Back to Journals » Patient Preference and Adherence » Volume 13
A survey on glycemic control rate of type 2 diabetes mellitus with different therapies and patients’ satisfaction in China
Authors Dong Q, Huang J, Liu S, Yang L, Li J, Li B, Zhao X, Li Z, Wu L
Received 19 December 2018
Accepted for publication 19 June 2019
Published 31 July 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 1303—1310
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S198908
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Qiaoliang Dong, Jin Huang, Shunying Liu, Lingfeng Yang, Juan Li, Bei Li, Xue Zhao, Zaizhao Li, Liaofang Wu
Clinical Nursing Teaching and Research Section, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan Province 410011, People’s Republic of China
Aim: To compare the blood glucose control of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) with different treatment methods, oral hypoglycemic agents (OHA) monotherapy, insulin injection and combined therapy (OHA + insulin injection) and evaluate their satisfaction with the medical care.
Methods: A total of 1512 T2DM patients were assessed, to compare the effects of different treatment methods on glycemic control in T2DM patients, the influencing factors of patients’ satisfaction with medical care measures and their relationship with glycemic control. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG), 2 hrs postprandial plasma glucose (2hPG) and HbA1c were measured as the standard of the glycemic control. Satisfaction was defined using the simplified version of DAWN of chronic disease care patient scale (PACIC - DSF).
Results: In this study, the FPG compliance rate, 2hPG compliance rate and HbA1c compliance rate were 25.5%, 22.7% and 19.5%, respectively. The differences in the glycemic control compliance rates of different treatment methods were not statistically significant. The total score of PACIC - DSF was 34.54±11.65(p>0.05), and the influencing factors included fast blood glucose (FBG) and 2hPG, 2hPG and PACIC - DSF were negatively correlated.
Conclusions: The T2DM glycemic control rate in China is currently low. From the score of the PACIC - DSF, there is no significant difference in general satisfaction with medical care measures in different treatments. What is more, education level, occupation and exercise of patients with type 2 diabetes had influence on PACIC - DSF score. Different treatment methods have no influence on the glycemic control of patients with T2DM. FPG value and the 2hPG value are negative correlation with the satisfaction of patients in medical care measures.
Keywords: type 2 diabetes mellitus, T2DM, glycemic control, PACIC - DSF
Introduction
With the rapid economic growth in China, people’s lifestyle has been greatly changed, and the prevalence rate of diabetes has also risen rapidly. According to a recent survey, an estimated 148.2 million Chinese adults have prediabetes.1 Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) accounts for ~90% of the 425 million people with diagnosed diabetes worldwide, and is projected to increase to ~629 million by 2045.2 Despite the variety of available glucose-lowering agents, many patients do not attain or maintain adequate glycemic control, emphasizing the need for further therapeutic options.3,4 T2DM incidence is increasing not only in adults but also in youths,5 making it the most urgent public health issue in both developed and developing countries.
T2DM is caused by insufficient insulin production from beta cells due to insulin resistance.6 A combination of lifestyle factors, most notably obesity, and genetic factors has been shown to exacerbate T2DM incidence.7–9 Good glycemic control can effectively reduce the occurrence of diabetes complications and improve the quality of life of patients. Oral hypoglycemic agents (OHA) and insulin therapy are commonly used in the treatment of T2DM method, and the treatment adherence for patients with high and low will directly affect the treatment effect and prognosis, medical treatment and nursing measures are very important, such as the effective health education can significantly improve diabetes blood glucose levels, so as to improve clinical treatment effect.10
Despite the increasing prevalence of T2DM in China, with over 110 million adult patients to date,11 medical treatment and nursing measures for glycemic control are limited. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the blood glucose control of T2DM patients with different treatment methods and their satisfaction with medical care measures was investigated, as well as the relationship between them.
