Back to Journals » International Journal of General Medicine » Volume 14
A Highly Responsive Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma with Liver Metastasis: A Rare Case Report
Authors Xu Y, Du J, Wang Y, Gong B, Wang Y, Qian L, Tan Y
Received 24 November 2020
Accepted for publication 27 January 2021
Published 16 February 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 487—496
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJGM.S293806
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Yixin Xu,1 Jianguo Du,1 Yibo Wang,1 Bo Gong,2 Yue Wang,3 Leiming Qian,4 Yulin Tan1
1Department of General Surgery, Changzhou Wujin People’s Hospital Affiliated to Jiangsu University; The Wujin Clinical College of Xuzhou Medical University, Changzhou, Jiangsu, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of Imaging, Changzhou Wujin People’s Hospital Affiliated to Jiangsu University; The Wujin Clinical College of Xuzhou Medical University, Changzhou, Jiangsu, People’s Republic of China; 3Department of Oncology, Changzhou Wujin People’s Hospital Affiliated to Jiangsu University; The Wujin Clinical College of Xuzhou Medical University, Changzhou, Jiangsu, People’s Republic of China; 4Department of Pathology, Changzhou Wujin People’s Hospital Affiliated to Jiangsu University; The Wujin Clinical College of Xuzhou Medical University, Changzhou, Jiangsu, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Yulin Tan Tel +86-0519-88587142
Email [email protected]
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the most refractory and lethal cancer. The overall survival is dismal due to the high frequency of recurrence and metastasis after surgery and resistance to chemotherapy. Patients with the locally advanced or metastatic disease usually have the poorest prognosis. Herein, we report a rare highly responsive PDAC with liver metastasis.
Case Presentation: A 49-year-old female presented with dull abdominal and back pain, discomfort after eating, fatigue, and recent weight loss of 5 kg. Clinical examination was normal and no relevant oncological history was observed. A routine blood test showed low red blood cell count and low hemoglobin level. Markedly increased carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and carbohydrate antigen (CA) 125 levels were detected. Computer tomography (CT) of the abdomen revealed a massive pancreatic tumor with the invasion of almost all important surrounding blood vessels and liver metastasis. After the genetic test and percutaneous biopsy for this tumor, a multidisciplinary team (MDT) discussion was initiated. Subsequently, oral chemotherapy (S-1) and 125I radiative seeds implantation were recommended. Surprisingly, the tumor shrank significantly after treatment. On August 14, 2019, pancreatoduodenectomy was performed. The tumor was successfully resected and liver metastasis was not detected. Based on the postoperative histopathological result, there was only fibrous tissue hyperplasia and inflammatory cell infiltration. Besides, no tumor tissue was found. Until now, through outpatient follow-up, no signs of recurrence and metastasis have been observed.
Conclusion: Although the therapeutic efficacy and prognosis of PDAC are dismal, we successfully cured a patient with a metastatic disease through multidisciplinary cooperation. However, the therapeutic experience should be summarized and further research should be performed to confirm whether it is appropriate for other PDAC patients.
Keywords: pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, metastasis, diagnosis, chemotherapy, multidisciplinary team
Introduction
According to the estimates of GLOBOCAN 2018, pancreatic cancer (PC) is the seventh leading cause of cancer mortality in both males and females worldwide.1 The incidence rates are 3 to 4-fold higher in higher human development index (HDI) countries. PC is projected to surpass breast cancer as the third leading cause of cancer death in European countries in the future. Additionally, its prognosis is rather poor: mortality (n = 432,000) is almost the same as the incidence of new cases (n = 459,000).
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the most common type among PC. The 5-year overall survival (OS) of PDAC is lower than 5%, which is the worst among all cancer types. Additionally, the 5-year OS would significantly reduce to a dismal 3% with distant metastasis.2,3 Several studies have shown that the 5-year OS of resected PDAC patients ranges from 8.1% to 30.7%.4–6 The significant differences of the 5-year OS between resectable PDAC and PDAC of all stages demonstrated even a poorer prognosis for the 5-year OS of unresectable PDAC patients. However, although chemotherapy could be the only choice, the therapeutic efficacy is far from satisfactory.
Because the early stage of PDAC has almost no symptoms and signs, patients presenting with abdominal pain, back pain, or jaundice often have locally advanced or metastatic disease.7 However, only 15–20% of patients are likely to receive a radical surgery at the time of presentation.8 Therefore, for most patients, this disease is almost incurable, and the survival time is rather short.
