Back to Journals » Cancer Management and Research » Volume 7
A profile of enzalutamide for the treatment of advanced castration resistant prostate cancer
Authors Greasley R, Khabazhaitajer M, Rosario D
Received 9 June 2014
Accepted for publication 7 September 2014
Published 12 June 2015 Volume 2015:7 Pages 153—164
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S50585
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Rosa Greasley,1 Mohammad Khabazhaitajer,1 Derek J Rosario2
1The Department of Oncology, The University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK; 2The Department of Urology, Sheffield Teaching Hospitals, The Royal Hallamshire Hospital, Sheffield, UK
Abstract: Recent advances in understanding the mechanisms underlying the development and progression of castration resistant prostate cancer from androgen-sensitive prostate cancer have provided new avenues exploring efficacious therapies in a disease which is the second leading cause of cancer deaths among men in the western world. In the evolution of second generation anti-androgens, enzalutamide, a novel androgen-receptor signaling inhibitor, has emerged targeting multiple steps within the androgenic stimulation pathway. This review discusses what is currently known of the mechanisms surrounding castration resistant prostate cancer development and the current human clinical trials to determine whether enzalutamide presents a new hope for men with advanced prostate cancer. The issues of therapy resistance, withdrawal effects and cross-resistance are briefly touched upon.
Keywords: enzalutamide, androgen receptor, metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer, MDV3100, anti-androgen
Introduction
Over 1.1 million cases of prostate cancer were recorded worldwide in 2012, making it the second most common malignancy among men, generating a heavy global health burden.1 Androgens, primarily testosterone and 5α-dihydrotestosterone, are responsible for growth and differentiation of cells within the prostate and consequentially are critically important in the development of prostate cancer. The disease is classified as castration responsive, when therapies known as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) which aim to remove circulating testosterone of gonadal origin, result in regression of the tumor. ADT can be achieved through surgical castration by bilateral orchiectomy or medical castration by gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs, either agonists or antagonists.2 Clinical response to ADT occurs in around 80% of cases, with clinical, radiological and biochemical improvement, potentially lasting several years (but typically is 2–2.5 years for men presenting with metastatic disease), a fact that signifies the pivotal role of the androgen receptor (AR) in most cases of prostate cancer. Progression and transition to a more lethal phenotype, which is distinguished by tumor growth at minimal levels of testosterone (<50 ng per deciliter) is known as castration resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). mCRPC is usually lethal and is responsible for an estimated 258,400 deaths annually.3
It was previously thought that loss of androgen responsiveness led to mCRPC development. More recent findings of ongoing active AR signaling in castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) cells, suggest that expression and functionality of the AR is almost never lost in this form of the disease.4 Indeed, what seems most likely is that AR sensitivity through a number of mechanisms, including overexpression, coactivator upregulation, gene amplification or AR mutation is retained in a significant proportion of cases of mCRPC, with stimulation and growth occurring at low levels of circulating androgens. As such, novel inhibitors of androgen synthesis and second generation anti-androgens have been identified, with better pharmacokinetic targeting, providing new hope for men with mCRPC. One of these is enzalutamide, recently approved by the US Food and Drug administration (FDA) at a dose of 160 mg/day, which has demonstrated significant efficacy in both pre-clinical and human based studies.
This article briefly illustrates the mechanisms thought to underlie the development of mCRPC from androgen responsive prostate cancer. We then provide a comprehensive narrative review of the clinical data involving enzalutamide to establish current knowledge on its efficacy, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
CRPC
Circulating androgens play a critical role in the development and progression of prostate cancer: ever since the initial description of orchiectomy for symptomatic metastatic prostate cancer by Huggins and Hodges,2 endocrine therapy in the form of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) has been the primary treatment for advanced prostate cancer.
Despite the initial response of prostate cancer to ADT in most cases, progression to CRPC is inevitable. mCRPC is the lethal form of prostate cancer; although there are a variety of treatment options available to ameliorate disease progression (Table 1), mCRPC remains incurable. Several in vitro and pre-clinical studies have suggested that androgenic stimulation continues to be involved in most cases of CRPC through several molecular and cellular mechanisms involving the AR. The AR (Figure 1) is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily of transcription factors (NR3C4 – nuclear receptor sub-family 3, group C, member 4).5 The receptor consists of a variety of functional motifs similar to other nuclear receptors. These functional motifs are composed of amino-terminal domain, DNA binding domain with two zinc-fingers, and a ligand binding domain (LBD). The amino-terminal domain and LBD contain activation function-1 and -2 domains respectively, essential for optimal transactivation. Mechanisms such as AR gene amplification6 and mutations, partial AR signaling blockade, AR splice-variant expression, AR co-regulator up and down regulation and stem cell involvement have all been implicated in enhancing AR functionality, resulting in promoting tumor growth, despite extremely low levels of circulating androgens4 (Figure 2).