Materials and methods
Study population
In the 2016 baseline survey, we studied 1512 subjects aged 18–80 years old from Hunan province in 18 units in third rate synthetic hospital, convenience sampling between January 2016 to April 2016 in 18 hospitals in the same period of OHA or insulin therapy in patients with T2DM (including outpatient and inpatient), inclusion criteria are: 1) in accordance with the 1999 World Health Organization diagnostic criteria;12 2) the course of diabetes is greater than or equal to 1 year; 3) oral administration of one or more hypoglycemic drugs and/or insulin for >3 months; 4) those with normal listening, speaking, reading and writing abilities; 5) those who agree to participate in this study and sign informed consent. Exclusion criteria are: 1) patients with type 1 diabetes, gestational diabetes and other patients with uncertain type of diabetes; 2) suffering from any mental illness or mental abnormality; 3) patients with other serious physical diseases (heart disease, tumor, etc.). A total of 1512 patients who met the standard were selected, and 1505 questionnaires were effectively recovered, and 7 subjects who were lost to follow-up, which yielded a follow-up rate of 99.5%. This study was approved by the ethics committee of The second Xiangya hospital of Central South University.
Assessments and diagnostic criteria
The general information questionnaire and the simplified version of DAWN (PACIC - DSF) of the chronic disease care patient scale were used. DAWN2™ is by far the largest diabetes psychology, wishes and requirements of the authority of the global research in the application research tools; PACIC - DSF scale13 was one of them; the scale has the patient as the center of a kind of evaluation method and is mainly used for evaluation of chronic disease care quality; it has a total of 12 items with 5 options, each score of 1~5, respectively. 1 point means “never” to 5 points means “always”. The total score is the sum of the scores of each question, with the highest score of 60. Significance of the score: the higher the score, the more support the patients received from the medical staff and the higher the satisfaction of the patients.
Fast blood glucose (FBG), 2 hrs postprandial plasma glucose (2hPG) and glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) values recently measured by the survey subjects in the outpatient and inpatient systems were collected by unit investigators as glycemic control indicators. The standards of the glycemic control were according to the guidelines for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes in China (2013 edition) formulated by the diabetes branch of Chinese medical association; successful glycemic control was defined as glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) <7% or fasting plasma glucose (FPG) <7.0 mmol/L; the goal of 2hPG was 4.4~10 mmol/L.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 18.0 (SPSS, Chicago, Illinois). Enumeration data were statistically described by frequency and rate (%), and measurement data were expressed as mean±SD. The glycemic control of T2DM patients with different treatment methods was compared with chi-square test. The influencing factors of the patients’ satisfaction with medical and nursing measures were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, and the correlation between the PACIC-DSF scale score and the glycemic control index was analyzed by Pearson correlation coefficient. All p-values are 2-tailed, and a p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Basic information about the research objects
A total of 1505 subjects aged from 18 to 80, with an average age of 60.62±11.29. There were 796 males (52.9%) and 709 females (47.1%). In terms of treatment methods, there were 489 patients (32.5%) receiving OHA (group A), 454 patients (30.2%) receiving insulin therapy (group B) and 562 patients (37.3%) receiving combined therapy (group C). Individual demographic characteristics including level of education, duration of T2DM, marital status, occupation and other parameters were obtained by a standardized interview. The glycemic control rates also differed significantly across subgroups defined by gender (p=0.005), occupation (p=0.018), chronic complications (p=0.028), history of drinking (p=0.003), duration of diabetes (p<0.001) in different treatment methods (Table 1).
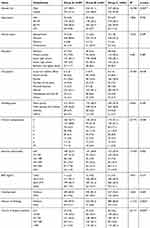 |
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of individuals with basic information at follow-up |
Subjects’ blood glucose control
Overall glycemic control of the FPG was between (9.50+4.08) mmol/L in patients with T2DM, and there were 384 cases with FPG between 4.4 and 7.0 mmol/L, and the control rate of FPG was 25.5%. There were 341 cases 2hPG in 4.4~10 mmol/L, and the control rate of 2hPG was 22.7%. There were 294 cases of HbA1c <7%, and the rate of reaching the standard of HbA1c was 19.5%.
