg/mL insulin in 25 wt% PAE-PCL-PEG-PCL-PAE solutions) for 15 days (Figure 5B).89 In a subsequent study, they investigated the different effects of various amounts of insulin and various concentrations of this pentablock copolymer in the hydrogel on the release.90 They concluded that the optimal insulin-loaded complex hydrogel containing 10 mg/mL insulin and 30 wt% PAE-PCL-PEG-PCL-PAE with sustained insulin release for over 1 week following a single subcutaneous injection could be used to treat diabetic rats.
 |
Figure 5 (A) Schematic diagram of the complexes between PAE and amino acid of insulin. Reprinted from Huynh DP, Nguyen MK, Pi BS et al Functionalized injectable hydrogels for controlled insulin delivery. Biomaterials. 2008;29(16):2527–2534. Copyright 2008, with permission from Elsevier.89 (B) The plasma release profile of insulin in SD rats. Reproduced from Huynh DP, Im GJ, Chae SY et al Controlled release of insulin from pH/temperature-sensitive injectable pentablock copolymer hydrogel. J Control Release. 2009;137(1):20–24. Copyright 2009, with permission from Elsevier.90 |
Lipid-Based Delivery System
As insulin is a hydrophilic compound, it is necessary to increase the lipophilicity of insulin to improve the efficiency of crossing the mucosa barrier. Zhou et al prepared complex compounds containing insulin and phospholipids with various mass ratios by a solvent evaporation method and investigated the physicochemical properties and the stability of the complex.91 The results indicated that the lipophilicity of insulin could be increased notably and that insulin was stable when the mass ratio of the phospholipids and insulin was 7.5:1 or higher. Therefore, the application of phospholipids is feasible and important in drug delivery systems for insulin.
Liposomes
Liposomes, small lipid spheres that are composed of concentric lipid bilayers surrounding aqueous compartments, are applicable as sustained delivery systems. Comparing equivalent amounts of insulin-loaded liposomes and free insulin with or without empty liposomes, Stevenson et al found that the insulin-loaded liposomes could prolong the duration of reduced glucose levels to at least 7 h following subcutaneous administration.92
Multivesicular liposomes (MLVs) consist of nonconcentric multiple lipid layers. As the diameter of MLVs is generally in the range of tens of microns, a high amount of drugs can be loaded to maintain sustained drug release. Zhang et al prepared liraglutide-loaded multivesicular liposomes (Lrg-MVLs) by the water-in-oil-in-water (W1/O/W2) double-emulsion method and studied the encapsulation efficiency and the release profile.93 The results showed that the encapsulation efficiency of liraglutide was 82.23±4.78%, and that liraglutide maintained a constant and stable hypoglycemic effect in vivo for over 144 h after a single subcutaneous injection.
Lipid Gels
Vesicular phospholipid gels (VPGs) are semisolid liposomal dispersions containing aqueous compartments in the core of the vesicles or between the vesicles; thus, they can be used to carry and sustain the release of hydrophilic, amphiphilic or lipophilic drugs.94 Zhang and coworkers fabricated exenatide-loaded VPGs containing various contents of phospholipids and studied their release profiles. They concluded that, considering the viscosity and release profiles, the formulation containing 30% (wt %) VPGs was optimal, and exenatide could be released from this formulation steadily for more than 10 days.95
Subsequently, they investigated another kind of lipid gel, the phospholipid-based phase separation gel (PPSG), which convert from the sol state to the solid or semisolid state after subcutaneous injection. They selected the optimal formulation containing biocompatible phospholipid S100 and medium-chain triglycerides (MCT) and found that exenatide-loaded PPSG showed hypoglycemic effects for 15 days in diabetic rats.96
Thus, exenatide-loaded lipid gels have the potential to be applied as a sustained and controlled release system for treating diabetes.
Inorganic Micro/Nanoparticles
Inorganic particles, such as mesoporous silicon (PSi) and silica, are applicable as novel long-lasting drug delivery systems. However, due to the limitation of small pore size and pore volume, there are few studies of this type of delivery system.
Huotari et al prepared different kinds of GLP-1-loaded PSi, including negatively charged thermally-oxidized mesoporous silicon (TOPSi) (pI 1.8), thermally-carbonized mesoporous silicon (TCPSi) (pI 2.6) and their corresponding positively charged amine-modified microparticles, TOPSi-NH2-D (pI 8.8) and TCPSi-NH2-D (pI 8.8).97 They found that, compared with free GLP-1 or GLP-1 loaded negative particles, the absorption of GLP-1 onto positive particles was significantly higher, however, the duration of GLP-1 action was not prolonged. Later, Chen et al encapsulated exenatide into well-ordered hexagonal mesoporous silica nanoparticles (EXT-SBA-15) and studied the in vitro release profile of exenatide from this system.98 The results showed that the encapsulation efficiency of exenatide was 15.2 ± 2.0% and that the blood glucose levels were controlled below 20 mmol/L for 25 days following subcutaneous injection of EXT-SBA-15. Therefore, EXT-SBA-15 could ensure the sustained release of exenatide.
The utility of modified large pore size mesoporous silicon nanoparticles is covered in part 3 of this review.
Stimuli-Responsive Subcutaneous Delivery Systems
In traditional delivery systems, the release behaviors of drugs are always passive and lack strict control over the blood sugar levels. To control blood sugar levels intelligently and steadily, several stimuli-responsive subcutaneous delivery systems have been developed.
Glucose-Responsive Systems
To enhance the link between continuous glucose-sensing and the delivery of insulin, several closed-loop delivery systems of insulin have been established in recent years. Most of these systems are designed by combining glucose-sensing components with responsive insulin-releasing components. To date, the enzymes glucose oxidase (GOx), glucose binding protein (GBP) and phenylboronic acid (PBA) have been commonly applied as glucose-sensing components.
GOx-Based Systems
GOx is a glucose-specific enzyme with high selectivity that can catalyze the transformation from glucose to gluconic acid (GlucA) effectively. GlucA molecules can cause pH-sensitive cationic or anionic hydrogels to swell or shrink, respectively. Therefore, it is common to use the combination of GOx and the pH-sensitive hydrogel to regulate the release rate of insulin.
A glucose-responsive delivery microdevice based on a bioinorganic nanocomposite membrane has been developed.99,100 GOx, catalase (CAT) and manganese dioxide (MnO2) nanoparticles were used in the transformation mentioned above, with the pH stimulus caused from GlucA molecules altering the volume of the hydrogel to change the permeability of the membrane. The in vivo studies showed that the regulated effect of blood glucose was maintained for 1 week. Nevertheless, a heavy fibrous capsule was easy to be generated when this device was implanted and the membrane degraded after 2 weeks. Therefore, this device was optimized by surface modification with 20-kDa PEG chains.101 After modification, it showed that the immune response was significantly reduced and the integrity of the membrane was improved. And the blood glucose levels could be controlled in diabetic rats for up to 18 days, which was markedly prolonged than before.