  | Table 1 Current treatment options for CRPC |
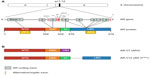  | Figure 1 Androgen receptor (AR) gene, protein and its constitutively active variants. |
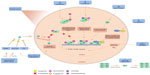  | Figure 2 Mechanism of castrate-resistant prostate cancer. |
It is clear that in most cases of mCRPC, a dynamic situation exists which poses an ongoing challenge to the development of truly effective disease-modifying treatments. Although many of the newer treatments for mCRPC continue to target the androgen axis, resistance to the agent with subsequent disease progression remains the norm. Anti-androgens in the form of flutamide and bicalutamide have been available for many years, with some evidence of providing additive benefit to ADT in terms of reduction in prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels (so-called complete androgen blockade or CAB) but little evidence of improved survival exists. Several phenomena such as the development of resistance to the initial agent and the anti-androgen withdrawal response demonstrate that adaptative changes such as co-activator upregulation with subsequent paradoxical agonist effects of the anti-androgen occur. Additionally, in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated the ability of anti-androgens to induce AR mutations, again resulting in paradoxical stimulation of tumor progression. Cross-resistance to agents with different mechanisms of action, such as abiraterone and enzalutamide, has been suggested by the results of smaller clinical trials, but the true benefits of simultaneous use and drug sequencing have yet to be demonstrated clinically. Finally, truly androgen independent tumor progression via cross-talk with MAP-kinase pathways (EGF and IGF-1) occurs, with some evidence to suggest that anti-androgens such as flutamide act directly on these pathways.7 Multiple mechanisms exist whereby resistance to novel anti-androgens develop and have been recently reviewed.8
Search strategy
A literature search was carried out (Figure 3) using the search engines Web of Science, Medline via Ovid, The Cochrane library, clinicaltrials.gov, and PubMed. The key search terms used were “Castrate resistant prostate cancer”, “CRPC”, “Enzalutamide”, “MDV3100”, “study”, “trial”, “safety”, “maximum tolerated dose”, and “side effect*” and literature was filtered by human studies and English language. Papers were assessed at abstract and title and subsequently full text. Exclusions were made if the papers were reviews, non-primary literature (ie, study or trials), and where enzalutamide was not the primary therapy tested. In addition, any primary literature which reported on results from a trial where there is already a leading full text article was also excluded, such as abstracts. Records obtained through clinicaltrials.gov were excluded where no results were available or where the trial had been published as a full text article. Following the initial literature search, the long awaited phase III PREVAIL trial was published.9 These new data are fundamental to our current knowledge of the efficacy of enzalutamide, so have also subsequently been included within our review.
Enzalutamide
Pharmacology and early results
The demonstration of a consistent increase in AR mRNA expression associated with CRPC development via anti-androgen resistance,10 led to the development of second generation anti-androgen therapeutics exploiting this characteristic.
Development of enzalutamide, formerly MDV3100, originated from the non-steroidal scaffolding chemical RU59063 where it was structurally and biochemically optimized for its use as an AR antagonist. In a human prostate cancer cell line engineered to overexpress wild-type AR (LNCaP/AR), enzalutamide was found to have a five- to eight-fold higher binding affinity to the AR than bicalutamide, a first generation anti-androgen in widespread clinical use.11 In addition, unlike the first generation anti-androgens, enzalutamide was a pure antagonist, apparently lacking any agonistic activity for AR targeted genes, PSA and transmembrane serine protease 2.11
Enzalutamide quickly demonstrated anti-tumor activity within LNCaP/HR and LAPC4/AR castration-resistant xenograft models,11 the results far superior to bicalutamide.
The findings of these pre-clinical studies subsequently led to early human studies with the initial aims of determining a safe dose and evidence of clinical efficacy.
Enzalutamide is rapidly absorbed with Cmax between 30 minutes and 4 hours following a single dose (160 mg/day).12 It has a long half-life of approximately 1 week (3–13 days irrespective of dose). Blood serum levels reach a steady state after a month and the concentrations observed at a daily dose of 150 mg are comparative to those in the xenograft models in preclinical studies of CRPC.12 In the first human trials conducted with enzalutamide, published in 2010,12 a total of 140 men with CRPC were enrolled. Cohorts of three to six men were treated with an initial oral dose of 30 mg/day and subsequent dose escalation. Sequential cohorts were treated at 30, 60, 150, 240, 360, 480, and 600 mg/day and enrollment was expanded by 24 men following a demonstration of a significant decrease in serum PSA levels of all of the first six men. Subsequent cohorts contained both chemotherapy naïve and post-chemotherapy men, with only the post-chemotherapy men receiving the highest doses at 480 and 600 mg/day.