Glycemic control standard of type 2 diabetes patients with different treatment methods: there were no statistically significant differences in FPG and 2hPG standard between these three groups, while there were statistically significant differences in HbA1c (p=0.000, p<0.01). The glycosylated blood glucose compliance rate of the OHA treatment group was higher than the other two groups, and the glycemic control was better than the other two groups (Table 2).
 |
Table 2 Glycemic control of the subjects |
Univariate analysis of the score of PACIC - DSF in T2DM patients with different treatment methods and their satisfaction with medical care measures
Respondents’ PACIC - DSF score was 34.54±11.65, total score of three groups of different treatment from PACIC - DSF which was no statistically significant difference. About the patients’ satisfaction with medical care measures, as the results are shown in Table 3, OHA +insulin group scored the highest points, OHA scored the second. Independent sample t-test and One-Way ANOVA were used to analyze the score of PACIC - DSF, and the results showed that the differences in education, occupation and exercise time of type 2 diabetes patients had an impact on the score of PACIC - DSF.
 |
Table 3 Scores of PACIC - DSF |
Level of education, occupation and exercise time were significant influence factors according to univariate analysis in Table 4. In agreement with this, One-Way ANOVA demonstrated that the more educated, the higher score they got (p<0.001), occupation (p<0.02), and the more exercise they had, the higher score they got (p<0.005), the factors above were significantly independent influence factors for the score of PACIC - DSF.
 |
Table 4 Single factor analysis of PAIC-DSF scores |
Correlation between PACIC - DSF score and blood glucose control index
Pearson correlation coefficient was used to analyze whether there was a linear correlation between the score of PACIC - DSF and the glycemic control indicators FPG, 2hPG and HbA1c (Table 5). The results showed that there was no correlation between HbA1c and the score of the PACIC - DSF scale. FPG and 2hPG showed a negative correlation with the score of the PACIC - DSF scale; that is, the lower the FPG and 2hPG, the higher the score of the PACIC - DSF scale.
 |
Table 5 Correlation between PACIC - DSF score and glycemic control index |
Discussion
Diabetes becomes a major public health issue and economic burden in China, so efficient glycemic control is considered a cornerstone of diabetic treatment. The results of this study showed that the compliance rate of HbA1c in the OHA group was higher than that in the other two groups, but the overall glycemic control was not good. FPG control compliance rate is 25.5%. The rate of reaching the target of 2hPG is 22.7%. A cross-sectional survey of T2DM patients in China conducted by the diabetes branch of the Chinese Medical Association for four consecutive years showed that the overall standard rate of HbA1c was low, with the four-year standard rate of 35.28%, 32.33%, 31.77% and 30.15%, respectively.14 The overall glycemic control rate in our study was 19.5%, lower than the 39.7% obtained in a study assessing individuals with HbA1c <7%.15 In a recent study in China, only 31.78% of 238,639 diabetes patients exhibited HbA1c <7% after treatment.16 The latter study assessed drug use (OADs and/or insulin) but did not include education level or lifestyle data. This may be related to the elderly in this study who are mainly retired, with more chronic complications and a longer course of disease because of the hyperglycemic memory.17 Furthermore, diabetic nephropathy accounts for high disability and mortality rates, and the management of the disease is far beyond satisfactory.18 In this study, the glycosylated glycemic compliance rate of the OHA group was higher than that of the other two groups, which may be related to the short course of disease, fewer chronic complications and relatively mild condition of the patients in the OHA group.
We evaluated smoking and drinking in diabetes complications, as they are proven risk factors for many chronic diseases. However, we found no significant effects for smoking but not for drinking, possibly due to the limited sample size and the larger impacts of other parameters studied, including education level, occupation and exercise time of T2DM. What is more, patients’ education could also help patients control drinking and smoking when these habits put them at risk. Therefore, significant efforts should be undertaken to monitor and encourage underclass patients, patients with low-level education, patients without sports to improve glycemic control, which would effectively improve treatment outcome in these individuals and decrease T2DM prevalence. The observation that individuals with high education levels have reduced risk of hyperglycemia may result from their better understanding of diabetes, obesity risks and glycemic control.19 These findings stress the importance of education in the epidemiology of T2DM.