Gu et al developed a crosslinked nanonetwork system composed of insulin, a pH-responsive matrix, and nanoparticles containing GOx and CAT, to regulate the release of insulin.102,103 Under hyperglycemic conditions, GOx generates a pH stimulus, which cause the network to dissociate and triggers the release of insulin according to the stimulus. Following a single subcutaneous administration, the blood glucose levels remained normal in the long term.
Afterwards, Tai et al assembled a type of GOx-loaded pH-sensitive nanovesicle consisting of a diblock copolymer. After injection, glucose was passively transported into the core of the nanovesicle, where it was enzymatically oxidized and generated an acidic environment in which the nanovesicle became hydrolyzed and triggered the insulin release from this system.104 In vivo studies showed that, after a single injection, the blood glucose level in diabetic mice was controlled to a normal level for 5 days.
Later, Mohamm et al developed a nanocomplex formulation by mixing oppositely charged chitosan and enzyme-loaded PLGA nanoparticles.105 The nanoparticles were dissociated in response to a pH stimulus, which resulted in the release of insulin from this system. The results showed that the blood glucose levels could be controlled for 98 hours in diabetic rats following a subcutaneous injection.
Yu et al developed a glucose-responsive microsphere formulation composed of insulin, a pH-sensitive hydrazone polymer (methoxypolyethylene glycol-hydrazone-4-methoxypolyethylene glycol benzoate, mPEG-Hz-mPEG4AB), PLGA, GOx and CAT.106 The hydrazone bond is unstable under hyperglycemic conditions, and more than half of the insulin was released within 15 hours. In contrast, insulin was nearly not released under normal blood glucose levels. The hypoglycemic effect was maintained in rats for 2 days after a single subcutaneous administration.
However, as the activity of glucose-sensing components is high, the permeability and pH value of most glucose-sensitive delivery systems that have been reported may change considerably, leading to over half of the loaded insulin being released despite the blood glucose level being lower than the normoglycemic level (< 7 mM), or may even cause hypoglycemia. Therefore, Xu et al designed a novel nanosystem by coating an enzyme-polymer consisting of GOx/CAT and PEI onto insulin-loaded silica vesicles with a layer-by-layer approach.107 Compared with the enzyme layers, the PEI layers have a stronger proton affinity and can buffer large changes in pH, thus increasing the insulin-release threshold (Figure 6). The insulin release switches to “ON” in a hyperglycemic state. In the normoglycemic state, it switches to “OFF”. The results showed that the blood glucose levels were maintained at normal levels for 84 hours following a single administration.
 |
Figure 6 Different insulin release situations under the physiological glucose-responsive system.107 Reprinted with permission from Xu C, Lei C, Huang L et al Glucose-responsive nanosystem mimicking the physiological insulin secretion via an enzyme-polymer layer-by-layer coating strategy. Chemistry of Materials. 2017;29(18):7725–7732. Copyright © 2017 American Chemical Society.107 |
To achieve both rapid and long-term release goals, Volpatti et al designed an insulin-loaded co-formulation containing modified acid-degradable acetalated-dextran polymers with different ratios (rapid-release: 55% cyclic modifications; extended-release: 71% cyclic modifications) and enzymes.108 The results showed that the glycemic level was controlled for 16 hours after injecting this formulation.
Recently, another novel delivery system (ZIF@Ins&GOx) utilizing zeolitic imidazole framework-8 (ZIF-8) nanocrystals to encapsulate insulin and GOx was developed.109 ZIF-8 is a metal-organic framework (MOF) that can protect the bioactivity of insulin even under adverse conditions and is degraded in response to a pH stimulus. Thus, insulin can be released from this system once glucose penetrates the cavities of the ZIF-8. In vivo studies demonstrated that this formulation significantly controlled the blood glucose levels in a diabetic mouse model for 3 days.
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is another byproduct that is rapidly generated at high glucose concentrations during the oxidation of glucose by GOx. Therefore, H2O2-sensitive materials can also be used as a responsive insulin release component.
Li et al developed glucose and H2O2 dual-sensitive polymeric nanogels composed of PEG, pentaerythritol tetra(3-mercaptopropionate) (QT) and acryloyl (4-(5-(hydroxymethyl)-5-methyl-1,3,2-dioxaborinan-2-yl) phenyl) methanol (AHMDM).110 AHMDM is a dual-responsive polymer because of the cyclic phenylboronic ester component, which can not only react with glucose, but also clear H2O2. Therefore, after encapsulating GOx and insulin into this system, the release of insulin can be controlled by both glucose and H2O2. In vivo tests demonstrated that the hypoglycemic effect was maintained for approximately 16 hours in diabetic mice after subcutaneous injection of these nanogels.
PBA-Based Systems
PBA is a nonenzymatic polymer sensitive to glucose. Unlike GOx, it will not cause an immunoreaction. It is also widely used to sense changes in blood glucose levels.
Wu et al developed an insulin-loaded monodisperse nanogel system composed of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), poly (3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid) and maleic acid–dextran.111 In vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that insulin was released from this system in response to glucose to decrease the blood glucose level to 51% of the baseline and maintain the effect for approximately 2 hours.
However, as the pore sizes of the hydrogel were large and its water content was high, insulin was released prematurely and even led to the risk of hypoglycemia. To solve this problem, Zhao et al designed a novel microparticle-hydrogel (MP-gel) hybrid system consisting of PBA-PLGA MPs and a dopamine-conjugated hyaluronic acid (DOP-HA) hydrogel.112 Under neutral pH conditions, DOP combines with PBA to terminate the release of insulin at normal glucose levels. However, if the glucose level is high, glucose reacts with PBA and the microparticles are released from the hydrogel to regulate the blood glucose level. In vivo studies demonstrated that after the injection of this MP-gel, the blood glucose levels in diabetic mice were regulated to normal levels for approximately 2 weeks.
Another insulin-loaded porous PLGA microsphere coated with poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) and a novel copolymer containing PBA (p(AAPBA-co-NVCL)) by the layer-by-layer approach has been developed.113 PVA can react with PBA and generate borate/diol complexes, and this complex polymer is disintegrated and insulin is released from this system when exposed to glucose. The results showed that the optimal system composed of eight alternating layers of each component had high drug loading and encapsulation efficiency (2.83 ± 0.15% and 82.6 ± 5.1%, respectively) and controlled the release of insulin in diabetic mice for up to 18 days.
Later, in consideration of the difficulties in verifying the availability of glucose-responsive delivery systems in large animal models, a novel charge-switchable polymeric complex composed of insulin and poly (EDAA-FPBA) was developed.114 This complex polymer can release insulin in response to the blood glucose levels via the reaction of PBA and causes glucose to switch its charge from positive to negative. In addition, in vivo studies showed that insulin was rapidly released from this system under hyperglycemic conditions in both diabetic mice and minipigs after subcutaneous injections.