Although the primary aim of these early studies was to establish the pharmacokinetics and safety of enzalutamide, significant dose-related anti-tumoral effects were observed: for example, results from the Scher et al 201212 study showed that at doses ranging from 60 mg to 480 mg per day, positron emission tomography (PET) scans indicated that 18-fluorodihydrotestosterone uptake was reduced by approximately 20%–100% (from baseline to 4 weeks post-treatment) in 18-fluorodihydrotestosterone avid lesions. Doses at 60 mg/day had a smaller reduction with a mean decrease of less than 50% when compared to higher doses which achieved a greater than 50% reduction. Differences between the higher doses were only apparent in the blood serum with enzalutamide concentrations at 12 μg/mL at 150 mg/day and >20 μg/mL at 150 mg and 480 mg/day.
This study established the presence of significant anti-tumor effects in a dose-dependent manner, however, a plateau appeared to be reached between 150–240 mg/day and a maximum tolerated dose of 240 mg/day was determined.
Clinical and radiological markers of the disease suggested considerable anti-tumor effects with a reduction in serum PSA levels greater than 50% seen in 51% of men in a post-chemotherapy setting and 62% in a chemotherapy naïve group. Radiological findings also demonstrated tumor regression (13/59 men), soft tissue stable disease (29/59 men) and stable disease in bone (61/109 men). In addition, the time to radiological progression was 47 weeks for all men; 29 weeks for the post-chemotherapeutic population, and not reached in chemotherapy naïve population. Circulating tumor cell counts, examined in 120 men, converted to favorable counts in 49% of the chemotherapy naïve population and 37% of the post-chemotherapy population. Of the men who entered the trial with favorable counts, 91% remained favorable.
Enzalutamide: current evidence
The early results seen with enzalutamide therapy led to the international phase III AFFIRM trial (A Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of the investigational drug MDV3100); a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial in men with prostate cancer who had received one or two previous chemotherapy treatments, one of which was docetaxel.13 The study recruited 1,199 men, randomized to enzalutamide (160 mg/day by oral administration) or placebo in a 2:1 ratio, resulting in 800 men within the enzalutamide arm and 399 men within the placebo arm. Baseline criteria included; demonstration of effective castration with circulating levels of testosterone at less than 1.7 nmol/L, previous treatment with docetaxel, and progressive disease (including increasing levels of PSA and radiographically confirmed progression). In addition, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status scores between 0–5 and pain intensity scores (the brief pain inventory short form 0–10) were recorded. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS); secondary endpoints included measures of response and progression (PSA and radiographic analysis), soft tissue response, quality of life (QoL) scores, and time to first skeletal event.
This study was terminated early at a planned interim analysis at 520 deaths. At this analysis, treatment with enzalutamide was associated with a 37% reduction in risk of death when compared with placebo. Consequentially, the trial was halted and men in the placebo arm were offered enzalutamide. The median OS with enzalutamide was 18.4 (95% confidence interval [CI] 17.3 – not yet reached) months compared to 13.6 (95% CI) months in the placebo arm. Superiority of enzalutamide over placebo was demonstrated in all secondary endpoints including PSA declines greater than 50% (54% versus [vs] 2%), soft tissue response (29% vs 4%), and improvement in QoL ( 43% vs 18%) in the enzalutamide group versus the placebo group respectively. Time to PSA progression was 8.3 months compared with 3.0 months, with similar findings for radiological progression. The median time on enzalutamide was 8.3 months compared to 3 months on placebo. Overall, within the intention-to-treat trial population, 39% on enzalutamide and 53% on placebo had died.
In summary, the study found that enzalutamide did indeed increase the survival of men who had previously been treated by chemotherapy for mCRPC.
More recent studies have assessed the efficacy of enzalutamide following prior treatment with docetaxel and abiraterone.14,15
The study by Schrader et al 2013,14 was conducted with 35 CRPC men from three German medical centers. At baseline, tumor specific data were obtained from medical records and clinical examination as well as PSA testing conducted every 3 weeks, for 1–12 weeks, and then every 6 weeks in follow-up. All men had previously progressed on abiraterone treatment with a mean termination of treatment 14 days prior to starting enzalutamide. The primary aim was to assess the efficacy of enzalutamide at a 160 mg/day oral dosage in a post-abiraterone setting.
A PSA decline of between 19%–99% on at least one occasion was found in 51.5% of men, with 28.6% (10/35) having a PSA decline of greater than 50%. At the time of analysis 13 men continued enzalutamide treatment for clinically stable disease or lack of better treatment options but the median duration of treatment was short at 5.1 months (3.8 months in men with a PSA regression less than 50% and 7.8 months in men with a regression greater than 50%). Men who failed to achieve a PSA decline of greater than 50% tended to have a high Gleason score (8–10) or more poorly-differentiated tumors. Three men who had no previous response to abiraterone were found to respond to enzalutamide. Two of the men who had no significant PSA decline (>50%) did not show a significant PSA response (≥50%) with first line ADT with luteinizing-hormone-releasing hormone analogs and bicalutamide; one had a Gleason score of 9 and demonstrated resistance to abiraterone previously and the other, with a Gleason of 7, responded well with abiraterone with a PSA decline of 99% but subsequent enzalutamide treatment was ineffective. A significant biochemical response to Enzalutamide was seen in 43.8% of men who had previously achieved >50% PSA decline on Abiraterone. Of 17 men assessed radiographically, only one demonstrated a partial response. Disease stability was demonstrated in 54.3% of men. The mean OS for all men was 7.1 months.