The total score of PACIC - DSF in the study was 34.54±11.65, lower than that of Wang wei et al.20 Support from the medical team needs to be improved. About 80% of people with diabetes are treated with OHA.21 In terms of nursing planning, patients receiving insulin treatment received less support, and the other two groups were relatively more, which may be different from OHA in various types and taking time. Different drugs combination in OHA also caused different results in HbA1c.22 As for specific drugs in monotherapy, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors (AGIs) were persistently the most commonly prescribed, while metformin ranked 2nd.23 Medical staff paid more attention to it, but the publicity and education of insulin use should not be ignored, especially the prevention of the harm of hypoglycemia. Overall, however, medical support for patients with T2DM needs to be strengthened.
Interestingly, we found the results of this study showed that FPG and 2hPG were negatively correlated with the satisfaction of medical care measures. Taken depression as an example, it was independently associated with satisfaction and quality-of-life, but not diabetes control.24 Glycemic control is crucial for patients with T2DM. FBG, 2hPG and HbA1c are important indicators to measure the glycemic control. Low HbA1c was associated with better OHA adherence. The results of a recent systematic review showed a significant negative correlation between OHA adherence and HbA1c irrespective of the measure used.25 What is more, HbA1c was significantly different among the groups while there was no difference in FPG or 2hPG, indicating that the questionnaire could be informative to some extent regarding glyco-metabolic parameters. Studies have confirmed the positive correlation between anxiety and abnormal glucose metabolism.26 Glycemic control has been demonstrated that is closely associated with complications and prognosis.27–29 Good glycemic control can improve the psychological status of patients with T2DM.
To sum up, the current situation of glycemic control in Chinese diabetic patients is still worrying. High diabetes-related distress was more common among younger patients and patients with poorer glycemic control. High diabetes-related distress was associated with poorer quality of life and early screening and management of DRD is recommended.30 Consequently, the medical and nursing support for diabetic patients needs to be strengthened. Furthermore, the quality of diabetes care is widely sub-optimal and most of the interventions depend on active involvement and participation of patients. Thus, working through patient satisfaction may be an important way of improving diabetes care.31 For example, in future clinical work, guidance application can be actively popularized, patient diabetes education can be strengthened, diabetes patients can be effectively managed together with the community, the link between patients with diabetes can be strengthened and psychological support for patients can be provided. We hope to improve the standard rate of glycemic control of diabetic patients, reduce the complications of diabetes, improve the quality of life of patients and reduce the burden of public health resources.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University. Participants have provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Acknowledgments
This work was sponsored by Project of Chinese Nursing Association under Grant No. (ZHKY201416).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Yang WY, Lu JM, Weng JP, et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(25):2425–2426. doi.org/10.1056/nejmc1004671
2. Carracher AM, Marathe PH, Close KL. International diabetes federation 2017. J Diabetes. 2018;10:353–356. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.12644.
3. Aschner P, Adler A, Bailey C, et al. IDF Clinical Practice Recommendations for Managing Type 2 Diabetes in Primary Care. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation, ISBN; 2017. 978-2-930229-85-0.
4. de Pablos-Velasco P, Parhofer KG, Bradley C, et al. Current level of glycaemic control and its associated factors in patients with type 2 diabetes across Europe: data from the PANORAMA study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014;80:47–56. doi:10.1111/cen.12119
5. Samaan MC. Management of pediatric and adolescent type 2 diabetes. Int J Pediatr. 2013;2013:972034. doi:10.1155/2013/841360
6. Gardner D, Shoback D. Greenspans Basic and Clinical Endocriniology 9/E INKLING (ENHANCED EBOOK). New York: cGraw-Hill Medical; 2011.
7. Ripsin CM, Kang H, Urban RJ. Management of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am Fam Physician. 2009;79:29–36.
8. Riserus U, Willett WC, Hu FB. Dietary fats and prevention of type 2 diabetes. Prog Lipid Res. 2009;48:44–51. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2008.10.002
9. Gardner D, Shoback D. Greenspan’s Basic & Clinical Endocrinology.
10. Lui MQ. Analysis of influence of education on blood glucose control in diabetic patients. Electron J Pract Clin Nurs. 2017;2:30.