GBP-Based Systems
GBP is a saccharide-binding protein that can interact with glucose selectively, which causes the bond between GBP and the polymer to break. Therefore, GBP can be utilized as a component in the glucose-sensitive delivery systems. Concanavalin A (Con A), a lectin from jack beans, is the most commonly used GBP.
Initially, it was found that the maltose-insulin derivative could reversibly bind to Con A and were released when exposed to the hyperglycemic environment by competitively substituting free glucose.115,116 Later, Kim and coworkers synthesized succinyl-amido-phenyl-glucopyranoside insulin (SAPG-insulin) and attached it to Con A to achieve the self-regulated release of insulin.117,118 However, this system needed a long time to respond to changes in glucose. Therefore, the same authors designed new hydrophilic nylon microcapsules. The response time could be reduced if there were at least two layers and each layer contained active Con A and SAPG-insulin.119
In addition, as Con A can reversibly bind to polysaccharides such as chitosan and mannose, it can also be applied to synthesize glucose-responsive hydrogels.
A complex hydrogel with Con A and poly (2-glucosyloxyethyl methacrylate) (poly (GEMA)) was synthesized. It was found that the use of Con A increased the density of this crosslinked network so that this system changed its swelling ratio in response to glucose.120 Yin et al prepared insulin-loaded genipin-crosslinked microgels containing Con A and a chitosan derivative (GEA-chitosan). In vitro results showed that insulin was quickly released via the expansion or hydrolysis of the hydrogel as the glucose levels increased.121,122 Subsequently, Con A was utilized in a crosslinked network of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (poly (NIPAM)).123 At physiological pH, this nanogel system swelled and stabilized within 1 s as the concentration of glucose ranged from 50 μM to 20.0 mM. In addition, the release of insulin in vitro was regulated by the glucose concentration in a pulsatile profile.
Polysaccharides and Con A can also be used in glucose-responsive nanoparticle delivery systems due to their mutual association. Wu et al developed a controlled delivery system consisting of Con A, mannose and mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs).124 Drug-loaded MSNs were functionalized with mannose epitopes and then covered by a layer of Con A via the interaction between carbohydrates and proteins. When exposed to a high concentration of glucose, the drug could be released from this system owing to the competitive binding of blood glucose.
Dual-Responsive System
Wang and coworkers developed a novel insulin-loaded cycloborate-based glycopolypeptide nanocarrier composed of a phenylboronic acid-containing homopolymer (PAAPBA), a PEG-b-P(Asp-co-AGA) and GOx.125 Cycloborate, formulated by binding PAAPBA with PEG-b-P(Asp-co-AGA), degraded when the following sequence occurred: glycosyl group replacement by glucose, glucose oxidization and hydrolyzation by H2O2 that was produced during the oxidation of glucose by GOx (Figure 7).
 |
Figure 7 Schematic diagram of the preparation and reaction of nanoparticles. Reprinted with permission from Wang Y, Fan Y, Zhang M et al Glycopolypeptide nanocarriers based on dynamic covalent bonds for glucose dual-responsiveness and self-regulated release of insulin in diabetic rats. Biomacromolecules. 2020;21(4):1507–1515. Copyright © 2020 American Chemical Society.125 |
Later, they developed insulin and GOx loaded poly(acrylamidophenylboronic acid)/sodium alginate nanoparticles based on the carrier above.126 In vivo studies demonstrated that blood glucose levels in diabetic mice decreased to a normal state within 0.5 h, and this effect could be maintained for up to 14 h.
Magnetic-Responsive Delivery
Alginate/chitosan microcapsules containing magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles were prepared by Finotellim et al to deliver insulin.127 The results showed that after being placed into an oscillating magnetic field, the release of insulin was noticeably enhanced, and the preliminary in vivo tests verified that the released insulin from this formulation retained its activity. Therefore, it is possible to use this delivery system to control the release of insulin.
Ultrasound-Facilitated Delivery
Ultrasound can also be actively used to control the delivery of drugs. Di and coworkers established a PLGA nanonetwork containing insulin and evaluated the release behavior of insulin under a focused ultrasound system (FUS). The results illustrated that this nanonetwork formulation regulated the blood glucose levels for over 1 week after a 30-s stimulus of FUS.128 However, the amount of insulin decreased rapidly after each FUS-trigger, thereby decreasing the hypoglycemic effect gradually. Afterwards, the same group developed chitosan microgels integrated with insulin-encapsulated PLGA nanocapsules (Figure 8A). The in vivo studies of STZ-induced type 1 diabetic mice showed that after the subcutaneous injection of this formulation, insulin was released passively from the nanocapsules and stored in the microgels temporarily to avoid the initial burst effect. Once stimulated by FUS for 30 s, insulin was released quickly. Moreover, even after the system had been activated six times, the regulation of the blood glucose levels did not decrease rapidly (Figure 8B).129 Therefore, this ultrasound-facilitated microgel formulation can control blood glucose levels more effectively for a long time period.
 |
Figure 8 (A) A schematic diagram of the integration of a chitosan microgel with insulin-loaded PLGA nanocapsules. (B) The blood glucose levels in STZ-induced diabetic mice following different conditions: 1) a subcutaneous injection of microgel with FUS treatment (950 kHz; 20 μs; 30 s) (red line); 2) a subcutaneous injection of microgel without FUS treatment (black line); 3) an injection of PBS solution with FUS treatment (green line) (n = 5). Reproduced by permission from Springer Nature. Di J, Yu J, Wang Q et al Ultrasound-triggered noninvasive regulation of blood glucose levels using microgels integrated with insulin nanocapsules. Nano Research. 2017;10(4): 1393–1402. Copyright 2017.129 |
Near-Infrared-Activated Insulin Delivery
A near-infrared (NIR) laser is another stimulus that is safe and applicable to real-time clinical systems to deliver drugs. A continuous-wave near-infrared laser was used to activate the release of insulin in a novel composite membrane device consisting of hydrophobic ethylcellulose and hollow gold nanoshells (AuNSs).130 Under the NIR laser, AuNSs absorb light and convert it to heat, which prompts the membrane to turn from impermeable to poriferous and triggers the release of insulin from this device (Figure 9A). In diabetic SD rats with subcutaneous implants of this device, the blood glucose levels were controlled for 14 days after repeated 30-min exposure to equal intensities of the NIR light (570 mW/cm2) (Figure 9B).