This study demonstrated only a moderate effect of enzalutamide following abiraterone treatment in CRPC men with 71.4% not achieving a PSA decline of greater than 50%. This suggests cross-resistance between abiraterone and enzalutamide. Nevertheless, three men previously insensitive to abiraterone were responsive to enzalutamide treatment, suggesting heterogeneity of response due to multiple drug targets.
Badrising et al15 conducted a multicenter observational study in mCRPC men who did not tolerate or progressed following docetaxel and abiraterone treatment. The study consisted of a total of 61 men given Enzalutamide 160 mg/day with the primary endpoint to determine the efficacy of enzalutamide following failed post-docetaxel and abiraterone. Baseline inclusion criteria included, evidence of progressive disease (PSA, radiographic or clinical) despite effective surgical or medical castration, ECOG score of 0–2 and, at the physicians discretion, no alternative treatment. Treatment was continued until clinical deterioration, disease progression, and/or unacceptable adverse effects at the discretion of the physician. Imaging studies were also performed, again at the discretion of the physician. Assessments were made monthly to evaluate progression-free survival (PFS) determined as PSA, radiographic, and clinical progression.
The median duration of enzalutamide treatment was 14.9 weeks and ≥30%, ≥50%, and ≥90% declines in PSA were observed in 46%, 21%, and 3% of men respectively. Eighteen men (30%) had no PSA decline at any time. Reasons for discontinuation included no initial activity (26% of men who discontinued), progressive disease (36% of men who discontinued), and death (3% of men who discontinued: one patient due to hemorrhagic stroke and one due to disease progression). One patient (2%) was intolerant, experiencing severe nausea and fatigue. At analysis, 19 men (31%) were still receiving enzalutamide. Median PFS was demonstrated at 12.0 weeks, median time to PSA progression 17.4 weeks, and median OS 31.6 weeks. There was no difference in maximum PSA response with enzalutamide treatment and duration of enzalutamide treatment between those who had had a greater than 50% PSA response or less than 50% PSA response on previous docetaxel or abiraterone treatment. This suggests that men who have previously progressed on abiraterone may have a modest PSA response on enzalutamide with previous response not predicting response to subsequent treatment.
The landmark study in the evolution of enzalutamide as treatment for mCRPC, the PREVAIL trial,9 included men who had not undergone any previous chemotherapy treatment and were at earlier stages of metastatic disease, unlike previous trials, including both mildly symptomatic and asymptomatic men. This study included a total of 1,717 men of ECOG status 0/1, who were randomly assigned to either enzalutamide 160 mg/day administered orally, or placebo. A total of 872 men were within the enzalutamide arm and 845 within the placebo control arm of the study. Criteria at baseline included histological or cytological confirmed prostate cancer with documented metastases and a PSA or radiographic progression in bone or soft tissue despite a serum testosterone level of ≤1.73 nmol following previous orchiectomy or luteinizing-hormone-releasing hormone therapy. Prior ADT was required and continued but men who had received previous cytotoxic chemotherapy, abiraterone or ketoconazole were excluded.
Treatment was discontinued if there was evidence of radiographic progression, initiation of chemotherapy or unacceptable adverse events. Radiographic disease was measured via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) with bone scans at the time of screening (9, 17, and 25 weeks with subsequent screening every 12 weeks after). Progression was measurable by the RECIST (Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors) criteria.16
The primary endpoints of this study were radiographic PFS and OS. Secondary endpoints included time until initiation of cytotoxic chemotherapy, time until the first skeletal event, best overall soft tissue response, time to PSA progression, and a PSA decline of ≥50% from the baseline. Further, exploratory endpoints included QoL (measurable by FACT-P [functional assessment of cancer therapy-prostate]) and a decline in PSA ≥90% from the baseline.
The study was halted at the planned interim review, given the strength of evidence showing superiority of enzalutamide over placebo in the primary endpoint of radiographic progression and all the planned secondary endpoints. The median duration of follow-up at this planned analysis was 22 months, with all endpoints reported for, at that point. There was a further updated analysis of OS after a further 116 additional deaths. The median time which men received enzalutamide was 16.6 months compared to 4.6 months for the placebo group. Radiographic PFS at 12 months was seen in 65% and 14% (enzalutamide vs placebo respectively) of men. The median time to radiographic progression was not reached in the enzalutamide group and was 3.9 months in the placebo group. As for OS, there were fewer deaths in the enzalutamide group when compared to the placebo group (28% vs 35% respectively); the hazard ratio indicating an overall risk reduction of death with enzalutamide of 21%. There was a modest improvement in median OS of approximately 2.2 months with enzalutamide, from 30.2 months to 32.4. When the additional deaths at a later unspecified interval were taken into account, the hazard ratio indicated a similar reduction in risk of death (27%) as at the planned interim analysis. Rather surprisingly, although the median OS on placebo remained similar (31.0 months) that for enzalutamide was not reached. The benefit of enzalutamide was evident as early as the first assessment at 2 months, thus indicating rapid early response.