11. Xu Y, Wang L, He J, Bi Y, Li M, Wang T. Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA. 2013;310:948–959. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.168118
12. World Health Organization. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications: report of a WHO consultation; 2013, March, Available from: http://www.staff.ncl.ac.uk/philip.home/who_dmg.pdf.
13. Aragones A, Eric W, Schaefer D, et al. Validation of the Spanish translation of the Patient Assessment of Chronic Illness Care (PACIC) survey. Prev Chronic Dis. 2008;5(4):A113, 31.
14. Gao LL, Ji LN, Lu JM. Current status of blood glucose control and treatment of type 2 diabetes in China 2009–2012. Chin J Diabetes. 2014;22(7):594–598.
15. Zhang SL, Chen ZC, Yan L, et al. Determinants for inadequate glycaemic control in Chinese patients with mild-to-moderate type 2 diabetes on oral antidiabetic drugs alone. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011;124:2461–2468.
16. Ji LN, Lu JM, Guo XH, et al. Glycemic control among patients in China with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving oral drugs or injectables. BMC Public Health. 2013;13:602. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-13-602
17. Zhang LW, Chen BH, Tang LS. Metabolic memory: mechanisms and implications for diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012;96:286–293. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2011.12.006
18. Hu J, Ye M, Zhou Z. Aptamers: novel diagnostic and therapeutic tools for diabetes mellitus and metabolic diseases. J Mol Med. 2017;95:249. doi:10.1007/s00109-016-1485-1
19. World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. 2013. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/.
20. Wang W, Lou Q, Zhao F, et al. Comparison of diabetes-related socialpsychological issues between China and other countries: resultsfrom diabetes attitudes, wishes and needs second study. Chin J Diabetes. 2016;2016(1):29–34.
21. Ha KH, Kim DJ. Current status of managing diabetes mellitus in Korea. Korean J Intern Med. 2016;31:845–850. doi:10.3904/kjim.2016.253
22. Moon MK, Hur KY, Ko SH, et al. Combination therapy of oral hypoglycemic agents in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(5):357–366. doi:10.4093/dmj.2017.41.5.357
23. Wang XW, Cao YY, Wu Y, et al. The prescription pattern of initial treatment for type 2 diabetes in Beijing from 2011 to 2015. Medicine. 2019;98(8):e14370. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000014370
24. Katerndahl D, Calmbach WL, Becho J. Effect of comorbid depression on outcomes in diabetes and its relationship to quality of care and patient adherence: a statewide primary care ambulatory research and resources consortium study. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2012;14. PCC.11m01269.
25. Doggrell SA, Warot S. The association between the measurement of adherence to anti-diabetes medicine and the HbA1c. Int J Clin Pharm. 2014;36(3):488–497. doi:10.1007/s11096-014-9929-6
26. Huaifen M, Juan D, Huanle F, et al. Correlation of anxiety state with blood glucose control, microinflammation and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Hainan Med Coll. 2017;23(17):2346–2352.
27. Oomichi T, Emoto M, Tabata T, et al. Impact of glycemic control on survival of diabetic patients on chronic regular hemodialysis: a 7-year observational study. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:1496–1500. doi:10.2337/dc05-1887
28. Yoo DE, Park JT, Oh HJ, et al. Good glycemic control is associated with better survival in diabetic patients on peritoneal dialysis: a prospective observational study. PLoS One. 2012;(7):e30072. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030072
29. Poolsup N, Suksomboon N, Rattanasookchit S. Meta-analysis of the benefits of self-monitoring of blood glucose on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients: an update. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2009;11:775–784. doi:10.1089/dia.2008.0043
30. Lim SM, Siaw MYL, Tsou K, et al. Risk factors and quality of life of patients with high diabetes-related distress in primary care: a cross-sectional, multicenter study. Qual Life Res. 2018. doi:10.1007/s11136-018-1994-1
31. Narayan KM, Gregg EW, Fagot-Campagna A, et al. Relationship between quality of diabetes care and patient satisfaction. J Natl Med Assoc. 2003;95:64–70.
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