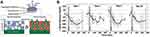 |
Figure 9 (A) Schematic diagram of developed device and the cross-section of membrane. (B) Blood glucose levels following repeated administration under the same irradiance (gray box; 570 mW/cm2; 30 min) in four stages within 14d (n = 3). Reproduced from Timko BP, Arruebo M, Shankarappa SA et al Near-infrared-actuated devices for remotely controlled drug delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(4):1349–1354. Copyright (2014) National Academy of Sciences.130 |
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Subcutaneous delivery systems with fast-acting and highly bioavailable delivery have been still widely used. As insulin and other biomacromolecular drugs are not stable in the gastrointestinal tract, subcutaneous delivery systems are more beneficial to ensure the stability of them. Moreover, due to the large surface area and higher permeability, the absorption of the drug will be faster and steadier by subcutaneous. However, there are several shortcomings of these systems. Long-term multiple injection may cause pain, infection, local tissue necrosis, psychological stress, or even hyperinsulinemia, leading to the poor patient compliance. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the frequency of administration and eliminate the injection discomfort.
Nowadays, a variety of formulations, materials and devices with sustained or stimuli-responsive mechanisms have been established and show remarkable therapeutic effectiveness at both the research and clinical levels. Novel systems which we summarized above, such as micro/nanocarriers, in situ hydrogels, and magnetic, ultrasound, NIR or glucose-responsive systems, have shown the quite potential to modify the stabilities and pharmacokinetic properties of biomacromolecules to improve the compliance of diabetic patients and their quality of life.
Despite the advances illustrated in this review, there are still issues that need to be addressed regarding potential clinical applications. First, precise doses and constant release of insulin are challenges for both stimulated release systems and depot-based systems. In most delivery systems now in use, the dose of insulin is excessive, and the long-term use of overdose may cause the change of cells or tissues, which is harm to the patients. These challenges can be addressed by developing more sensitive glucose response sensors and new polymerization techniques. Second, achieving consistency between the in vitro and in vivo formulations is another urgent problem that needs to be solved. Although the expected fast in vitro action has been shown in many studies, the in vivo behavior is not satisfactory. A possible solution is to add or improve new glucose-response moieties in the materials or devices to achieve stronger associated consistency.131 Finally, the biocompatibility and toxicity of novel materials and devices need to be further evaluated because any possible side effects may lead to serious health issues in long-term treated diabetic patients. In particular, the in vivo toxicity of these materials and their degradation products should be further assessed in detail to confirm their safety as implanted biomaterials. Therefore, a precise release dose, suitable biodegradability and biocompatibility, satisfactory sustained release and accurate stimuli-responsive capability are important for the development of subcutaneous delivery systems for insulin and GLP-1 agonist polypeptides in diabetes treatment.
Abbreviations
DM, diabetes mellitus; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide 1; GLP-1Ras, GLP-1 receptor agonists; SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; DPP-4, dipeptidyl peptidase 4; AGIs, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors; TZDs, thiazolidinediones; NPH, neutral protamine Hagedorn; FDA, Food and Drug Administration; EMA, European Medicine Agency; PLGA, Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid); INPs, insulin nanoparticles; PF-127, Pluronic F-127; MRT, mean residence time; PEG, polyethylene glycol; Ex4, Exendin-4; AcHES, poly (acryloyl hydroxyethyl starch); ISPPLG NPs, insulin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles; CA, cholic acid; PEI, polyethylenimine; PLA, poly (lactic acid); CS, chitosan; HTCC, N-(2-hydroxyl) propyl-3-trimethyl ammonium chitosan chloride; PT-70%, the time period of the blood glucose level lower than 70%; PHBHHx, poly (hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyhexanoate; EE, encapsulation efficiency; BA, benzyl alcohol; BB, benzyl benzoate; ZDF, Zucker Diabetic Fatty; PLA-PEG-PLA, poly (D, L-lactide)-poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (D, L-lactide); PCGA-PEG-PCGA, poly (ε-caprolactone-co-glycolic acid)-poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (ε-caprolactone-co-glycolic acid); PEO–PPO–PEO, poly (ethylene oxide)–poly (propylene oxide)–poly (ethylene oxide); CS/β-Gp, chitosan/β-glycerol phosphate; DA-GC, decanoic acid-modified glycol chitosan; PPRXs, polypseudorotaxanes; CyDs, cyclodextrins; AUCG, the area under the plasma glucose level-time curve; PEG-PAF, poly (ethylene glycol)-block-poly (alanine-co-phenyl alanine); PAE, poly (β-amino ester); PCL-PEG-PCL, poly (ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone); MLVs, multivesicular liposomes; Lrg-MVLs, liraglutide-loaded multivesicular liposomes; W1/O/W2, water-in-oil-in-water; VPGs, vesicular phospholipid gels; PPSG, phospholipid-based phase separation gel; MCT, medium-chain triglycerides; PSi, mesoporous silicon; TOPSi, thermally-oxidized mesoporous silicon; TCPSi, thermally-carbonized mesoporous silicon; GOx, glucose oxidase; GBP, glucose binding protein; PBA, phenylboronic acid; GlucA, gluconic acid; CAT, catalase; MnO2, manganese dioxide; mPEG-Hz-mPEG4AB, methoxypolyethylene glycol-hydrazone-4-methoxypolyethylene glycol benzoate; ZIF-8, zeolitic imidazole framework-8; MOF, metal-organic framework; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; QT, pentaerythritol tetra(3-mercaptopropionate); AHMDM, acryloyl (4-(5-(hydroxymethyl)-5-methyl-1,3,2-dioxaborinan-2-yl) phenyl) methanol; MP-gel, microparticle-hydrogel; DOP-HA, dopamine-conjugated hyaluronic acid; PVA, poly (vinyl alcohol); Con A, concanavalin A; SAPG-insulin, succinyl-amido-phenyl-glucopyranoside insulin; poly (GEMA), poly(2-glucosyloxyethyl methacrylate); poly (NIPAM), poly(N-isopropylacrylamide); MSNs, mesoporous silica nanoparticles; PAAPBA, phenylboronic acid-containing homopolymer; FUS, focused ultrasound system; STZ, streptozotocin.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81703427), Doctoral Research Fund of Liaoning Province (No. 20170520001), Project Fund of China Medical University (No. XZR20160007), and Fund of the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University (No. FSFH201718).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Stumvoll M, Goldstein BJ, Van Haeften TW. Type 2 diabetes: principles of pathogenesis and therapy. Lancet. 2005;365(9467):1333–1346. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)61032-X
2. Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;138:271–281. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2018.02.023
3. Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, et al. Consensus statement by the American association of clinical endocrinologists and American college of endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm - 2019 executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2019;25(1):69–100.