Herein, we document a rare highly responsive PDAC with liver metastasis. In this case, the patient received a satisfactory therapeutic result through our multidisciplinary team (MDT) treatment.
Case Presentation
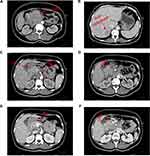
A 49 year-old female patient visited our outpatient department on March 11, 2019, and presented with dull abdominal and back pain, discomfort after eating, fatigue, and a recent weight loss of 5 kg. These symptoms lasted for about two months and were not relieved. Clinical examination was normal. Besides, there was no relevant tumor or family medical history. Blood routine test showed moderate anemia: low red blood cell count (3.21 × 109/L; normal 3.80–5.10 × 109/L), low hemoglobin level (70.0 g/L; normal 115.0–150.0 g/L). However, markedly increased carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) (941.60 ng/mL; normal 0–5.00 ng/mL) and carbohydrate antigen (CA) 125 (271.60 U/mL; normal 0–20.00 U/mL) levels were detected. Computer tomography (CT) of the abdomen revealed a huge PC with the right liver metastasis (Figure 1).
After preliminary evaluation by our department, surgery could not be performed for this patient due to the huge volume of tumor, liver metastasis, invasion of gastroduodenal artery (GDA), superior mesenteric artery (SMA), superior mesenteric vein (SMV), and anterior wall of portal vein (PV).
Subsequently, an MDT treatment was employed. The imaging department, interventional department, and oncology department were invited for a discussion and development of a detailed therapeutic plan.
First, a genetic test for the patient was performed. The result showed that there was no somatic and germline mutation, no genetic mutation covered by the Chinese society of clinical oncology (CSCO) guideline for diagnosis and treatment of PC, and low tumor mutation burden (1.9/Mb). Besides, compared to other chemotherapeutic drugs, a relative lower toxic side effect of fluorouracil drugs was detected.
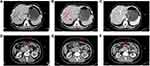
Second, percutaneous biopsy guided by CT for the primary lesion was performed by interventional department doctors. Histopathological results showed that this tumor was a poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma (Figure 2). Tumor immunohistochemistry results were as follows: CK (+), CK7 (+), CK20 (+), Villin (-), P63 (-), P40 (-), Syn (-), and CgA (-).
 |
Figure 2 The histopathological result of percutaneous biopsy guided by CT. (A) 4×10 magnification; (B) 10×10 magnification; (C) 20×10 magnification. |
Subsequently, transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), chemotherapy, and radiative seeds implantation were performed based on National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) clinical practice guidelines for pancreatic adenocarcinoma9 and the results of genetic test and percutaneous biopsy.
The primary lesion and right liver metastasis were stained through the superior mesenteric artery and celiac trunk angiography (Figure 3). After entering the blood supply artery of PC using an ultramicro catheter (MC-PE27131, TERUMO, Japan), chemotherapeutic drugs (gemcitabine 1.0 mg + cisplatin 40 mg + recombinant human endostatin 15mg) were given. A similar procedure was performed for the right liver metastasis but with different dosages (gemcitabine 0.2 mg + cisplatin 20 mg + recombinant human endostatin 15mg). TACE has performed again on April 18, 2019 with a similar procedure as the previous one.
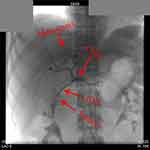 |
Figure 3 The X-ray image during TACE. Abbreviation: TACE, transarterial chemoembolization. |
In addition, S-1 (20mg per capsule) was given with a dose of 60 mg, twice a day. The whole therapeutic cycle was 28 days, and an interval of 14 days was between 2 cycles. S-1 is composed of tegafur (FT, a precursor of 5-FU) and gimeracil (CDHP. It can inhibit the catabolism of 5-FU released from FT by dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase.), and otilasi (Oxo. It can block the phosphorylation of 5-FU and reduce the toxicity of 5-FU.).
On May 20, 125I radiative seeds were implanted around the primary lesion using laparoscopy.
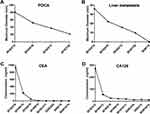
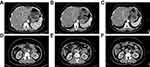
CT-chest-abdomen, CEA, and CA-125 were performed on April, May, and July, respectively. Surprisingly, we noted that the tumor shrunk rapidly (Figure 4) and concurrently with tumor biomarkers decrease (Figure 5).