Perhaps the most telling secondary endpoint was the prolongation of median time to cytotoxic treatment of around 18 months with enzalutamide. This was accompanied by a demonstrable increase in time to QoL deterioration of approximately 6 months. This indicates significant benefit in terms of QoL, particularly given the negative attitude most men have toward systemic chemotherapy.
Adverse events
Adverse effects have been graded on the National Cancer Institute common terminology criteria for adverse events. Some of the studies, for example Schrader et al 2014,14 did not report adverse event outcomes. The first reported human study of enzalutamide12 noted the most common adverse effect was fatigue at doses of 240 (one of 29), 360 (three of 28), and 480 mg/day (five of 22). Dose reduction resulted in resolution of symptoms. Grade 2 adverse events found to be most common were nausea, constipation, diarrhea, and anorexia; one patient ceasing treatment due to nausea but it was noted this was also present at baseline. There were two witnessed seizures at doses of 600 and 360 mg/day and one possible seizure at 480 mg/day. However, all these men had extensive complicated medical histories. An additional two men discontinued treatment due to a rash and one man due to myocardial infarction; this patient had also had a complicated medical history. It is likely that men with more complex medical histories may be at an increased risk of more severe adverse events and further complications, so results may not truly reflect enzalutamide’s toxicity.
The study by Badrising et al15 similarly concluded that the majority of adverse events were grade 1 (65%), with grade 2 and 3 adverse events being notably less common (26% and 9% respectively). Grade 1 adverse events included hot flashes and the most common grade 2/3 events were fatigue, observed in 59% of men, followed by musculoskeletal pain in 27% of men.
Within the phase III AFFIRM trial, fatigue, hot flashes, and diarrhea were all reported in higher numbers within the enzalutamide group when compared to the placebo controls. Seizures occurred in five men (0.6%) within the enzalutamide group with none in the placebo group. However, the enzalutamide group exhibited lower numbers of grade 3 or above adverse events when compared to the placebo group (45.3% vs 53.1%) with the time to events significantly longer (12.6 and 4.2 months respectively). Cardiac disorders within the enzalutamide group were 6% and 8% for the placebo group, however, hypertension appeared marginally higher in the enzalutamide group (6.6% vs 3.3%). There were no other significant differences in adverse events within the two groups. Interestingly, this study reported no musculoskeletal pain which was present in 27% of the men in the phase I/II study by Badrising et al.15
Within the enzalutamide group in the PREVAIL study, common adverse events which occurred 20% more and at least two percentage points more than in the placebo group were fatigue, back pain, constipation, and arthralgia. After adjusting for length of exposure, events which were higher within the enzalutamide group when compared to the placebo group were hot flashes, hypertension, and falls, with hypertension the most common grade 3 or higher event (reported in 7% of patients). The most common cardiac event was atrial fibrillation, reported in 2% of patients within the enzalutamide group and 1% of the placebo group. One patient within each study arm reported a seizure. There was no evidence of hepatotoxicity.
The PREVAIL study was carried out in a pre-chemotherapy setting and for mPCa patients who were mildly symptomatic or asymptomatic. The median reporting time to adverse events, which reflected the increased period of exposure of patients to enzalutamide, was 17.1 months. Adverse events at grade 3 or higher occurred in 43% of men in the enzalutamide group and 37% within the placebo group. Unfortunately, the median time to emergence of the first grade 3 (or greater) adverse event was 22 months, with physical deterioration leading to death being the most common. As such, it is impossible to assign causality to the adverse events. The data from this trial subsequently suggest a promising side effect profile in a pre-chemotherapy setting, albeit with a median length of follow-up at only 22 months. Although tolerability appeared relatively good within the early trials, prior to the PREVAIL study, men presenting at earlier stages are less likely to have complex clinical disease than those who are post-chemotherapeutic, so it could be argued that the adverse event data in the PREVAIL trial give a better indication of enzalutamide’s true toxicity. However, given that these men are likely to survive for longer, there remains insufficient evidence examining less acute or chronic side effects such as cardiovascular morbidity. The only studies to have specifically been designed to examine adverse events and safety have been the smaller phase I/II studies. The evidence to date does not provide sufficient data in terms of the number of men enrolled or the length of follow-up to justify completely what was concluded as an “excellent side-effect profile”, particularly as the drug is likely to be initiated earlier in the disease, given the demonstration of improved OS. Currently, the true lond-term adverse event rate of enzalutamide cannot be determined until treatment for men with earlier stage disease is approved. Thus, there is an ongoing need for the adverse eventsof enzalutamide to be studied and documented.