4. Zaric BL, Obradovic M, Sudar-Milovanovic E, et al. Drug delivery systems for diabetes treatment. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(2):166–173. doi:10.2174/1381612825666190306153838
5. Rosenfeld L. Insulin: discovery and controversy. Clin Chem. 2002;48(12):2270–2288. doi:10.1093/clinchem/48.12.2270
6. Cheng AYY, Patel DK, Reid TS, et al. Differentiating basal insulin preparations: understanding how they work explains why they are different. Adv Ther. 2019;36(5):1018–1030. doi:10.1007/s12325-019-00925-6
7. Lovshin JA, Drucker DJ. Incretin-based therapies for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2009;5(5):262–269. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2009.48
8. Knudsen LB, Nielsen PF, Huusfeldt PO, et al. Potent derivatives of glucagon-like peptide-1 with pharmacokinetic properties suitable for once daily administration. J Med Chem. 2000;43(9):1664–1669. doi:10.1021/jm9909645
9. Kolterman OG, Buse JB, Fineman MS, et al. Synthetic exendin-4 (exenatide) significantly reduces postprandial and fasting plasma glucose in subjects with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88(7):3082–3089. doi:10.1210/jc.2002-021545
10. Lovshin JA. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: a class update for treating type 2 diabetes. Can J Diabetes. 2017;41(5):524–535. doi:10.1016/j.jcjd.2017.08.242
11. Werner U, Haschke G, Herling AW, et al. Pharmacological profile of lixisenatide: a new GLP-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Regul Pept. 2010;164(2–3):58–64. doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2010.05.008
12. Bolli GB, Munteanu M, Dotsenko S, et al. Efficacy and safety of lixisenatide once daily vs. placebo in people with type 2 diabetes insufficiently controlled on metformin (GetGoal-F1). Diabet Med. 2014;31(2):176–184. doi:10.1111/dme.12328
13. Bolli GB, Munteanu M, Dotsenko S, et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of albiglutide, a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 mimetic, in healthy subjects. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009;11(5):498–505. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2008.00992.x
14. Nauck MA, Stewart MW, Perkins C, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly GLP-1 receptor agonist albiglutide (HARMONY 2): 52 week primary endpoint results from a randomised, placebo-controlled trial in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with diet and exercise. Diabetologia. 2016;59(2):266–274. doi:10.1007/s00125-015-3795-1
15. Glaesner W, Vick AM, Millican R, et al. Engineering and characterization of the long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue LY2189265, an Fc fusion protein. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2010;26(4):287–296. doi:10.1002/dmrr.1080
16. Jendle J, Grunberger G, Blevins T, et al. Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a comprehensive review of the dulaglutide clinical data focusing on the AWARD Phase 3 clinical trial program. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;32(8):776–790. doi:10.1002/dmrr.2810
17. Lau J, Bloch P, Schäffer L, et al. Discovery of the once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue semaglutide. J Med Chem. 2015;58(18):7370–7380. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00726
18. Sharma G, Sharma AR, Nam J-S, et al. Nanoparticle based insulin delivery system: the next generation efficient therapy for type 1 diabetes. J Nanobiotechnology. 2015;13(1):74. doi:10.1186/s12951-015-0136-y
19. Easa N, Alany RG, Carew M, et al. A review of non-invasive insulin delivery systems for diabetes therapy in clinical trials over the past decade. Drug Discov Today. 2019;24(2):440–451. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2018.11.010
20. Fink JB, Molloy L, Patton JS, et al. Good things in small packages: an innovative delivery approach for inhaled insulin. Pharm Res. 2017;34(12):2568–2578. doi:10.1007/s11095-017-2215-2
21. Chen MC, Sonaje K, Chen KJ, et al. A review of the prospects for polymeric nanoparticle platforms in oral insulin delivery. Biomaterials. 2011;32(36):9826–9838. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.08.087
22. Eldor R, Arbit E, Corcos A, et al. Glucose-reducing effect of the ORMD-0801 oral insulin preparation in patients with uncontrolled type 1 diabetes: a pilot study. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e59524. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059524
23. Luzio SD, Dunseath G, Lockett A, et al. The glucose lowering effect of an oral insulin (Capsulin) during an isoglycaemic clamp study in persons with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010;12(1):82–87. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2009.01146.x
24. Stote R, Miller M, Marbury T, et al. Enhanced absorption of nasulin, an ultrarapid-acting intranasal insulin formulation, using single nostril administration in normal subjects. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2011;5(1):113–119. doi:10.1177/193229681100500116
25. Shahani S, Shahani L. Use of insulin in diabetes: a century of treatment. Hong Kong Med J. 2015;21(6):553–559. doi:10.12809/hkmj154557
26. Pettus J, Santos Cavaiola T, Tamborlane WV, et al. The past, present, and future of basal insulins. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;32(6):478–496. doi:10.1002/dmrr.2763
27. Heise T, Mathieu C. Impact of the mode of protraction of basal insulin therapies on their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties and resulting clinical outcomes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19(1):3–12. doi:10.1111/dom.12782
28. Villegas MR, Baeza A, Vallet-Regí M. Nanotechnological strategies for protein delivery. Molecules. 2018;23(5):1008. doi:10.3390/molecules23051008
29. Kovalainen M, Mönkäre J, Riikonen J, et al. Novel delivery systems for improving the clinical use of peptides. Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67(3):541–561. doi:10.1124/pr.113.008367
30. Kumari A, Yadav SK, Yadav SC. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2010;75(1):1–18. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.09.001
31. Danhier F, Ansorena E, Silva JM, et al. PLGA-based nanoparticles: an overview of biomedical applications. J Control Release. 2012;161(2):505–522. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.01.043
32. Barichello JM, Morishita M, Takayama K, et al. Encapsulation of hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs in PLGA nanoparticles by the nanoprecipitation method. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1999;25(4):471–476. doi:10.1081/DDC-100102197
33. Barichello JM, Morishita M, Takayama K, et al. Absorption of insulin from pluronic F-127 gels following subcutaneous administration in rats. Int J Pharm. 1999;184(2):189–198. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(99)00119-2
34. Shenoy DB, D’Souza RJ, Tiwari SB, et al. Potential applications of polymeric microsphere suspension as subcutaneous depot for insulin. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2003;29(5):555–563. doi:10.1081/DDC-120018644
35. Lassalle V, Ferreira ML. PLGA based drug delivery systems (DDS) for the sustained release of insulin: insight into the protein/polyester interactions and the insulin release behavior. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2010;85(12):1588–1596. doi:10.1002/jctb.2470
36. Cui F, Shi K, Zhang L, et al. Biodegradable nanoparticles loaded with insulin–phospholipid complex for oral delivery: preparation, in vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation. J Control Release. 2006;114(2):242–250.