On August 14, after evaluation by the general surgery department surgeons and imaging department doctors, the tumor shrunk significantly and the invasion of surrounding blood vessels also reduced. As a result, pancreatoduodenectomy was performed. During surgery, we found that there was a hard, irregular mass (2×2×1.5 cm) at the head of the pancreas (Figure 6). It adhered to the SMA and the anterior wall of the PV. However, through careful dissection, it was completely removed. Subsequently, the right liver was carefully examined for metastasis using intraoperative color doppler ultrasound, based on the images of the CT before surgery, but nothing was found. Finally, after thorough hemostasis and cleaning, two drainage tubes were placed in the surgical site. Generally, this operation was a great success.
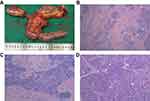 |
Figure 6 The postoperative specimen and histopathological result. (A) Postoperative specimen; (B) 4×10 magnification; (C) 10×10 magnification; (D) 20×10 magnification. |
Postoperative histopathological results showed that there were only fibrous tissue hyperplasia, and inflammatory cell infiltration. Besides, peripheral and mesenteric lymph nodes showed reactive hyperplasia (Figure 6). However, no neoplastic tissue was found.
After surgery, the patient recovered smoothly without any postoperative complication, and was finally discharged on August 31, 2019.
During postoperative follow-up, the patient visited our outpatient department every three months for examinations. The CT-chest-abdomen showed no signs of recurrence and metastasis (Figure 7). Tumor biomarkers (CEA and CA-125) remained within the normal range (Figure 5). The whole therapeutic process is shown in Figure 8. The last follow-up examination was performed on October 14, 2020. All main laboratory test results are shown in Table 1.
 |
Figure 8 The flow chart of multidisciplinary treatment. |
 |
Table 1 Main Laboratory Test Results |
At present, a regular dose of S-1 per therapeutic cycle has been recommended for this patient. Afterward, positron emission tomography-CT (PET-CT) will be arranged for the patient to check for potential recurrence and metastasis.
Discussion
Although the OS of PDAC is dismal, we report a case of a PDAC patient with liver metastasis who successfully recovered through multiple therapeutic procedures, including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgery. Until now, the patient is well and has shown no signs of recurrence and metastasis.
According to NCCN clinical practice guidelines for pancreatic adenocarcinoma, if metastatic PC patients have a good Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS) 0–1, good biliary drainage and adequate nutritional intake, systemic therapy is recommended.9 The preferred regimens are as follows: (1) FOLFIRINOX or modified FOLFIRINOX; (2) Gemcitabine + albumin-bound paclitaxel; and (3) Gemcitabine + cisplatin (only for Known BRCA1/2 or PALB 2 mutations). In our case, due to personal reasons and the unwillingness of the family members to disclose the actual condition to the patient, the oncology department doctor recommended oral chemotherapy (S-1). Initially, doctors and the patient’s family members believed that she would not survive for a long time. However, this tumor was surprisingly highly responsive to chemotherapy and this patient finally received a satisfactory therapeutic effect.
Therefore, several issues merit further elucidation:
First, it is imprecise if the therapeutic effect was brought about by S-1. A previous randomized phase ш study enrolled 834 patients with locally advanced or metastatic PDAC.10 They were randomly assigned to receive only gemcitabine, only S-1, or gemcitabine plus S-1. The result showed that the median OS was 8.8 months in the gemcitabine group, 9.7 months in the S-1 group, and 10.1 months in the gemcitabine plus S-1 group. The difference in the OS between the S-1 and the gemcitabine group was statistically significant. Based on this study, Okusaka et al prolonged the follow-up time. The result still confirmed the superiority of S-1.11 In addition, S-1 not benefits only patients with locally advanced or metastatic PDAC, but also those with resected PDAC for adjuvant therapy.12,13 Although the optimal regimen and duration warrants further evaluation and verification by appropriate comparison, several studies have successfully confirmed the efficacy of neoadjuvant therapies.14–16 Among them, FOLFIRINOX appears to be the most effective candidate. It is also recommended as the preferred regimen by NCCN.9 Although S-1 monotherapy is even not in the list of the recommended regimens of NCCN, it had a good curative effect in our case. However, whether it is an individual case still needs further investigation.