Cross resistance
One of the major mechanisms that have been postulated to be responsible for an overall resistance to conventional and next generation ADT is the synthesis of AR splice variants (AR-V) (Figure 2) that lack the LBD. Indeed, the transcriptionally active NDT and presence of DNA binding domains are sufficient enough for AR-V to function as a transcription factor in a ligand-independent manner. Over-expression of AR-V at mRNA and protein levels in prostate cancer tissue is associated with disease progression and poor prognosis.17
Recent studies show that enzalutamide is moderately effective after abiraterone failure. In vitro studies revealed that induction of AR-V is responsible for prompt resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone.18 However, a small number of abiraterone-insensitive patients responded to enzalutamide which demonstrates that there are other possible mechanisms of resistance. One possible mechanism for abiraterone resistance can be gain-of-function AR mutations which sensitizes AR to non-androgenic steroids through the promiscuous pathway (Figure 2). Evaluating the therapy responses in the reverse sequence, enzalutamide-abiraterone, demonstrates fewer responses to abiraterone treatment after enzalutamide. AR LBD mutations are known to cause conversion of steroidal and non-steroidal anti-androgens such as bicalutamide from antagonist to an agonist. This could suggest the role of such mutations in resistance to enzalutamide in abiraterone-sensitive patients.14
Cost-effectiveness
A press release by NICE (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence) published in 201319 concluded that the cost per quality of life years (QALY) for enzalutamide, although uncertain when compared with abiraterone, is below the NICE guideline of £30,000 per QALY gained. The cost for a single pack of 112 40 mg capsules is £2,734.67 and this, when based on an average length of treatment around 8.5 months and a dosage per day of 160 mg, amounts to an average of £25,269.
Conversely, a study by Wilson et al, comparatively assessed cost-effectiveness of the three major treatment options for CRPC post-docetaxel; abiraterone, cabazitaxel, and enzalutamide; to a placebo group.20 It concluded that enzalutamide was less cost-effective than abiraterone (Table 2) after adjustments were made against the other trials’ placebo controls due to large differences between survival of the study groups. In this case, Wilson et al concluded that abiraterone was the most cost-effective treatment available for CRPC and recommended its use over the other treatment options. However, had these adjustments not been made, enzalutamide’s cost per QALY would fall to $33,532/QALY, well below the US threshold of US$100,000, and making it the most cost effective. Additionally, more recent data presented at the 2014 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium21 also found that abiraterone was more cost effective per QALY than enzalutamide. The population, intervention, comparison, and outcomes approach was used to compare the data from the abiraterone study COU-AA-301 and the AFFIRM trial. The data suggested that abiraterone was substantially cheaper than enzalutamide with an average saving of US$13,322 per patient.
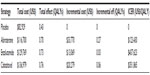  | Table 2 Cost effectiveness analysis – results |
However, the cost-effectiveness data have been obtained from studies which focused on the use of enzalutamide in a post-chemotherapy setting, therefore no data are available on the longer term use of enzalutamide prior to chemotherapy, which may result in long-term effects, potential risks, and excess treatment costs. In addition, the efficacy of enzalutamide demonstrated at late stage CRPC will surely warrant its use in earlier stages of disease. As a result, true cost-effectiveness data cannot be demonstrated until evaluated with data from studies involving greater long-term follow-up and earlier stage prostate cancer.
Ongoing issues
Uncertainty remains around the timing, sequence, and additive benefits of the treatment options available for the treatment of mCRPC. Enzalutamide has clear advantages over some of the other options (Table 1) in terms of ease of administration, no requisite co-medication (eg, steroids,) and a favorable side effect profile (eg, compared to systemic docetaxel). The current evidence would suggest significant delay in QoL deterioration, disease progression and requirement for further therapy, but with only a modest improvement in OS shown to date. Combining treatments has a rationale (eg, abiraterone with enzalutamide) as many of the options have different mechanisms of action, however the long-term results and cost-effectiveness of such an approach are yet to be demonstrated. Similarly, the results of trials evaluating the effects of enzalutamide in maximal androgen blockade, monotherapy, and in earlier stage disease are awaited.
Conclusion
The disease-modifying effects of enzalutamide are clear from the clinical trial data and match the expectation raised by the early in vivo models. That there is considerable benefit at all stages of metastatic CRPC is equally clear, however questions remain around optimal timing of initiation of therapy, identification of men most likely to benefit, and cost-effectiveness of the treatment when compared with other options, either in isolation, or as is most likely in such a progressive lethal disease, in combination. Equally, it is not clear yet as to the long-term effects enzalutamide may pose for these men. Current data on more acute adverse events within these trials are very promising, but with little information given on the long-term follow-up of these men, further data are essential and eagerly awaited.
In conclusion, enzalutamide, a second generation anti-androgen, is among a number of agents demonstrating promise for men progressing with mCRPC. Clinical trials have clearly demonstrated enzalutamide’s efficacy for men with advanced disease but further data involving its use in less advanced stages will give a greater insight into the potential of enzalutamide. We have yet to establish the full benefit this drug may have for men with prostate cancer, but the future looks brighter for men with a hitherto essentially untreatable condition.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to acknowledge Chidi Molokwu as clinical advisor.