37. Yin D, Lu Y, Zhang H, et al. Preparation of glucagon-like peptide-1 loaded PLGA microspheres: characterizations, release studies and bioactivities in vitro/in vivo. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2008;56(2):156–161. doi:10.1248/cpb.56.156
38. Youn YS, Kwon MJ, Na DH, et al. Improved intrapulmonary delivery of site-specific PEGylated salmon calcitonin: optimization by PEG size selection. J Control Release. 2008;125(1):68–75. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.10.008
39. Kim TH, Park CW, Kim HY, et al. Low molecular weight (1 kDa) polyethylene glycol conjugation markedly enhances the hypoglycemic effects of intranasally administered exendin-4 in type 2 diabetic db/db mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(7):1076–1083. doi:10.1248/bpb.b12-00029
40. Lim SM, Eom HN, Jiang HH, et al. Evaluation of PEGylated exendin-4 released from poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres for antidiabetic therapy. J Pharm Sci. 2015;104(1):72–80. doi:10.1002/jps.24238
41. Wu J, Wu L, Xu X, et al. Microspheres made by w/o/o emulsion method with reduced initial burst for long-term delivery of endostar, a novel recombinant human endostatin. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98(6):2051–2058. doi:10.1002/jps.21589
42. Xuan J, Lin Y, Huang J, et al. Exenatide-loaded PLGA microspheres with improved glycemic control: in vitro bioactivity and in vivo pharmacokinetic profiles after subcutaneous administration to SD rats. Peptides. 2013;46:172–179. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2013.06.005
43. Kim BS, Oh JM, Hyun H, et al. Insulin-loaded microcapsules for in vivo delivery. Mol Pharm. 2009;6(2):353–365. doi:10.1021/mp800087t
44. Jiang G, Qiu W, DeLuca PP. Preparation and in vitro/in vivo evaluation of insulin-loaded poly(acryloyl-hydroxyethyl starch)-PLGA composite microspheres. Pharm Res. 2003;20(3):452–459. doi:10.1023/A:1022668507748
45. Dozier JK, Distefano MD. Site-specific PEGylation of therapeutic proteins. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(10):25831–25864. doi:10.3390/ijms161025831
46. Saravanan SS, Malathi MS. Hydrophilic poly (ethylene glycol) capped poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid nanoparticles for subcutaneous delivery of insulin in diabetic rats. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;95:1190–1198. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.11.009
47. Kang HC, Lee JE, Bae YH. Nanoscaled buffering zone of charged (PLGA)n-b-bPEI micelles in acidic microclimate for potential protein delivery application. J Control Release. 2012;160(3):440–450. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.02.024
48. Wang J, Li S, Chen T, et al. Nanoscale cationic micelles of amphiphilic copolymers based on star-shaped PLGA and PEI cross-linked PEG for protein delivery application. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(8):93. doi:10.1007/s10856-019-6294-y
49. Xiong XY, Li QH, Li YP, et al. Pluronic P85/poly(lactic acid) vesicles as novel carrier for oral insulin delivery. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013;111:282–288. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.06.019
50. Giovino C, Ayensu I, Tetteh J, et al. An integrated buccal delivery system combining chitosan films impregnated with peptide loaded PEG-b-PLA nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013;112:9–15. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.07.019
51. Yeh MK, Chen JL, Chiang CH. In vivo and in vitro characteristics for insulin-loaded PLA microparticles prepared by w/o/w solvent evaporation method with electrolytes in the continuous phase. J Microencapsul. 2004;21(7):719–728. doi:10.1080/02652040400008481
52. Pérez C, Castellanos IJ, Costantino HR, et al. Recent trends in stabilizing protein structure upon encapsulation and release from bioerodible polymers. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2002;54(3):301–313. doi:10.1211/0022357021778448
53. Ibrahim MA, Ismail A, Fetouh MI, et al. Stability of insulin during the erosion of poly(lactic acid) and poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres. J Control Release. 2005;106(3):241–252. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2005.02.025
54. Manoharan C, Singh J. Insulin loaded PLGA microspheres: effect of zinc salts on encapsulation, release, and stability. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98(2):529–542. doi:10.1002/jps.21445
55. Sheshala R, Peh KK, Darwis Y. Preparation, characterization, and in vivo evaluation of insulin-loaded PLA-PEG microspheres for controlled parenteral drug delivery. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2009;35(11):1364–1374. doi:10.3109/03639040902939213
56. Halim A, Keong L, Zainol I, et al. In: Sarmento B, Neves JD, editors. Chitosan-Based Systems for Biopharmaceuticals: Delivery, Targeting and Polymer Therapeutics. John Wiley & Sons; 2012:57–73.
57. Sun Y, Wan A. Preparation of nanoparticles composed of chitosan and its derivatives as delivery systems for macromolecules. J Appl Polym Sci. 2007;105(2):552–561. doi:10.1002/app.26038
58. Zhang Z, Cai H, Liu Z, et al. Effective enhancement of hypoglycemic effect of insulin by liver-targeted nanoparticles containing cholic acid-modified chitosan derivative. Mol Pharm. 2016;13(7):2433–2442. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.6b00188
59. Li H, Zhang Z, Bao X, et al. Fatty acid and quaternary ammonium modified chitosan nanoparticles for insulin delivery. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;170:136–143. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.05.063
60. Yao YC, Zhan XY, Zhang J, et al. A specific drug targeting system based on polyhydroxyalkanoate granule binding protein PhaP fused with targeted cell ligands. Biomaterials. 2008;29(36):4823–4830. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.09.008
61. Peng Q, Zhang ZR, Gong T, et al. A rapid-acting, long-acting insulin formulation based on a phospholipid complex loaded PHBHHx nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2012;33(5):1583–1588. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.10.072
62. Peng Q, Yang YJ, Zhang T, et al. The implantable and biodegradable PHBHHx 3D scaffolds loaded with protein-phospholipid complex for sustained delivery of proteins. Pharm Res. 2013;30(4):1077–1085. doi:10.1007/s11095-012-0944-9
63. Peng Q, Sun X, Gong T, et al. Injectable and biodegradable thermosensitive hydrogels loaded with PHBHHx nanoparticles for the sustained and controlled release of insulin. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(2):5063–5069. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2012.09.034
64. Kumar N, Langer RS, Domb AJ. Polyanhydrides: an overview. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2002;54(7):889–910. doi:10.1016/S0169-409X(02)00050-9
65. Manoharan C, Singh J. Evaluation of polyanhydride microspheres for basal insulin delivery: effect of copolymer composition and zinc salt on encapsulation, in vitro release, stability, in vivo absorption and bioactivity in diabetic rats. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98(11):4237–4250. doi:10.1002/jps.21741
66. Qiu Y, Park K. Environment-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;53(3):321–339. doi:10.1016/S0169-409X(01)00203-4
67. Dhawan S, Kapil R, Kapoor DN. Development and evaluation of in situ gel-forming system for sustained delivery of insulin. J Biomater Appl. 2011;25(7):699–720. doi:10.1177/0885328209359959
68. Choi S, Kim SW. Controlled release of insulin from injectable biodegradable triblock copolymer depot in ZDF rats. Pharm Res. 2003;20(12):2008–2010. doi:10.1023/B:PHAM.0000008050.99985.5c
69. Al-Tahami K, Oak M, Mandke R, et al. Basal level insulin delivery: in vitro release, stability, biocompatibility, and in vivo absorption from thermosensitive triblock copolymers. J Pharm Sci. 2011;100(11):4790–4803. doi:10.1002/jps.22685
70. Sharma D, Singh J. Long-term glycemic control and prevention of diabetes complications in vivo using oleic acid-grafted-chitosan‑zinc-insulin complexes incorporated in thermosensitive copolymer. J Control Release. 2020;323:161–178. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.04.012
71. Li K, Yu L, Liu X, et al. A long-acting formulation of a polypeptide drug exenatide in treatment of diabetes using an injectable block copolymer hydrogel. Biomaterials. 2013;34(11):2834–2842. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.01.013
72. Yu L, Li K, Liu X, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a once-weekly formulation of an antidiabetic peptide drug exenatide in an injectable thermogel. J Pharm Sci. 2005;106(3):4140–4149. doi:10.1002/jps.23735
73. Chen Y, Li Y, Shen W, et al. Controlled release of liraglutide using thermogelling polymers in treatment of diabetes. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):31593. doi:10.1038/srep31593
74. Zhuang Y, Yang X, Li Y, et al. Sustained release strategy designed for lixisenatide delivery to synchronously treat diabetes and associated complications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(33):29604–29618. doi:10.1021/acsami.9b10346
75. Schmolka IR. Artificial skin. I. Preparation and properties of pluronic F-127 gels for treatment of burns. J Biomed Mater Res. 1972;6(6):571–582.