Second, tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy are “hot” topics recently. Cytotoxic chemotherapy has been demonstrated to benefit patients not only through its tumor-killing effect but also through the immune stimulus brought by the therapy.17 The key pathway of this process is called immunogenic cell death (ICD).18 It is a tumor cell endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis event caused by systemic therapy. These dead tumor cells provide a potent “find me and eat me signal” to attract tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), dendritic cells (DCs), macrophages, and other types of immune cells to the site.19 This process also suppresses T regulatory cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and modulates the tumor microenvironment, which is helpful for CD8+, CD4+, and NK cells to infiltrate.20 However, the immune-response effect varies with the dose, schedule and combination of the chemotherapy.21 This highlights the need to investigate the molecular mechanism of these immune responses and the optimal combination of chemotherapy. In our case, we found considerable fibrous tissue hyperplasia and inflammatory cell infiltration in the postoperative histopathological section. We supposed that similar chemotherapy-induced immune responses in vivo occurred during the application of S-1. However, whether adding immunotherapy could consolidate the current therapeutic effect warrants further attention. A previous study reported that patients with PDCA could benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy plus immunotherapy.22
Third, Patients with cancer always present a negative attitude towards engagement and compliance with the treatment, as well as dissatisfaction with health care service, family care, and quality of life.23,24 This kind of distress and depression syndrome was significantly associated experiencing problems with participation in therapy and decision-making of primary care.25 Thus, psychosocial intervention for cancer patients is as important as oncological treatment. Appropriate psychological counseling, a moderate amount of physical activity, and even certain pharmacologic strategies can break the cycle of cancer and stress.26 In the current case, despite the good therapeutic effect and lack of signs of disease progression, the patient still suffered from severe psychological burden and fear of cancer recurrence. Therefore, mental care is recommended for this patient to alleviate such kind of psychological problem.
Fourth, previous studies suggested that MDT care and treatment could significantly increase the accuracy of diagnosis, shorten the duration from diagnosis to treatment, and finally bring survival benefits to cancer patients.26,27 In our case, after confirming a massive primary lesion with liver metastasis through CT-abdomen, the MDT discussion and treatment was initiated. Subsequently, a satisfactory therapeutic result was achieved through MDT efforts.
Finally, until now, the therapeutic efficacy of this patient seems is quite good, and no signs of recurrence and metastasis have been observed. However, because the follow-up time was just one year and three months after surgery, the long-term survival result remains to be seen.
Conclusion
The patient in the present case was successfully treated. However, the long-term therapeutic efficacy will be determined through follow-up. Although this could, perhaps, be a special case, whether the experience of this case could be used to treat other patients with PDAC warrants further exploration.
Abbreviations
CA, carbohydrate antigen; CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen; PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; GDA, gastroduodenal artery; SMA, superior mesenteric artery; SMV, superior mesenteric vein; PV, portal vein; CT, computed tomography; MDT, multidisciplinary team; HDI, human development index; OS, overall survival; TACE, transarterial chemoembolization; 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil; FT, tegafur; CDHP, gimeracil; Oxo, otilasi; PET, positron emission tomography; NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; PS, performance status; ICD, immunogenic cell death; TILs, tumor infiltrating lymphocytes; DCs, dendritic cells; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells.
Ethics and Consent Statement
Based on the regulation of the department of research of the Jiangsu University and Xuzhou Medical University, institutional review board approval is not required for case report.
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Haifeng Tang for the assistance during the surgery.
Author Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed on the journal to which the article will be submitted; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Funding
No funding received.
Disclosure
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare for this work.
References
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. doi:10.3322/caac.21492
2. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(3):145–164. doi:10.3322/caac.21601
3. Bengtsson A, Andersson R, Ansari D. The actual 5-year survivors of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on real-world data. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):16425. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-73525-y
4. Schnelldorfer T, Ware AL, Sarr MG, et al. Long-term survival after pancreatoduodenectomy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma: is cure possible? Ann Surg. 2008;247(3):456–462. doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181613142
5. Picozzi VJ, Oh SY, Edwards A, et al. Five-year actual overall survival in resected pancreatic cancer: a contemporary single-institution experience from a multidisciplinary perspective. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017;24(6):1722–1730. doi:10.1245/s10434-016-5716-z
6. Ferrone CR, Pieretti-Vanmarcke R, Bloom JP, et al. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: long-term survival does not equal cure. Surgery. 2012;152(3 Suppl 1):S43–9. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2012.05.020
7. Li D, Xie K, Wolff R, Abbruzzese JL. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2004;363(9414):1049–1057. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15841-8
8. Alexakis N, Halloran C, Raraty M, Ghaneh P, Sutton R, Neoptolemos JP. Current standards of surgery for pancreatic cancer. Br J Surg. 2004;91(11):1410–1427. doi:10.1002/bjs.4794
9. Network NCC. NCCN guidelines for treatment of cancer by site: pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Available from: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/pancreatic.pdf.