Disclosure
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose in this work.
References
globocan.iarc.fr [homepage on the Internet]. Prostate Cancer: Estimated incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide in 2012. GLOBOCAN 2012. Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_cancer.aspx. Accessed May 8, 2014. | |
Huggins C, Hodges CV. Studies on prostatic cancer. I. The effect of castration, of estrogen and androgen injection on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. CA Cancer J Clin. 1972;22(4):232–240. | |
Scher HI, Halabi S, Tannock I, et al. Design and end points of clinical trials for patients with progressive prostate cancer and castrate levels of testosterone: recommendations of the Prostate Cancer Clinical Trials Working Group. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(7):1148–1159. | |
Feldman BJ, Feldman D. The development of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001;1(1):34–45. | |
Lu NZ, Wardell SE, Burnstein KL, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. LXV. The pharmacology and classification of the nuclear receptor superfamily: glucocorticoid, mineralocorticoid, progesterone, and androgen receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2006;58(4):782–797. | |
Visakorpi T, Hyytinen E, Koivisto P, et al. In vivo amplification of the androgen receptor gene and progression of human prostate cancer. Nat Genet. 1995;9(4):401–406. | |
Zhu ML, Kyprianou N. Androgen receptor and growth factor signaling cross-talk in prostate cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2008;15(4):841–849. | |
Yuan X, Cai C, Chen S, Yu Z, Balk SP. Androgen receptor functions in castration-resistant prostate cancer and mechanisms of resistance to new agents targeting the androgen axis. Oncogene. 2014;33(22):2815–2825. | |
Beer TM, Armstrong AJ, Rathkopf DE, et al. Enzalutamide in Metastatic Prostate Cancer before Chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(5):424–433. | |
Chen CD, Welsbie DS, Tran C, et al. Molecular determinants of resistance to antiandrogen therapy. Nat Med. 2004;10(1):33–39. | |
Tran C, Ouk S, Clegg NJ, et al. Development of a second- generation antiandrogen for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Science. 2009;324(5928):787–790. | |
Scher HI, Beer TM, Higano CS, et al. Antitumour activity of MDV3100 in castration-resistant prostate cancer: a phase 1–2 study. Lancet. 2010;375(9724):1437–1446. | |
Scher HI, Fizazi K, Saad F, et al. Increased Survival with Enzalutamide in Prostate Cancer after Chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(13):1187–1197. | |
Schrader AJ, Boegemann M, Ohlmann CH, et al. Enzalutamide in Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer Patients Progressing after Docetaxel and Abiraterone. Eur Urol. 2014;65(1):30–36. | |
Badrising S, van der Noort V, van Oort IM, et al. Clinical activity and tolerability of enzalutamide (MDV3100) in patients with metastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer who progress after docetaxel and abiraterone treatment. Cancer. 2014;120(7):968–975. | |
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 2009;45(2):228–247. | |
Li Y, Chan SC, Brand LJ, Hwang TH, Silverstein KAT, Dehm SM. Androgen receptor splice variants mediate enzalutamide resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2013;73(2):483–489. | |
Mostaghel EA, Marck BT, Plymate SR, et al. Resistance to CYP17A1 inhibition with abiraterone in castration-resistant prostate cancer: induction of steroidogenesis and androgen receptor splice variants. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(18):5913–5925. | |
nice.org.uk [homepage on the Internet]. NICE says yes to new prostate cancer drug; 2013. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Available from: http://www.nice.org.uk/News/Press-and-Media/nice-says-yes-to-new-prostate-cancer-drug. Accessed May 29, 2014. | |
Wilson L, Tang J, Zhong L, et al. New therapeutic options in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Can cost-effectiveness analysis help in treatment decisions? J Oncol Pharm Pract. Epub November 14, 2013. | |
Tracy L, Thompson M. An indirect treatment comparison (ITC) and cost-effectiveness analysis of abiraterone acetate and enzalutamide for the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) post-chemotherapy. In: General Poster Session B: Prostate, Penile, Urethral, and Testicular Cancers, and Urothelial Carcinoma; qGenitourinary Cancers Symposium. | |
Zhang H, Zhan Y, Liu X, et al. Splicing variants of androgen receptor in prostate cancer. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2013;1(1):18–24. | |
Hornberg E, Ylitalo EB, Crnalic S, et al. Expression of androgen receptor splice variants in prostate cancer bone metastases is associated with castration-resistance and short survival. PLoS One. 2011;6(4):e19059. | |
De Bono JS, Logothetis CJ, Molina A, et al. Abiraterone and Increased Survival in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(21):1995–2005. | |
Ishizaki F, Nishiyama T, Kawasaki T, et al. Androgen deprivation promotes intratumoral synthesis of dihydrotestosterone from androgen metabolites in prostate cancer. Sci Rep. 2013;3:1528. | |