76. Nasir F, Iqbal Z, Khan A, et al. Development and evaluation of pluronic- and methylcellulose-based thermoreversible drug delivery system for insulin. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2014;40(11):1503–1508. doi:10.3109/03639045.2013.831441
77. Li J, Chu MK, Lu B, et al. Enhancing thermal stability of a highly concentrated insulin formulation with pluronic F-127 for long-term use in microfabricated implantable devices. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2017;7(4):529–543. doi:10.1007/s13346-017-0381-8
78. Chen X, Wong BCK, Chen H, et al. Long-lasting insulin treatment via a single subcutaneous administration of liposomes in thermoreversible pluronic(R) F127 based hydrogel. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;23(39):6079–6085. doi:10.2174/1381612823666170509123844
79. Oh KS, Kim JY, Yoon BD, et al. Sol-gel transition of nanoparticles/polymer mixtures for sustained delivery of exenatide to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2014;88(3):664–669. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2014.08.004
80. Ghasemi Tahrir F, Ganji F, Mani AR, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of thermosensitive chitosan hydrogel for sustained release of insulin. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(3):1038–1046. doi:10.3109/10717544.2014.932861
81. Lee C, Choi JS, Kim I, et al. Decanoic acid-modified glycol chitosan hydrogels containing tightly adsorbed palmityl-acylated exendin-4 as a long-acting sustained-release anti-diabetic system. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(2):812–820. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2013.10.009
82. Higashi T, Hirayama F, Arima H, et al. Polypseudorotaxanes of pegylated insulin with cyclodextrins: application to sustained release system. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007;17(7):1871–1874. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.01.029
83. Higashi T, Hirayama F, Misumi S, et al. Design and evaluation of polypseudorotaxanes of pegylated insulin with cyclodextrins as sustained release system. Biomaterials. 2008;29(28):3866–3871. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.06.019
84. Higashi T, Abu Hashim II, Anno T, et al. Potential use of gamma-cyclodextrin polypseudorotaxane hydrogels as an injectable sustained release system for insulin. Int J Pharm. 2010;392(1–2):83–91. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.03.026
85. Jeong Y, Joo MK, Bahk KH, et al. Enzymatically degradable temperature-sensitive polypeptide as a new in-situ gelling biomaterial. J Control Release. 2009;137(1):25–30. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.03.008
86. Schneider EL, Henise J, Reid R, et al. Hydrogel drug delivery system using self-cleaving covalent linkers for once-a-week administration of exenatide. Bioconjug Chem. 2016;27(5):1210–1215. doi:10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00690
87. Schneider EL, Hearn BR, Pfaff SJ, et al. A hydrogel-microsphere drug delivery system that supports once-monthly administration of a GLP-1 receptor agonist. ACS Chem Biol. 2017;12(8):2107–2116. doi:10.1021/acschembio.7b00218
88. Schneider EL, Reid R, Parkes DG, et al. A once-monthly GLP-1 receptor agonist for treatment of diabetic cats. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2020;70:106373. doi:10.1016/j.domaniend.2019.07.001
89. Huynh DP, Nguyen MK, Pi BS, et al. Functionalized injectable hydrogels for controlled insulin delivery. Biomaterials. 2008;29(16):2527–2534. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.02.016
90. Huynh DP, Im GJ, Chae SY, et al. Controlled release of insulin from pH/temperature-sensitive injectable pentablock copolymer hydrogel. J Control Release. 2009;137(1):20–24. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.02.021
91. Zhou C, Xia X, Liu Y, et al. The preparation of a complex of insulin-phospholipids and their interaction mechanism. J Pept Sci. 2012;18(9):541–548. doi:10.1002/psc.2423
92. Stevenson RW, Patel HM, Parsons JA, et al. Prolonged hypoglycemic effect in diabetic dogs due to subcutaneous administration of insulin in liposomes. Diabetes. 1982;31(6 Pt 1):506–511. doi:10.2337/diab.31.6.506
93. Zhang L, Ding L, Tang C, Li Y, Yang L. Liraglutide-loaded multivesicular liposome as a sustained-delivery reduces blood glucose in SD rats with diabetes. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(9):3358–3363. doi:10.1080/10717544.2016.1180723
94. Brandl M. Vesicular phospholipid gels: a technology platform. J Liposome Res. 2007;17(1):15–26. doi:10.1080/08982100601186490
95. Zhang Y, Zhong Y, Hu M, et al. In vitro and in vivo sustained release of exenatide from vesicular phospholipid gels for type II diabetes. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016;42(7):1042–1049. doi:10.3109/03639045.2015.1107090
96. Hu M, Zhang Y, Xiang N, et al. Long-acting phospholipid gel of exenatide for long-term therapy of type II diabetes. Pharm Res. 2016;33(6):1318–1326. doi:10.1007/s11095-016-1873-9
97. Huotari A, Xu W, Mönkäre J, et al. Effect of surface chemistry of porous silicon microparticles on glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) loading, release and biological activity. Int J Pharm. 2013;454(1):67–73. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.06.063
98. Chen C, Zheng H, Xu J, et al. Sustained-release study on exenatide loaded into mesoporous silica nanoparticles: in vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation. Daru. 2017;25(1):20. doi:10.1186/s40199-017-0186-9
99. Gordijo CR, Koulajian K, Shuhendler AJ, et al. Nanotechnology-enabled closed loop insulin delivery device: in vitro and in vivo evaluation of glucose-regulated insulin release for diabetes control. Adv Funct Mater. 2011;21(1):73–82. doi:10.1002/adfm.201001762
100. Chu MKL, Chen J, Gordijo CR, et al. In vitro and in vivo testing of glucose-responsive insulin-delivery microdevices in diabetic rats. Lab Chip. 2012;12(14):2533–2539. doi:10.1039/c2lc40139h
101. Chu MKL, Gordijo CR, Li J, et al. In vivo performance and biocompatibility of a subcutaneous implant for real-time glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2015;17(4):255–267. doi:10.1089/dia.2014.0229
102. Gu Z, Dang TT, Ma M, et al. Glucose-responsive microgels integrated with enzyme nanocapsules for closed-loop insulin delivery. ACS Nano. 2013;7(8):6758–6766. doi:10.1021/nn401617u