10. Ueno H, Ioka T, Ikeda M, et al. Randomized Phase III study of gemcitabine plus S-1, S-1 alone, or gemcitabine alone in patients with locally advanced and metastatic pancreatic cancer in Japan and Taiwan: GEST study. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(13):1640–1648. doi:10.1200/jco.2012.43.3680
11. Okusaka T, Miyakawa H, Fujii H, et al. Updated results from GEST study: a randomized, three-arm phase III study for advanced pancreatic cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017;143(6):1053–1059. doi:10.1007/s00432-017-2349-y
12. Maeda A, Boku N, Fukutomi A, et al. Randomized phase III trial of adjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine versus S-1 in patients with resected pancreatic cancer: Japan adjuvant study group of pancreatic cancer (JASPAC-01). Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2008;38(3):227–229. doi:10.1093/jjco/hym178
13. Uesaka K, Boku N, Fukutomi A, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy of S-1 versus gemcitabine for resected pancreatic cancer: a Phase 3, open-label, randomised, non-inferiority trial (JASPAC 01). Lancet. 2016;388(10041):248–257. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)30583-9
14. Casadei R, Di Marco M, Ricci C, et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and surgery versus surgery alone in resectable pancreatic cancer: a single-center prospective, randomized, controlled trial which failed to achieve accrual targets. J Gastrointest Surg. 2015;19(10):1802–1812. doi:10.1007/s11605-015-2890-4
15. Schwarz L, Vernerey D, Bachet JB, et al. Resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma neo-adjuvant FOLF(IRIN)OX-based chemotherapy - a multicenter, non-comparative, randomized, Phase II trial (PANACHE01-PRODIGE48 study). BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):762. doi:10.1186/s12885-018-4663-4
16. Tachezy M, Gebauer F, Petersen C, et al. Sequential neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (CRT) followed by curative surgery vs. primary surgery alone for resectable, non-metastasized pancreatic adenocarcinoma: NEOPA- a randomized multicenter phase III study (NCT01900327, DRKS00003893, ISRCTN82191749). BMC Cancer. 2014;14(1):411. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-14-411
17. Chang JH, Jiang Y, Pillarisetty VG. Role of immune cells in pancreatic cancer from bench to clinical application: an updated review. Medicine. 2016;95(49):e5541. doi:10.1097/md.0000000000005541
18. Green DR, Ferguson T, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. Immunogenic and tolerogenic cell death. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9(5):353–363. doi:10.1038/nri2545
19. Obeid M, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F, et al. Calreticulin exposure dictates the immunogenicity of cancer cell death. Nat Med. 2007;13(1):54–61. doi:10.1038/nm1523
20. Michels T, Shurin GV, Naiditch H, Sevko A, Umansky V, Shurin MR. Paclitaxel promotes differentiation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells into dendritic cells in vitro in a TLR4-independent manner. J Immunotoxicol. 2012;9(3):292–300. doi:10.3109/1547691x.2011.642418
21. Wu J, Waxman DJ. Immunogenic chemotherapy: dose and schedule dependence and combination with immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2018;419:210–221. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2018.01.050
22. Amin S, Baine M, Meza J, Lin C. The impact of neoadjuvant and adjuvant immunotherapy on the survival of pancreatic cancer patients: a retrospective analysis. BMC Cancer. 2020;20(1):538. doi:10.1186/s12885-020-07016-8
23. Walker J, Waters RA, Murray G, et al. Better off dead: suicidal thoughts in cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(29):4725–4730. doi:10.1200/jco.2007.11.8844
24. Deshields T, Tibbs T, Fan MY, Taylor M. Differences in patterns of depression after treatment for breast cancer. Psycho-Oncology. 2006;15(5):398–406. doi:10.1002/pon.962
25. Mackenzie L, Mansfield E, Herrmann A, Grady A, Evans TJ, Sanson-Fisher R. Perceived problems with involvement in decision making about breast cancer treatment and care: a cross-sectional study. Patient Educ Couns. 2020. doi:10.1016/j.pec.2020.08.044
26. Hung HY, Tseng YH, Chao HS, et al. Multidisciplinary team discussion results in survival benefit for patients with stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 2020;15(10):e0236503. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0236503
27. Kowalczyk A, Jassem J. Multidisciplinary team care in advanced lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020;9(4):1690–1698. doi:10.21037/tlcr.2019.11.33
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.