Wilson EM. More evidence intratumoral DHT synthesis drives castration-resistant prostate cancer. Asian J Androl. 2014;16(1):99–100. | |
Holzbeierlein J, Lal P, LaTulippe E, et al. Gene expression analysis of human prostate carcinoma during hormonal therapy identifies androgen-responsive genes and mechanisms of therapy resistance. Am J Pathol. 2004;164(1):217–227. | |
Bubendorf L, Kononen J, Koivisto P, et al. Survey of gene amplifications during prostate cancer progression by high-throughout fluorescence in situ hybridization on tissue microarrays. Cancer Res. 1999;59(4):803–806. | |
Mao X, Yu Y, Boyd LK, et al. Distinct genomic alterations in prostate cancers in Chinese and Western populations suggest alternative pathways of prostate carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2010;70(13):5207–5212. | |
Edwards J, Krishna NS, Grigor KM, Bartlett JM. Androgen receptor gene amplification and protein expression in hormone refractory prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 2003;89(3):552–556. | |
Gregory CW, Johnson RT, Mohler JL, French FS, Wilson EM. Androgen receptor stabilization in recurrent prostate cancer is associated with hypersensitivity to low androgen. Cancer Res. 2001;61(7):2892–2898. | |
Scher HI, Sawyers CL. Biology of progressive, castration-resistant prostate cancer: directed therapies targeting the androgen-receptor signaling axis. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(32):8253–8261. | |
Beltran H, Yelensky R, Frampton GM, et al. Targeted next-generation sequencing of advanced prostate cancer identifies potential therapeutic targets and disease heterogeneity. Eur Urol. 2013;63(5):920–926. | |
Marcelli M, Ittmann M, Mariani S, et al. Androgen receptor mutations in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2000;60(4):944–949. | |
Taplin ME, Bubley GJ, Shuster TD, et al. Mutation of the androgen-receptor gene in metastatic androgen-independent prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 1995;332(21):1393–1398. | |
Gottlieb B, Beitel LK, Nadarajah A, Paliouras M, Trifiro M. The androgen receptor gene mutations database: 2012 update. Hum Mutat. 2012;33(5):887–894. | |
Zhao XY, Malloy PJ, Krishnan AV, et al. Glucocorticoids can promote androgen-independent growth of prostate cancer cells through a mutated androgen receptor. Nat Med. 2000;6(6):703–706. | |
Zhang X, Morrissey C, Sun S, et al. Androgen receptor variants occur frequently in castration resistant prostate cancer metastases. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27970. | |
Watson PA, Chen YF, Balbas MD, et al. Constitutively active androgen receptor splice variants expressed in castration-resistant prostate cancer require full-length androgen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(39):16759–16765. | |
Watson PA, Chen YF, Balbas MD, et al. Constitutively active androgen receptor splice variants expressed in castration-resistant prostate cancer require full-length androgen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(39):16759–16765. | |
Agoulnik IU, Weigel NL. Androgen receptor action in hormone-dependent and recurrent prostate cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2006;99(2):362–372. | |
Koochekpour S. Androgen receptor signaling and mutations in prostate cancer. Asian J Androl. 2010;12(5):639–657. | |
Wang Q, Li W, Zhang Y, et al. Androgen receptor regulates a distinct transcription program in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cell. 2009;138(2):245–256. | |
McDonnell TJ, Troncoso P, Brisbay SM, et al. Expression of the protooncogene bcl-2 in the prostate and its association with emergence of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1992;52(24):6940–6944. | |
Raffo AJ, Perlman H, Chen MW, Day ML, Streitman JS, Buttyan R. Overexpression of bcl-2 protects prostate cancer cells from apoptosis in vitro and confers resistance to androgen depletion in vivo. Cancer Res. 1995;55(19):4438–4445. | |
Debes JD, Tindall DJ. Mechanisms of androgen-refractory prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(15):1488–1490. | |
Colombel M, Symmans F, Gil S, et al. Detection of the apoptosis-suppressing oncoprotein bc1-2 in hormone-refractory human prostate cancers. Am J Pathol. 1993;143(2):390–400. | |
Collins AT, Berry PA, Hyde C, Stower MJ, Maitland NJ. Prospective identification of tumorigenic prostate cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65(23):10946–10951. | |
Toivanen R, Frydenberg M, Murphy D, et al. A preclinical xenograft model identifies castration-tolerant cancer-repopulating cells in localized prostate tumors. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5(187):187ra171. | |
Parker C, Nilsson S, Heinrich D, et al. Alpha Emitter Radium-223 and Survival in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(3):213–223. | |
Karantanos T, Corn PG, Thompson TC. Prostate cancer progression after androgen deprivation therapy: mechanisms of castrate resistance and novel therapeutic approaches. Oncogene. 2013;32(49):5501. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.