103. Gu Z, Aimetti AA, Wang Q, et al. Injectable nano-network for glucose-mediated insulin delivery. ACS Nano. 2013;7(5):4194–4201. doi:10.1021/nn400630x
104. Tai W, Mo R, Di J, et al. Bio-inspired synthetic nanovesicles for glucose-responsive release of insulin. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15(10):3495–3502. doi:10.1021/bm500364a
105. Mohammadpour F, Hadizadeh F, Tafaghodi M, et al. Preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of PLGA/Chitosan based nano-complex as a novel insulin delivery formulation. Int J Pharm. 2019;572:118710. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118710
106. Yu J, Wang Q, Liu H, et al. Glucose-responsive microspheres as a smart drug delivery system for controlled release of insulin. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2020;45(1):113–121. doi:10.1007/s13318-019-00588-2
107. Xu C, Lei C, Huang L, et al. Glucose-responsive nanosystem mimicking the physiological insulin secretion via an enzyme-polymer layer-by-layer coating strategy. Chem Mater. 2017;29(18):7725–7732. doi:10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b01804
108. Volpatti LR, Matranga MA, Cortinas AB, et al. Glucose-responsive nanoparticles for rapid and extended self-regulated insulin delivery. ACS Nano. 2020;14(1):488–497. doi:10.1021/acsnano.9b06395
109. Zhang C, Hong S, Liu MD, et al. pH-sensitive MOF integrated with glucose oxidase for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. J Control Release. 2020;320:159–167. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.01.038
110. Li C, Liu X, Liu Y, et al. Glucose and H2O2 dual-sensitive nanogels for enhanced glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Nanoscale. 2019;11(18):9163–9175. doi:10.1039/C9NR01554J
111. Mandal D, Mandal SK, Ghosh M, et al. Phenylboronic acid appended pyrene-based low-molecular-weight injectable hydrogel: glucose-stimulated insulin release. Chemistry. 2015;21(34):12042–12052. doi:10.1002/chem.201501170
112. Zhao F, Wu D, Yao D, et al. An injectable particle-hydrogel hybrid system for glucose-regulatory insulin delivery. Acta Biomater. 2017;64:334–345. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2017.09.044
113. Wu JZ, Williams GR, Li HY, et al. Insulin-loaded PLGA microspheres for glucose-responsive release. Drug Deliv. 2017;24(1):1513–1525. doi:10.1080/10717544.2017.1381200
114. Wang J, Yu J, Zhang Y, et al. Charge-switchable polymeric complex for glucose-responsive insulin delivery in mice and pigs. Sci Adv. 2019;5(7):eaaw4357. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aaw4357
115. Brownlee M, Cerami A. A glucose-controlled insulin-delivery system: semisynthetic insulin bound to lectin. Science. 1979;206(4423):1190–1191. doi:10.1126/science.505005
116. Brownlee M, Cerami A. Glycosylated insulin complexed to concanavalin A. biochemical basis for a closed-loop insulin delivery system. Diabetes. 1983;32(6):499–504. doi:10.2337/diab.32.6.499
117. Seminoff LA, Gleeson JM, Zheng J, et al. A self-regulating insulin delivery system. II. in vivo characteristics of a synthetic glycosylated insulin. Int J Pharm. 1989;54(3):251–257. doi:10.1016/0378-5173(89)90102-6
118. Makino K, Mack EJ, Okano T, et al. A microcapsule self-regulating delivery system for insulin. J Control Release. 1990;12(3):235–239. doi:10.1016/0168-3659(90)90104-2
119. Makino K, Mack EJ, Okano T, et al. Self-regulated delivery of insulin from microcapsules. Biomater Artif Cells Immobilization Biotechnol. 1991;19(1):219–228. doi:10.3109/10731199109117829
120. Miyata T, Jikihara A, Nakamae K, et al. Preparation of poly(2-glucosyloxyethyl methacrylate)-concanavalin A complex hydrogel and its glucose-sensitivity. Macromol Chem Phys. 1996;197(3):1135–1146.
121. Yin R, Tong Z, Yang D, et al. Glucose-responsive insulin delivery microhydrogels from methacrylated dextran/concanavalin A: preparation and in vitro release study. Carbohydr Polym. 2012;89(1):117–123. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.02.059
122. Yin R, Wang K, Du S, et al. Design of genipin-crosslinked microgels from concanavalin A and glucosyloxyethyl acrylated chitosan for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;103:369–376. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.12.067
123. Ye T, Yan S, Hu Y, et al. Synthesis and volume phase transition of concanavalin A-based glucose-responsive nanogels. Polym Chem. 2014;5(1):186–194. doi:10.1039/C3PY00778B
124. Wu S, Huang X, Du X. Glucose- and pH-responsive controlled release of cargo from protein-gated carbohydrate-functionalized mesoporous silica nanocontainers. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013;52(21):5580–5584. doi:10.1002/anie.201300958
125. Wang Y, Fan Y, Zhang M, et al. Glycopolypeptide nanocarriers based on dynamic covalent bonds for glucose dual-responsiveness and self-regulated release of insulin in diabetic rats. Biomacromolecules. 2020;21(4):1507–1515. doi:10.1021/acs.biomac.0c00067
126. Chai Z, Dong H, Sun X, et al. Development of glucose oxidase-immobilized alginate nanoparticles for enhanced glucose-triggered insulin delivery in diabetic mice. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;159:640–647. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.097
127. Finotelli PV, Da Silva D, Sola-Penna M, et al. Microcapsules of alginate/chitosan containing magnetic nanoparticles for controlled release of insulin. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2010;81(1):206–211. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.07.008
128. Di J, Price J, Gu X, et al. Ultrasound-triggered regulation of blood glucose levels using injectable nano-network. Adv Healthc Mater. 2014;3(6):811–816. doi:10.1002/adhm.201300490
129. Di J, Yu J, Wang Q, et al. Ultrasound-triggered noninvasive regulation of blood glucose levels using microgels integrated with insulin nanocapsules. Nano Res. 2017;10(4):1393–1402. doi:10.1007/s12274-017-1500-z
130. Timko BP, Arruebo M, Shankarappa SA, et al. Near-infrared-actuated devices for remotely controlled drug delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(4):1349–1354. doi:10.1073/pnas.1322651111
131. Veiseh O, Tang BC, Whitehead KA, et al. Managing diabetes with nanomedicine: challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015;14(1):45–57. doi:10.1038/nrd4477
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
